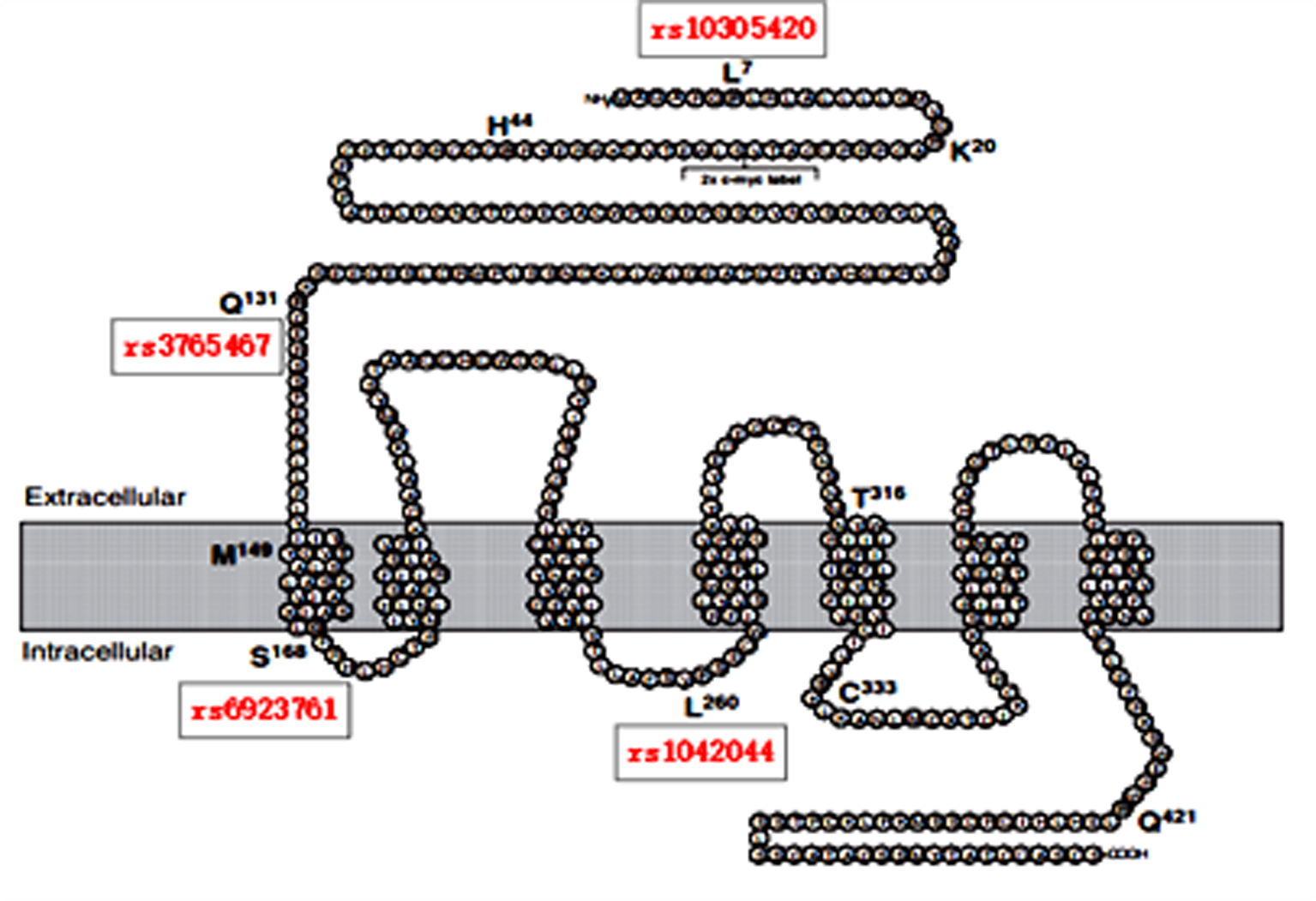
Clinical Focus ›› 2025, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 90-96.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.01.015
-
Received:2024-03-11Online:2025-01-20Published:2025-01-17
CLC Number:
Cite this article
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2025.01.015
| [1] |
Reisberg S, Galwey N, Avillach P, et al. Comparison of variation in frequency for SNPs associated with asthma or liver disease between Estonia, HapMap populations and the 1000 genome project populations[J]. Int J Immunogenet, 2019, 46(2):49-58.
doi: 10.1111/iji.12413 pmid: 30659741 |
| [2] | Taylor DJ, Chhetri SB, Tassia MG, et al. Sources of gene expression variation in a globally diverse human cohort[J]. Nature, 2024, 632(8023):122-130. |
| [3] |
Simó R, Hernández C. GLP-1R as a target for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy: Friend or foe?[J]. Diabetes, 2017, 66(6): 1453-1460.
doi: 10.2337/db16-1364 pmid: 28533296 |
| [4] | Li Y, Yang Z, Ren S, et al. Association between GLP-1R gene polymorphism and dyslipidemia in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A case-control study[J]. Gene, 2023, 878:147589. |
| [5] | 杨静静, 黄帅, 吴倩, 等. 胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂治疗肥胖的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(5):477-480. |
| [6] |
Zhang L, He J, Sun X, et al. Relationship between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene polymorphism and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women in Shanghai[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2020, 9(4): 1732-1741.
doi: 10.21037/apm-19-396 pmid: 32527131 |
| [7] |
O'Neil PM, Rubino DM. Exploring the wider benefits of semaglutide treatment in obesity: Insight from the STEP program[J]. Postgrad Med, 2022, 134(sup1): 28-36.
doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2150006 pmid: 36691307 |
| [8] | Hinnen D. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists for type 2 diabetes[J]. Diab Spectr, 2017, 30(3): 202-210. |
| [9] | Song G, Yang D, Wang Y, et al. Human GLP-1 receptor transmembrane domain structure in complex with allosteric modulators[J]. Nature, 2017, 546(7657):312-315. |
| [10] | Ben Nasr M, Usuelli V, Dellepiane S, et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor is a T cell-negative costimulatory molecule[J]. Cell Metab, 2024, 36(6):1302-1319.e12. |
| [11] | Zhao X, Wang M, Wen Z, et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists: Beyond their pancreatic effects[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12:721135. |
| [12] | Meurot C, Jacques C, Martin C, et al. Targeting the GLP-1/GLP-1R axis to treat osteoarthritis: A new opportunity?[J]. J Orthop Translat, 2022, 32:121-129. |
| [13] | Grill HJ. A role for GLP-1 in treating hyperphagia and obesity[J]. Endocrinology, 2020, 161(8):bqaa093. |
| [14] | El Eid L, Reynolds CA, Tomas A, et al. Biased agonism and polymorphic variation at the GLP-1 receptor: Implications for the development of personalised therapeutics[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2022, 184: 106411. |
| [15] |
Parthier C, Reedtz-Runge S, Rudolph R, et al. Passing the baton in class B GPCRs: Peptide hormone activation via helix induction?[J]. Trends Biochem Sci, 2009, 34(6):303-310.
doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2009.02.004 pmid: 19446460 |
| [16] |
Elashi AA, Toor SM, Umlai UI, et al. Genome-wide association study and trans-ethnic meta-analysis identify novel susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. BMC Med Genomics, 2024, 17(1):115.
doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01855-1 pmid: 38685053 |
| [17] |
Scott RA, Scott LJ, Mägi R, et al. An expanded genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Europeans[J]. Diabetes, 2017, 66(11): 2888-2902.
doi: 10.2337/db16-1253 pmid: 28566273 |
| [18] |
Wessel J, Chu AY, Willems SM, et al. Low-frequency and rare exome chip variants associate with fasting glucose and type 2 diabetes susceptibility[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 5897.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms6897 pmid: 25631608 |
| [19] |
Anderson SL, Trujillo JM, McDermott M, et al. Determining predictors of response to exenatide in type 2 diabetes[J]. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003), 2012, 52(4): 466-471.
doi: 10.1331/JAPhA.2012.10217 pmid: 22825226 |
| [20] | Dawed AY, Mari A, Brown A, et al. Pharmacogenomics of GLP-1 receptor agonists: A genome-wide analysis of observational data and large randomised controlled trials[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2023, 11(1):33-41. |
| [21] |
De Luis D, Aller R, Izaola-Jauregui O, et al. Evaluation of weight loss and adipocytokine levels after two hypocaloric diets with different macronutrient distribution in obese subjects with the rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor[J]. Ann Nutr Metab, 2013, 63(4):277-282.
doi: 10.1159/000356710 pmid: 24334921 |
| [22] |
de Luis DA, Aller R, Izaola O, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors and adipocytokines levels after two hypocaloric diets with different fat distribution in obese subjects and rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2014, 37(9): 853-859.
doi: 10.1007/s40618-014-0116-3 pmid: 24969551 |
| [23] |
De Luis D, Bachiller R, Izaola-Jauregui O, et al. Relation of the rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor to metabolic syndrome in obese subjects[J]. Ann Nutr Metab, 2014, 65(4): 253-258.
doi: 10.1159/000365295 pmid: 25376528 |
| [24] | De Luis D, Pacheco D, Aller R, et al. Roles of rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor on weight, cardiovascular risk factor and serum adipokine levels in morbid obese patients[J]. Nutr Hosp, 2014, 29(4): 889-893. |
| [25] |
De Luis D, Aller R, La Fuente RA-D, et al. Relation of the rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor with weight, cardiovascular risk factor, and serum adipokine levels in obese female subjects[J]. J Clin Lab Anal, 2015, 29(2): 100-105.
doi: 10.1002/jcla.21735 pmid: 24687535 |
| [26] |
De Luis D, Aller R, Izaola O, et al. Effects of a high-protein/low-carbohydrate versus a standard hypocaloric diet on adipocytokine levels and cardiovascular risk factors during 9 months, role of rs6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2015, 38(11): 1183-1189.
doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0304-9 pmid: 26015316 |
| [27] | Michałowska J, Miller-Kasprzak E, Seraszek-Jaros A, et al. Association of GLP1R variants rs2268641 and rs6923761 with obesity and other metabolic parameters in a Polish cohort[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2022, 13: 1000185. |
| [28] | de Luis DA, Diaz Soto G, Izaola O, et al. Evaluation of weight loss and metabolic changes in diabetic patients treated with liraglutide, effect of RS 6923761 gene variant of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor[J]. J Diabetes Complications, 2015, 29(4): 595-598. |
| [29] |
de Luis DA, Aller R, Izaola O, et al. Role of rs6923761 gene variant in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor in basal GLP-1 levels, cardiovascular risk factor and serum adipokine levels in naïve type 2 diabetic patients[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2015, 38(2): 143-147.
doi: 10.1007/s40618-014-0161-y pmid: 25200998 |
| [30] |
Rathmann W, Bongaerts B. Pharmacogenetics of novel glucose-lowering drugs[J]. Diabetologia, 2021, 64(6): 1201-1212.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-021-05402-w pmid: 33594477 |
| [31] |
Jensterle M, Pirš B, Goriˇcar K, et al. Genetic variability in GLP-1 receptor is associated with inter-individual differences in weight lowering potential of liraglutide in obese women with PCOS: A pilot study[J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2015, 71(7): 817-824.
doi: 10.1007/s00228-015-1868-1 pmid: 25991051 |
| [32] |
Javorsky M, Gotthardova I, Klimcakova L, et al. A missense variant in GLP1R gene is associated with the glycaemic response to treatment with gliptins[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2016, 18(9): 941-944.
doi: 10.1111/dom.12682 pmid: 27160388 |
| [33] |
Urgeova A, Javorsky M, Klimcakova L, et al. Genetic variants associated with glycemic response to treatment with dipeptidylpeptidase 4 inhibitors[J]. Pharmacogenomics, 2020, 21(5): 317-323.
doi: 10.2217/pgs-2019-0147 pmid: 32308134 |
| [34] |
Suzuki K, Akiyama M, Ishigaki K, et al. Identification of 28 new susceptibility loci for type 2 diabetes in the Japanese population[J]. Nat Genet, 2019, 51(3): 379-386.
doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0332-4 pmid: 30718926 |
| [35] |
Li W, Li P, Li R, et al. GLP1R single-nucleotide polymorphisms rs3765467 and rs10305492 affect β cell insulin secretory capacity and apoptosis through GLP-1[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2020, 39(9): 1700-1710.
doi: 10.1089/dna.2020.5424 pmid: 32721233 |
| [36] |
Nishiya Y, Daimon M, Mizushiri S, et al. Nutrient consumption-dependent association of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene polymorphism with insulin secretion[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 16382.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71853-7 pmid: 33009421 |
| [37] | Fang Y, Zhang J, Ji L, et al. GLP1R rs3765467 polymorphism is associated with the risk of early onset type 2 diabetes[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2023, 2023:8729242. |
| [38] | Nasykhova YA, Tonyan ZN, Mikhailova AA, et al. Pharmacogenetics of type 2 diabetes-progress and prospects[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(18):6842. |
| [39] | Guan Z, Du Y, Li R, et al. Association between glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene polymorphism and treatment response to GLP1R agonists in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study[J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2022, 78(5): 793-799. |
| [40] | Long JC, Liu YJ, Duan YQ, et al. Effect of GLP 1R rs2254336 and rs3765467 polymorphisms on gastrointestinal adverse reactions in type 2 diabetes patients treated with liraglutide[J]. Eur J Clin Pharmacol, 2022, 78(4): 589-596. |
| [41] | Han E, Park HS, Kwon O, et al. A genetic variant in GLP1R is associated with response to DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2016, 95(44): e5155. |
| [42] | Kwak SH, Chae J, Lee S, et al. Nonsynonymous variants in PAX4 and GLP1R are associated with type 2 diabetes in an East Asian population[J]. Diabetes, 2018, 67(9): 1892-1902. |
| [43] |
Kinzig KP, D'Alessio DA, Herman JP, et al. CNS glucagon-like peptide-1 receptors mediate endocrine and anxiety responses to interoceptive and psychogenic stressors[J]. J Neurosci, 2003, 23(15): 6163-6170.
pmid: 12867498 |
| [44] |
Steptoe A, van Jaarsveld CH, Semmler C, et al. Heritability of daytime cortisol levels and cortisol reactivity in children[J]. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2009, 34(2): 273-280.
doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2008.09.006 pmid: 18938040 |
| [45] | Sheikh HI, Dougherty LR, Hayden EP, et al. Glueagon-like peptide-l receptor gene polymorphism(Leu260Phe)is associated with morning cortisol in preschoolers[J]. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry, 2010, 34(6): 980-983. |
| [46] | Diz-Chaves Y, Herrera-Pérez S, González-Matías LC, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) in the integration of neural and endocrine responses to stress[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(11):3304. |
| [47] |
Ramsey TL, Brennan MD. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP1R) haplotypes correlate with altered response to multiple antipsychotics in the CATIE trial[J]. Schizophr Res, 2014, 160(1-3): 73-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.09.038 pmid: 25449714 |
| [48] | Eser HY, Appadurai V, Eren CY, et al. Association between GLP-1 receptor gene polymorphisms with reward learning, anhedonia and depression diagnosis[J]. Acta Neuropsychiatr, 2020, 32(4): 218-225. |
| [49] | Gopinath V. Osteoporosis[J]. Med Clin North Am, 2023, 107(2): 213-225. |
| [50] | Park S, Daily JW, Song MY, et al. Gene-gene and gene-lifestyle interactions of AKAP11, KCNMA1, PUM1, SPTBN1, and EPDR1 on osteoporosis risk in middle-aged adults[J]. Nutrition, 2020, 79-80:110859. |
| [51] |
Yamada C, Yamada Y, Tsukiyama K, et al. The murine glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor is essential for control of bone resorption[J]. Endocrinology, 2008, 149(2): 574-579.
pmid: 18039776 |
| [52] | Xiang S, Qi L, Zhao F, et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene polymorphism is associated with fat mass in Chinese nuclear families with male offspring[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2019, 51(5): 545-547. |
| [53] | Liu C, Bao X, Tian Y, et al. Polymorphisms in the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor gene and their interactions on the risk of osteoporosis in postmenopausal Chinese women[J]. PLoS One, 2023, 18(12): e0295451. |
| [54] | Abdul-Maksoud RS, Elsayed WSH, Rashad NM, et al. GLP-1R polymorphism (rs1042044) and expression are associated with the risk of papillary thyroid cancer among the Egyptian population[J]. Gene, 2022, 834:146597. |
| [55] |
Yu MJ, Wang KY, Liu HM, et al. GLP1R variant is associated with response to exenatide in overweight Chinese type 2 diabetes patients[J]. Pharmacogenomics, 2019, 20(4): 273-277.
doi: 10.2217/pgs-2018-0159 pmid: 30883264 |
| [56] | Vogrinc D, Redenšek Trampuž S, Blagus T, et al. Genetic variability of incretin receptors affects the occurrence of neurodegenerative diseases and their characteristics[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(20):e39157. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||