Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 612-619.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.07.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation of triglyceride-glucose index combined with obesity indicators with diabetic retinopathy
Yan Tianmei1,3, Wu Yanan2,3, Liu Yueying1,3, Wei Limin3( )
)
- 1. Graduate School, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, China
2. Graduate School, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
3. Department of Endocrinology, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050000, China
-
Received:2023-12-27Online:2024-07-20Published:2024-08-02 -
Contact:Wei Limin E-mail:15133130672@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yan Tianmei, Wu Yanan, Liu Yueying, Wei Limin. Correlation of triglyceride-glucose index combined with obesity indicators with diabetic retinopathy[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(7): 612-619.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.07.005
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男) [例(%)] | 吸烟史 [例(%)] | 饮酒史 [例(%)] | 年龄 (岁) | 糖尿病病程 (月) | 身高 (cm) | 体重 (kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非DR组 | 261 | 156(59.8) | 68(26.1) | 64(24.5) | 56(46,66) | 60(12,132) | 168(160,174.25) | 73±13.54 | |||||||
| DR组 | 112 | 63(56.3) | 32(28.6) | 28(25.0) | 61(50,67) | 144(84,240) | 168(159,172) | 74(66,82) | |||||||
| χ2/ | 0.401 | 1.256 | 0.443 | -2.300 | -7.065 | -0.856 | -0.990 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.527 | 0.262 | 0.506 | 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.392 | 0.322 | ||||||||
| 组别 | BMI (kg/m2) | WC (cm) | 臀围 (cm) | WHR | WHtR | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | ||||||||
| 非DR组 | 25.95±3.54 | 92(86,100) | 100.36±9.22 | 0.93(0.88,0.96) | 0.55±0.06 | 132(121,146) | 83.07±12.39 | ||||||||
| DR组 | 26.37(24.58,28.73) | 95(88,101) | 100(96,105) | 0.94±0.07 | 0.56(0.53,0.61) | 136(121,150) | 81.39±11.66 | ||||||||
| -1.683 | -2.093 | -0.335 | -2.435 | -2.405 | -1.775 | 1.497 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.092 | 0.036 | 0.738 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.076 | 0.135 | ||||||||
Tab.1 General data between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别(男) [例(%)] | 吸烟史 [例(%)] | 饮酒史 [例(%)] | 年龄 (岁) | 糖尿病病程 (月) | 身高 (cm) | 体重 (kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非DR组 | 261 | 156(59.8) | 68(26.1) | 64(24.5) | 56(46,66) | 60(12,132) | 168(160,174.25) | 73±13.54 | |||||||
| DR组 | 112 | 63(56.3) | 32(28.6) | 28(25.0) | 61(50,67) | 144(84,240) | 168(159,172) | 74(66,82) | |||||||
| χ2/ | 0.401 | 1.256 | 0.443 | -2.300 | -7.065 | -0.856 | -0.990 | ||||||||
| P值 | 0.527 | 0.262 | 0.506 | 0.021 | <0.001 | 0.392 | 0.322 | ||||||||
| 组别 | BMI (kg/m2) | WC (cm) | 臀围 (cm) | WHR | WHtR | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | ||||||||
| 非DR组 | 25.95±3.54 | 92(86,100) | 100.36±9.22 | 0.93(0.88,0.96) | 0.55±0.06 | 132(121,146) | 83.07±12.39 | ||||||||
| DR组 | 26.37(24.58,28.73) | 95(88,101) | 100(96,105) | 0.94±0.07 | 0.56(0.53,0.61) | 136(121,150) | 81.39±11.66 | ||||||||
| -1.683 | -2.093 | -0.335 | -2.435 | -2.405 | -1.775 | 1.497 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.092 | 0.036 | 0.738 | 0.015 | 0.016 | 0.076 | 0.135 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | TC(mmol/L) | TG(mmol/L) | LDL-C(mmol/L) | HDL-C(mmol/L) | SCr(mmol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非DR组 | 261 | 4.785(4.04, 5.53) | 1.44(0.99, 2.02) | 3.105(2.54, 3.68) | 1.1(0.99, 1.28) | 67.9(59.18, 74.1) | ||||
| DR组 | 112 | 4.9(4.31, 5.86) | 1.56(1.15, 2.44) | 3.15(2.75, 3.86) | 1.08(0.88, 1.24) | 70.3(59.9, 85.7) | ||||
| -1.363 | -2.321 | -1.269 | -1.607 | -3.024 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.173 | 0.020 | 0.204 | 0.108 | 0.002 | |||||
| 组别 | BUN(mmol/L) | UA(mmol/L) | GFR (mL/min) | FBG(mmol/L) | HbA1c(%) | |||||
| 非DR组 | 5.2(4.4, 6) | 304.64(240.75, 356) | 98.79(88.76, 107.3) | 7.61(6.1, 9.485) | 8.3(7.1, 9.9) | |||||
| DR组 | 5.5(4.6, 7.3) | 318.5(260.3, 371.3) | 92.87(70.84, 103.07) | 8.375(6.63, 11.585) | 8.9(7.5, 10.7) | |||||
| -3.197 | -1.436 | -3.924 | -2.845 | -2.810 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.001 | 0.151 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.005 | |||||
Tab.2 Biochemical indicators between groups[ M(P25,P75)]
| 组别 | 例数 | TC(mmol/L) | TG(mmol/L) | LDL-C(mmol/L) | HDL-C(mmol/L) | SCr(mmol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非DR组 | 261 | 4.785(4.04, 5.53) | 1.44(0.99, 2.02) | 3.105(2.54, 3.68) | 1.1(0.99, 1.28) | 67.9(59.18, 74.1) | ||||
| DR组 | 112 | 4.9(4.31, 5.86) | 1.56(1.15, 2.44) | 3.15(2.75, 3.86) | 1.08(0.88, 1.24) | 70.3(59.9, 85.7) | ||||
| -1.363 | -2.321 | -1.269 | -1.607 | -3.024 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.173 | 0.020 | 0.204 | 0.108 | 0.002 | |||||
| 组别 | BUN(mmol/L) | UA(mmol/L) | GFR (mL/min) | FBG(mmol/L) | HbA1c(%) | |||||
| 非DR组 | 5.2(4.4, 6) | 304.64(240.75, 356) | 98.79(88.76, 107.3) | 7.61(6.1, 9.485) | 8.3(7.1, 9.9) | |||||
| DR组 | 5.5(4.6, 7.3) | 318.5(260.3, 371.3) | 92.87(70.84, 103.07) | 8.375(6.63, 11.585) | 8.9(7.5, 10.7) | |||||
| -3.197 | -1.436 | -3.924 | -2.845 | -2.810 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.001 | 0.151 | <0.001 | 0.004 | 0.005 | |||||
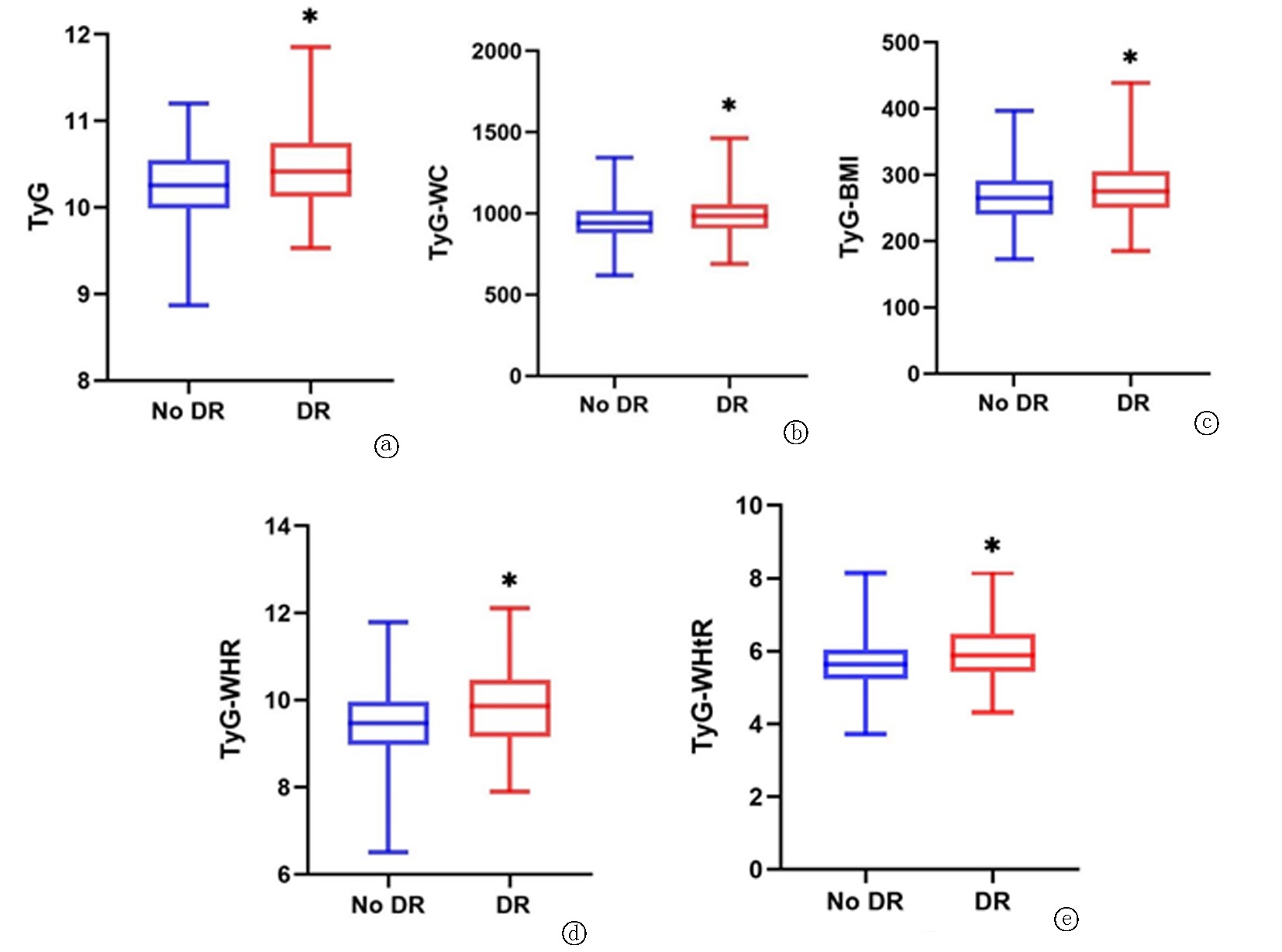
| 组别 | 例数 | TyG | TyG-WC | TyG-BMI | TyG-WHR | TyG-WHtR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非DR组 | 261 | 10.26±0.43 | 942.36(878.89, 1016.43) | 266.32±38.74 | 9.48(8.98, 9.98) | 5.63(5.24, 6.05) |
| DR组 | 112 | 10.43±0.44 | 975.19(906.71, 1055.61) | 275.08(251.63, 303.48) | 9.83±0.83 | 5.86(5.43, 6.48) |
| -3.581 | -3.151 | -2.587 | -3.762 | -3.437 | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
Tab.3 TyG and TyG combined with obesity indicators between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | TyG | TyG-WC | TyG-BMI | TyG-WHR | TyG-WHtR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 非DR组 | 261 | 10.26±0.43 | 942.36(878.89, 1016.43) | 266.32±38.74 | 9.48(8.98, 9.98) | 5.63(5.24, 6.05) |
| DR组 | 112 | 10.43±0.44 | 975.19(906.71, 1055.61) | 275.08(251.63, 303.48) | 9.83±0.83 | 5.86(5.43, 6.48) |
| -3.581 | -3.151 | -2.587 | -3.762 | -3.437 | ||
| P值 | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.010 | <0.001 | 0.001 |
| T2DM合并DR | ||
|---|---|---|
| P值 | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.119 | 0.021 |
| 性别 | 0.033 | 0.528 |
| 糖尿病病程(月) | 0.366 | <0.001 |
| WC(cm) | 0.109 | 0.036 |
| WHR | 0.126 | 0.015 |
| WHtR | 0.125 | 0.016 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 0.071 | 0.173 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 0.120 | 0.020 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 0.066 | 0.205 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | -0.083 | 0.108 |
| SCr(mmol/L) | 0.157 | 0.002 |
| BUN(mmol/L) | 0.166 | 0.001 |
| UA(mmol/L) | 0.074 | 0.151 |
| GFR (mL/min) | -0.204 | <0.001 |
| FBG(mmol/L) | 0.148 | 0.004 |
| HbA1c(%) | 0.147 | 0.005 |
| TyG | 0.165 | 0.001 |
| TyG-WC | 0.163 | 0.002 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.134 | 0.010 |
| TyG-WHR | 0.195 | <0.001 |
| TyG-WHtR | 0.178 | 0.001 |
Tab.4 Correlation analysis between DR and various indicators in T2DM patients
| T2DM合并DR | ||
|---|---|---|
| P值 | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 0.119 | 0.021 |
| 性别 | 0.033 | 0.528 |
| 糖尿病病程(月) | 0.366 | <0.001 |
| WC(cm) | 0.109 | 0.036 |
| WHR | 0.126 | 0.015 |
| WHtR | 0.125 | 0.016 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 0.071 | 0.173 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 0.120 | 0.020 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 0.066 | 0.205 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | -0.083 | 0.108 |
| SCr(mmol/L) | 0.157 | 0.002 |
| BUN(mmol/L) | 0.166 | 0.001 |
| UA(mmol/L) | 0.074 | 0.151 |
| GFR (mL/min) | -0.204 | <0.001 |
| FBG(mmol/L) | 0.148 | 0.004 |
| HbA1c(%) | 0.147 | 0.005 |
| TyG | 0.165 | 0.001 |
| TyG-WC | 0.163 | 0.002 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.134 | 0.010 |
| TyG-WHR | 0.195 | <0.001 |
| TyG-WHtR | 0.178 | 0.001 |
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.940 | 0.271 | 12.032 | 0.001 | 2.561 | 1.505 | 4.356 |
| model2 | 1.190 | 0.309 | 14.823 | <0.001 | 3.288 | 1.794 | 6.025 |
| model3 | 0.921 | 0.466 | 3.911 | 0.048 | 2.513 | 1.008 | 6.261 |
Tab.5 Regression analysis of DR and TyG in T2DM patients
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.940 | 0.271 | 12.032 | 0.001 | 2.561 | 1.505 | 4.356 |
| model2 | 1.190 | 0.309 | 14.823 | <0.001 | 3.288 | 1.794 | 6.025 |
| model3 | 0.921 | 0.466 | 3.911 | 0.048 | 2.513 | 1.008 | 6.261 |
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 11.500 | 0.001 | 1.003 | 1.001 | 1.005 |
| model2 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 15.313 | <0.001 | 1.013 | 1.006 | 1.020 |
| model3 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 4.634 | 0.031 | 1.011 | 1.001 | 1.021 |
Tab.6 Regression analysis of DR and TyG-WC in T2DM patients
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.003 | 0.001 | 11.500 | 0.001 | 1.003 | 1.001 | 1.005 |
| model2 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 15.313 | <0.001 | 1.013 | 1.006 | 1.020 |
| model3 | 0.011 | 0.005 | 4.634 | 0.031 | 1.011 | 1.001 | 1.021 |
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 10.578 | 0.001 | 1.009 | 1.004 | 1.014 |
| model2 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 11.526 | 0.001 | 1.016 | 1.007 | 1.026 |
| model3 | 0.020 | 0.006 | 11.506 | 0.031 | 1.020 | 1.009 | 1.032 |
Tab.7 Regression analysis of DR and TyG-BMI in T2DM patients
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 10.578 | 0.001 | 1.009 | 1.004 | 1.014 |
| model2 | 0.016 | 0.005 | 11.526 | 0.001 | 1.016 | 1.007 | 1.026 |
| model3 | 0.020 | 0.006 | 11.506 | 0.031 | 1.020 | 1.009 | 1.032 |
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.572 | 0.144 | 15.650 | <0.001 | 1.771 | 1.334 | 2.351 |
| model2 | 1.297 | 0.330 | 15.437 | <0.001 | 3.660 | 1.916 | 6.991 |
| model3 | 1.044 | 0.496 | 4.436 | 0.035 | 2.840 | 1.075 | 7.503 |
Tab.8 Regression analysis of DR and TyG-WHR in T2DM patients
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.572 | 0.144 | 15.650 | <0.001 | 1.771 | 1.334 | 2.351 |
| model2 | 1.297 | 0.330 | 15.437 | <0.001 | 3.660 | 1.916 | 6.991 |
| model3 | 1.044 | 0.496 | 4.436 | 0.035 | 2.840 | 1.075 | 7.503 |
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.594 | 0.162 | 13.374 | <0.001 | 1.811 | 1.317 | 2.490 |
| model2 | 2.135 | 0.549 | 15.108 | <0.001 | 8.455 | 2.882 | 24.810 |
| model3 | 1.793 | 0.833 | 4.632 | 0.031 | 6.008 | 1.174 | 30.751 |
Tab.9 Regression analysis of DR and TyG-WHtR in T2DM patients
| 回归 系数 | 标准误 | wald χ2值 | P值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| model1 | 0.594 | 0.162 | 13.374 | <0.001 | 1.811 | 1.317 | 2.490 |
| model2 | 2.135 | 0.549 | 15.108 | <0.001 | 8.455 | 2.882 | 24.810 |
| model3 | 1.793 | 0.833 | 4.632 | 0.031 | 6.008 | 1.174 | 30.751 |
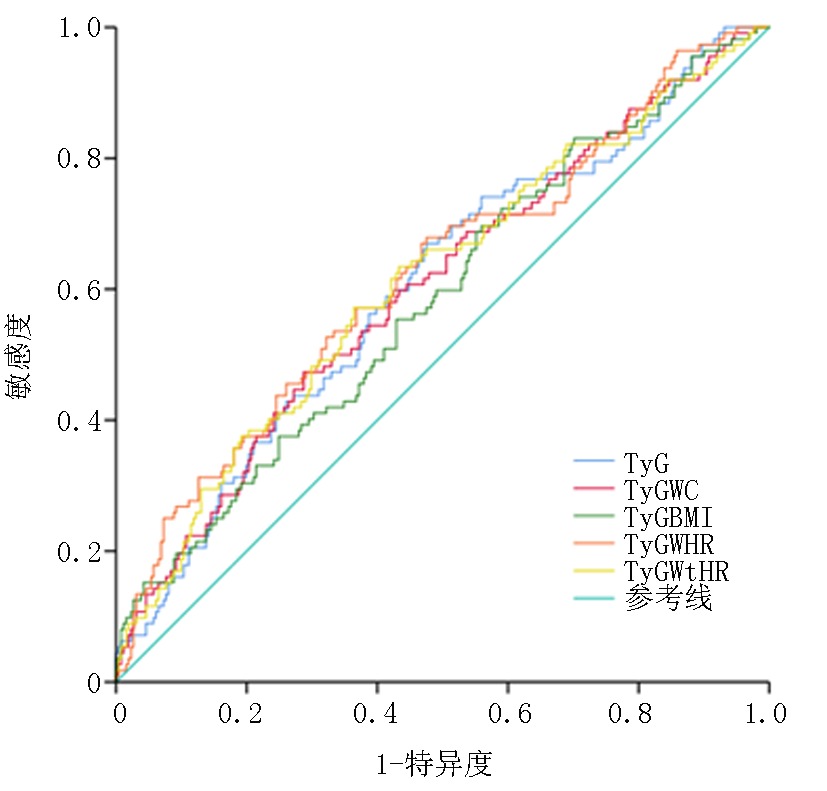
| AUC | 95% | P值 | 敏感度 | 特异性 | 约登指数 | 界值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||||
| TyG | 0.604 | 0.541 | 0.667 | 0.001 | 0.670 | 0.525 | 0.195 | 10.2834 |
| TyG-WC | 0.603 | 0.540 | 0.666 | 0.002 | 0.473 | 0.713 | 0.186 | 999.6353 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.584 | 0.521 | 0.428 | 0.010 | 0.696 | 0.441 | 0.137 | 259.0222 |
| TyG-WHR | 0.623 | 0.560 | 0.686 | <0.001 | 0.527 | 0.678 | 0.205 | 9.8027 |
| TyG-WHtR | 0.612 | 0.549 | 0.676 | 0.001 | 0.571 | 0.636 | 0.207 | 5.8247 |
Tab.10 Predictive value of each index for DR in T2DM patients
| AUC | 95% | P值 | 敏感度 | 特异性 | 约登指数 | 界值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||||
| TyG | 0.604 | 0.541 | 0.667 | 0.001 | 0.670 | 0.525 | 0.195 | 10.2834 |
| TyG-WC | 0.603 | 0.540 | 0.666 | 0.002 | 0.473 | 0.713 | 0.186 | 999.6353 |
| TyG-BMI | 0.584 | 0.521 | 0.428 | 0.010 | 0.696 | 0.441 | 0.137 | 259.0222 |
| TyG-WHR | 0.623 | 0.560 | 0.686 | <0.001 | 0.527 | 0.678 | 0.205 | 9.8027 |
| TyG-WHtR | 0.612 | 0.549 | 0.676 | 0.001 | 0.571 | 0.636 | 0.207 | 5.8247 |
| [1] | Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the international diabetes federation diabetes atlas, 9(th) edition[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2019, 157: 107843. |
| [2] | NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants[J]. Lancet, 2016, 387(10027): 1513-1530. |
| [3] | Lin KY, Hsih WH, Lin YB, et al. Update in the epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and treatment of diabetic retinopathy[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2021, 12(8): 1322-1325. |
| [4] |
Stumvoll M, Goldstein BJ, Van Haeften TW. Type 2 diabetes: Principles of pathogenesis and therapy[J]. Lancet, 2005, 365(9467): 1333-1346.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)61032-X pmid: 15823385 |
| [5] |
Wang X, Liu J, Cheng Z, et al. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index and the risk of diabetes: A general population-based cohort study[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2021, 20(1): 99.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01532-7 pmid: 34488806 |
| [6] |
Zeng ZY, Liu SX, Xu H, et al. Association of triglyceride glucose index and its combination of obesity indices with prehypertension in lean individuals: A cross-sectional study of Chinese adults[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2020, 22(6): 1025-1032.
doi: 10.1111/jch.13878 pmid: 32442359 |
| [7] |
Sheng G, Lu S, Xie Q, et al. The usefulness of obesity and lipid-related indices to predict the presence of Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Lipids Health Dis, 2021, 20(1): 134.
doi: 10.1186/s12944-021-01561-2 pmid: 34629059 |
| [8] | Du Z, Xing L, Lin M, et al. Estimate of prevalent ischemic stroke from triglyceride glucose-body mass index in the general population[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2020, 20(1): 483. |
| [9] |
Forbes JM, Fotheringham AK. Vascular complications in diabetes: Old messages, new thoughts[J]. Diabetologia, 2017, 60(11): 2129-2138.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-017-4360-x pmid: 28725914 |
| [10] |
Litwak L, Goh SY, Hussein Z, et al. Prevalence of diabetes complications in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with baseline characteristics in the multinational A1chieve study[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2013, 5(1): 57.
doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-57 pmid: 24228724 |
| [11] |
Simó-Servat O, Hernández C, Simó R. Diabetic retinopathy in the context of patients with diabetes[J]. Ophthalmic Res, 2019, 62(4): 211-217.
doi: 10.1159/000499541 pmid: 31129667 |
| [12] | Parmar MS. Evaluation and care of patients with diabetic retinopathy[J]. N Engl J Med, 2020, 383(5): e31. |
| [13] | Liu Y, Wu N. Progress of nanotechnology in diabetic retinopathy treatment[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2021, 16: 1391-1403. |
| [14] |
Teo ZL, Tham YC, Yu M, et al. Global prevalence of diabetic retinopathy and projection of burden through 2045: Systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Ophthalmology, 2021, 128(11): 1580-1591.
doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2021.04.027 pmid: 33940045 |
| [15] |
Stitt AW, Curtis TM, Chen M, et al. The progress in understanding and treatment of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Prog Retin Eye Res, 2016, 51: 156-186.
doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2015.08.001 pmid: 26297071 |
| [16] |
Heintz E, Wiréhn AB, Peebo BB, et al. Prevalence and healthcare costs of diabetic retinopathy: A population-based register study in Sweden[J]. Diabetologia, 2010, 53(10): 2147-2154.
doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1836-3 pmid: 20596693 |
| [17] | American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes——2006[J]. Diabetes Care, 2006, 29(Suppl 1): S4-42. |
| [18] | Vujosevic S, Aldington SJ, Silva P, et al. Screening for diabetic retinopathy: New perspectives and challenges[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2020, 8(4): 337-347. |
| [19] | Tung TH, Shih HC, Tsai ST, et al. A community-based study of the relationship between insulin resistance/beta-cell dysfunction and diabetic retinopathy among type II diabetics in Kinmen, Taiwan[J]. Ophthalmic Epidemiol, 2007, 14(3): 148-154. |
| [20] | Sharma VR, Matta ST, Haymond MW, et al. Measuring insulin resistance in humans[J]. Horm Res Paediatr, 2020, 93(11-12): 577-588. |
| [21] |
Simental-Mendía LE, Rodríguez-Morán M, Guerrero-Romero F. The product of fasting glucose and triglycerides as surrogate for identifying insulin resistance in apparently healthy subjects[J]. Metab Syndr Relat Disord, 2008, 6(4): 299-304.
doi: 10.1089/met.2008.0034 pmid: 19067533 |
| [22] | 庞敏, 魏祎, 翁孝刚. 2型糖尿病视网膜病变危险因素分析[J]. 新乡医学院学报, 2020, 37(3):270-273. |
| [23] |
Costagliola C. Oxidative state of glutathione in red blood cells and plasma of diabetic patients: In vivo and in vitro study[J]. Clin Physiol Biochem, 1990, 8(4): 204-210.
pmid: 2078922 |
| [24] |
Ellis TP, Choudhury RH, Kaul K, et al. Diabetic retinopathy and atherosclerosis: Is there a link?[J]. Curr Diabetes Rev, 2013, 9(2): 146-160.
doi: 10.2174/1573399811309020006 pmid: 23094754 |
| [25] | Costagliola C, Romano V, De Tollis M, et al. TNF-alpha levels in tears: A novel biomarker to assess the degree of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2013, 2013: 629529. |
| [26] |
Semeraro F, Cancarini A, Morescalchi F, et al. Serum and intraocular concentrations of erythropoietin and vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with type 2 diabetes and proliferative retinopathy[J]. Diabetes Metab, 2014, 40(6): 445-451.
doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2014.04.005 pmid: 24878492 |
| [27] |
Cancarini A, Costagliola C, Dell'omo R, et al. Effect of intravitreal bevacizumab on serum, aqueous, and vitreous humor levels of erythropoietin in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy[J]. Minerva Endocrinol, 2014, 39(4): 305-311.
pmid: 25371057 |
| [28] |
Costagliola C, Daniele A, Dell'omo R, et al. Aqueous humor levels of vascular endothelial growth factor and adiponectin in patients with type 2 diabetes before and after intravitreal bevacizumab injection[J]. Exp Eye Res, 2013, 110: 50-54.
doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2013.02.004 pmid: 23454098 |
| [29] | Tarr JM, Kaul K, Chopra M, et al. Pathophysiology of diabetic retinopathy[J]. ISRN Ophthalmol, 2013, 2013: 343560. |
| [30] | Semeraro F, Cancarini A, Dell'omo R, et al. Diabetic retinopathy: Vascular and inflammatory disease[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2015, 2015: 582060. |
| [31] | Kowluru RA. Diabetic retinopathy and NADPH oxidase-2: A sweet slippery road[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2021, 10(5):783. |
| [32] | Er LK, Wu S, Chou HH, et al. Triglyceride glucose-body mass index is a simple and clinically useful surrogate marker for insulin resistance in nondiabetic individuals[J]. PLoS One, 2016, 11(3): e0149731. |
| [33] | Zheng S, Shi S, Ren X, et al. Triglyceride glucose-waist circumference, a novel and effective predictor of diabetes in first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetes patients: Cross-sectional and prospective cohort study[J]. J Transl Med, 2016, 14(1): 260. |
| [34] |
Vekasi J, Marton ZS, Kesmarky G, et al. Hemorheological alterations in patients with diabetic retinopathy[J]. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc, 2001, 24(1): 59-64.
pmid: 11345235 |
| [35] | Williams MD, Nadler JL. Inflammatory mechanisms of diabetic complications[J]. Curr Diab Rep, 2007, 7(3): 242-248. |
| [36] | Kawai T, Autieri MV, Scalia R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2021, 320(3): C375-C391. |
| [37] |
El-Asrar AM. Role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy[J]. Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol, 2012, 19(1): 70-74.
doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.92118 pmid: 22346117 |
| [38] |
Van Greevenbroek MM, Schalkwijk CG, Stehouwer CD. Obesity-associated low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Causes and consequences[J]. Neth J Med, 2013, 71(4): 174-187.
pmid: 23723111 |
| [39] | Kwon H, Pessin JE. Adipokines mediate inflammation and insulin resistance[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2013, 4: 71. |
| [40] | Fuentes E, Fuentes F, Vilahur G, et al. Mechanisms of chronic state of inflammation as mediators that link obese adipose tissue and metabolic syndrome[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2013, 2013: 136584. |
| [41] |
Gray N, Picone G, Sloan F, et al. Relation between BMI and diabetes mellitus and its complications among US older adults[J]. South Med J, 2015, 108(1): 29-36.
doi: 10.14423/SMJ.0000000000000214 pmid: 25580754 |
| [42] | Zhu W, Wu Y, Meng YF, et al. Association of obesity and risk of diabetic retinopathy in diabetes patients: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018, 97(32): e11807. |
| [43] |
Heymsfield SB, Cefalu WT. Does body mass index adequately convey a patient's mortality risk?[J]. Jama, 2013, 309(1): 87-88.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2012.185445 pmid: 23280230 |
| [44] | Després JP. Body fat distribution and risk of cardiovascular disease: An update[J]. Circulation, 2012, 126(10): 1301-1313. |
| [45] |
Björntorp P. Metabolic implications of body fat distribution[J]. Diabetes Care, 1991, 14(12): 1132-1143.
doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.12.1132 pmid: 1773700 |
| [46] | Masuzaki H, Flier JS. Tissue-specific glucocorticoid reactivating enzyme, 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 (11 beta-HSD1)--a promising drug target for the treatment of metabolic syndrome[J]. Curr Drug Targets Immune Endocr Metabol Disord, 2003, 3(4): 255-262. |
| [47] |
Blüher M, Engeli S, Klöting N, et al. Dysregulation of the peripheral and adipose tissue endocannabinoid system in human abdominal obesity[J]. Diabetes, 2006, 55(11): 3053-3060.
doi: 10.2337/db06-0812 pmid: 17065342 |
| [48] | Côté M, Matias I, Lemieux I, et al. Circulating endocannabinoid levels, abdominal adiposity and related cardiometabolic risk factors in obese men[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2007, 31(4): 692-699. |
| [49] |
Panagiotakos DB, Pitsavos C, Yannakoulia M, et al. The implication of obesity and central fat on markers of chronic inflammation: The ATTICA study[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2005, 183(2): 308-315.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.03.010 pmid: 16285994 |
| [50] |
Man RE, Sabanayagam C, Chiang PP, et al. Differential association of generalized and abdominal obesity with diabetic retinopathy in asian patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. JAMA Ophthalmol, 2016, 134(3): 251-257.
doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.5103 pmid: 26720805 |
| [51] | Van Leiden HA, Dekker JM, Moll AC, et al. Risk factors for incident retinopathy in a diabetic and nondiabetic population: The Hoorn study[J]. Arch Ophthalmol, 2003, 121(2): 245-251. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||