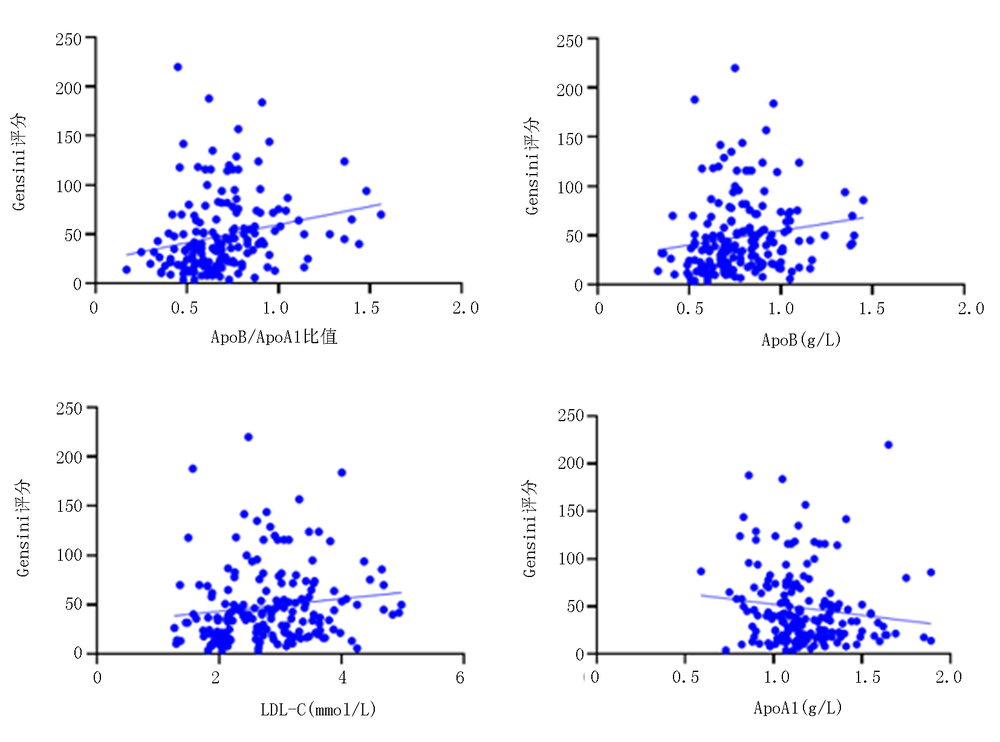
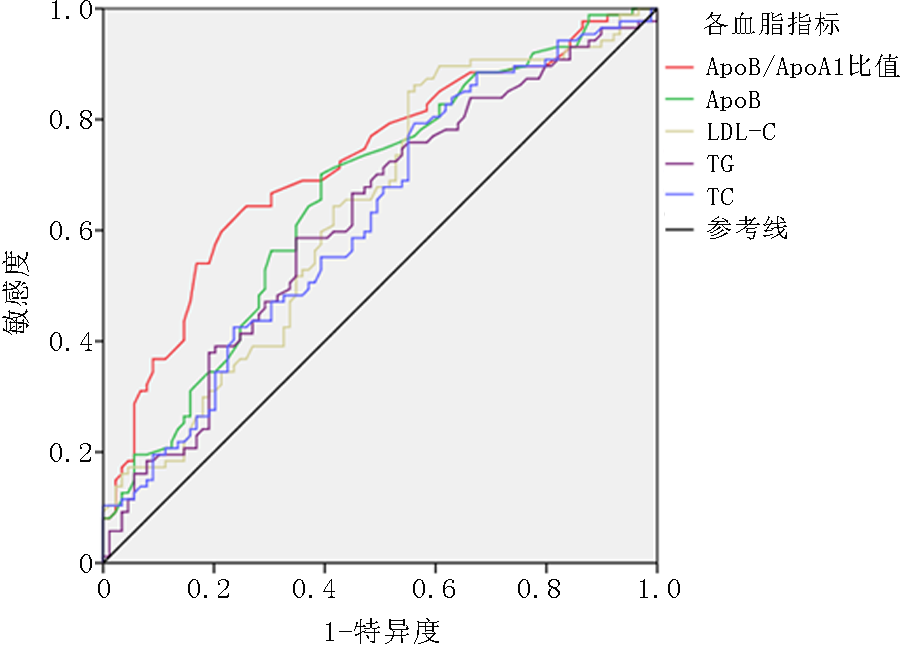
| [1] |
国家卫生计生委合理用药专家委员会, 中国药师协会. 冠心病合理用药指南(第2版)[J]. 中国医学前沿杂志(电子版), 2018, 10(6): 1-130.
|
| [2] |
胡春燕, 吕蓓, 沈卫峰, 等. 不稳定型心绞痛经皮冠状动脉介入治疗与内科保守治疗的比较[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2002, 11(5): 332-335.
|
| [3] |
韩秀, 田雨灵, 卓小桢, 等. 载脂蛋白A、载脂蛋白B/载脂蛋白A比值与冠脉病变严重程度的相关性[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2019, 40(2): 255-258.
|
| [4] |
中华医学会心血管病学分会, 中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会. 非ST段抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征诊断和治疗指南(2016)[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2017, 45(5): 359-376.
|
| [5] |
Gensini GG. A more meaningful scoring system for determining the severity of coronary heart disease[J]. Am J Cardiol, 1983, 51(3): 606.
pmid: 6823874
|
| [6] |
Sonny D, Alexandre FRS, Li C, et al. Gene dosage of the common variant 9p21 predicts severity of coronary artery disease[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2010, 56(6): 479-486.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2009.10.092
URL
|
| [7] |
张洋, 张建华, 汪跃国, 等. 血清ApoB/ApoA-I比值与冠心病患者冠脉病变严重程度的相关性[J]. 安徽医药, 2014, 18(4): 633-637.
|
| [8] |
王晓旭, 徐丹. apoB/apoA1比值与冠心病患者冠脉病变及预后相关性的研究[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2018, 43(8): 1041-1046.
|
| [9] |
Hong LF, Yan XN, Fan Y, et al. Is the ratio of apoB/apoA-1 the best predictor for the severity of coronary artery lesions in Chinese diabetics with stable angina pectoris? An assessment based on Gensini scores[J]. J Geriatr Cardiol, 2015, 12(4): 402-409.
|
| [10] |
Yaseen RI, El-Leboudy MH, El-Deeb HM. The relation between ApoB/ApoA-1 ratio and the severity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Egypt Heart J, 2021, 73(1): 24.
doi: 10.1186/s43044-021-00150-z
URL
|
| [11] |
Song Y, Yang Y, Zhang J, et al. The apoB100/apoAI ratio is independently associated with the severity of coronary heart disease: A cross sectional study in patients undergoing coronary angiography[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2015, 14(1): 150.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-015-0155-6
URL
|
| [12] |
Carr SS, Hooper AJ, Sullivan DR, et al. Non-HDL-cholesterol and apolipoprotein B compared with LDL-cholesterol in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk assessment[J]. Pathology, 2019, 51(2): 148-154.
doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2018.11.006
URL
|
| [13] |
中国成人血脂异常防治指南修订联合委员会. 中国成人血脂异常防治指南(2016年修订版)[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2016, 44(10): 833-853.
|
| [14] |
李鹏, 王桂云, 逯建华. apoB/apoA1值与冠心病相关性研究进展[J]. 内蒙古医学杂志, 2014, 46(1): 43-45.
|
| [15] |
Ertek S. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) dysfunction and the future of HDL[J]. Curr Vasc Pharmacol, 2018, 16(5): 490-498.
doi: 10.2174/1570161115666171116164612
URL
|
| [16] |
苏广胜, 付茜, 庞文跃. 载脂蛋白B/载脂蛋白A1比值与青年冠心病患者冠状动脉病变严重程度的研究[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2021, 37(7): 663-667.
|
 )
)