Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (8): 694-701.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.08.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive effect of parathyroid hormone combined with carotid intima-media thickness on coronary artery calcification
- Department of Internal Medicine-Cardiovascular, the First Affiliated Hospital of Dali University, Dali 671000, China
-
Received:2023-06-19Online:2023-08-20Published:2023-09-27 -
Contact:KuangShiquan E-mail:15125265568@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Guofei, KuangShiquan . Predictive effect of parathyroid hormone combined with carotid intima-media thickness on coronary artery calcification[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 694-701.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.08.003
| 临床资料 | 非钙化组 (n=63) | 钙化组 (n=101) | χ2/t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||
| 男 女 | 38(60.3) 25(39.7) | 70(69.3) 31(30.7) | 1.394 | 0.238 |
| 高血压史 | ||||
| 有 无 | 37(58.7) 26(41.3) | 46(45.5) 55(54.5) | 2.699 | 0.100 |
| 吸烟史 | ||||
| 有 无 | 30(47.6) 33(52.4) | 50(49.5) 51(50.5) | 0.128 | 0.720 |
| 饮酒史 | ||||
| 有 无 | 40(63.5) 23(36.5) | 63(62.4) 38(37.6) | 0.021 | 0.886 |
| 年龄(岁) | 55.92±12.33 | 65.09±9.57 | -5.330 | <0.01 |
| ALP( U/L) | 81.83±23.06 | 86.57±28.12 | -1.125 | 0.262 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 72.79±17.12 | 79.26±26.20 | -1.739 | 0.084 |
| 钙(mmol/L) | 2.27±0.42 | 2.24±0.14 | 0.757 | 0.450 |
| 磷(mmol/L) | 1.07±0.19 | 1.07±0.18 | -0.109 | 0.913 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 5.06±1.17 | 5.83±2.47 | -2.320 | 0.022 |
| 果糖胺(mmol/L) | 1.61±0.40 | 1.57±0.22 | 0.911 | 0.363 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 2.23±2.68 | 1.84±0.95 | 1.344 | 0.181 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.34±0.99 | 4.44±0.97 | -0.604 | 0.547 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.16±0.26 | 1.12±0.29 | 1.028 | 0.306 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.51±0.82 | 2.64±0.80 | -0.987 | 0.325 |
| 载脂蛋A1( g/L) | 1.08±0.20 | 1.08±0.22 | -0.057 | 0.955 |
| 载脂蛋白B(g/L) | 0.81±0.32 | 0.83±0.20 | -0.042 | 0.659 |
| PTH(pg/ml) | 71.33±13.73 | 102.97±14.97 | -13.581 | 0.000 |
| IMT(mm) | 1.018±0.071 | 1.040±0.063 | -1.267 | 0.036 |
Tab.1 Comparison of clinical data between groups
| 临床资料 | 非钙化组 (n=63) | 钙化组 (n=101) | χ2/t值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别 | ||||
| 男 女 | 38(60.3) 25(39.7) | 70(69.3) 31(30.7) | 1.394 | 0.238 |
| 高血压史 | ||||
| 有 无 | 37(58.7) 26(41.3) | 46(45.5) 55(54.5) | 2.699 | 0.100 |
| 吸烟史 | ||||
| 有 无 | 30(47.6) 33(52.4) | 50(49.5) 51(50.5) | 0.128 | 0.720 |
| 饮酒史 | ||||
| 有 无 | 40(63.5) 23(36.5) | 63(62.4) 38(37.6) | 0.021 | 0.886 |
| 年龄(岁) | 55.92±12.33 | 65.09±9.57 | -5.330 | <0.01 |
| ALP( U/L) | 81.83±23.06 | 86.57±28.12 | -1.125 | 0.262 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 72.79±17.12 | 79.26±26.20 | -1.739 | 0.084 |
| 钙(mmol/L) | 2.27±0.42 | 2.24±0.14 | 0.757 | 0.450 |
| 磷(mmol/L) | 1.07±0.19 | 1.07±0.18 | -0.109 | 0.913 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 5.06±1.17 | 5.83±2.47 | -2.320 | 0.022 |
| 果糖胺(mmol/L) | 1.61±0.40 | 1.57±0.22 | 0.911 | 0.363 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 2.23±2.68 | 1.84±0.95 | 1.344 | 0.181 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.34±0.99 | 4.44±0.97 | -0.604 | 0.547 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.16±0.26 | 1.12±0.29 | 1.028 | 0.306 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.51±0.82 | 2.64±0.80 | -0.987 | 0.325 |
| 载脂蛋A1( g/L) | 1.08±0.20 | 1.08±0.22 | -0.057 | 0.955 |
| 载脂蛋白B(g/L) | 0.81±0.32 | 0.83±0.20 | -0.042 | 0.659 |
| PTH(pg/ml) | 71.33±13.73 | 102.97±14.97 | -13.581 | 0.000 |
| IMT(mm) | 1.018±0.071 | 1.040±0.063 | -1.267 | 0.036 |
| 钙化程度分组 | CACS积分 |
|---|---|
| 少量钙化组 | ≤10 |
| 轻度钙化组 | 10~99.9 |
| 中度钙化组 | 100~399.9 |
| 重度钙化组 | ≥400 |
Tab. 2 Classification criteria for calcification degree using CACS method
| 钙化程度分组 | CACS积分 |
|---|---|
| 少量钙化组 | ≤10 |
| 轻度钙化组 | 10~99.9 |
| 中度钙化组 | 100~399.9 |
| 重度钙化组 | ≥400 |
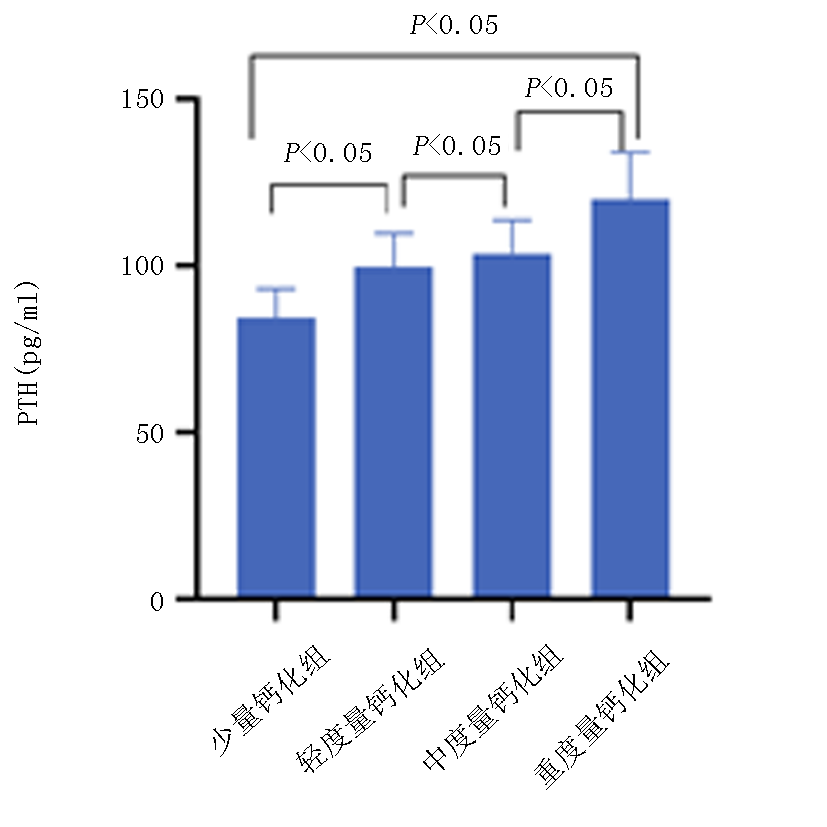
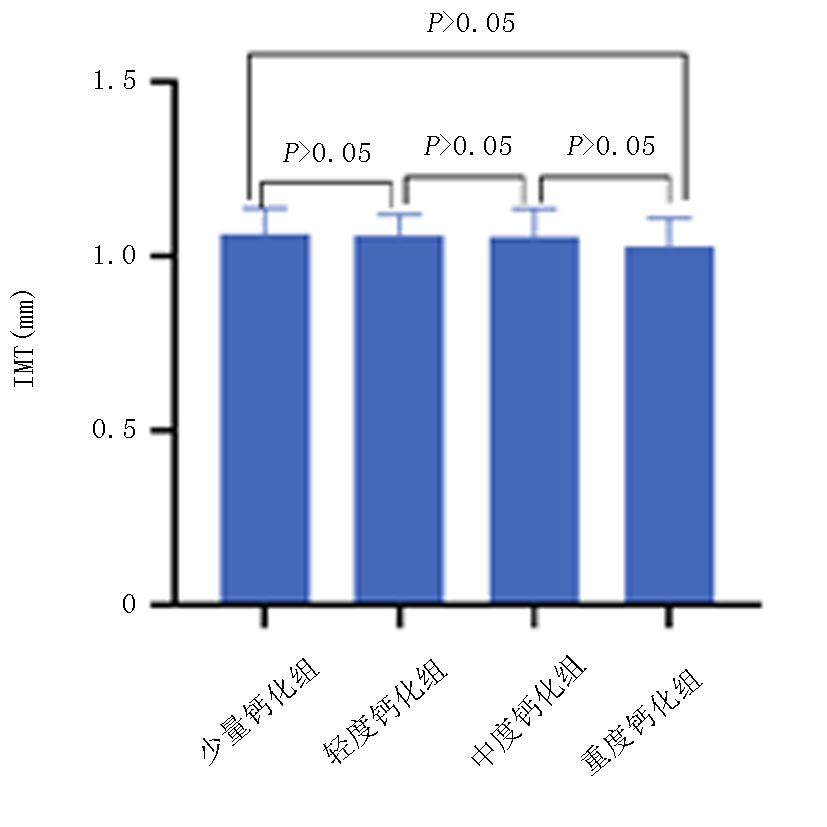
| 组别 | 例数 | PTH(pg/ml) | IMT(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 少量钙化组 | 14 | 84.43±8.82 | 1.021±0.058 |
| 轻度钙化组 | 34 | 99.82±10.07* | 1.017±0.072 |
| 中度钙化组 | 33 | 103.76±10.06*# | 1.024±0.075 |
| 重度钙化组 | 20 | 120.00±14.24*#△ | 1.048±0.055 |
| F值 | 30.978 | 0.861 | |
| P值 | 0.000 | 0.464 |
Tab. 3 Comparison of PTH and IMT levels among four groups with different degrees of calcification
| 组别 | 例数 | PTH(pg/ml) | IMT(mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 少量钙化组 | 14 | 84.43±8.82 | 1.021±0.058 |
| 轻度钙化组 | 34 | 99.82±10.07* | 1.017±0.072 |
| 中度钙化组 | 33 | 103.76±10.06*# | 1.024±0.075 |
| 重度钙化组 | 20 | 120.00±14.24*#△ | 1.048±0.055 |
| F值 | 30.978 | 0.861 | |
| P值 | 0.000 | 0.464 |
| 因素 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR值 | P值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| HDL-C | -0.209 | 0.111 | 4.911 | <0.000 | 0.027 | 0.000~0.248 | |
| PTH | 0.014 | 0.001 | 12.630 | 1.531 | <0.01 | 1.210~1.936 | |
| IMT | 1.016 | 0.027 | 6.833 | 32.841 | 0.009 | 21.754~48.990 | |
| TG | -0.049 | 0.022 | 3.978 | 0.064 | 0.004 | 0.004~0.954 | |
Tab. 4 Single factor logistic regression analysis
| 因素 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR值 | P值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| HDL-C | -0.209 | 0.111 | 4.911 | <0.000 | 0.027 | 0.000~0.248 | |
| PTH | 0.014 | 0.001 | 12.630 | 1.531 | <0.01 | 1.210~1.936 | |
| IMT | 1.016 | 0.027 | 6.833 | 32.841 | 0.009 | 21.754~48.990 | |
| TG | -0.049 | 0.022 | 3.978 | 0.064 | 0.004 | 0.004~0.954 | |
| 因素 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR值 | P值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTH | 0.016 | 0.001 | 42.068 | 1.193 | <0.01 | 1.131~1.259 |
| IMT | 1.035 | 0.027 | 10.679 | 5.655 | 0.001 | 2.001~15.984 |
Tab.5 Multivariate logistic regression analysis(forward introduction method for screening variables)
| 因素 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | OR值 | P值 | 95%CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTH | 0.016 | 0.001 | 42.068 | 1.193 | <0.01 | 1.131~1.259 |
| IMT | 1.035 | 0.027 | 10.679 | 5.655 | 0.001 | 2.001~15.984 |
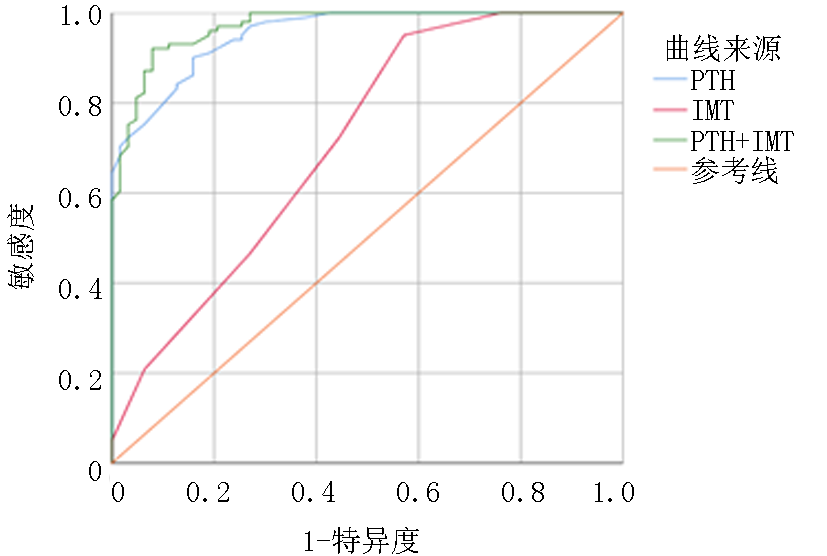
| 截断值 | 最佳约登 指数 | 敏感性 (%) | 特异性 (%) | 阳性预 测值(%) | 阴性预 测值(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTH=77.0 | 0.670 | 97.0 | 70.0 | 83.83 | 93.57 |
| IMT=0.98 | 0.329 | 95.0 | 37.9 | 71.03 | 82.54 |
| IMT+PTH=0.763 | 0.613 | 92.1 | 84.2 | 90.34 | 86.92 |
Tab. 6 ROC curve analysis of PTH, IMT and PTH+IMT
| 截断值 | 最佳约登 指数 | 敏感性 (%) | 特异性 (%) | 阳性预 测值(%) | 阴性预 测值(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTH=77.0 | 0.670 | 97.0 | 70.0 | 83.83 | 93.57 |
| IMT=0.98 | 0.329 | 95.0 | 37.9 | 71.03 | 82.54 |
| IMT+PTH=0.763 | 0.613 | 92.1 | 84.2 | 90.34 | 86.92 |
| 变量 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | PTH | IMT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | P值 | Z值 | P值 | |||||
| PTH | 0.954 | <0.01 | 0.926~0.981 | / | / | 5.535 | <0.01 | |
| IMT | 0.711 | <0.01 | 0.627~0.796 | 5.535 | <0.01 | / | / | |
| PTH+IMT | 0.970 | <0.01 | 0.948~0.992 | 1.905 | 0.0429 | 6.220 | <0.01 | |
Tab. 7 Comparison of area under ROC curve of PTH, IMT and PTH+IMT in predicting CAC
| 变量 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | PTH | IMT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z值 | P值 | Z值 | P值 | |||||
| PTH | 0.954 | <0.01 | 0.926~0.981 | / | / | 5.535 | <0.01 | |
| IMT | 0.711 | <0.01 | 0.627~0.796 | 5.535 | <0.01 | / | / | |
| PTH+IMT | 0.970 | <0.01 | 0.948~0.992 | 1.905 | 0.0429 | 6.220 | <0.01 | |
| [1] |
Detrano R, Guerci AD, Carr JJ, et al. Coronary calcium as a predictor of coronary events in four racial or ethnic groups[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 358(13):1336-1345.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa072100 URL |
| [2] |
Wayhs R, Zelinger A, Raggi P. High coronary artery calcium scores pose an extremely elevated risk for hard events[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2002, 39(2):225-230.
doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(01)01737-5 pmid: 11788211 |
| [3] |
Tota-Maharaj R, Blaha MJ, Blankstein R, et al. Association of coronary artery calcium and coronary heart disease events in young and elderly participants in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis: A secondary analysis of a prospective, population-based cohort[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2014, 89(10):1350-1359.
doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2014.05.017 pmid: 25236430 |
| [4] |
Mcclelland RL, Jorgensen NW, Budoff M, et al. Ten-year coronary heart disease risk prediction using coronary artery calcium and traditional risk factors: Derivation in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis with validation in the heinznixdorf recall study and the dallas heart study[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015, 66(15):1643-1653.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.035 URL |
| [5] | Qazi AH, Zallaghi F, Torres-Acosta N, et al. Computed tomography for coronary artery calcification scoring: Mammogram for the heart[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2016:529-536. |
| [6] |
Blaha MJ, Silverman MG, Budoff MJ. Is there a role for coronary artery calcium scoring for management of asymptomatic patients at risk for coronary artery disease? clinical risk scores are sufficient to define primary prevention treatment strategies among asymptomatic patients[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2014, 7(2):398-408.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.113.000341 URL |
| [7] |
Nasir K, Rubin J, Blaha MJ, et al. Interplay of coronary artery calcification and traditional risk factors for the prediction of all-cause mortality in asymptomatic individualsclinical perspective[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging, 2012, 5(4):467-473.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.111.964528 pmid: 22718782 |
| [8] |
Sarwar A, Shaw LJ, Shapiro MD, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of absence of coronary artery calcification[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2009, 2(6): 675-688.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2008.12.031 pmid: 19520336 |
| [9] |
Budoff MJ, Mcclelland RL, Nasir K, et al. Cardiovascular events with absent or minimal coronary calcification: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA)[J]. Am Heart J, 2009, 158(4):554-561.
doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2009.08.007 pmid: 19781414 |
| [10] |
Nakanishi R LiD, Blaha MJ, et al. The relationship between coronary artery calcium score and the long-term mortality among patients with minimal or absent coronary artery risk factors[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2015, 185:275-281.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2015.03.146 pmid: 25818539 |
| [11] |
Sakakura K, Nakano M, Otsuka F, et al. Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis plaque progression[J]. Heart Lung Circ, 2013, 22(6): 399-411.
doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2013.03.001 pmid: 23541627 |
| [12] |
Wu GY, Xu BD, Wu T, et al. Correlation between serum parathyroid hormone levels and coronary artery calcification in patients without renal failure[J]. Biomed Rep, 2016, 5(5): 601-606.
doi: 10.3892/br.2016.761 URL |
| [13] |
Naqvi TZ, Lee MS. Carotid intima-media thickness and plaque in cardiovascular risk assessment[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging, 2014, 7(10):1025-1038.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2013.11.014 pmid: 25051948 |
| [14] |
Lee MY, Lai WT. Plasma renin level and aldosterone to renin ratio are associated with presence of carotid plaques in patients with stable coronary artery disease[J]. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst, 2015, 16(4):1159-1167.
doi: 10.1177/1470320314548743 URL |
| [15] |
Mori H, Torii S, Kutyna M, et al. Coronary artery calcification and its progression what does it really mean?[J]. JACC Cardiovascular Imaging, 2018, 11(1):127-142.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.10.012 URL |
| [16] |
McClelland RL, Jorgensen NW, Budoff M, et al. Ten-year coronary heart disease risk prediction using coronary artery calcium and traditional risk factors: Derivation in the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis with validation in the heinz nixdorf recall study and the dallas heart study[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2015, 66(15):1643-1653.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.035 pmid: 26449133 |
| [17] |
Richard A, Kronmal RA, Detrano RC, et al. Coronary artery calcification compared with carotid intima-media thickness in the prediction of cardiovascular disease incidence: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA).[J]. Archives of Internal Medicine, 2008, 168(12):1333-1339.
doi: 10.1001/archinte.168.12.1333 pmid: 18574091 |
| [18] |
Kronmal RA, McClelland RL, Detrano R, et al. Risk factors for the progression of coronary artery calcification in asymptomatic subjects: Results from the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA)[J]. Circulation, 2007, 115(21): 2722-2730.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.106.674143 pmid: 17502571 |
| [19] |
Chen NX, Duan D, O'Neill KD, et al. High glucose increases the expression of Cbfa1 and BMP-2 and enhances the calcification of vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2006, 21(12): 3435-3442.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfl429 URL |
| [20] |
Neves KR, Graciolli FG, dos Reis LM, et al. Vascular calcification: contribution of parathyroid hormone in renal failure[J]. Kidney Int, 2007, 71(12):1262-1270.
pmid: 17410101 |
| [21] |
Bundy JD, Chen J, Yang W, et al. Risk factors for progression of coronary artery calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease: The CRIC study[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2018, 271:53-60.
doi: S0021-9150(18)30072-8 pmid: 29459266 |
| [22] |
Kablak-Ziembicka A, Tracz W, Przewlocki T, et al. Association of increased carotid intima-media thickness with the extent of coronary artery disease[J]. Heart, 2004, 90(11):1286-1290.
doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.025080 pmid: 15486123 |
| [23] |
Falk E, Nakano M, Bentzon JF, et al. Update on acute coronary syndromes:the pathologists' view[J]. Eur Heart J, 2013, 34(10):719-728.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehs411 URL |
| [24] |
Al-Aly Z, Shao JS, Lai CF, et al. Aortic Msx2-Wnt calcification cascade is regulated by TNF-alpha-dependent signals in diabetic Ldlr-/- mice[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2007, 27(12):2589-2596.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.153668 pmid: 17932314 |
| [25] |
Mori H, Torii S, Kutyna M, et al. Coronary artery calcification and its progression: What does it really mean?[J]. JACC Cardiovascular Imaging, 2018, 11(1):127-142.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2017.10.012 URL |
| [26] |
Merkel KD, Erdmann JM, McHugh KP, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates orthopedic implant osteolysis[J]. Am J Pathol, 1999, 154(1): 203-210.
doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)65266-2 pmid: 9916934 |
| [27] |
Malluche HH, Blomquist G, Monier-Faugere MC, et al. High parathyroid hormone level and osteoporosis predict progression of coronary artery calcification in patients on dialysis[J]. Am Soc Nephrol, 2015, 26(10): 2534-2544.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2014070686 URL |
| [28] | Wu XY, Ying T, Yin CQ, et al. Clinical efficacy of different treatments and their impacts on the quality of life of octogenarians with coronary artery disease[J]. Chin Med (Engl), 2019, 132(22):2657-2663. |
| [29] |
Tasca A, Cacciola A, Ferrarese P, et al. Bone alterations in patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria and calcium nephrolithiasis[J]. Urology, 2002, 59(6): 865-869.
pmid: 12031370 |
| [30] |
Lisowska A, Musia WJ, Lisowski P, et al. Intima-media thickness is a useful marker of the extent of coronary artery disease in patients with impaired renal function[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2009, 202(2):470-475.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.05.051 pmid: 18621374 |
| [31] |
Belhassen L, Carville C, Pelle G, et al. Evaluation of carotid artery and aortic intima-media thickness measurements for exclusion of significant coronary atherosclerosis in patients scheduled for heart valve surgery[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2002, 39(7):1139-1144.
pmid: 11923037 |
| [32] |
Kanadai M, Cayli M, San M, et al. The presence of a calcific plaque in the common carotid artery as a predictor of coronary atherosclerosis[J]. Angiology, 2006, 57(5):585-592.
pmid: 17067981 |
| [33] |
Zhang Y, Guallar E, Ye Q, et al. Is carotid intima-media thickness as predictive as other noninvasive techniques for the detection of coronary artery disease?[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2014, 34(7):1341-1345.
doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302075 pmid: 24764454 |
| [34] | Murphy DJ, Crinion SJ, Redmond CE, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of carotid intima media thickness in predicting coronary plaque burden on coronary computed tomography angiography in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea[J]. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr, 2017:227-233. |
| [35] |
Matsushima Y, Kawano H, Koide Y, et al. Relationship of carotid intima-media thickness, pulse wave velocity, and ankle brachial index to the severity of coronary artery atherosclerosis[J]. Clinical Cardiology, 2010, 27(11):629-634.
doi: 10.1002/clc.4960271110 URL |
| [36] | Bhuriya R, Li S, Chen SC, et al. Plasma parathyroid hormone level and prevalent cardiovascular disease in CKD Stages 3 and 4: An analysis from the kidney early evaluation program (KEEP)[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2009, 53(4 Suppl 4):S3-10. |
| [37] |
Chartsrisak K, Vipattawat K, Assanatham M, et al. Mineral metabolism and outcomes in chronic kidney disease stage 2-4 patients[J]. Bmc Nephrology, 2013, 14(1):14.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-14 URL |
| [38] | Lamarche MC, Hopman WM, Garland JS, et al. Relationship of coronary artery calcification with renal function decline and mortality in predialysis chronic kidney disease patients[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2018, (10):1715-1722. |
| [39] |
Barbarash O, Zykov M, Kashtalap V, et al. Increased serum parathyroid hormone, osteocalcin and alkaline phosphatase are associated with a long-term adverse cardiovascular outcome after coronary artery bypass graft surgery[J]. Diagnostics, 2019, 9(4):143.
doi: 10.3390/diagnostics9040143 URL |
| [40] |
Kamycheva E, Sundsfjord J, Jorde R. Serum parathyroid hormone levels predict coronary heart disease: the Troms Study[J]. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil, 2016, 11(1):69-74.
doi: 10.1097/01.hjr.0000114706.27531.01 URL |
| [41] | Monego G, Arena V, Pasquini S, et al. Ischemic injury activates PTHrP and PTH1R expression in human ventricular cardiomyocytes[J]. Basic Research in Cardiology Basic Res Cardiol, 2009, 104(4):427-434. |
| [42] |
Saleh FN, Schirmer H, Sundsfjord J, et al. Parathyroid hormone and left ventricular hypertrophy[J]. Eur Heart J, 2003, (22):2054-60.
pmid: 14613742 |
| [43] |
Tyralla K, Amann K. Morphology of the heart and arteries in renal failure[J]. Kidney Int, 2003, 63(84):S80-S83.
doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.63.s84.1.x URL |
| [44] |
Nishimura M, Tsukamoto K, Tamaki N, et al. Risk stratification for cardiac death in hemodialysis patients without obstructive coronary artery disease[J]. Kidney Int, 2011, 79(3):363-371.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.392 pmid: 20944544 |
| [45] |
Reis JP, Muhlen DV, Kritz-Silverstein D, et al. Vitamin D, parathyroid hormone levels, and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in community-dwelling older adults[J]. Diabetes Care, 2007, 30(6):1549-1555.
doi: 10.2337/dc06-2438 pmid: 17351276 |
| [46] |
Martín-Ventura JL, Ortego M, Esbrit P, et al. Possible role of parathyroid hormone-related protein as a proinflammatory cytokine in atherosclerosis[J]. Stroke, 2003, 34(7):1783-1789.
doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000078371.00577.76 pmid: 12805493 |
| [47] |
Shekarkhar S, Foroughi M, Moatamedi M, et al. The association of serum parathyroid hormone and severity of coronary artery diseases[J]. Coron Artery Dis, 2014, 25(4):339-342.
doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000089 pmid: 24487940 |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 24
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 171
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||