Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 101-110.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.02.001
Therapy on left ventricular thrombus:Systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhou Huixian, Zhou Yaqing, Guo Ganlin, Cui Wei( )
)
- The First Department of Cardiology, The Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Hebei Cardiovascular Institute, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
-
Received:2022-11-03Online:2023-02-20Published:2023-03-31 -
Contact:Cui Wei E-mail:cuiwei21c@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhou Huixian, Zhou Yaqing, Guo Ganlin, Cui Wei. Therapy on left ventricular thrombus:Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 101-110.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.02.001
| 作者 | 发表 年份 | 研究类型 | 随访年限 | LVT的原因 | DOAC vs VKA | LVT的消失率 (DOAC vs VKA) | 出血事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herald[ | 2022 | 回顾性队列研究 | 中位数:3.4年 | 未记录 | 134 vs 299 | 未记录 | 27.6% vs 37.8%[ | ||||||
| Zhang[ | 2022 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 24个月 | STEMI-PCI术后 | 33 vs 31 | 6个月:42.4% vs 19.4% [ 12个月:69.7% vs 48.4%[ 18个月:78.8% vs 64.5%[ | 6.1% vs 9.7%[ | ||||||
| Tamimi[ | 2022 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 6个月 | 131例患者(66.4%)有缺血性心肌病,其他患者不详 | 48 vs 116 | 66.6% vs 79.3% ( | 10.0% vs 8.0% ( | ||||||
| Aldaas[ | 2022 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 中位数:7.2个月(新型口服抗凝药),10个月(华法林) | 未记录 | 76 vs 146 | 13.2% vs 16.4%[HR 0.08(95% | 未记录 | ||||||
| Varwan[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 2年 | 心肌梗死(28%),慢性缺血性心肌病(42%),非缺血性心肌病(30%) | 58 vs 34 | 55.6% vs 64.0% ( | 5.2% vs 5.9% ( | ||||||
| Jones[ | 2020 | 单中心、观察性、前瞻性研究 | 中位数:2.2年 | 心肌梗死 | 41 vs 60 | 151天:70.7% vs 48.3% ( 1年: 82.0% vs 64.4% ( 利伐沙班、阿哌沙班和依度沙班的LVT消失率:88%, 93%, 100% | 14.6% vs 36.7% ( | ||||||
| Albabtain[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 利伐沙班治疗的中位数:9.5个月(25%~75%的可信区间:6~32.5个月),华法林治疗的中位数:14个月(25%~75%的可信区间:3~41个月) | 心肌梗死,扩张型心肌病,心力衰竭 | 28 vs 35 | 71.4% vs 68.6% LVT消失的中位时间: 3(2~11.5)个月vs 9 (4~20)个月( | 7.1% vs 2.9% ( | ||||||
| Mihm[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性队列研究 | 6个月 | 心肌梗死,心肌病,心力衰竭,瓣膜性心脏病 | 33 vs 75 | 58.3% vs 65% | 15.2% vs 2.7% ( | ||||||
| Xu[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性队列研究 | 2.37±2.1年 vs 2.24±2.5年 | 未记录 | 25 vs 62 | 76.0% vs 74.2% ( | 4.0% vs 3.2% ( | ||||||
| Bass[ | 2021 | 多中心,回顾性队列研究 | 90 d | 未记录 | 180 vs 769 | 未记录 | 7.8% vs 10.9% ( | ||||||
| Abdelnabi[ | 2021 | 多中心、开放性、前瞻性、随机临床试验 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 39 vs 40 | 1个月 :71.8% vs 47.5% ( 3个月:76.9% vs 67.5%( 6个月:87.2% vs 80.0%( | 5.1% vs 15% ( | ||||||
| Alcalai[ | 2021 | 多中心、开放性、前瞻性、随机临床试验 | 3个月 | 心肌梗死后 | 17 vs 15 | 94.1% vs 93.3% | 0.0%vs 13.3% | ||||||
| Guddeti[ | 2020 | 多中心、回顾性研究 | 随访中位数:1年,平均随访时间: 10.4±3.4 个月 | 缺血性心肌病和非缺血性心肌病 | 19 vs 80 | 80.0% vs 81.0% ( | 5.3% vs 5.0%( | ||||||
| Robinson[ | 2020 | 多中心、队列研究 | 随访中位数:351 天 | 缺血性心肌病和非缺血性心肌病 | 121 vs 236 | NR | 6.6% vs 8.1% | ||||||
| Ratnayake[ | 2020 | 单中心、回顾性、观察性、队列研究 | 6个月 | ST段抬高型心肌梗死 | 2 vs 42 | 50.0% vs 81.0% | 未记录 | ||||||
| Iqbal[ | 2020 | 单中心、回顾性、观察性、队列研究 | 评价随访时间: 3.0±1.4年 | 缺血性心肌病、扩张型心肌病、肥厚性心肌病、病因不详 | 22 vs 62 | 65.0% vs 76.0% ( | 0.0% vs 10.0% ( | ||||||
| Ali[ | 2020 | 单中心、回顾性研究 | 1年 | 慢性缺血性心肌病(58%),非缺血性心肌病(23%) | 32 vs 60 | 56.3% vs 62.0% ( | 0.0% vs 3.3% | ||||||
| Willeford[ | 2021 | 单中心、回顾性研究 | 1年 | 心肌梗死,心力衰竭,冠心病 | 22 vs 129 | 59.1% vs 48.8% ( | 4.5% vs 3.9% ( | ||||||
| Alcalai[ | 2021 | 多中心、开放性、前瞻性、随机临床试验 | 3个月 | 心肌梗死 | 13 vs 12 | 92.3% vs 100% | 0.0% vs 16.7% | ||||||
| Alizadeh[ | 2019 | 前瞻性、观察性研究 | 中位数:1.8年 | 心肌梗死 | 38 vs 60 | 75.0% vs 53.0% ( | 0.0% vs 5.0% ( | ||||||
| Gama[ | 2019 | 单中心、回顾性、队列研究 | 未记录 | 心肌梗死,射血分数减低的心力衰竭 | 12 vs 52 | 91.7% vs 59.6% | 未记录 | ||||||
| Cochran[ | 2021 | 回顾性研究 | 12个月 | 未记录 | 14 vs 59 | 76.3% vs 85.7% ( | 14.3% vs 13.65 ( | ||||||
| Daher[ | 2020 | 观察性、回顾性研究 | 3个月 | 心肌梗死,缺血性心肌病 | 17 vs 42 | 70.6% vs 71.4%( | 未记录 | ||||||
| Jaidka[ | 2018 | 回顾性研究 | 6个月 | 心肌梗死 | 12 vs 37 | 88.9% vs 69.2% ( | 25.0% vs16.2% | ||||||
| Yunis[ | 2020 | 回顾性队列研究 | 24个月 | 未记录 | 64 vs 200 | 97.0% vs 100.0%( | 6个月:3.2% vs 1.5%( 12个月:5.1% vs 2.1%( 24个月:5.1% vs 4.9%( | ||||||
| 作者 | 严重出血事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | 轻微出血事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | 脑卒中 (DOAC vs VKA) | 全身栓塞事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | 全因死亡率 (DOAC vs VKA) | ||||||||
| Herald[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 19.4% vs 24.4%[ | 21.6% vs 28.1%[ | 23.9% vs 46.2%[ | ||||||||
| Zhang[ | 24个月:0.0% vs 3.2% | 24个月:6.0% vs 6.4% | 未记录 | 24个月:3.0% vs 12.9%[ | 24个月:3.0% vs 12.9%[ | ||||||||
| Tamimi[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Aldaas[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Varwan[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 1.7% vs 2.9%( | 1.7% vs 2.9%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Jones[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 2.4% vs 5%( | 2.4% vs 5%( | 0.0% vs 0.0% | ||||||||
| Albabtain[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 3.8% vs 2.9%( | 3.8% vs 0.0% | 7.14% vs 8.57%( | ||||||||
| Mihm[ | 15.2% vs 2.7% ( | 未记录 | 6.1% vs 5.3% | 9.1% vs 5.4% | 12.1% vs 8% | ||||||||
| Xu[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 4.0% vs 4.8% ( | 4.0% vs 6.5% ( | 8.0% vs 4.8% ( | ||||||||
| Bass[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 7.8% vs 11.7% ( | 33.0% vs 30.6% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Abdelnabi[ | 5.1% vs 15% ( | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 10.0% ( | 0.0%vs 15.0% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Alcalai[ | 0.0% vs 13.3% | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 6.7% | 5.9% vs 0.0% | ||||||||
| Guddeti[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 2.5%( | 0.0% vs 2.5%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Robinson[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 14.0% vs 5.9%( | 11.6% vs 13.6% | ||||||||
| Ratnayake[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Iqbal[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 2.0%( | 0.0% vs 4.0%( | 14.0% vs 10.0%( | ||||||||
| Ali[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 2 vs 7 | 6.7% vs 20% | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Willeford[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0% vs 5.4%( | 0.0% vs 6.2%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Alcalai[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 0.0% | 0.0% vs 0.0% | 0.0% vs 0.0% | ||||||||
| Alizadeh[ | 0.0% vs 5.0% ( | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Gama[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Cochran[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 15.3% ( | 0.0% vs 15.3% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Daher[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 11.8% vs 9.5%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Jaidka[ | 8.3% vs 0.0% ( | 16.7% vs 16.2% ( | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 5.4% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Yunis[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 6个月:0.0% vs 1.1% ( 12个月:5.3% vs 4.1% ( 24个月:12.4% vs 5.4% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
Tab. 1 Characteristics of included studies of the meta-analysis
| 作者 | 发表 年份 | 研究类型 | 随访年限 | LVT的原因 | DOAC vs VKA | LVT的消失率 (DOAC vs VKA) | 出血事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herald[ | 2022 | 回顾性队列研究 | 中位数:3.4年 | 未记录 | 134 vs 299 | 未记录 | 27.6% vs 37.8%[ | ||||||
| Zhang[ | 2022 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 24个月 | STEMI-PCI术后 | 33 vs 31 | 6个月:42.4% vs 19.4% [ 12个月:69.7% vs 48.4%[ 18个月:78.8% vs 64.5%[ | 6.1% vs 9.7%[ | ||||||
| Tamimi[ | 2022 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 6个月 | 131例患者(66.4%)有缺血性心肌病,其他患者不详 | 48 vs 116 | 66.6% vs 79.3% ( | 10.0% vs 8.0% ( | ||||||
| Aldaas[ | 2022 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 中位数:7.2个月(新型口服抗凝药),10个月(华法林) | 未记录 | 76 vs 146 | 13.2% vs 16.4%[HR 0.08(95% | 未记录 | ||||||
| Varwan[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 2年 | 心肌梗死(28%),慢性缺血性心肌病(42%),非缺血性心肌病(30%) | 58 vs 34 | 55.6% vs 64.0% ( | 5.2% vs 5.9% ( | ||||||
| Jones[ | 2020 | 单中心、观察性、前瞻性研究 | 中位数:2.2年 | 心肌梗死 | 41 vs 60 | 151天:70.7% vs 48.3% ( 1年: 82.0% vs 64.4% ( 利伐沙班、阿哌沙班和依度沙班的LVT消失率:88%, 93%, 100% | 14.6% vs 36.7% ( | ||||||
| Albabtain[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性研究 | 利伐沙班治疗的中位数:9.5个月(25%~75%的可信区间:6~32.5个月),华法林治疗的中位数:14个月(25%~75%的可信区间:3~41个月) | 心肌梗死,扩张型心肌病,心力衰竭 | 28 vs 35 | 71.4% vs 68.6% LVT消失的中位时间: 3(2~11.5)个月vs 9 (4~20)个月( | 7.1% vs 2.9% ( | ||||||
| Mihm[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性队列研究 | 6个月 | 心肌梗死,心肌病,心力衰竭,瓣膜性心脏病 | 33 vs 75 | 58.3% vs 65% | 15.2% vs 2.7% ( | ||||||
| Xu[ | 2021 | 单中心,回顾性队列研究 | 2.37±2.1年 vs 2.24±2.5年 | 未记录 | 25 vs 62 | 76.0% vs 74.2% ( | 4.0% vs 3.2% ( | ||||||
| Bass[ | 2021 | 多中心,回顾性队列研究 | 90 d | 未记录 | 180 vs 769 | 未记录 | 7.8% vs 10.9% ( | ||||||
| Abdelnabi[ | 2021 | 多中心、开放性、前瞻性、随机临床试验 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 39 vs 40 | 1个月 :71.8% vs 47.5% ( 3个月:76.9% vs 67.5%( 6个月:87.2% vs 80.0%( | 5.1% vs 15% ( | ||||||
| Alcalai[ | 2021 | 多中心、开放性、前瞻性、随机临床试验 | 3个月 | 心肌梗死后 | 17 vs 15 | 94.1% vs 93.3% | 0.0%vs 13.3% | ||||||
| Guddeti[ | 2020 | 多中心、回顾性研究 | 随访中位数:1年,平均随访时间: 10.4±3.4 个月 | 缺血性心肌病和非缺血性心肌病 | 19 vs 80 | 80.0% vs 81.0% ( | 5.3% vs 5.0%( | ||||||
| Robinson[ | 2020 | 多中心、队列研究 | 随访中位数:351 天 | 缺血性心肌病和非缺血性心肌病 | 121 vs 236 | NR | 6.6% vs 8.1% | ||||||
| Ratnayake[ | 2020 | 单中心、回顾性、观察性、队列研究 | 6个月 | ST段抬高型心肌梗死 | 2 vs 42 | 50.0% vs 81.0% | 未记录 | ||||||
| Iqbal[ | 2020 | 单中心、回顾性、观察性、队列研究 | 评价随访时间: 3.0±1.4年 | 缺血性心肌病、扩张型心肌病、肥厚性心肌病、病因不详 | 22 vs 62 | 65.0% vs 76.0% ( | 0.0% vs 10.0% ( | ||||||
| Ali[ | 2020 | 单中心、回顾性研究 | 1年 | 慢性缺血性心肌病(58%),非缺血性心肌病(23%) | 32 vs 60 | 56.3% vs 62.0% ( | 0.0% vs 3.3% | ||||||
| Willeford[ | 2021 | 单中心、回顾性研究 | 1年 | 心肌梗死,心力衰竭,冠心病 | 22 vs 129 | 59.1% vs 48.8% ( | 4.5% vs 3.9% ( | ||||||
| Alcalai[ | 2021 | 多中心、开放性、前瞻性、随机临床试验 | 3个月 | 心肌梗死 | 13 vs 12 | 92.3% vs 100% | 0.0% vs 16.7% | ||||||
| Alizadeh[ | 2019 | 前瞻性、观察性研究 | 中位数:1.8年 | 心肌梗死 | 38 vs 60 | 75.0% vs 53.0% ( | 0.0% vs 5.0% ( | ||||||
| Gama[ | 2019 | 单中心、回顾性、队列研究 | 未记录 | 心肌梗死,射血分数减低的心力衰竭 | 12 vs 52 | 91.7% vs 59.6% | 未记录 | ||||||
| Cochran[ | 2021 | 回顾性研究 | 12个月 | 未记录 | 14 vs 59 | 76.3% vs 85.7% ( | 14.3% vs 13.65 ( | ||||||
| Daher[ | 2020 | 观察性、回顾性研究 | 3个月 | 心肌梗死,缺血性心肌病 | 17 vs 42 | 70.6% vs 71.4%( | 未记录 | ||||||
| Jaidka[ | 2018 | 回顾性研究 | 6个月 | 心肌梗死 | 12 vs 37 | 88.9% vs 69.2% ( | 25.0% vs16.2% | ||||||
| Yunis[ | 2020 | 回顾性队列研究 | 24个月 | 未记录 | 64 vs 200 | 97.0% vs 100.0%( | 6个月:3.2% vs 1.5%( 12个月:5.1% vs 2.1%( 24个月:5.1% vs 4.9%( | ||||||
| 作者 | 严重出血事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | 轻微出血事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | 脑卒中 (DOAC vs VKA) | 全身栓塞事件 (DOAC vs VKA) | 全因死亡率 (DOAC vs VKA) | ||||||||
| Herald[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 19.4% vs 24.4%[ | 21.6% vs 28.1%[ | 23.9% vs 46.2%[ | ||||||||
| Zhang[ | 24个月:0.0% vs 3.2% | 24个月:6.0% vs 6.4% | 未记录 | 24个月:3.0% vs 12.9%[ | 24个月:3.0% vs 12.9%[ | ||||||||
| Tamimi[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Aldaas[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Varwan[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 1.7% vs 2.9%( | 1.7% vs 2.9%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Jones[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 2.4% vs 5%( | 2.4% vs 5%( | 0.0% vs 0.0% | ||||||||
| Albabtain[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 3.8% vs 2.9%( | 3.8% vs 0.0% | 7.14% vs 8.57%( | ||||||||
| Mihm[ | 15.2% vs 2.7% ( | 未记录 | 6.1% vs 5.3% | 9.1% vs 5.4% | 12.1% vs 8% | ||||||||
| Xu[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 4.0% vs 4.8% ( | 4.0% vs 6.5% ( | 8.0% vs 4.8% ( | ||||||||
| Bass[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 7.8% vs 11.7% ( | 33.0% vs 30.6% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Abdelnabi[ | 5.1% vs 15% ( | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 10.0% ( | 0.0%vs 15.0% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Alcalai[ | 0.0% vs 13.3% | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 6.7% | 5.9% vs 0.0% | ||||||||
| Guddeti[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 2.5%( | 0.0% vs 2.5%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Robinson[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 14.0% vs 5.9%( | 11.6% vs 13.6% | ||||||||
| Ratnayake[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Iqbal[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 2.0%( | 0.0% vs 4.0%( | 14.0% vs 10.0%( | ||||||||
| Ali[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 2 vs 7 | 6.7% vs 20% | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Willeford[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0% vs 5.4%( | 0.0% vs 6.2%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Alcalai[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 0.0% | 0.0% vs 0.0% | 0.0% vs 0.0% | ||||||||
| Alizadeh[ | 0.0% vs 5.0% ( | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Gama[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Cochran[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 15.3% ( | 0.0% vs 15.3% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Daher[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 11.8% vs 9.5%( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Jaidka[ | 8.3% vs 0.0% ( | 16.7% vs 16.2% ( | 未记录 | 0.0% vs 5.4% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| Yunis[ | 未记录 | 未记录 | 未记录 | 6个月:0.0% vs 1.1% ( 12个月:5.3% vs 4.1% ( 24个月:12.4% vs 5.4% ( | 未记录 | ||||||||
| DOAC(%) | VKA(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
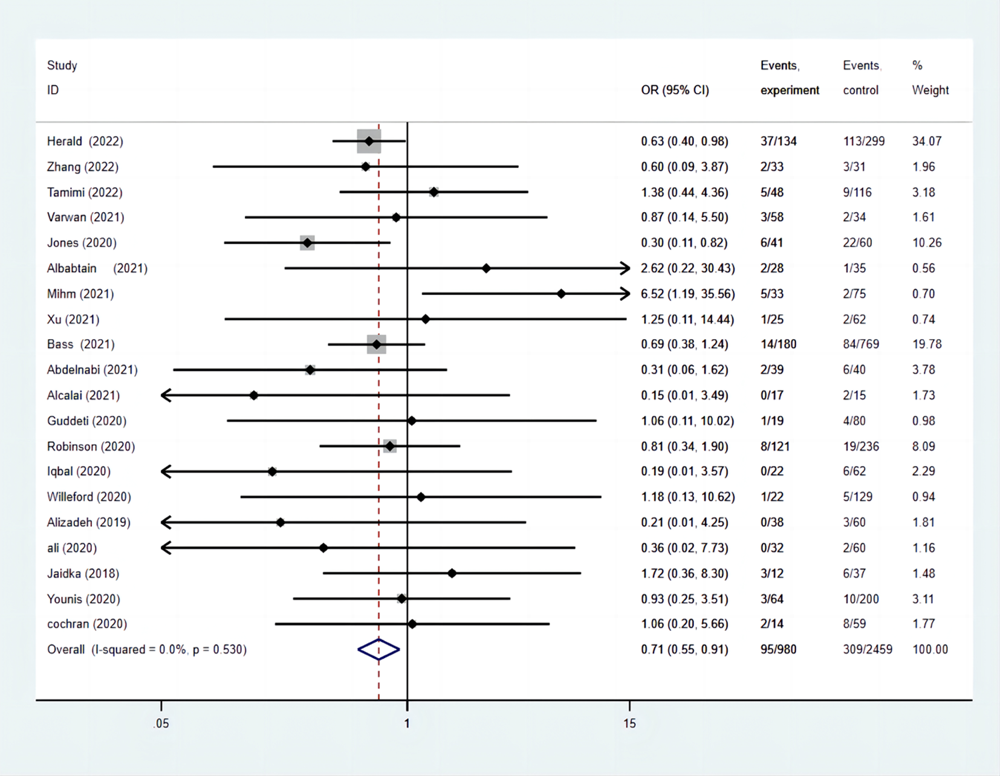
| 出血事件发生率 | 9.69 | 12.57 | 0.71(0.55-0.91) |
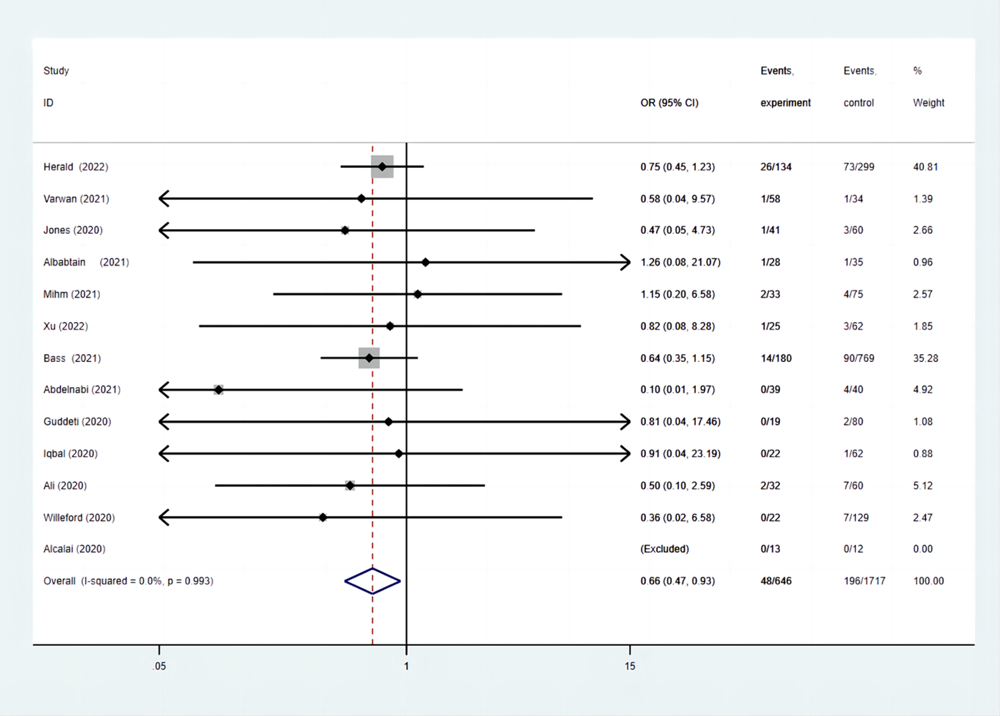
| 卒中事件发生率 | 7.43 | 11.42 | 0.66(0.47-0.93) |
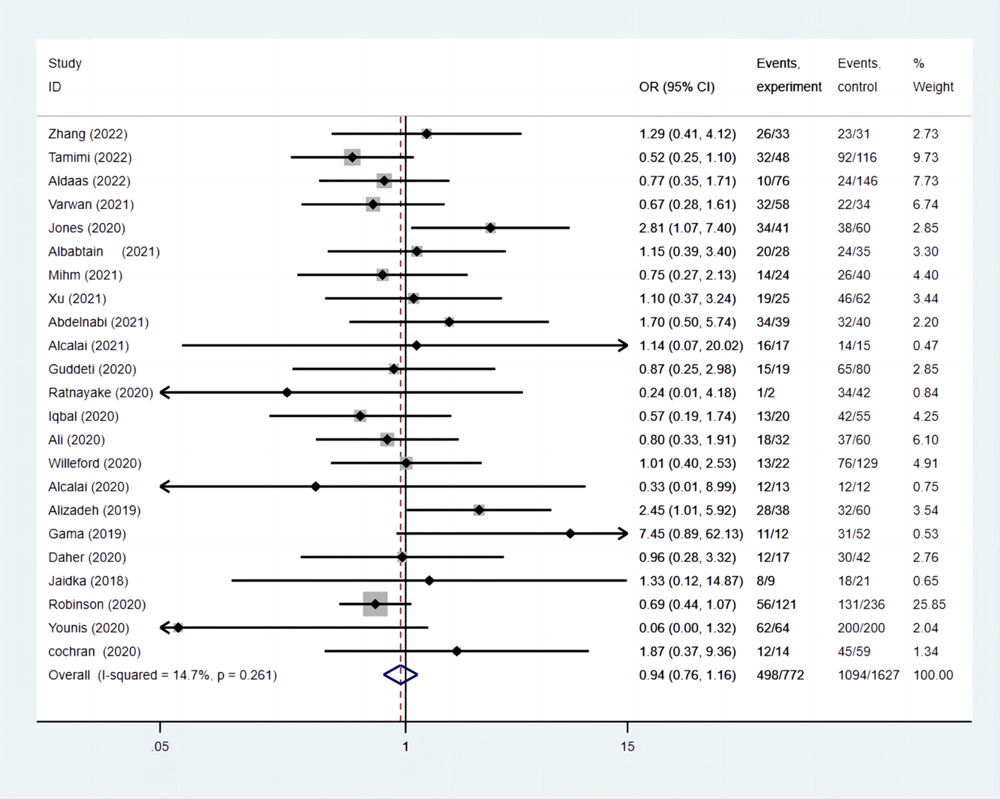
| LVT消失率 | 64.51 | 67.24 | 0.94(0.76-1.16) |
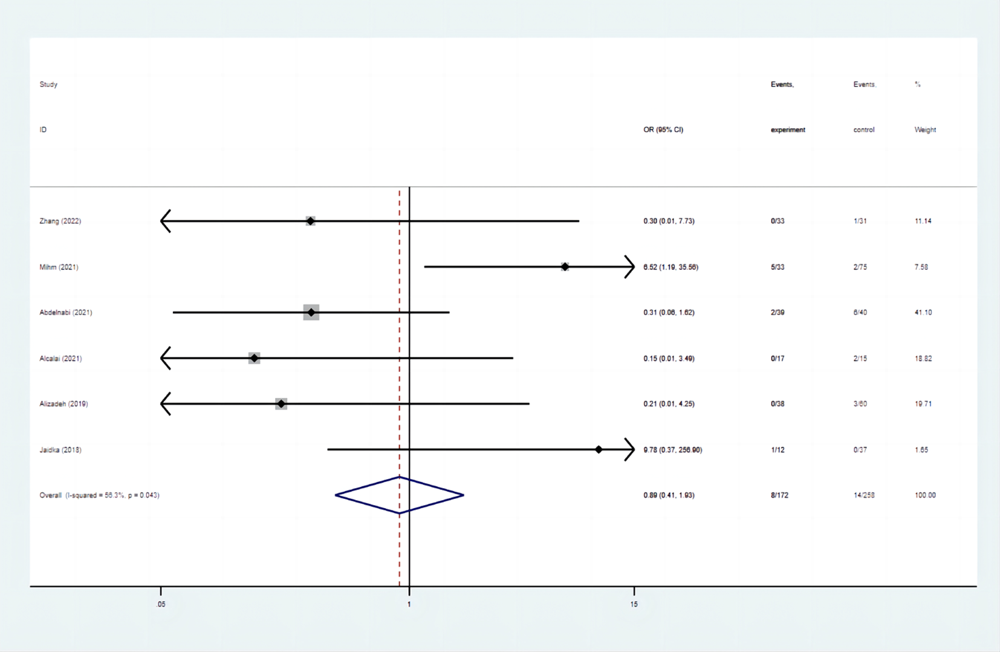
| 严重出血事件发生率 | 4.65 | 5.43 | 0.89(0.41-1.03) |
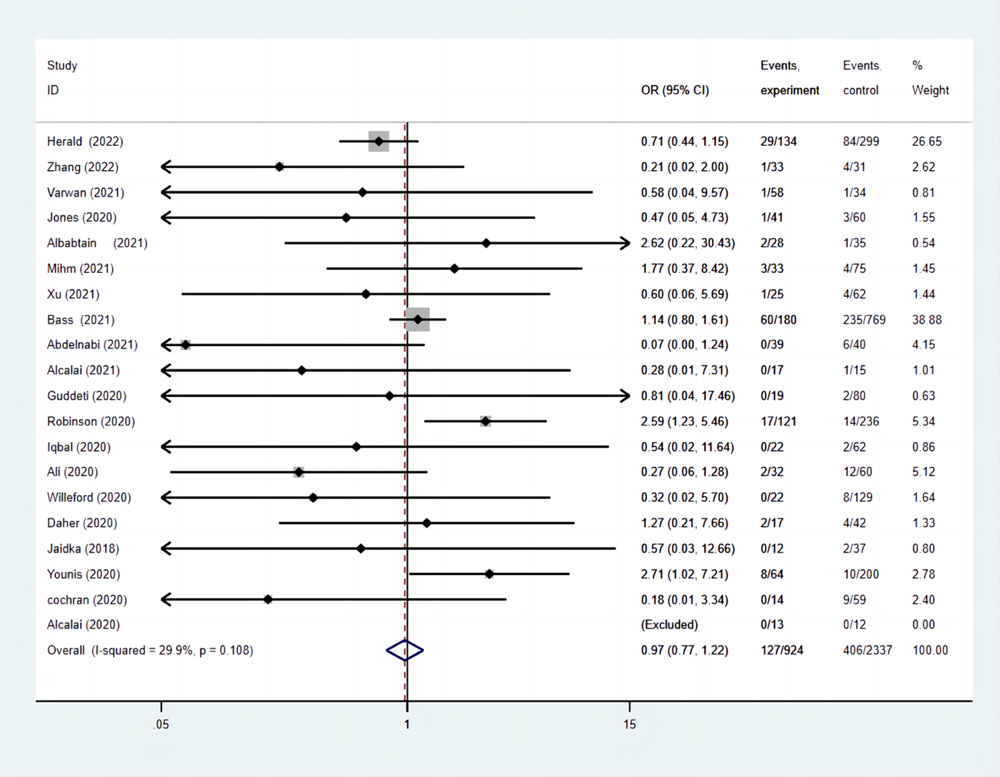
| 全身血栓栓塞事件发生率 | 13.74 | 17.37 | 0.97(0.77-1.22) |
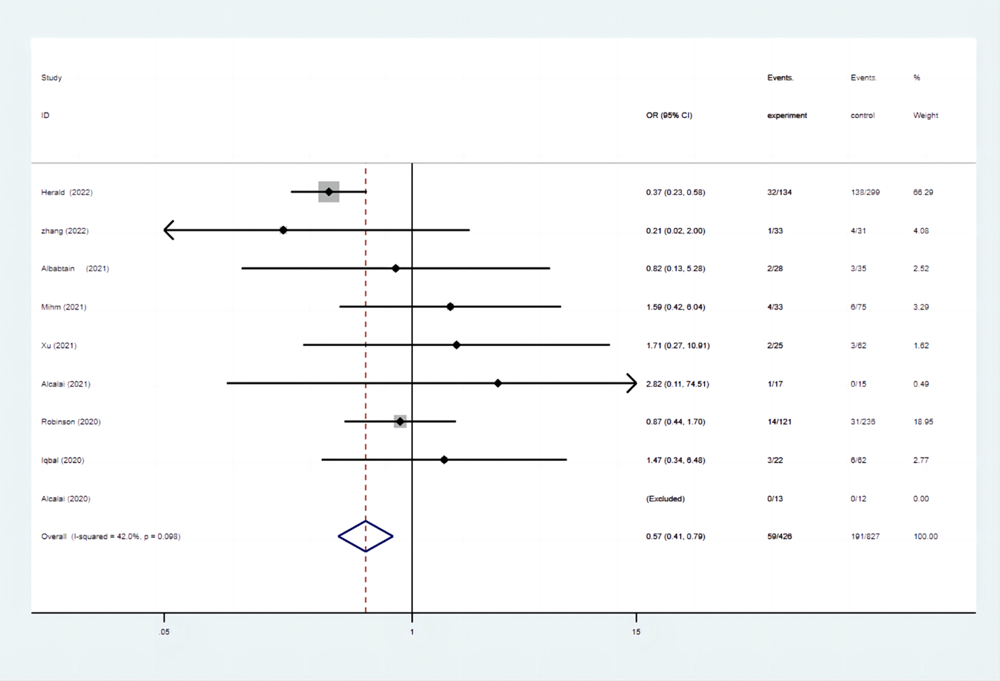
| 全因死亡率 | 13.85 | 23.10 | 0.57(0.41-0.79) |
Tab. 2 The meta-analysis results of DOAC versus VKA in the treatment of LVT
| DOAC(%) | VKA(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 出血事件发生率 | 9.69 | 12.57 | 0.71(0.55-0.91) |
| 卒中事件发生率 | 7.43 | 11.42 | 0.66(0.47-0.93) |
| LVT消失率 | 64.51 | 67.24 | 0.94(0.76-1.16) |
| 严重出血事件发生率 | 4.65 | 5.43 | 0.89(0.41-1.03) |
| 全身血栓栓塞事件发生率 | 13.74 | 17.37 | 0.97(0.77-1.22) |
| 全因死亡率 | 13.85 | 23.10 | 0.57(0.41-0.79) |
| 作者 | 例数 | 溶栓药物 | 方法 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kremer[ | 16 | 尿激酶 | 60.000 U/h输注×2~8天,静脉应用肝素200 U/kg×12 h;溶栓结束后给予双香豆素持续抗凝。应用普通经胸超声心动图对血栓进行评估 | 10例患者血栓完全消失,4例患者血栓减小,2例患者血栓无明显变化。溶栓治疗过程中,无患者发生全身血栓栓塞事件,有2例患者发生血尿,其中1例患者因此停止溶栓治疗。6个月后应用超声心动图进行随访,血栓完全消失的患者未新发血栓 |
| Yeh[ | 1 | rt-PA | rt-PA 15 mg负荷量,随后30分钟内给予50 mg静脉输注,其后1小时内给予35 mg静脉输注;输注完成后静脉应用肝素维持活化凝血酶原时间为正常值的1.5~2倍。后续华法林持续抗凝 | 溶栓完成后2、4、16、40 h超声心动图示血栓逐渐减小最终消失,治疗过程中无出血或者全身栓塞事件等并发症发生 |
Tab. 3 Thrombolytic therapy for LVT
| 作者 | 例数 | 溶栓药物 | 方法 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kremer[ | 16 | 尿激酶 | 60.000 U/h输注×2~8天,静脉应用肝素200 U/kg×12 h;溶栓结束后给予双香豆素持续抗凝。应用普通经胸超声心动图对血栓进行评估 | 10例患者血栓完全消失,4例患者血栓减小,2例患者血栓无明显变化。溶栓治疗过程中,无患者发生全身血栓栓塞事件,有2例患者发生血尿,其中1例患者因此停止溶栓治疗。6个月后应用超声心动图进行随访,血栓完全消失的患者未新发血栓 |
| Yeh[ | 1 | rt-PA | rt-PA 15 mg负荷量,随后30分钟内给予50 mg静脉输注,其后1小时内给予35 mg静脉输注;输注完成后静脉应用肝素维持活化凝血酶原时间为正常值的1.5~2倍。后续华法林持续抗凝 | 溶栓完成后2、4、16、40 h超声心动图示血栓逐渐减小最终消失,治疗过程中无出血或者全身栓塞事件等并发症发生 |
| 作者 | 例数 | 药物及用药方法 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kouvaras[ | 60 | 60例继发心肌梗死的LVT患者随机均分为抗凝组(口服抗凝药治疗,凝血酶原时间延长至1.6~2倍)、抗血小板组(阿司匹林 650 mg/d)及对照组(未给予任何抗栓治疗)。应用超声心动图每3个月进行1次随访,共随访9~24个月(平均16±5个月) | 3个月后随访发现:抗凝组12例患者血栓消失,3例患者血栓明显减小;抗血小板组9例患者血栓消失,4例患者血栓明显减小;对照组2例患者血栓消失。抗凝组与抗血小板组的血栓消失率与血栓减小率相当;而对照组血栓自发消失率及血栓减小率很低 |
| Kupferschmid[ | 3 | 3例扩张型心肌病患者。第1例应用阿司匹林(25 mg/kg)和双嘧达莫(6 mg/kg);第2例应用阿司匹林和双嘧达莫(具体剂量不详);第3例应用抗血小板治疗(具体不详) | 虽然治疗过程中,LVT消失,但在继续抗血小板治疗的随访过程中,LVT再次出现,提示单独抗血小板治疗对于治疗LVT无效 |
| Stratton[ | 16 | 将16例主要继发于陈旧性心肌梗死的LVT患者分为苯磺唑酮组(200 mg, 4次/d;7人次),阿司匹林联合双嘧达莫组(阿司匹林325 mg,1次/d,双嘧达莫75 mg, 3次/d ;6人次), 全剂量华法林组(4人次) | 应用铟-111血小板成像和超声心动图进行随访,苯磺唑酮组中铟-111血小板成像:3例患者转阴,2例变得模糊,2例无任何变化;超声心动图发现7例患者血栓大小无变化。阿司匹林联合双嘧达莫组铟-111血小板成像:1例患者患者转阴,3例变得模糊,2例无任何变化;超声心动图发现1例患者血栓减小,6例患者血栓大小无变化。华法林组:铟-111血小板成像:3例患者患者转阴,1例无任何变化;超声心动图发现1例血栓减小,2例血栓大小无变化。发现与应用抗凝剂相比,联合应用抗血小板药物(阿司匹林、双嘧达莫)可以抑制血小板在LVT表面聚集,但无法使血栓消失或变小 |
| Bellotti[ | 32 | 32例继发于陈旧性心肌梗死的LVT患者分为噻氯匹定组(6例患者250 mg, 1次/d,5例患者 500 mg/d),吲哚布芬组(12例患者:400 mg/d),未治疗组(9例患者) | (40±11) d后,In-oxine血小板成像检查:噻氯匹定组2例(500 mg/d)血小板沉积完全消失,5例(2例:500 mg/d,3例:250 mg/d)血小板沉积减少;吲哚布芬组5例和未治疗组1例血小板沉积减少。超声心动图检查:只有噻氯匹定组1例(25 0mg 1/日)血栓减小。结果表明应用抗血小板药物(吲哚布芬、噻氯匹定)虽可抑制血小板在血栓表面聚集,但无助于血栓的缩小或消失 |
Tab. 4 Anti-platelet therapy for LVT
| 作者 | 例数 | 药物及用药方法 | 结果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kouvaras[ | 60 | 60例继发心肌梗死的LVT患者随机均分为抗凝组(口服抗凝药治疗,凝血酶原时间延长至1.6~2倍)、抗血小板组(阿司匹林 650 mg/d)及对照组(未给予任何抗栓治疗)。应用超声心动图每3个月进行1次随访,共随访9~24个月(平均16±5个月) | 3个月后随访发现:抗凝组12例患者血栓消失,3例患者血栓明显减小;抗血小板组9例患者血栓消失,4例患者血栓明显减小;对照组2例患者血栓消失。抗凝组与抗血小板组的血栓消失率与血栓减小率相当;而对照组血栓自发消失率及血栓减小率很低 |
| Kupferschmid[ | 3 | 3例扩张型心肌病患者。第1例应用阿司匹林(25 mg/kg)和双嘧达莫(6 mg/kg);第2例应用阿司匹林和双嘧达莫(具体剂量不详);第3例应用抗血小板治疗(具体不详) | 虽然治疗过程中,LVT消失,但在继续抗血小板治疗的随访过程中,LVT再次出现,提示单独抗血小板治疗对于治疗LVT无效 |
| Stratton[ | 16 | 将16例主要继发于陈旧性心肌梗死的LVT患者分为苯磺唑酮组(200 mg, 4次/d;7人次),阿司匹林联合双嘧达莫组(阿司匹林325 mg,1次/d,双嘧达莫75 mg, 3次/d ;6人次), 全剂量华法林组(4人次) | 应用铟-111血小板成像和超声心动图进行随访,苯磺唑酮组中铟-111血小板成像:3例患者转阴,2例变得模糊,2例无任何变化;超声心动图发现7例患者血栓大小无变化。阿司匹林联合双嘧达莫组铟-111血小板成像:1例患者患者转阴,3例变得模糊,2例无任何变化;超声心动图发现1例患者血栓减小,6例患者血栓大小无变化。华法林组:铟-111血小板成像:3例患者患者转阴,1例无任何变化;超声心动图发现1例血栓减小,2例血栓大小无变化。发现与应用抗凝剂相比,联合应用抗血小板药物(阿司匹林、双嘧达莫)可以抑制血小板在LVT表面聚集,但无法使血栓消失或变小 |
| Bellotti[ | 32 | 32例继发于陈旧性心肌梗死的LVT患者分为噻氯匹定组(6例患者250 mg, 1次/d,5例患者 500 mg/d),吲哚布芬组(12例患者:400 mg/d),未治疗组(9例患者) | (40±11) d后,In-oxine血小板成像检查:噻氯匹定组2例(500 mg/d)血小板沉积完全消失,5例(2例:500 mg/d,3例:250 mg/d)血小板沉积减少;吲哚布芬组5例和未治疗组1例血小板沉积减少。超声心动图检查:只有噻氯匹定组1例(25 0mg 1/日)血栓减小。结果表明应用抗血小板药物(吲哚布芬、噻氯匹定)虽可抑制血小板在血栓表面聚集,但无助于血栓的缩小或消失 |
| [1] | Levine GN, McEvoy JW, Fang JC, et al. Management of patients at risk for and with left ventricular thrombus: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2022, 146(15):e205-e223. |
| [2] |
Herald J, Goitia J, Duan L, et al. Safety and effectiveness of direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for treating left ventricular thrombus[J]. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs, 2022, 22(4):437-444.
doi: 10.1007/s40256-022-00533-w |
| [3] |
Zhang Z, Si D, Zhang Q, et al. Rivaroxaban versus vitamin K antagonists (warfarin) based on the triple therapy for left ventricular thrombus after ST-elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Heart Vessels, 2022, 37(3):374-384.
doi: 10.1007/s00380-021-01921-z |
| [4] | Tamimi FA, Rana YP, Omar A, et al. Management and clinical outcomes of left ventricular thrombus[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 15(Suppl 9):S11-12. |
| [5] |
Aldaas OM, Ji-hyun K, Palakodeti S, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants compared with warfarin for the treatment of left ventricular thrombi[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2022, 79(9 Suppl A):1756.
doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(22)02747-4 URL |
| [6] |
Varwani MH, Shah J, Ngunga M, et al. Treatment and outcomes in patients with left ventricular thrombus - experiences from the Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi - Kenya[J]. Pan Afr Med J, 2021, 39:212.
doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.39.212.28585 pmid: 34630824 |
| [7] |
Jones DA, Wright P, Alizadeh MA, et al. The use of novel oral anticoagulants compared to vitamin K antagonists (warfarin) in patients with left ventricular thrombus after acute myocardial infarction[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, 2021, 7(5):398-404.
doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvaa096 URL |
| [8] |
Albabtain MA, Alhebaishi Y, Al-Yafi O, et al. Rivaroxaban versus warfarin for the management of left ventricle thrombus[J]. Egypt Heart J, 2021, 73(1):41.
doi: 10.1186/s43044-021-00164-7 pmid: 33932172 |
| [9] |
Mihm AE, Hicklin HE, Cunha AL, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin for the treatment of left ventricular thrombosis[J]. Intern Emerg Med, 2021, 16(8):2313-2317.
doi: 10.1007/s11739-021-02788-8 pmid: 34165680 |
| [10] |
Xu Z, Li X, Li X, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus vitamin K antagonists for patients with left ventricular thrombus[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10(9):9427-9434.
doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1683 pmid: 34628868 |
| [11] |
Bass ME, Kiser TH, Page RL 2nd, et al. Comparative effectiveness of direct oral anticoagulants and warfarin for the treatment of left ventricular thrombus[J]. J Thromb Thrombolysis, 2021, 52(2):517-522.
doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02371-6 |
| [12] |
Abdelnabi M, Saleh Y, Fareed A, et al. Comparative study of oral anticoagulation in left ventricular thrombi (No-LVT Trial)[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2021, 77(12):1590-1592.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2021.01.049 pmid: 33766266 |
| [13] | Alcalai R, Butnaru A, Moravsky G, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with left ventricular thrombus, a prospective multicenter randomized clinical trial[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, 2021, 52(2):517-522. |
| [14] |
Guddeti RR, Anwar M, Walters RW, et al. Treatment of left ventricular thrombus with direct oral anticoagulants: A retrospective observational study[J]. Am J Med, 2020, 133(12):1488-1491.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.05.025 pmid: 32598904 |
| [15] |
Robinson AA, Trankle CR, Eubanks G, et al. Off-label use of direct oral anticoagulants compared with warfarin for left ventricular thrombi[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2020, 5(6):685-692.
doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0652 pmid: 32320043 |
| [16] | Ratnayake C, Liu B, Benatar J, et al. Left ventricular thrombus after ST segment elevation myocardial infarction: A single-centre observational study[J]. N Z Med J, 2020, 133(1526):45-54. |
| [17] | Iqbal H, Straw S, Craven TP, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants compared to vitamin K antagonist for the management of left ventricular thrombus[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2020, 7(5):2032-2041. |
| [18] |
Ali Z, Isom N, Dalia T, et al. Direct oral anticoagulant use in left ventricular thrombus[J]. Thromb J, 2020, 18:29.
doi: 10.1186/s12959-020-00242-x pmid: 33132763 |
| [19] |
Willeford A, Zhu W, Stevens C, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants versus warfarin in the treatment of left ventricular thrombus[J]. Ann Pharmacother, 2021, 55(7):839-845.
doi: 10.1177/1060028020975111 pmid: 33191781 |
| [20] | Alcalai R, Butnaru A, Moravsky G, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with left ventricular thrombus, a prospective multicenter randomized clinical trial[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother, 2021, 55(7):839-845. |
| [21] | Alizadeh MAS, Fhadil SRR, Guttmann OKC, et al. The use of direct oral anti-coagulations (DOACs) compared to vitamin K antagonist in patients with left ventricular thrombus after acute myocardial infarction[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(Suppl 1):4026. |
| [22] | Gama F, Freitas P, Trabulo M, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants are an effective therapy for left ventricular thrombus formation[J]. Eur Heart J, 2019, 40(Suppl 1):166. |
| [23] |
Cochran JM, Jia X, Kaczmarek J, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants in the treatment of left ventricular thrombus: A retrospective, multicenter study and meta-analysis of existing data[J]. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther, 2021, 26(2):173-178.
doi: 10.1177/1074248420967644 URL |
| [24] |
Daher J, Da Costa A, Hilaire C, et al. Management of left ventricular thrombi with direct oral anticoagulants: Retrospective comparative study with vitamin K antagonists[J]. Clin Drug Investig, 2020, 40(4):343-353.
doi: 10.1007/s40261-020-00898-3 |
| [25] |
Jaidka A, Zhu T, Lavi S, et al. Treatment of left ventricular thrombus using warfarin versus direct oral anticoagulants following anterior myocardial infarction[J]. Can J Cardiol, 2018, 34(10):S143.
doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2018.07.194 URL |
| [26] |
Yunis A, Seese LM, Stearns B, et al. Direct oral anticoagulants are effective therapy in treating left ventricular thrombi[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 75(11 suppl 1):948.
doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(20)31575-8 URL |
| [27] |
Vecchio C, Chiarella F, Lupi G, et al. Left ventricular thrombus in anterior acute myocardial infarction after thrombolysis. A GISSI-2 connected study[J]. Circulation, 1991, 84(2):512-519.
pmid: 1860196 |
| [28] |
Heik SC, Kupper W, Hamm C, et al. Efficacy of high dose intravenous heparin for treatment of left ventricular thrombi with high embolic risk[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1994, 24(5):1305-1309.
doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(94)90113-9 pmid: 7930254 |
| [29] |
Meurin P, Tabet JY, Renaud N, et al. Treatment of left ventricular thrombi with a low molecular weight heparin[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2005, 98(2):319-323.
pmid: 15686785 |
| [30] |
Kremer P, Fiebig R, Tilsner V, et al. Lysis of left ventricular thrombi with urokinase[J]. Circulation, 1985, 72(1):112-118.
doi: 10.1161/01.cir.72.1.112 pmid: 4006122 |
| [31] |
Yeh KH, Hung KC, Lin FC, et al. Successful lysis of right and left heart thrombus by tissue plasminogen activator[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2000, 49(1):91-96.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1522-726X URL |
| [32] |
Kouvaras G, Chronopoulos G, Soufras G, et al. The effects of long-term antithrombotic treatment on left ventricular thrombi in patients after an acute myocardial infarction[J]. Am Heart J, 1990, 119(1):73-78.
pmid: 2296877 |
| [33] |
Kupferschmid C, Schmaltz AA, Tacke E, et al. Left ventricular thrombi in three children with dilated cardiomyopathy: Diagnostic procedure and clinical course[J]. Pediatr Cardiol, 1984, 5(1):65-69.
pmid: 6462932 |
| [34] |
Stratton JR, Ritchie JL. The effects of antithrombotic drugs in patients with left ventricular thrombi: Assessment with indium-111 platelet imaging and two-dimensional echocardiography[J]. Circulation, 1984, 69(3):561-568.
pmid: 6692517 |
| [35] |
Bellotti P, Claudiani F, Chiarella F, et al. Left ventricular thrombi: Changes in size and in platelet deposition during treatment with indobufen and ticlopidine[J]. Cardiology, 1990, 77(4):272-279.
pmid: 2073644 |
| [36] |
Tanaka D, Unai S, Diehl JT, et al. Surgical removal of a large mobile left ventricular thrombus via left atriotomy[J]. World J Clin Cases, 2014, 2(2):32-35.
doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i2.32 pmid: 24579068 |
| [37] |
Eranki A, Villanueva C, Collins N, et al. Video assisted, transaortic removal of left ventricular thrombus during concurrent cardiac surgery: A case report[J]. J Cardiothorac Surg, 2021, 16(1):242.
doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01626-4 pmid: 34446037 |
| [38] |
Nili M, Deviri E, Jortner R, et al. Surgical removal of a mobile, pedunculated left ventricular thrombus: Report of 4 cases[J]. Ann Thorac Surg, 1988, 46(4):396-400.
pmid: 3178348 |
| [39] |
Kuh JH, Seo Y. Transatrial resection of a left ventricular thrombus after acute myocarditis[J]. Heart Vessels, 2005, 20(5):230-232.
pmid: 16160906 |
| [40] |
Stavridis GT, Vasili M, Ashrafian H, et al. Trans-aortic endoscopic ventricular thrombectomy in a patient with HIT and concomitant aortic and ventricular thromboses[J]. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg, 2016, 64(10):621-624.
doi: 10.1007/s11748-015-0540-0 URL |
| [41] |
Fukumoto Y, Hosoba S, Takagi S, et al. Totally three-dimensional endoscopic transmitral left ventricular apical thrombectomy[J]. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, 2021, 59(1):278.
doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezaa247 pmid: 32864707 |
| [42] |
Lee JM, Park JJ, Jung HW, et al. Left ventricular thrombus and subsequent thromboembolism, comparison of anticoagulation, surgical removal, and antiplatelet agents[J]. J Atheroscler Thromb, 2013, 20(1):73-93.
pmid: 22986555 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||