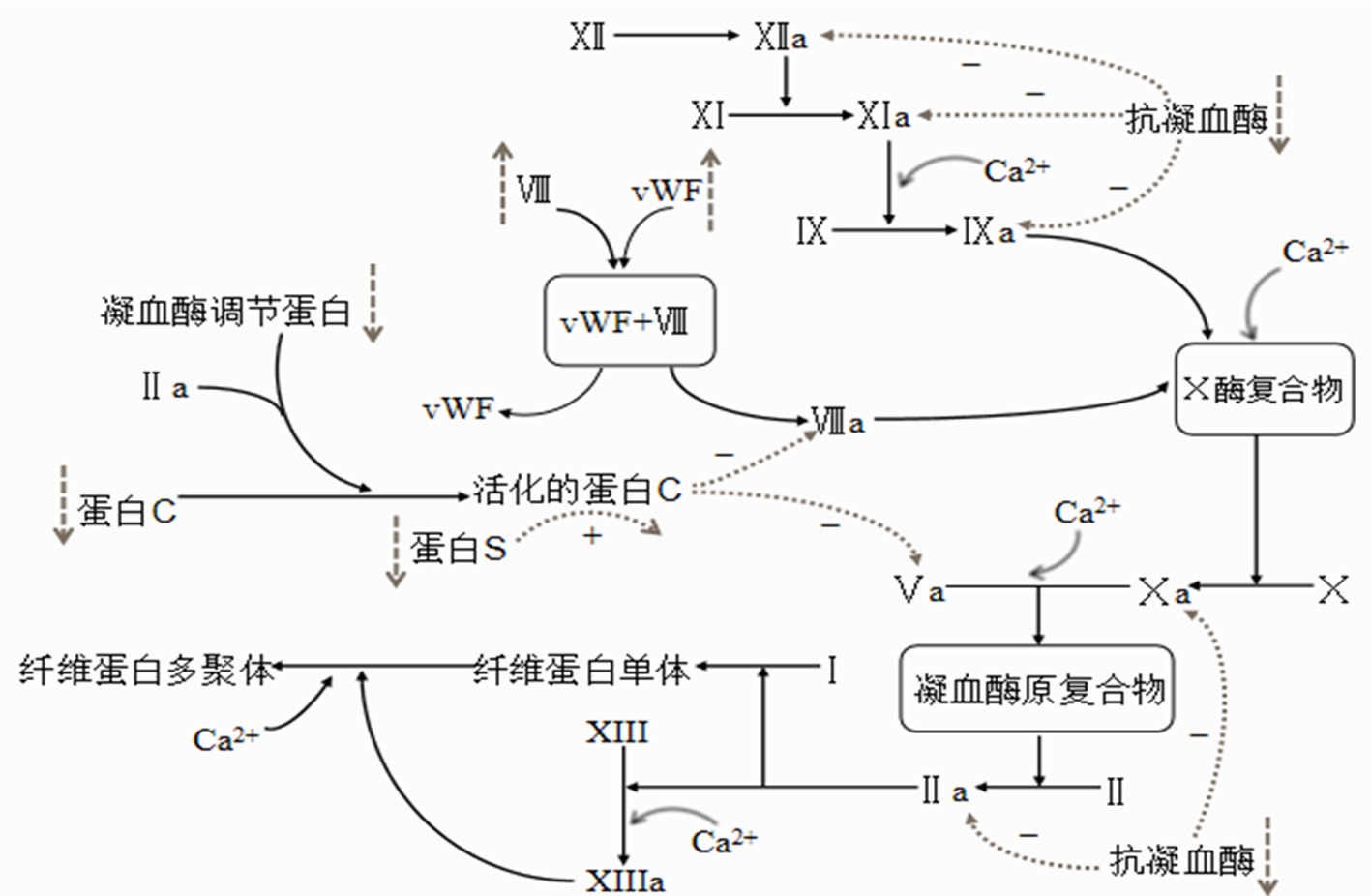
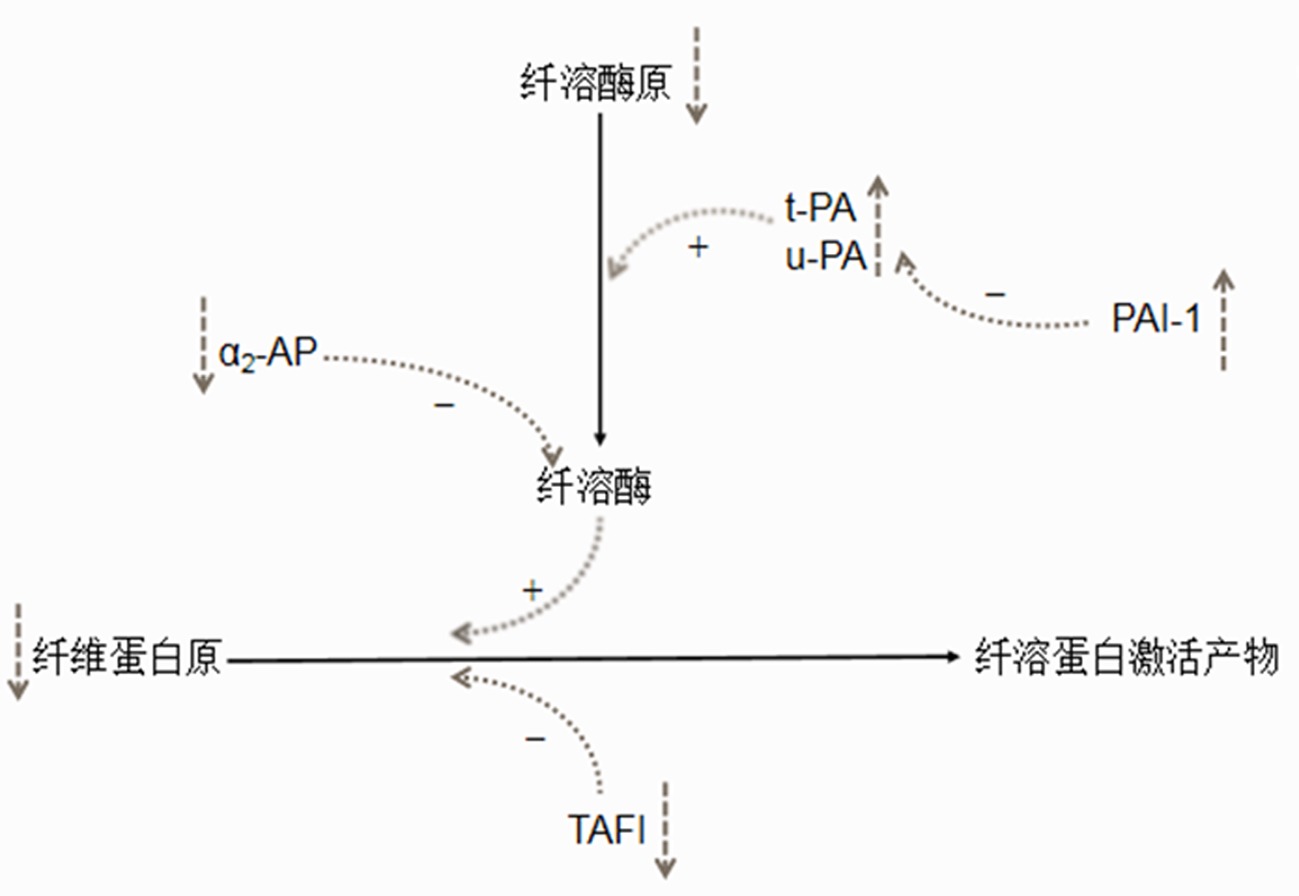
Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (7): 658-663.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.07.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
-
Received:2023-12-10Online:2024-07-20Published:2024-08-02
CLC Number:
Cite this article
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.07.014
| [1] |
Carnevale R, Raparelli V, Nocella C, et al. Gut-derived endotoxin stimulates factor VIII secretion from endothelial cells. Implications for hypercoagulability in cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2017, 67(5): 950-956.
doi: S0168-8278(17)32145-1 pmid: 28716745 |
| [2] |
Koupenova M, Kehrel BE, Corkrey HA, et al. Thrombosis and platelets: An update[J]. Eur Heart J, 2017, 38(11): 785-791.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehw550 pmid: 28039338 |
| [3] |
张译之, 陈煜. 肝硬化患者的止血平衡改变[J]. 肝脏, 2020, 25(8): 786-788.
doi: 10.1159/000339151 pmid: 22796658 |
| [4] |
Hugenholtz GCG, Lisman T, Stravitz RT. Thromboelastography does not predict outcome in different etiologies of cirrhosis[J]. Res Pract Thromb Haemost, 2017, 1(2): 275-285.
doi: 10.1002/rth2.12037 pmid: 30046697 |
| [5] |
Fisher C, Patel VC, Stoy SH, et al. Balanced haemostasis with both hypo- and hyper-coagulable features in critically ill patients with acute-on-chronic-liver failure[J]. J Crit Care, 2018, 43: 54-60.
doi: S0883-9441(17)30275-7 pmid: 28843665 |
| [6] | 丁靖诺, 赵卫峰. 肝硬化状态对血小板数目及功能变化的影响分析[J]. 胃肠病学和肝病学杂志, 2022, 31(7):725-730. |
| [7] | Naohisa W, Haruki U, Takashi S, et al. Impact of anti-GPIIb/IIIa antibody-producing B cells as a predictor of the response to lusutrombopag in thrombocytopenic patients with liver disease[J]. Digestive diseases, 2021, 39(3):234-242. |
| [8] | Lisman T, Arefaine B, Adelmeijer J, et al. Global hemostatic status in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure and septics without underlying liver disease[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2021, 19(1): 85-95. |
| [9] |
Tripodi A, Primignani M, Chantarangkul V, et al. An imbalance of pro- vs anti-coagulation factors in plasma from patients with cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 2009, 137(6): 2105-2111.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.045 pmid: 19706293 |
| [10] |
Lisman T, Bos S, Intagliata NM. Mechanisms of enhanced thrombin-generating capacity in patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2018, 16(6): 1128-1131.
doi: 10.1111/jth.14020 pmid: 29633495 |
| [11] |
El Bokl MA, Shawky A, Riad GS, et al. Procoagulant versus anticoagulant factors in cirrhotic patients[J]. Arab J Gastroenterol, 2014, 15(3-4): 123-129.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajg.2014.08.003 pmid: 25249231 |
| [12] |
Tripodi A, Primignani M, Lemma L, et al. Detection of the imbalance of procoagulant versus anticoagulant factors in cirrhosis by a simple laboratory method[J]. Hepatology, 2010, 52(1): 249-255.
doi: 10.1002/hep.23653 pmid: 20578143 |
| [13] | Wilhelm AR, Parsons NA, Samelson-Jones BJ, et al. Activated protein C has a regulatory role in factor VIII function[J]. Blood, 2021, 137(18):2532-2543. |
| [14] |
EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on prevention and management of bleeding and thrombosis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(5): 1151-1184.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.09.003 pmid: 35300861 |
| [15] |
Francis JL, Armstrong DJ. Fibrinogen-bound sialic acid levels in the dysfibrinogenaemia of liver disease[J]. Haemostasis, 1982, 11(4): 215-222.
doi: 10.1159/000214666 pmid: 6290353 |
| [16] |
Hugenholtz GC, Macrae F, Adelmeijer J, et al. Procoagulant changes in fibrin clot structure in patients with cirrhosis are associated with oxidative modifications of fibrinogen[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2016, 14(5): 1054-1066.
doi: 10.1111/jth.13278 pmid: 26833718 |
| [17] |
Colucci M, Binetti BM, Branca MG, et al. Deficiency of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor in cirrhosis is associated with increased plasma fibrinolysis[J]. Hepatology, 2003, 38(1): 230-237.
pmid: 12830006 |
| [18] |
Rijken DC, Kock EL, Guimarães AH, et al. Evidence for an enhanced fibrinolytic capacity in cirrhosis as measured with two different global fibrinolysis tests[J]. J Thromb Haemost, 2012, 10(10): 2116-2122.
doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04901.x pmid: 22906184 |
| [19] |
Leebeek FW, Kluft C, Knot EA, et al. A shift in balance between profibrinolytic and antifibrinolytic factors causes enhanced fibrinolysis in cirrhosis[J]. Gastroenterology, 1991, 101(5): 1382-1390.
doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90092-y pmid: 1718809 |
| [20] |
Hersch SL, Kunelis T, Francis RB. The pathogenesis of accelerated fibrinolysis in liver cirrhosis: A critical role for tissue plasminogen activator inhibitor[J]. Blood, 1987, 69(5): 1315-1319.
pmid: 2436684 |
| [21] |
Labidi A, Baccouche H, Fekih M, et al. The relationship between coagulation disorders and the risk of bleeding in cirrhotic patients[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2019, 18(4): 627-632.
doi: S1665-2681(19)30071-7 pmid: 31097395 |
| [22] |
Northup PG, Garcia-Pagan JC, Garcia-Tsao G, et al. Vascular liver disorders, portal vein thrombosis, and procedural bleeding in patients with liver disease: 2020 Practice guidance by the American association for the study of liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 73(1): 366-413.
doi: 10.1002/hep.31646 pmid: 33219529 |
| [23] | 黄志寅, 高锦航. 保护门静脉——从病理生理到临床处理决策[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(12): 2760-2763. |
| [24] |
Muciño-Bermejo J, Carrillo-Esper R, Uribe M, et al. Coagulation abnormalities in the cirrhotic patient[J]. Ann hepatol, 2013, 12(5): 713-724.
pmid: 24018489 |
| [25] |
Giannini EG, Greco A, Marenco S, et al. Incidence of bleeding following invasive procedures in patients with thrombocytopenia and advanced liver disease[J]. Clin Gastroenterol H, 2010, 8(10): 899-902; quiz e109.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2010.06.018 pmid: 20601131 |
| [26] | 唐承薇. 慢性肝病与血小板减少:临床处理观念的转变[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2019, 22(4): 457-458. |
| [27] | Fries D, Martini WZ. Role of fibrinogen in trauma-induced coagulopathy[J]. Brit J Anaesth, 2010, 105(2): 116-121. |
| [28] |
Giannini EG, Giambruno E, Brunacci M, et al. Low fibrinogen levels are associated with bleeding after varices ligation in thrombocytopenic cirrhotic patients[J]. Ann Hepatol, 2018, 17(5): 830-835.
doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0012.0775 pmid: 30145561 |
| [29] |
Drolz A, Horvatits T, Roedl K, et al. Coagulation parameters and major bleeding in critically ill patients with cirrhosis[J]. Hepatology, 2016, 64(2): 556-568.
doi: 10.1002/hep.28628 pmid: 27124745 |
| [30] |
Budnick IM, Davis JPE, Sundararaghavan A, et al. Transfusion with cryoprecipitate for very low fibrinogen levels does not affect bleeding or survival in critically Ill cirrhosis patients[J]. Thromb Haemostasis, 2021, 121(10): 1317-1325.
doi: 10.1055/a-1355-3716 pmid: 33450778 |
| [31] |
Lisman T, Caldwell SH, Intagliata NM. Haemostatic alterations and management of haemostasis in patients with cirrhosis[J]. J Hepatol, 2022, 76(6): 1291-1305.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.11.004 pmid: 35589251 |
| [32] | 祁兴顺, 杨玲. 肝硬化门静脉血栓管理专家共识(2020年,上海)[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2020, 36(12): 2667-2674. |
| [33] |
Jepsen P, Tapper EB, Deleuran T, et al. Risk and outcome of venous and arterial thrombosis in patients with cirrhosis: A danish nation-wide cohort study[J]. Hepatology, 2021, 74(5): 2725-2734.
doi: 10.1002/hep.32019 pmid: 34137045 |
| [34] |
Violi F, Ferro D. Clotting activation and hyperfibrinolysis in cirrhosis: Implication for bleeding and thrombosis[J]. Semin Thromb Hemost, 2013, 39(4): 426-433.
doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1334144 pmid: 23487343 |
| [35] |
Semeraro N, Biondi A, Lorenzet R, et al. Direct induction of tissue factor synthesis by endotoxin in human macrophages from diverse anatomical sites[J]. Immunology, 1983, 50(4): 529-535.
pmid: 6654386 |
| [36] |
Moore KL, Andreoli SP, Esmon NL, et al. Endotoxin enhances tissue factor and suppresses thrombomodulin expression of human vascular endothelium in vitro[J]. J Clin Invest, 1987, 79(1): 124-130.
doi: 10.1172/JCI112772 pmid: 3025256 |
| [37] | Lin HC, Yang YY, Tsai TH, et al. The relationship between endotoxemia and hepatic endocannabinoids in cirrhotic rats with portal hypertension[J]. J Hepatol, 2011, 54(6): 1145-1153. |
| [38] |
Schierwagen R, Alvarez-Silva C, Madsen MSA, et al. Circulating microbiome in blood of different circulatory compartments[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(3): 578-580.
doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2018-316227 pmid: 29581241 |
| [39] |
Violi F, Ferro D, Basili S, et al. Ongoing prothrombotic state in the portal circulation of cirrhotic patients[J]. Thromb haemostasis, 1997, 77(1): 44-47.
pmid: 9031447 |
| [40] |
Turon F, Driever EG, Baiges A, et al. Predicting portal thrombosis in cirrhosis: A prospective study of clinical, ultrasonographic and hemostatic factors[J]. J Hepatol, 2021, 75(6): 1367-1376.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.07.020 pmid: 34333101 |
| [41] |
He Y, Yuan S, Guo X, et al. Association of thromboelastography profile with severity of liver cirrhosis and portal venous system thrombosis[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2021, 21(1): 253.
doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01832-3 pmid: 34098892 |
| [42] | Driever EG, Von Meijenfeldt FA, Adelmeijer J, et al. Nonmalignant portal vein thrombi in patients with cirrhosis consist of intimal fibrosis with or without a fibrin-rich thrombus[J]. Hepatology, 2022, 75(4): 898-911. |
| [43] | Anwar MA, Shalhoub J, Lim CS, et al. The effect of pressure-induced mechanical stretch on vascular wall differential gene expression[J]. J Vasc Res, 2012, 49(6): 463-478. |
| [44] | Ahanchi SS, Tsihlis ND, Kibbe MR. The role of nitric oxide in the pathophysiology of intimal hyperplasia[J]. J Vasc Surg, 2007, 45 (Suppl A): A64-73. |
| [45] |
Sigel B, Swami V, Can A, et al. Intimal hyperplasia producing thrombus organization in an experimental venous thrombosis model[J]. J Vasc Surg, 1994, 19(2): 350-360.
pmid: 8114194 |
| [46] | 肖春桃, 李贤秋, 甘佩灵, 等. 基于倾向性评分匹配分析门静脉血栓对肝硬化患者预后的影响[J]. 临床肝胆病杂志, 2021, 37(8):1829-1835. |
| [47] | 何青莲, 余保平, 肖勇. 肝硬化食管胃静脉曲张出血患者内镜治疗后再出血的危险因素分析[J]. 肝脏, 2023, 28(1):55-60. |
| [48] | Wang L, Guo X, Bai Z, et al. Impact of asymptomatic superior mesenteric vein thrombosis on the outcomes of patients with liver cirrhosis[J]. Thromb Haemostasis, 2022, 122(12): 2019-2029. |
| [49] | Rugivarodom M, Charatcharoenwitthaya P. Nontumoral portal vein thrombosis: A challenging consequence of liver cirrhosis[J]. J Clin Transl Hepato, 2020, 8(4): 432-444. |
| [50] | Nery F, Chevret S, Condat B, et al. Causes and consequences of portal vein thrombosis in 1, 243 patients with cirrhosis: Results of a longitudinal study[J]. Hepatology, 2015, 61(2): 660-667. |
| [51] |
Noronha Ferreira C, Marinho RT, Cortez-Pinto H, et al. Incidence, predictive factors and clinical significance of development of portal vein thrombosis in cirrhosis: A prospective study[J]. Liver int, 2019, 39(8): 1459-1467.
doi: 10.1111/liv.14121 pmid: 31021512 |
| [52] |
De Gottardi A, Trebicka J, Klinger C, et al. Antithrombotic treatment with direct-acting oral anticoagulants in patients with splanchnic vein thrombosis and cirrhosis[J]. Liver int, 2017, 37(5): 694-699.
doi: 10.1111/liv.13285 pmid: 27778440 |
| [53] |
Hum J, Shatzel JJ, Jou JH, et al. The efficacy and safety of direct oral anticoagulants vs traditional anticoagulants in cirrhosis[J]. Eur J Haematol, 2017, 98(4): 393-397.
doi: 10.1111/ejh.12844 pmid: 28009449 |
| [54] |
Mort JF, Davis JPE, Mahoro G, et al. Rates of bleeding and discontinuation of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with decompensated cirrhosis[J]. Clin Gastroenterol H, 2021, 19(7): 1436-1442.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.08.007 pmid: 32777555 |
| [55] |
Semmler G, Pomej K, Bauer DJM, et al. Safety of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with advanced liver disease[J]. Liver int, 2021, 41(9): 2159-2170.
doi: 10.1111/liv.14992 pmid: 34152697 |
| [1] | Wang Qingli;Yang Lin;Liu Qi. Clinical observation on effect of coffeic acid on leukocyte anal platelet count in patients with cirrhosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(9): 1027-1.0281e+007. |
| [2] | Ge Xiuzhen;Wang Yuming;Zheng Zhongqing;Wang Tao;Wang Bangmao. Risk factors in poor prognosis after endoscopic variceal ligation and endoscopic injection sclerotherapy of esophageal varices caused by liver cirrhosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(3): 250-252256. |
| [3] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2014, 29(3): 350-350. |
| [4] | HE Qing-hong;HUANG Wei. Application of color Doppler sonography predicting cirrhotic portal hypertension with esophageal varices rupture hemorrhage [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2014, 29(3): 295-297. |
| [5] | XIAO Qi;FENG Ai-dong;LIU Zhi-quan;FENG Jun-hua;DU Rui-qing;YE Li-hong;MEI Zhi-qin;DAI Er-hei. Value and impact factors of transient edoi:graphy in diagnosis of hepatitis B cirrhosis [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2013, 28(8): 855-857860. |
| [6] | ZHAO Tian-yu;MA Chun-ye;LI Chun-yan. Analysis of cirrhosis patients with hepatic encephalopathy prognostic factors [J]. Clinical Focus, 2013, 28(4): 406-408. |
| [7] | WANG Jun-ming;CHEN Chun-yan;LI Yan;HANG Jing-xian;ZHANG Zhi-gang. Relationship between fatty liver and carotid atherosclerosis in different age populations [J]. Clinical Focus, 2013, 28(1): 11-13. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jing;SANG Hai-tong. Impact of hepatorenal function and clinical outcomes in patients with liver cirrhosis combined with systemic inflammatory response syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2012, 27(24): 2117-2120. |
| [9] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2012, 27(22): 1979-1980. |
| [10] | LI Chun-sheng;GUO Jin-bo;XU Yun-feng;TIAN Hui;WEI Juan;ZHANG Guo-zun;LIU Lei;FANG Shu-ming;ZHANG Xiao-lan. Effects of salvia miltiorrhiza monomer IH764-3 on collagen metabolism and mechanism in hepatic stellate cells [J]. Clinical Focus, 2012, 27(17): 1502-1505. |
| [11] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2012, 27(6): 550-552. |
| [12] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2012, 27(3): 222-223. |
| [13] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2011, 26(24): 2158-2159. |
| [14] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2011, 26(22): 2005-2006. |
| [15] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2011, 26(19): 1718-1719. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||