Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 431-436.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.05.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of clinical characteristics of 61 cases of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders and the influence of NLR and ELR on disease severity
- 1. Gradute School of Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
2. Department of Neurology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University,Jinzhou 121000,China
-
Received:2022-03-22Online:2022-05-20Published:2022-06-22 -
Contact:Li Jian E-mail:Kathyli1005@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yangfan, Li Jian. Analysis of clinical characteristics of 61 cases of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders and the influence of NLR and ELR on disease severity[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(5): 431-436.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.05.008
| 项目 | NMOSD组 (n=61) | 对照组 (n=61) | χ2/t/ Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA (μmol/L) | 182.43±40.36 | 194.49±32.46 | 0.348 | 0.367 |
| CysC (mg/L) | 0.78±0.23 | 0.62±0.38 | -2.076 | 0.156 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 6.46±2.38 | 4.35±3.85 | -2.489 | 0.023 |
| NLR | 2.32(1.46,4.57) | 1.77±0.66 | -3.999 | <0.01 |
| ELR | 0.12(0.04,0.33) | 0.11±0.05 | -2.790 | 0.005 |
| MLR | 0.30(0.21,0.41) | 0.13±0.06 | -6.679 | <0.01 |
| PLR | 149.25(106.27,218.69) | 110.38±30.93 | -4.713 | <0.01 |
| 项目 | NMOSD组 (n=61) | 对照组 (n=61) | χ2/t/ Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA (μmol/L) | 182.43±40.36 | 194.49±32.46 | 0.348 | 0.367 |
| CysC (mg/L) | 0.78±0.23 | 0.62±0.38 | -2.076 | 0.156 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 6.46±2.38 | 4.35±3.85 | -2.489 | 0.023 |
| NLR | 2.32(1.46,4.57) | 1.77±0.66 | -3.999 | <0.01 |
| ELR | 0.12(0.04,0.33) | 0.11±0.05 | -2.790 | 0.005 |
| MLR | 0.30(0.21,0.41) | 0.13±0.06 | -6.679 | <0.01 |
| PLR | 149.25(106.27,218.69) | 110.38±30.93 | -4.713 | <0.01 |
| 项目 | 轻症组 (n=25) | 中重症组 (n=36) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女,例) | 4/21 | 6/30 | Fisher | 1.000 |
| 首次发病年龄(岁) | 46.3±18.4 | 48.2±12.8 | t=-0.441 | 0.661 |
| AQP抗体阳性[例( %)] | 22(88.0) | 31(86.1) | Fisher | 1.000 |
| 合并其他抗体[例(%)] | 2(8.0) | 18(50.0) | Fisher | 0.027 |
| 项目 | 轻症组 (n=25) | 中重症组 (n=36) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(男/女,例) | 4/21 | 6/30 | Fisher | 1.000 |
| 首次发病年龄(岁) | 46.3±18.4 | 48.2±12.8 | t=-0.441 | 0.661 |
| AQP抗体阳性[例( %)] | 22(88.0) | 31(86.1) | Fisher | 1.000 |
| 合并其他抗体[例(%)] | 2(8.0) | 18(50.0) | Fisher | 0.027 |
| 项目 | 轻症组 (n=25) | 中重症组 (n=36) | t/Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | 6.23±2.35 | 6.49±3.16 | 0.259 | 0.875 |
| NLR | 1.44(1.13,1.87) | 3.42(2.40,6.00) | -5.104 | <0.001 |
| ELR | 0.03(0.02,0.05) | 0.17(0.11,0.87) | -4.724 | <0.001 |
| MLR | 0.25(0.17,0.38) | 0.32(0.20,0.43) | -1.940 | 0.052 |
| PLR | 148.47(98.24,218.69) | 174.42(126.11,250.40) | -1.045 | 0.296 |
| 项目 | 轻症组 (n=25) | 中重症组 (n=36) | t/Z值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CRP (mg/L) | 6.23±2.35 | 6.49±3.16 | 0.259 | 0.875 |
| NLR | 1.44(1.13,1.87) | 3.42(2.40,6.00) | -5.104 | <0.001 |
| ELR | 0.03(0.02,0.05) | 0.17(0.11,0.87) | -4.724 | <0.001 |
| MLR | 0.25(0.17,0.38) | 0.32(0.20,0.43) | -1.940 | 0.052 |
| PLR | 148.47(98.24,218.69) | 174.42(126.11,250.40) | -1.045 | 0.296 |
| 项目 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 合并其他抗体 | 2.255 | 1.972 | 1.309 | 0.038 | 0.105 | 0.002 | 4.997 |
| NLR | 1.407 | 0.733 | 3.680 | 0.035 | 4.082 | 0.970 | 7.177 |
| ELR | 1.712 | 4.625 | 2.137 | 0.045 | 5.541 | 0.001 | 8.225 |
| 项目 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 合并其他抗体 | 2.255 | 1.972 | 1.309 | 0.038 | 0.105 | 0.002 | 4.997 |
| NLR | 1.407 | 0.733 | 3.680 | 0.035 | 4.082 | 0.970 | 7.177 |
| ELR | 1.712 | 4.625 | 2.137 | 0.045 | 5.541 | 0.001 | 8.225 |
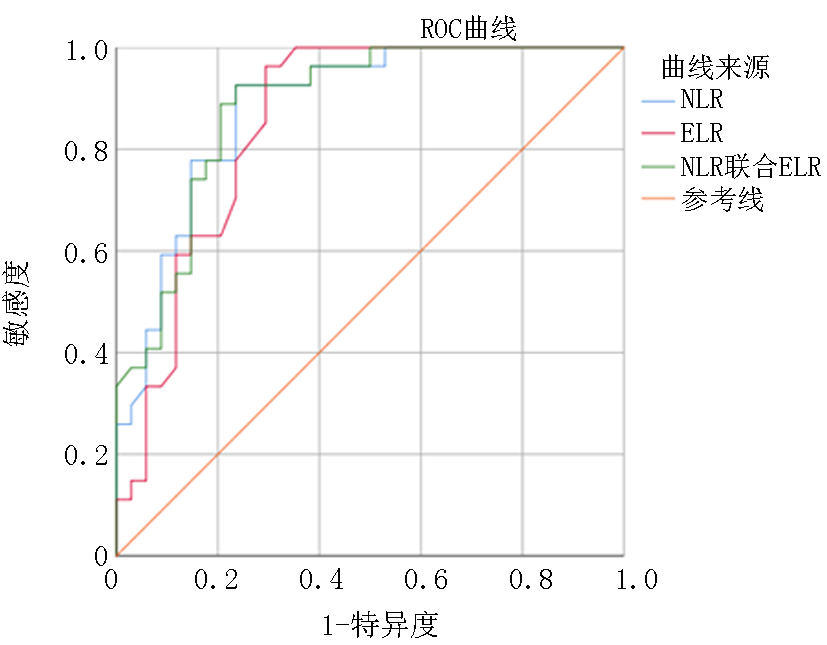
| 项目 | 曲线下 面积 | 临界值 | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||
| NLR | 0.883 | 2.230 | 0.926 | 0.765 | 0.800 | 0.966 |
| ELR | 0.854 | 0.085 | 0.963 | 0.706 | 0.758 | 0.950 |
| NLR联合ELR | 0.885 | 0.299 | 0.926 | 0.765 | 0.803 | 0.967 |
| 项目 | 曲线下 面积 | 临界值 | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||
| NLR | 0.883 | 2.230 | 0.926 | 0.765 | 0.800 | 0.966 |
| ELR | 0.854 | 0.085 | 0.963 | 0.706 | 0.758 | 0.950 |
| NLR联合ELR | 0.885 | 0.299 | 0.926 | 0.765 | 0.803 | 0.967 |
| [1] |
Jasiak-Zatonska M, Kalinowska-Lyszczarz A, Michalak S, et al. The immunology of neuromyelitis optica-current knowledge, clinical implications, controversies and future perspectives[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2016, 17(3):273.
doi: 10.3390/ijms17030273 pmid: 26950113 |
| [2] |
Lennon VA, Wingerchuk DM, Kryzer TJ, et al. A serum autoantibody marker of neuromyelitis optica: Distinction from multiple sclerosis[J], Lancet, 2004, 364(9451):2106.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(04)17551-X pmid: 15589308 |
| [3] |
Yang X, Ransom BR, Ma JF. The role of AQP4 in neuromyelitis optica: More answers, more questions[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2016, 298:63-70.
doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2016.06.002 pmid: 27609277 |
| [4] |
Wingerchuk DM, Banwell B, Bennett JL, et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders[J]. Neurology, 2015, 85(2):177-189.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001729 pmid: 26092914 |
| [5] |
Peng YF, Cao WY, Zhang Q, et al. Assessment of the relationship between red cell distribution width and multiple sclerosis[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2015, 94(29):e1182.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001182 URL |
| [6] |
Maecker HT, McCoy JP, Nussenblatt R. Standardizing immunophenotyping for the human immunology project[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2012, 12(3):191-200.
doi: 10.1038/nri3158 pmid: 22343568 |
| [7] |
Masuda H, Mori M, Uzawa A, et al. Serum antinuclear antibody may be associated with less severe disease activity in neuromyelitis optica[J]. Eur J Neurol, 2016, 23(2):276-281.
doi: 10.1111/ene.12714 pmid: 25903772 |
| [8] |
Georgakopoulou VE, Garmpis N, Damaskos C, et al. The impact of peripheral eosinophil counts and eosinophil to lymphocyte ratio (ELR) in the clinical course of COVID-19 patients: A retrospective study[J]. In Vivo, 2021, 35(1):641-648.
doi: 10.21873/invivo.12303 pmid: 33402521 |
| [9] |
Lian Z, Liu J, Shi Z, et al. Association of TNFSF4 polymorphisms with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in a Chinese population[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2017, 63(3-4):396-402.
doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-0990-1 URL |
| [10] | Shan Y, Tan S, Zhang L, et al. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 is associated with disease status in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders in south China[J]. J Neuroimmunol, 2016, 299:188-123. |
| [11] |
Sellner J, Kalluri SR, Cepok S, et al. Thyroid antibodies in aquaporin-4 antibody positive central nervous system autoimmunity and multiple sclerosis[J]. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf), 2011, 75(2):271-272.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2011.04024.x URL |
| [12] | 刘苗. 血清AQP4抗体与IL-6、IL-27表达检测在视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病患者病情及预后评价中的应用观察[D]. 山东大学, 2019. |
| [13] |
Zhao GX, Liu Y, Li ZX, et al. Variants in the promoter region of CYP7A1 are associated with neuromyelitis optica but not with multiple sclerosis in the Han Chinese population[J]. Neurosci Bull, 2013, 29(5):525-530.
doi: 10.1007/s12264-013-1347-6 URL |
| [14] |
Pereira WLCJ, Reiche EMV, Kallaur AP, et al. Frequency of autoimmune disorders and autoantibodies in patients with neuromyelitis optica[J]. Acta Neuropsychiatr, 2017, 29(3):170-178.
doi: 10.1017/neu.2016.49 URL |
| [15] | 贾红娟, 叶静, 赵义, 等. 抗核抗体谱阳性的视神经脊髓炎患者的临床和磁共振特征分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2012, 92(43):3042-3045. |
| [16] |
Chen C, Xiaobo S, Yuge W, et al. Multiple autoantibodies and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders[J]. Neuroimmunomodulation, 2016, 23(3): 151-156.
pmid: 27603214 |
| [17] |
Saadoun S, Bridges LR, Verkman AS, et al. Paucity of natural killer and cytotoxic T cells in human neuromyelitis optica lesions[J], Neuroreport, 2012, 23(18):1044-1047.
doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32835ab480 pmid: 23108041 |
| [18] |
Piatek P, Domowicz M, Lewkowicz N, et al. C5a-Preactivated neutrophils are critical for autoimmune-induced astrocyte dysregulation in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder[J], Front Immunol, 2018, 9:1694.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01694 pmid: 30083159 |
| [19] | 贾昆, 刘小姣, 周冰洁, 等. 血清白介素-27水平与视神经脊髓炎患者疾病严重程度的关系[J]. 中国神经精神疾病杂志, 2017, 43(08):480-484. |
| [20] |
Yang Z, Zhang Z, Lin F, et al. Comparisons of neutrophil-, monocyte-, eosinophil-, and basophil- lymphocyte ratios among various systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases[J]. APMIS, 2017, 125(10):863-871.
doi: 10.1111/apm.12722 URL |
| [21] |
Michael BD, Elsone L, Griffiths MJ, et al. Post-acute serum eosinophil and neutrophil-associated cytokine/chemokine profile can distinguish between patients with neuromyelitis optica and multiple sclerosis; and identifies potential pathophysiological mechanisms-a pilot study[J]. Cytokine, 2013, 64(1):90-96.
doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2013.07.019 pmid: 23941778 |
| [22] |
Correale J, Fiol M. Activation of humoral immunity and eosinophils in neuromyelitis optica[J]. Neurology, 2004, 63 (12):2363-2370.
pmid: 15623701 |
| [23] |
Akaza M, Tanaka K, Tanaka M, et al. Can anti-AQP4 antibody damage the blood-brain barrier?[J]. Eur Neurol, 2014, 72(5-6): 273-277.
doi: 10.1159/000360619 pmid: 25323016 |
| [24] | Yıldız F, Gökmen O. Haematologic indices and disease activity index in primary Sjogren's syndrome[J]. Int J Clin Pract, 2021, 75(3):e13992. |
| [25] |
Vayá A, Alis R, Hernández JL, et al. RDW in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Influence of anaemia and inflammatory markers[J]. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc, 2013, 54(3):333-339.
doi: 10.3233/CH-131738 URL |
| [26] |
Rodríguez-Carrio J, Alperi-López M, López P, et al. Red cell distribution width is associated with endothelial progenitor cell depletion and vascular-related mediators in rheumatoid arthritis[J], Atherosclerosis, 2015, 240(1):131-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.03.009 pmid: 25778627 |
| [27] | 周一凡, 方羚, 黄巧. 嗜酸性粒细胞在视神经脊髓炎谱系疾病中的机制研究[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2017, 33(8):1252-1254. |
| [28] |
Brescia G, Barion U, Zanotti C, et al. Pre- and postoperative blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratios in patients with sinonasal polyps: A preliminary investigation[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2017, 38(5):64-69.
doi: 10.2500/aap.2017.38.4068 URL |
| [29] |
Muroishi T, Sakai K, Yanase D, et al. Serum anti-aquaporin-4 antibody-positive neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder presenting as acute eosinophilic encephalomyelitis[J]. J Clin Neurosci, 2018, 48:93-94.
doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.10.074 URL |
| [30] |
Rattanathamsakul N, Kaveeta C, Siritho S, et al. The 2015 IPND criteria increases the yield in diagnosis of neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder in thai patients compared to the 2006 diagnostic criteria[J]. Mult Scler Relat Disord, 2020, 43:102218.
doi: 10.1016/j.msard.2020.102218 URL |
| [31] |
Tong Y, Yang T, Wang J, et al. Elevated plasma chemokines for eosinophils in neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders during remission[J]. Front Neuro, 2018, 9:44.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00044 URL |
| [32] |
Wu Y, Chen Y, Yang X, et al. Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2016, 36: 94-99.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.04.006 URL |
| [33] | 曹阳月, 王佳伟. 25例NMOSD患者的中性粒细胞/淋巴细胞计数比值及血小板/淋巴细胞计数比值分析[J]. 中国神经免疫学和神经病学杂志, 2019, 26(6):410-414. |
| [34] | 尹文文, 周霞, 余先锋, 等. 血液学指标在评估视神经脊髓炎谱系病患者疾病严重程度和治疗效果中的价值[J]. 安徽医学, 2021, 42(4):355-360. |
| [1] | Wang Zhenzhen, Zhao shiyi, Feng Siran, Ma Boqing. Predictive value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for microalbuminuria of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(9): 808-812. |
| [2] | Wang Jiaqi, Gao Man, Zhang Feifei, Li Yingxiao, Dang Yi, Qi Xiaoyong. Predicting value of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio combined with GRACE score on in-hospital major adverse cardiovascular events of postoperative PCI in acute STEMI patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(5): 412-417. |
| [3] | Gao Meiling1, Wang Xiaomei2. Evaluation value of RDW, NLR and hsCRP detection on the severity of acute pancreatitis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(8): 724-726. |
| [4] | Jin Jiamin1, Ma Cuihong2, Fan Kunpeng1, Zhang Junlian1, Zhu Haibao2. Predictive value of plasma NLR, PLR and their combinedindex in prognosis of thrombolysis in patients with cerebral infarction [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 228-232. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||