Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 26-29.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.01.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation analysis between neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio and degree of coronary artery stenosis
- Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Graduate Training Base of Jinzhou Central Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121001, China
-
Received:2021-09-27Online:2022-01-20Published:2022-01-20 -
Contact:Jiang Shan E-mail:Jiangshan_j@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chen Xi, Jiang Shan. Correlation analysis between neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio and degree of coronary artery stenosis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(1): 26-29.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.01.004
| 项目 | 冠心病组 (n=322) | 非冠心病组 (n=84) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄( | 64.04±9.77 | 57.67±9.41 | t=-5.268 | 0.000 |
| 男性[例(%)] | 211(65.5) | 42(50.0) | χ2=6.840 | 0.009 |
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 87(27.0) | 16(19.0) | χ2=2.236 | 0.135 |
| 高血压史[例(%)] | 188(58.4) | 42(50.0) | χ2=1.907 | 0.167 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 112(34.8) | 20(23.8) | χ2=3.656 | 0.056 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 61(18.9) | 11(13.1) | χ2=1.562 | 0.211 |
| BMI( | 25.43±1.86 | 25.07±2.63 | t=-1.841 | 0.066 |
| 项目 | 冠心病组 (n=322) | 非冠心病组 (n=84) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄( | 64.04±9.77 | 57.67±9.41 | t=-5.268 | 0.000 |
| 男性[例(%)] | 211(65.5) | 42(50.0) | χ2=6.840 | 0.009 |
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 87(27.0) | 16(19.0) | χ2=2.236 | 0.135 |
| 高血压史[例(%)] | 188(58.4) | 42(50.0) | χ2=1.907 | 0.167 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 112(34.8) | 20(23.8) | χ2=3.656 | 0.056 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 61(18.9) | 11(13.1) | χ2=1.562 | 0.211 |
| BMI( | 25.43±1.86 | 25.07±2.63 | t=-1.841 | 0.066 |
| 项目 | 冠心病组(n=322) | 非冠心病组(n=84) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中性粒细胞百分比(%) | 67.44±11.35 | 62.03±7.80 | t=-4.124 | 0.000 |
| 淋巴细胞计数(×109/L) | 1.86±0.82 | 1.91±0.57 | t=-1.916 | 0.055 |
| 血清白蛋白(g/L) | 41.62±4.75 | 43.62±3.50 | t=-3.591 | 0.005 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 67.02±15.44 | 63.80±14.29 | t=-1.634 | 0.102 |
| 尿素(mmol/L) | 5.72±2.83 | 5.37±1.38 | t=-0.958 | 0.338 |
| 尿酸 (μmol/L) | 314.58±87.92 | 317.90±100.33 | t=0.299 | 0.765 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.72±1.15 | 4.78±0.96 | t=-0.682 | 0.495 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 2.40±8.99 | 1.68±1.00 | t=-0.963 | 0.336 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 1.17±0.30 | 1.23±0.29 | t=-1.818 | 0.069 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 3.09±1.05 | 3.07±0.84 | t=-0.073 | 0.942 |
| 高敏C反应蛋白(mg/L) | 9.97±29.52 | 2.49±3.44 | t=-4.766 | 0.000 |
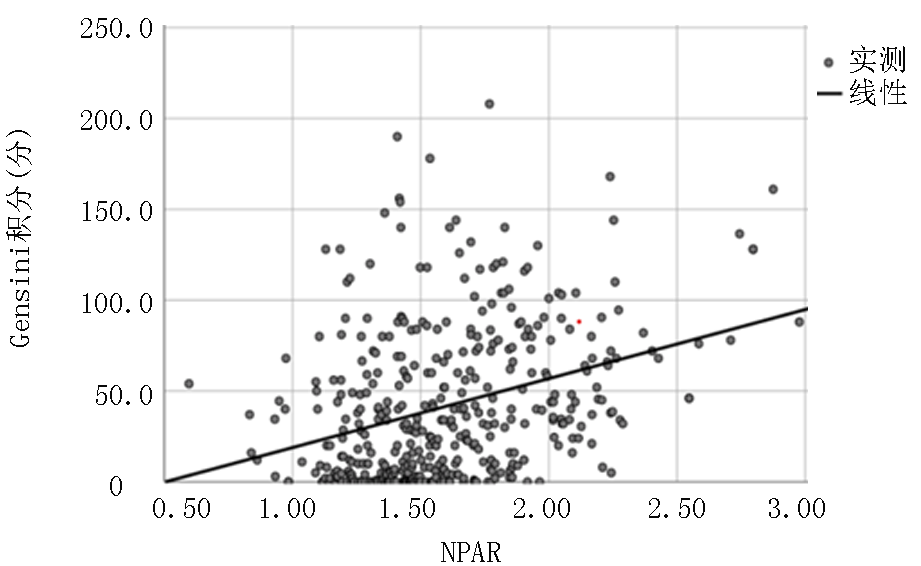
| NPAR | 1.65±0.38 | 1.43±0.21 | t=-5.046 | 0.000 |
| 项目 | 冠心病组(n=322) | 非冠心病组(n=84) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中性粒细胞百分比(%) | 67.44±11.35 | 62.03±7.80 | t=-4.124 | 0.000 |
| 淋巴细胞计数(×109/L) | 1.86±0.82 | 1.91±0.57 | t=-1.916 | 0.055 |
| 血清白蛋白(g/L) | 41.62±4.75 | 43.62±3.50 | t=-3.591 | 0.005 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 67.02±15.44 | 63.80±14.29 | t=-1.634 | 0.102 |
| 尿素(mmol/L) | 5.72±2.83 | 5.37±1.38 | t=-0.958 | 0.338 |
| 尿酸 (μmol/L) | 314.58±87.92 | 317.90±100.33 | t=0.299 | 0.765 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.72±1.15 | 4.78±0.96 | t=-0.682 | 0.495 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 2.40±8.99 | 1.68±1.00 | t=-0.963 | 0.336 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 1.17±0.30 | 1.23±0.29 | t=-1.818 | 0.069 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 3.09±1.05 | 3.07±0.84 | t=-0.073 | 0.942 |
| 高敏C反应蛋白(mg/L) | 9.97±29.52 | 2.49±3.44 | t=-4.766 | 0.000 |
| NPAR | 1.65±0.38 | 1.43±0.21 | t=-5.046 | 0.000 |
| 因素 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 0.072 | 0.015 | 20.408 | 0.000 | 1.075 | 1.043 | 1.108 |
| 性别 | 1.116 | 0.295 | 14.266 | 0.000 | 3.052 | 1.710 | 5.445 |
| 高敏C反应蛋白 | 0.125 | 0.043 | 8.439 | 0.004 | 1.133 | 1.042 | 1.233 |
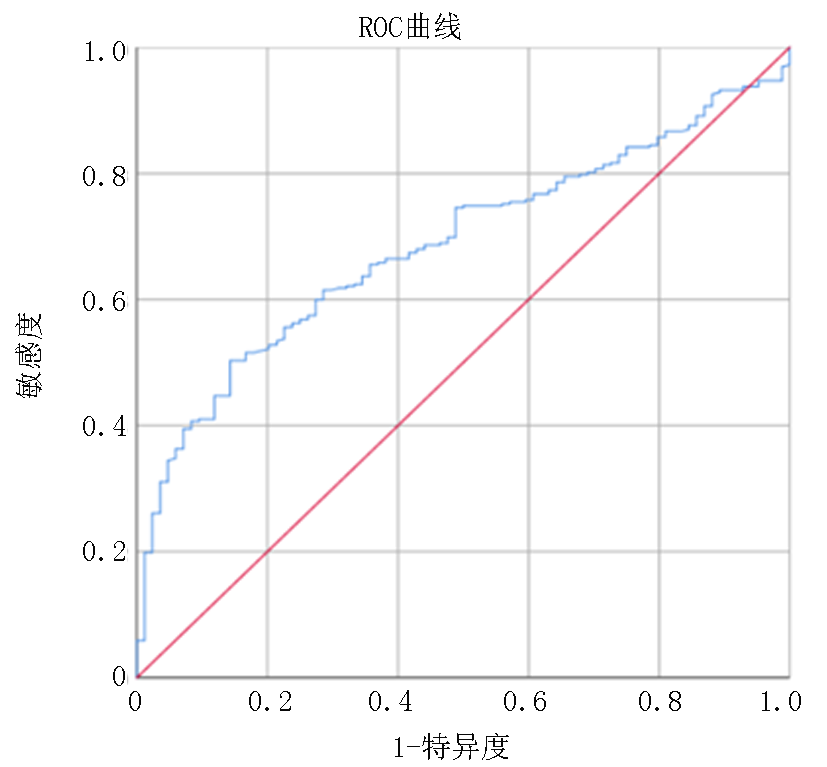
| NPAR | 1.542 | 0.473 | 10.624 | 0.001 | 4.674 | 1.849 | 11.813 |
| 因素 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 0.072 | 0.015 | 20.408 | 0.000 | 1.075 | 1.043 | 1.108 |
| 性别 | 1.116 | 0.295 | 14.266 | 0.000 | 3.052 | 1.710 | 5.445 |
| 高敏C反应蛋白 | 0.125 | 0.043 | 8.439 | 0.004 | 1.133 | 1.042 | 1.233 |
| NPAR | 1.542 | 0.473 | 10.624 | 0.001 | 4.674 | 1.849 | 11.813 |
| [1] |
Bonaventura A, Montecucco F, Dallegri F, et al. Novel findings in neutrophil biology and their impact on cardiovascular disease[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2019, 115(8):1266-1285.
doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz084 pmid: 30918936 |
| [2] |
Pérez-Olivares L, Soehnlein O. Contemporary lifestyle and neutrophil extracellular traps: An emerging link in atherosclerosis disease[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(8):1985.
doi: 10.3390/cells10081985 URL |
| [3] |
Pende A, Artom N, Bertolotto M, et al. Role of neutrophils in atherogenesis: An update[J]. Eur J Clin Invest, 2016, 46(3):252-263.
doi: 10.1111/eci.12566 pmid: 26573245 |
| [4] | 徐明星, 刘文秀, 赵德超. 中性粒细胞及其相关因子与血管内皮功能障碍的研究进展[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2021, 20(8):846-849. |
| [5] | 王玲, 屠剑刚. 中性粒细胞弹性蛋白酶与皮层下动脉硬化性脑病的相关性研究[J]. 现代实用医学, 2018, 30(8):1006-1007. |
| [6] |
Sheinenzon A, Shehadeh M, Michelis R, et al. Serum albumin levels and inflammation[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2021, 184:857-862.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.140 URL |
| [7] |
Plakht Y, Gilutz H, Shiyovich A. Decreased admission serum albumin level is an independent predictor of long-term mortality in hospital survivors of acute myocardial infarction. Soroka Acute Myocardial Infarction II (SAMI-II) project[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016, 219:20-24.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.05.067 pmid: 27257851 |
| [8] |
Wada H, Dohi T, Miyauchi K, et al. Impact of serum albumin levels on long-term outcomes in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Heart Vessels, 2017, 32(9):1085-1092.
doi: 10.1007/s00380-017-0981-8 URL |
| [9] |
Artigas A, Wernerman J, Arroyo V, et al. Role of albumin in diseases associated with severe systemic inflammation: Pathophysiologic and clinical evidence in sepsis and in decompensated cirrhosis[J]. J Crit Care, 2016, 33:62-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.12.019 URL |
| [10] | 王雅, 嵇泽胜, 王瑞. 血清白蛋白与对比剂诱导的急性肾损伤的研究进展[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2020, 33(6):1257-1260. |
| [11] | 付静, 熊秋璨, 王霞, 等. 老年冠心病患者血清Lp-PLA2、hs-CRP、IL-27及MMP-9水平与Gensini积分的相关性研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2019, 19(1):137-140. |
| [12] |
Groh L, Keating ST, Joosten LAB, et al. Monocyte and macrophage immunometabolism in atherosclerosis[J]. Semin Immunopathol, 2018, 40(2):203-214.
doi: 10.1007/s00281-017-0656-7 URL |
| [13] | 陈秀, 刘小熊, 夏豪. 中性粒细胞在心肌梗死中的作用研究进展[J]. 中国心血管杂志, 2020, 25(4):389-392. |
| [14] |
Wolf D, Anto-Michel N, Blankenbach H, et al. A ligand-specific blockade of the integrin Mac-1 selectively targets pathologic inflammation while maintaining protective host-defense[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1):525.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02896-8 URL |
| [15] |
Ma Y. Role of neutrophils in cardiac injury and repair following myocardial infarction[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(7):1676.
doi: 10.3390/cells10071676 URL |
| [16] | 李炬颖. APAR、NPAR与急性冠脉综合征患者冠脉病变严重程度的相关性研究[D]. 延安:延安大学, 2021. |
| [17] | 张良峰, 孟庆利. 血清白蛋白水平与冠心病严重程度的关系(英文)[J]. 心血管康复医学杂志, 2012, 21(5):466-469. |
| [18] |
Xia M, Zhang C, Gu J, et al. Impact of serum albumin levels on long-term all-cause, cardiovascular, and cardiac mortality in patients with first-onset acute myocardial infarction[J]. Clin Chim Acta, 2018, 477:89-93.
doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.12.014 URL |
| [19] |
Chien SC, Chen CY, Lin CF, et al. Critical appraisal of the role of serum albumin in cardiovascular disease[J]. Biomark Res, 2017, 5:31.
doi: 10.1186/s40364-017-0111-x URL |
| [20] |
Umeki Y, Adachi H, Enomoto M, et al. Serum albumin and cerebro-cardiovascular mortality during a 15-year study in a community-based cohort in Tanushimaru, a cohort of the seven countries study[J]. Intern Med, 2016, 55(20):2917-2925.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.55.6931 URL |
| [21] |
Kurtul A, Murat SN, Yarlioglues M, et al. Usefulness of serum albumin concentration to predict high coronary SYNTAX score and in-hospital mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Angiology, 2016, 67(1):34-40.
doi: 10.1177/0003319715575220 URL |
| [22] |
Wang X, Wang J, Wu S, et al. Association between the neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio and outcomes in cardiac intensive care unit patients[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2021, 14:4933-4943.
doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S328882 pmid: 34483683 |
| [23] | 董磊, 樊泽元. 中性粒细胞百分比/白蛋白比值(NPAR)对冠状动脉支架内再狭窄的预测价值[J]. 吉林医学, 2020, 41(11):2565-2567. |
| [24] |
Cui H, Ding X, Li W, et al. The neutrophil percentage to albumin ratio as a new predictor of in-hospital mortality in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2019, 25:7845-7852.
doi: 10.12659/MSM.917987 URL |
| [25] | 黄超, 胡良淼, 江涛, 等. hs-CRP、LP-PLA2和TPS与高血压合并冠心病的相关性研究[J]. 国际检验医学杂志, 2018, 39(20):2534-2537. |
| [26] | 康晓平, 郭秀花, 苏彦萍, 等. 血浆HCY、hs-CRP水平与高血压病人颈动脉粥样硬化的相关性及其危险因素分析[J]. 内蒙古医科大学学报, 2020, 42(4):345-349. |
| [27] |
Silva D, Pais de Lacerda A. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a biomarker of risk in coronary artery disease[J]. Rev Port Cardiol, 2012, 31(11):733-745.
doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2012.02.018 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||