Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (9): 860-864.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.09.019
-
Received:2022-06-21Online:2022-09-20Published:2022-11-21
CLC Number:
Cite this article
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.09.019
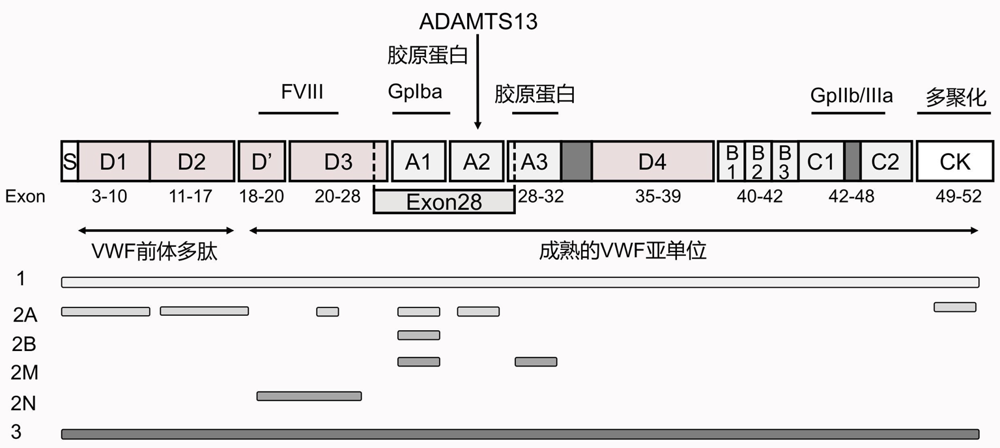
| VWD 类型 | 遗传 模式 | 实验室检测 | 外显子 变异位置 | 结构域 变异位置 | 致病机制 | 热点突变 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VWF:Ag | VWF:RCo | FVIII:C | VWF:RCo/ VWF:Ag | RIPA | ||||||
| 1 | AD | ↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | >0.7 | ↓ | 1~52 | 全部 | VWF的合成或分泌受影响;血浆VWF的清除加快 | C2257S,L2207P,W1144G,I1415N等 |
| 2A | AD,AR | ↓↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | <0.7 | ↓ | 2~28, 51~52 | A1,A2 | VWF对ADAMTS13 水解酶敏感性增加 | S1506L,Y1605S,R1597W等 |
| D',D3, | VWF在胞内滞留 | C1149R等 | ||||||||
| D1,D2,CK | VWF多聚化受影响 | E248G等 | ||||||||
| 2B | AD | ↓↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | <0.7 | ↑ | 28 | A1 | 血小板清除率增加;高分子量VWF多聚体丢失 | R1306W,R1308C,V1316M,R1341Q等 |
| 2M | AD | ↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | <0.7 | ↓ | 28~32 | A1,A2, A3 | VWF与血小板的黏附能力减弱 | 204delC,S1387I等 |
| 2N | AR | N | N | ↓ | >0.7 | N | 17~27 | D2,D',D3 | FVIII失去保护被降解 | R760C,R763G,Y795C,C788Y等 |
| 3 | AR | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓ | - | ↓↓↓ | 1~52 | 全部 | VWF在胞内滞留;基因缺失干扰VWF的正确折叠和生物合成 | R1659X,S85P,C2671Y,C2739Y等 |
| VWD 类型 | 遗传 模式 | 实验室检测 | 外显子 变异位置 | 结构域 变异位置 | 致病机制 | 热点突变 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VWF:Ag | VWF:RCo | FVIII:C | VWF:RCo/ VWF:Ag | RIPA | ||||||
| 1 | AD | ↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | >0.7 | ↓ | 1~52 | 全部 | VWF的合成或分泌受影响;血浆VWF的清除加快 | C2257S,L2207P,W1144G,I1415N等 |
| 2A | AD,AR | ↓↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | <0.7 | ↓ | 2~28, 51~52 | A1,A2 | VWF对ADAMTS13 水解酶敏感性增加 | S1506L,Y1605S,R1597W等 |
| D',D3, | VWF在胞内滞留 | C1149R等 | ||||||||
| D1,D2,CK | VWF多聚化受影响 | E248G等 | ||||||||
| 2B | AD | ↓↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | <0.7 | ↑ | 28 | A1 | 血小板清除率增加;高分子量VWF多聚体丢失 | R1306W,R1308C,V1316M,R1341Q等 |
| 2M | AD | ↓ | ↓ | N/↓ | <0.7 | ↓ | 28~32 | A1,A2, A3 | VWF与血小板的黏附能力减弱 | 204delC,S1387I等 |
| 2N | AR | N | N | ↓ | >0.7 | N | 17~27 | D2,D',D3 | FVIII失去保护被降解 | R760C,R763G,Y795C,C788Y等 |
| 3 | AR | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓ | ↓↓↓ | - | ↓↓↓ | 1~52 | 全部 | VWF在胞内滞留;基因缺失干扰VWF的正确折叠和生物合成 | R1659X,S85P,C2671Y,C2739Y等 |
| [1] |
Fogarty H, Doherty D, O'Donnell JS. New developments in von Willebrand disease[J]. Br J Haematol, 2020, 191(3):329-339.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.16681 URL |
| [2] |
Leebeek FWG, Atiq F. How I manage severe von Willebrand disease[J]. Br J Haematol, 2019, 187(4):418-430.
doi: 10.1111/bjh.16186 URL |
| [3] |
Sharma R, Flood VH. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of von Willebrand disease[J]. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program, 2017, 2017(1):379-384.
doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.379 pmid: 29222282 |
| [4] |
Baronciani L, Peyvandi F. How we make an accurate diagnosis of von Willebrand disease[J]. Thromb Res, 2020, 196:579-589.
doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2019.07.010 pmid: 31353031 |
| [5] |
Weyand AC, Flood VH. Von Willebrand disease: Current status of diagnosis and management[J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2021, 35(6):1085-1101.
doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2021.07.004 URL |
| [6] |
Vinkšel M, Writzl K, Maver A, et al. Improving diagnostics of rare genetic diseases with NGS approaches[J]. J Community Genet, 2021, 12(2):247-256.
doi: 10.1007/s12687-020-00500-5 pmid: 33452619 |
| [7] |
Yadegari H, Oldenburg J. The current understanding of molecular pathogenesis of quantitative von Willebrand disease, types 1 and 3[J]. Hamostaseologie, 2020, 40(1):105-118.
doi: 10.1055/s-0039-3400260 pmid: 31968368 |
| [8] |
Sacco M, Lancellotti S, Ferrarese M, et al. Noncanonical type 2B von Willebrand disease associated with mutations in the VWF D'D3 and D4 domains[J]. Blood Adv, 2020, 4(14):3405-3415.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002334 pmid: 32722784 |
| [9] |
Starke RD, Paschalaki KE, Dyer CE, et al. Cellular and molecular basis of von Willebrand disease: Studies on blood outgrowth endothelial cells[J]. Blood, 2013, 121(14):2773-2784.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-06-435727 pmid: 23355534 |
| [10] |
Pagliari MT, Baronciani L, Cordiglieri C, et al. The dominant p.Thr274Pro mutation in the von Willebrand factor propeptide causes the von Willebrand disease type 1 phenotype in two unrelated patients[J]. Haemophilia, 2022, 28(2):292-300.
doi: 10.1111/hae.14494 pmid: 35064738 |
| [11] |
Gill JC, Endres-Brooks J, Bauer PJ, et al. The effect of ABO blood group on the diagnosis of von Willebrand disease[J]. Blood, 1987, 69(6):1691-1695.
pmid: 3495304 |
| [12] |
Arisz RA, de Vries JJ, Schols SEM, et al. Interaction of von Willebrand factor with blood cells in flow models: A systematic review[J]. Blood Adv, 2022, 6(13):3979-3990.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006405 pmid: 35816358 |
| [13] | Doherty D, Lavin M, Byrne MB, et al. Enhanced VWF clearance in low VWF pathogenesis-limitations of VWFpp/VWF: Ag ratio and clinical significance[J]. Blood Adv, 2022, bloodadvances.2022007340. |
| [14] |
Prior C, Sims K, Seligman K, et al. Peripartum management of a parturient with type 1C (clearance) von Willebrand disease[J]. Int J Obstet Anesth, 2020, 44:112-115.
doi: S0959-289X(20)30110-2 pmid: 32942216 |
| [15] |
Manderstedt E, Lind-Halldén C, Lethagen S, et al. Genetic variation in the C-type lectin receptor CLEC4M in type 1 von Willebrand disease patients[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(2):e0192024.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192024 URL |
| [16] |
Swystun LL, Notley C, Georgescu I, et al. The endothelial lectin clearance receptor CLEC4M binds and internalizes factor VIII in a VWF-dependent and independent manner[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2019, 17(4):681-694.
doi: 10.1111/jth.14404 pmid: 30740857 |
| [17] |
Lind-Hallden C, Manderstedt E, Carlberg D, et al. Genetic variation in the syntaxin-binding protein STXBP5 in type 1 von Willebrand disease patients[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2018, 118(8): 1382-1389.
doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1661352 URL |
| [18] |
Sabater-Lleal M, Huffman JE, de Vries PS, et al. Genome-Wide association transethnic meta-analyses identifies novel associations regulating coagulation factor VIII and von Willebrand factor plasma levels[J]. Circulation, 2019, 139(5):620-635.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.034532 pmid: 30586737 |
| [19] |
Shigekiyo T, Udaka K, Sekimoto E, et al. Identification of a homozygous missense mutation (p.Cys379Gly) in the D1 domain of von Willebrand factor propeptide in a family with type 2A (IIC) von Willebrand disease circulation[J]. Haemophilia, 2018, 24(6):e422-e425.
doi: 10.1111/hae.13605 URL |
| [20] |
Woods AI, Paiva J, Primrose DM, et al. Type 2A and 2M von Willebrand disease: Differences in phenotypic parameters according to the affected domain by disease-causing variants and assessment of pathophysiological mechanisms[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2021, 47(7):862-874.
doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1726097 pmid: 34130347 |
| [21] | Othman M, Favaloro EJ. 2B von Willebrand disease diagnosis: Considerations reflecting on 2021 multisociety guidelines[J]. Res Pract Thromb Haemost, 2021, 5(8):e12635. |
| [22] |
Bury L, Falcinelli E, Kuchi Bhotla H, et al. A p.Arg127Gln variant in GPIbα LRR5 allosterically enhances affinity for VWF: A novel form of platelet-type VWD[J]. Blood Adv, 2022, 6(7):2236-2246.
doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005463 URL |
| [23] |
de Jong A, Eikenboom J. Von Willebrand disease mutation spectrum and associated mutation mechanisms[J]. Thromb Res, 2017, 159:65-75.
doi: S0049-3848(17)30510-8 pmid: 28987708 |
| [24] |
Maas DPMSM, Atiq F, Blijlevens NMA, et al. Von Willebrand disease type 2M: Correlation between genotype and phenotype[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2022, 20(2):316-327.
doi: 10.1111/jth.15586 URL |
| [25] |
Shida Y, Rydz N, Stegner D, et al. Analysis of the role of von Willebrand factor, platelet glycoprotein VI-, and α2β1-mediated collagen binding in thrombus formation[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(11):1799-1807.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-09-521484 pmid: 25051961 |
| [26] |
Michiels JJ, Gadisseur A, Vangenegten I, et al. Recessive von Willebrand disease type 2 Normandy: Variable expression of mild hemophilia and VWD type 1[J]. Acta Haematol, 2009, 121(2-3):119-127.
doi: 10.1159/000214852 URL |
| [27] |
Casonato A, Cozzi MR, Ferrari S, et al. The lesson learned from the new c.2547-1G>T mutation combined with p.R854Q: When a type 2N mutation reveals a quantitative von Willebrand factor defect[J]. Thromb Haemost, 2022, 122(9):1479-1485.
doi: 10.1055/a-1777-6881 URL |
| [28] |
Casonato A, Galletta E, Sarolo L, et al. Type 2N von Willebrand disease: Characterization and diagnostic difficulties[J]. Haemophilia, 2018, 24(1):134-140.
doi: 10.1111/hae.13366 pmid: 29115006 |
| [29] |
Bowman M, Tuttle A, Notley C, et al. The genetics of Canadian type 3 von Willebrand disease: Further evidence for co-dominant inheritance of mutant alleles[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2013, 11 (3):512-520.
doi: 10.1111/jth.12130 pmid: 23311757 |
| [30] |
Kim HJ, Kim SK, Yoo KY, et al. Molecular genetics of von Willebrand disease in Korean patients: Novel variants and limited diagnostic utility of multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification analyses[J]. Ann Lab Med, 2019, 39(6):545-551.
doi: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.6.545 pmid: 31240882 |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||