Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 370-375.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.04.013
Previous Articles Next Articles
-
Received:2023-08-27Online:2024-04-20Published:2024-06-28
CLC Number:
Cite this article
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.04.013
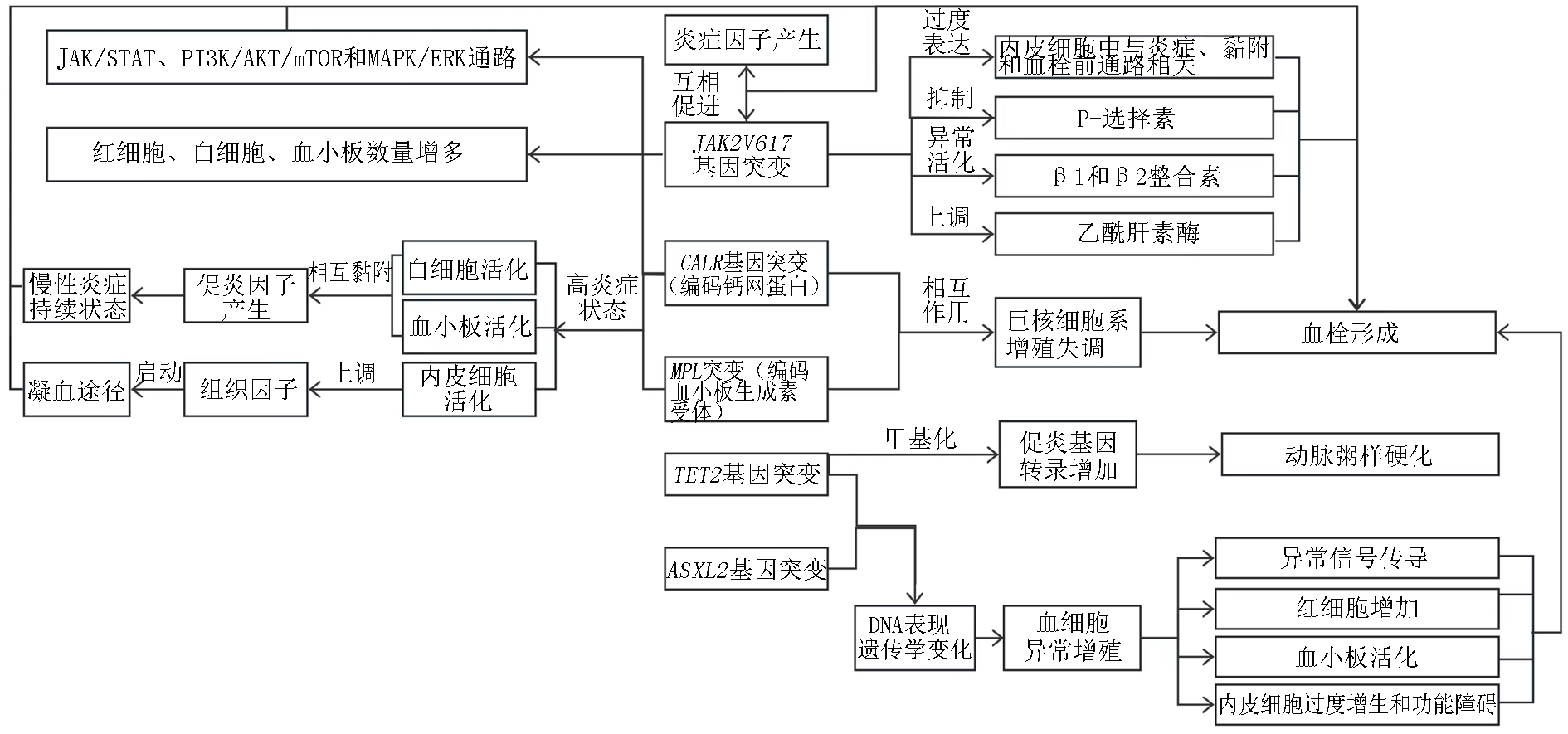
Fig 1. Mechanism of thrombosis caused by gene mutations Note:JAK:janus kinase;STAT:signal transducer and activator of transcription;PI3K:phosphatidylinositol 3;mTOR:mammalian target of rapamycin;MAPK/EPK:mitogen-activated protein kinase
| [1] | De Stefano V, Vannucchi AM, Ruggeri M, et al. Splanchnic vein thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms: Risk factors for recurrences in a cohort of 181 patients[J]. Blood Cancer J, 2016, 6(11):e493. |
| [2] | Rungjirajittranon T, Owattanapanich W, Ungprasert P, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of thrombosis and bleeding at diagnosis of Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. BMC cancer, 2019, 19:1-9. |
| [3] | Song IC, Yeon SH, Lee MW, et al. Thrombotic and hemorrhagic events in 2016 World Health Organization-defined Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasm[J]. Korean J Intern Med, 2021, 36(5):1190. |
| [4] |
Kim J, Byun JM, Hong J, et al. Incidence, characteristics and risk factors of thromboembolic events in East Asian patients with BCR-ABL1 negative myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Scientific Reports, 2021, 11(1):17819.
doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97464-4 pmid: 34497309 |
| [5] | Gecht J, Tsoukakis I, Kricheldorf K, et al. Kidney dysfunction is associated with thrombosis and disease severity in myeloproliferative neoplasms: Implications from the German Study Group for MPN Bioregistry[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(16):4086. |
| [6] | Zhang Y, Zhou Y, Wang Y, et al. Thrombosis among 1537 patients with JAK2V617F-mutated myeloproliferative neoplasms: Risk factors and development of a predictive model[J]. Cancer medicine, 2020, 9(6):2096-2105. |
| [7] | Wille K, Deventer E, Sadjadian P, et al. Arterial and venous thromboembolic complications in 832 patients with BCR-ABL-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Hamostaseologie, 2023. |
| [8] | Mulas O, Mola B, Costa A, et al. Renin-angiotensin inhibitors reduce thrombotic complications in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera patients with arterial hypertension[J]. Ann Hematol, 2023, 102(10):2717-2723. |
| [9] | 秦福丽, 郭志强. JAK2阳性骨髓增殖性肿瘤患者65例临床特征分析[J]. 临床内科杂志, 2020, 37(10):737-739. |
| [10] | 刘雯丽. Ⅰ JAK2突变在动脉粥样硬化与血栓形成中的作用和机制研究 Ⅱ ω3多不饱和脂肪酸代谢产物在早期非酒精性脂肪肝中的作用和机制研究[D]. 天津医科大学, 2018. |
| [11] |
Singh K VP, Ahuja A, et al. Correlation of thrombosis and clinicohematological parameters with JAK2V617F mutation in Philadelphia-negative CMPNs: A study from India[J]. J Lab Physicians, 2022, 14(4):394-397.
doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1757230 pmid: 36531548 |
| [12] | Bader MS, Meyer SC. JAK2 in myeloproliferative neoplasms: still a protagonist[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2022, 15(2):160. |
| [13] | 胡慧平. 骨髓增殖性肿瘤JAK2V617F基因突变与血栓栓塞相关性分析[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2020, 20(21):3597-3599. |
| [14] | Olschok K, Altenburg B, et al. The telomerase inhibitor imetelstat differentially targets JAK2V617F versus CALR mutant myeloproliferative neoplasm cells and inhibits JAK-STAT signaling[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13:1277453. |
| [15] | Fan C, Zhang Y, Yang R, et al. Leukocyte-associated immunoglobulin-like receptor 1 (LAIR-1) inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human HEL cells with JAK2V617F mutation by blocking the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways[J]. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2024, 40(3):207-214. |
| [16] | Dunbar A, Bowman RL, Park Y, et al. JAK2V617F reversible activation shows an essential requirement for JAK2V617F in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs)[J]. Blood, 2022, 140(Supplement 1):803-804. |
| [17] |
Kesarwani M, Kincaid Z, Azhar M, et al. MAPK-negative feedback regulation confers dependence to JAK2V617F signaling[J]. Leukemia, 2023, 37(8):1686-1697.
doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-01959-0 pmid: 37430058 |
| [18] | Reeves BN, Beckman JD. Novel pathophysiological mechanisms of thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Curr Hematol Malig Rep, 2021, 16:304-313. |
| [19] | Bhuria V, Baldauf CK, Schraven B, et al. Thromboinflammation in myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN)-a puzzle still to be solved[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(6):3206. |
| [20] | Papageorgiou L, Elalamy I, Vandreden P, et al. Thrombotic and hemorrhagic issues associated with myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost, 2022, 28:10760296221097969. |
| [21] | Castiglione M, Jiang YP, Mazzeo C, et al. Endothelial JAK2V617F mutation leads to thrombosis, vasculopathy, and cardiomyopathy in a murine model of myeloproliferative neoplasm[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2020, 18(12):3359-3370. |
| [22] | Hamed H, Abdelhady EA, Elrazzaz MK, et al. Value of assessment of factor XI in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms with and without thrombotic events[J]. J Hematol Egy, 2020, 45(1):40. |
| [23] | Guijarro-Hernández A, Eder-Azanza L, Hurtado C, et al. Transcriptomic analysis reveals JAK2/MPL-independent effects of calreticulin mutations in a C. elegans model[J]. Cells, 2023, 12(1):186. |
| [24] | Behrens K, Kauppi M, Viney EM, et al. Differential in vivo roles of MPL cytoplasmic tyrosine residues in murine hematopoiesis and myeloproliferative disease[J]. Leukemia, 2024:1-11. |
| [25] | Furuya C, Hashimoto Y, Morishita S, et al. MPL gene mutation is a possible risk factor for thrombosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia in Japan[J]. Hematology, 2023, 28(1):2229131. |
| [26] |
Marty C, Pecquet C, Nivarthi H, et al. Calreticulin mutants in mice induce an MPL-dependent thrombocytosis with frequent progression to myelofibrosis[J]. Blood, 2016, 127(10):1317-1324.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-679571 pmid: 26608331 |
| [27] |
Pich A, Riera L, Francia di Celle P, et al. JAK2V617F, CALR, and MPL mutations and bone marrow histology in patients with essential thrombocythaemia[J]. Acta Haematologica, 2018, 140(4):234-239.
doi: 10.1159/000493970 pmid: 30404086 |
| [28] | Lussana F, Carobbio A, Salmoiraghi S, et al. Driver mutations (JAK2V617F, MPLW515L/K or CALR), pentraxin-3 and C-reactive protein in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2017, 10(1):54. |
| [29] |
Marty C, Pecquet C, Nivarthi H, et al. Calreticulin mutants in mice induce an MPL-dependent thrombocytosis with frequent progression to myelofibrosis[J]. Blood, 2016, 127(10):1317-1324.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-679571 pmid: 26608331 |
| [30] | Faille D, Lamrani L, Loyau S, et al. Interferon alpha therapy increases pro-thrombotic biomarkers in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2020, 12(4):992. |
| [31] |
Rumi E, Pietra D, Pascutto C, et al. Clinical effect of driver mutations of JAK2, CALR, or MPL in primary myelofibrosis[J]. Blood, 2014, 124(7):1062-1069.
doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-05-578435 pmid: 24986690 |
| [32] |
Helbig G. Classical Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms: Focus on mutations and JAK2 inhibitors[J]. Med Oncol, 2018, 35(9):119.
doi: 10.1007/s12032-018-1187-3 pmid: 30074114 |
| [33] | Chan TS, Hwang YY, Tse E. Risk assessment of venous thromboembolism in hematological cancer patients: A review[J]. Expert Rev Hematol, 2020, 13(5):471-480. |
| [34] | Wang Z, Liu W, Wang D, et al. TET2 mutation may be more valuable in predicting thrombosis in ET patients compared to PV patients: A preliminary report[J]. J Clin Med, 2022, 11(22):6615. |
| [35] | Chia YC, Siti Asmaa MJ, Ramli M, et al. Molecular genetics of thrombotic myeloproliferative neoplasms: Implications in precision oncology[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2023, 13(1):163. |
| [36] |
Aswad MH, Kissová J, Ovesná P, et al. The clinical significance of circulating microparticles concerning thrombosis in BCR/ABL1-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. In Vivo, 2021, 35(6):3345-3353.
doi: 10.21873/invivo.12632 pmid: 34697168 |
| [37] | 马强. 血细胞计数预测骨髓增殖性肿瘤患者血栓形成的意义[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2020, 42(8):735-738. |
| [38] | 冯一鸣, 史家岚. 血小板在骨髓增殖性肿瘤血栓形成中的作用机制[J]. 中国临床研究, 2021, 34(12):1700-1704, 1710. |
| [39] |
Marin Oyarzún CP, Heller PG. Platelets as mediators of thromboinflammation in chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10:1373.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01373 pmid: 31258539 |
| [40] | Nasillo V, Riva G, Paolini A, et al. Inflammatory microenvironment and specific T cells in myeloproliferative neoplasms: Immunopathogenesis and novel immunotherapies[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4):1906. |
| [41] | Masselli E, Pozzi G, Gobbi G, et al. Cytokine profiling in myeloproliferative neoplasms: Overview on phenotype correlation, outcome prediction, and role of genetic variants[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(9):2136. |
| [42] | Ferrer-Marín F, Cuenca-Zamora EJ, Guijarro-Carrillo PJ, et al. Emerging role of neutrophils in the thrombosis of chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(3):1143. |
| [43] | Šefer D, Milji'c P, Kraguljac-Kurtovi'c N, et al. Correlation between leukocyte-platelet aggregates and thrombosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Int J Lab Hematol, 2022, 44(2):302-312. |
| [44] | Huang MJ, He ZP, Tian HY, et al. Clinical features and risk factors of vein thrombosis in 259 patients with chronic myelofiberation neoplasms[J]. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi, 2017, 38(7):623-625. |
| [45] |
Panova-Noeva M, Marchetti M, Spronk HM, et al. Platelet-induced thrombin generation by the calibrated automated thrombogram assay is increased in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera[J]. Am J Hematol, 2011, 86(4):337-342.
doi: 10.1002/ajh.21974 pmid: 21442635 |
| [46] | Schafer AI. Thrombotic, vascular, and bleeding complications of the myeloproliferative neoplasms[J]. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am, 2021, 35(2):305-324. |
| [47] | Vannucchi AM, Guglielmelli P. Acute myocardial infarction and chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms: Friend and enemy, depending on circumstances[J]. JACC Cardio Oncol, 2023, 5(4):469-471. |
| [48] |
Pasquer H, Daltro de Oliveira R, Vasseur L, et al. Distinct clinico-molecular arterial and venous thrombosis scores for myeloproliferative neoplasms risk stratification[J]. Leukemia, 2024, 38(2):326-339.
doi: 10.1038/s41375-023-02114-5 pmid: 38148396 |
| [49] | Baysal M, Bayrak M, Eʂkazan AE. Current evidence on the use of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasm: A systematic review[J]. Expert Rev Hematol, 2023, 16(2):131-140. |
| [50] | Al-Mashdali AF, Aldapt MB, Rahhal A, et al. Pediatric Philadelphia-Negative myeloproliferative neoplasms in the era of WHO classification: A systematic review[J]. Diagnostics (Basel), 2023, 13(3):377. |
| [1] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(7): 654-658. |
| [2] | Leng Wantong, Tao Jie. Risk factors of postoperative venous thromboembolism in patients with multiple myeloma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 340-345. |
| [3] | Zhang Lihong, Ma Bing. Correlation between serum β-CTx and TRACP-5b and the severity and prognosis of multiple myeloma bone disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(7): 623-627. |
| [4] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(4): 447-450. |
| [5] | Chen Guanghua;Lin Fengru. Misdiagnosis cause analysis in multiple myeloma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(10): 1120-1122. |
| [6] | . @@ [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(10): 1186-1188. |
| [7] | Li Yingwei;Shen Yuanyuan;Li Sasa;Wang Huiping;Zhang Cui;Qin Hui;Zhai Zhimin. Ultra small dose decitabine treatment to elderly patients with myelodysplastic syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(7): 773-776. |
| [8] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(6): 710-714. |
| [9] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(4): 476-480. |
| [10] | . @@ [J]. Clinical Focus, 2014, 29(12): 1419-0. |
| [11] | ZHENG Dong. Updates on treatment and standard of multiple myeloma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2014, 29(10): 1130-1133. |
| [12] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2014, 29(7): 803-804. |
| [13] | HAN Xiu-hua;SUN Li-hua;ZOU Jian;MEN Ya-hong;FAN Xiao-hong;WANG Xue-lian. Protective effect of reduced glutathione on peripheral neuropathy by thalidomide in multiple myeloma [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2014, 29(4): 410-413. |
| [14] | LIU Zhu-zhen;LI Guang-lun;YANG Jie;CUI Zhong-guang. Effects of different treatments on function of endothelial cells in multiple myeloma patients [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2014, 29(2): 155-158. |
| [15] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2013, 28(1): 102-0. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||