Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 425-431.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.05.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
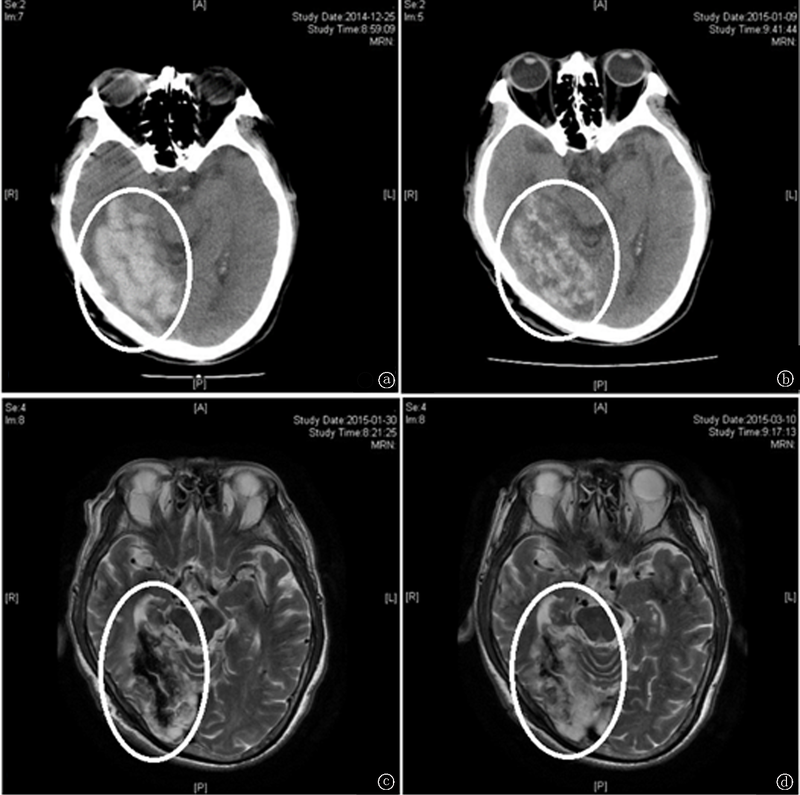
Effect of sodium citrate anticoagulation in continuous renal replacement therapy on uremic patients with cerebral hemorrhage
Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Li Jun, Tian Fen, Cui Li, Chen Yipeng, Zhang Xiaofan, Xing Guangqun( )
)
- Department of Nephropathy, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266555, China
-
Received:2021-03-24Online:2021-05-20Published:2021-06-09 -
Contact:Xing Guangqun E-mail:gqx99monash@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Li Jun, Tian Fen, Cui Li, Chen Yipeng, Zhang Xiaofan, Xing Guangqun. Effect of sodium citrate anticoagulation in continuous renal replacement therapy on uremic patients with cerebral hemorrhage[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(5): 425-431.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.05.008
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄(岁) | 既往高血压 病史 [例(%)] | 既往糖尿 病史 [例(%)] | 既往脑血管 病史 [例(%)] | 既往多囊肾 病史 [例(%)] | 脑出血前常规 血液透析使用 肝素/低分子 肝素[例(%)] | 日常使用 华法林 [例(%)] | 日常使用 阿司匹林 [例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 6(35.2) | 55.31±12.24 | 15(88.2) | 6(35.3) | 12(70.6) | 2(11.8) | 17(100) | 7(41.2) | 4(23.5) |
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 15(55.6) | 12(44.4) | 55.15±13.62 | 26(96.3) | 17(63.0) | 20(74.1) | 2(7.4) | 27(100) | 11(40.7) | 8(29.6) |
| 统计值 | χ2= 0.361 | t=-0.040 | χ2=1.067 | χ2=3.201 | χ2=0.064 | χ2=0.202 | χ2=0.000 | χ2=0.001 | χ2=0.196 | ||
| P值 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄(岁) | 既往高血压 病史 [例(%)] | 既往糖尿 病史 [例(%)] | 既往脑血管 病史 [例(%)] | 既往多囊肾 病史 [例(%)] | 脑出血前常规 血液透析使用 肝素/低分子 肝素[例(%)] | 日常使用 华法林 [例(%)] | 日常使用 阿司匹林 [例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 6(35.2) | 55.31±12.24 | 15(88.2) | 6(35.3) | 12(70.6) | 2(11.8) | 17(100) | 7(41.2) | 4(23.5) |
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 15(55.6) | 12(44.4) | 55.15±13.62 | 26(96.3) | 17(63.0) | 20(74.1) | 2(7.4) | 27(100) | 11(40.7) | 8(29.6) |
| 统计值 | χ2= 0.361 | t=-0.040 | χ2=1.067 | χ2=3.201 | χ2=0.064 | χ2=0.202 | χ2=0.000 | χ2=0.001 | χ2=0.196 | ||
| P值 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||
| 项目 | 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组(n=17) | 无肝素CRRT组(n=27) | Z值/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出血量(ml) | 31.690(15.549,39.061) | 17.298(6.756,51.687) | -0.845 | 0.398 |
| 格拉斯哥评分(分) | 10.000(4.000,15.000) | 10.000(3.750,13.250) | -0.328 | 0.743 |
| 破入脑室[例(%)] | 3(6.8) | 2(4.6) | 1.086 | 0.297 |
| 脑出血部位[例(%)] | 4.475 | 0.929 | ||
| 基底节区 | 4(23.5) | 8(29.6) | 0.196 | 0.658 |
| 额顶颞枕叶 | 4(23.5) | 7(25.9) | 0.032 | 0.858 |
| 蛛网膜下腔 | 3(17.6) | 3(11.1) | 0.378 | 0.538 |
| 脑干 | 1(5.9) | 4(14.8) | 0.826 | 0.363 |
| 丘脑 | 2(11.8) | 2(7.4) | 0.240 | 0624 |
| 放射冠区 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.736 |
| 小脑 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.735 |
| 硬膜下血肿 | 0 | 1(3.7) | 0.644 | 0.422 |
| 脑室旁 | 1(5.9) | 0 | 1.625 | 0.202 |
| 项目 | 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组(n=17) | 无肝素CRRT组(n=27) | Z值/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出血量(ml) | 31.690(15.549,39.061) | 17.298(6.756,51.687) | -0.845 | 0.398 |
| 格拉斯哥评分(分) | 10.000(4.000,15.000) | 10.000(3.750,13.250) | -0.328 | 0.743 |
| 破入脑室[例(%)] | 3(6.8) | 2(4.6) | 1.086 | 0.297 |
| 脑出血部位[例(%)] | 4.475 | 0.929 | ||
| 基底节区 | 4(23.5) | 8(29.6) | 0.196 | 0.658 |
| 额顶颞枕叶 | 4(23.5) | 7(25.9) | 0.032 | 0.858 |
| 蛛网膜下腔 | 3(17.6) | 3(11.1) | 0.378 | 0.538 |
| 脑干 | 1(5.9) | 4(14.8) | 0.826 | 0.363 |
| 丘脑 | 2(11.8) | 2(7.4) | 0.240 | 0624 |
| 放射冠区 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.736 |
| 小脑 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.735 |
| 硬膜下血肿 | 0 | 1(3.7) | 0.644 | 0.422 |
| 脑室旁 | 1(5.9) | 0 | 1.625 | 0.202 |
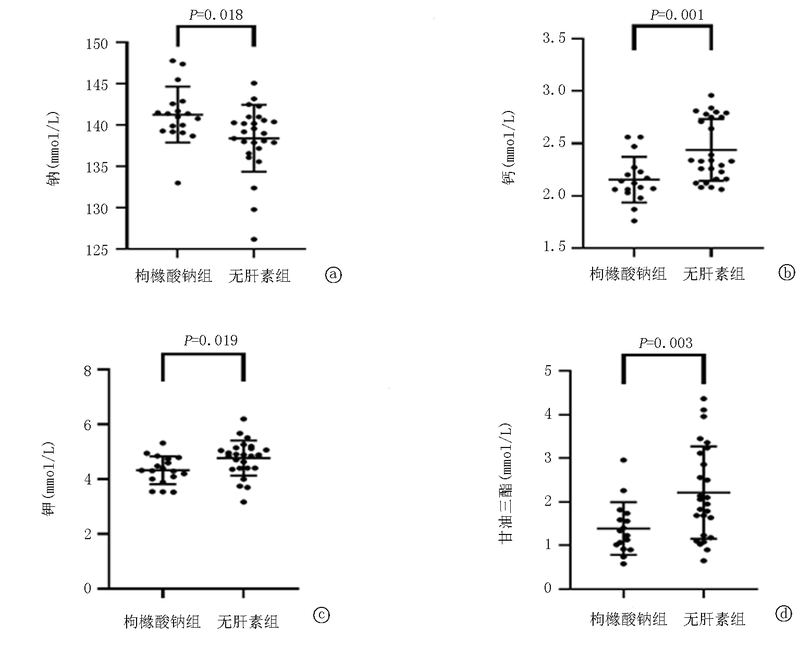
| 组别 | 例数 | 钠(mmol/L) | 钙(mmol/L) | 磷(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 135.725±6.064 | 141.289±3.382 | 2.217±0.218 | 2.155±0.219 | 1.460(1.345, 2.315) | 1.745(1.485, 2.103) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 138.548±4.678 | 138.415±4.061 | 2.082±0.293 | 2.438±0.296 | 1.560(1.320, 2.230) | 1.960(1.530, 2.420) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-1.712 | t=2.466 | t=0.163 | t=-3.603 | Z=-0.274 | Z=-1.299 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.095 | 0.018 | 0.103 | 0.001 | 0.784 | 0.194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 钾(mmol/L) | 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 尿素氮(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 4.908±0.987 | 4.327±0.507 | 821.050±337.104 | 570.378±186.234 | 25.205(16.800, 34.013) | 21.310(14.590,28.183) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 4.706±0.703 | 4.771±0.643 | 635.562±309.111 | 698.715±337.762 | 22.560(15.815, 36.775) | 21.135(17.460,33.510) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.756 | t=-2.445 | t=1.793 | t=-1.462 | Z=-0.428 | Z=-1.098 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.454 | 0.019 | 0.081 | 0.151 | 0.669 | 0.272 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | ALT(U/L) | AST(U/L) | 白蛋白(g/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 16.119±2.611 | 20.069±2.362 | 13.300(9.350, 15.700) | 15.750(12.275,23.923) | 35.994±5.104 | 35.006±4.868 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 14.676±1.484 | 24.402±4.285 | 15.200(11.650, 21.625) | 18.700(12.150,25.375) | 32.610±6.642 | 31.339±7.922 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=0.516 | t=-0.784 | Z=-1.657 | Z=-0.418 | t=1.724 | t=1.899 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.609 | 0.437 | 0.098 | 0.676 | 0.093 | 0.065 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 总蛋白(g/L) | 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 60.150(53.550, 67.050) | 60.500(57.675,64.025) | 2.270±0.439 | 1.391±0.604 | 4.080(3.533, 4.258) | 4.110(3.223,5.193) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 61.215(52.325, 67.775) | 62.550(58.300,69.200) | 2.480±0.338 | 2.215±1.060 | 4.585(3.743, 5.335) | 3.990(3.775,4.380) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=0.041 | Z=-1.386 | t=-0.382 | t=-3.206 | Z=0.594 | Z=-0.084 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.967 | 0.166 | 0.704 | 0.003 | 0.553 | 0.993 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | LDL-C(mmol/L) | HDL-C(mmol/L) | 血糖(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 2.501±0.717 | 2.632±0.873 | 1.160(0.890, 1.283) | 1.120(0.890,1.535) | 5.660(4.415, 8.783) | 7.755(4.790,10.190) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 2.658±1.028 | 2.523±0.824 | 1.180(1.010, 1.280) | 1.085(0.943,1.275) | 6.010(5.183, 7.795) | 6.340(5.323,8.295) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.530 | t=0.415 | Z=-0.360 | Z=-0.842 | Z=-0.152 | Z=-0.776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.599 | 0.680 | 0.719 | 0.400 | 0.879 | 0.438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | DD(μg/L) | CRP(mg/L) | 白细胞计数(×109/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 580.000 (265.000, 1180.000) | 450.000 (317.500,542.500) | 6.430 (2.245, 19.760) | 2.030 (0.500,7.750) | 6.010 (5.285, 8.960) | 5.975 (4.513,7.308) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 850.000 (530.000, 1222.000) | 845.000 (405.000,1360.000) | 9.670 (1.770, 38.270) | 14.920 (1.323,41.463) | 7.895 (6.248, 10.095) | 7.410 (6.633,8.623) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-1.290 | Z=-2.244 | Z=-0.145 | Z=-2.784 | Z=-1.354 | Z=-2.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.197 | 0.025 | 0.885 | 0.005 | 0.176 | 0.021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 血小板计数(×109/L) | 血红蛋白(g/L) | 尿酸(μmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 170.130±60.650 | 193.00±59.754 | 100.310±22.123 | 97.940±18.580 | 414.944±102.891 | 362.513±98.781 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 183.540±71.768 | 148.92±63.082 | 97.580±23.204 | 91.310±21.346 | 397.808±118.975 | 384.042±165.014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.615 | t=2.292 | t=0.371 | t=1.068 | t=0.470 | t=-0.515 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.542 | 0.027 | 0.713 | 0.292 | 0.641 | 0.609 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PTH(pmol/L) | BNP(pg/ml) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 204.350(90.005, 281.625) | 210.650(148.475,519.975) | 1454.850(393.600, 3978.750) | 265.200(102.475, 627.600) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 199.100(137.200, 334.500) | 195.960(118.300,526.400) | 375.050(144, 325, 804.325) | 617.300(195.400, 930.900) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-0.675 | Z=-0.605 | Z=-2.620 | Z=-1.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.511 | 0.545 | 0.009 | 0.189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 钠(mmol/L) | 钙(mmol/L) | 磷(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 135.725±6.064 | 141.289±3.382 | 2.217±0.218 | 2.155±0.219 | 1.460(1.345, 2.315) | 1.745(1.485, 2.103) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 138.548±4.678 | 138.415±4.061 | 2.082±0.293 | 2.438±0.296 | 1.560(1.320, 2.230) | 1.960(1.530, 2.420) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-1.712 | t=2.466 | t=0.163 | t=-3.603 | Z=-0.274 | Z=-1.299 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.095 | 0.018 | 0.103 | 0.001 | 0.784 | 0.194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 钾(mmol/L) | 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 尿素氮(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 4.908±0.987 | 4.327±0.507 | 821.050±337.104 | 570.378±186.234 | 25.205(16.800, 34.013) | 21.310(14.590,28.183) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 4.706±0.703 | 4.771±0.643 | 635.562±309.111 | 698.715±337.762 | 22.560(15.815, 36.775) | 21.135(17.460,33.510) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.756 | t=-2.445 | t=1.793 | t=-1.462 | Z=-0.428 | Z=-1.098 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.454 | 0.019 | 0.081 | 0.151 | 0.669 | 0.272 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | ALT(U/L) | AST(U/L) | 白蛋白(g/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 16.119±2.611 | 20.069±2.362 | 13.300(9.350, 15.700) | 15.750(12.275,23.923) | 35.994±5.104 | 35.006±4.868 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 14.676±1.484 | 24.402±4.285 | 15.200(11.650, 21.625) | 18.700(12.150,25.375) | 32.610±6.642 | 31.339±7.922 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=0.516 | t=-0.784 | Z=-1.657 | Z=-0.418 | t=1.724 | t=1.899 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.609 | 0.437 | 0.098 | 0.676 | 0.093 | 0.065 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 总蛋白(g/L) | 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 60.150(53.550, 67.050) | 60.500(57.675,64.025) | 2.270±0.439 | 1.391±0.604 | 4.080(3.533, 4.258) | 4.110(3.223,5.193) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 61.215(52.325, 67.775) | 62.550(58.300,69.200) | 2.480±0.338 | 2.215±1.060 | 4.585(3.743, 5.335) | 3.990(3.775,4.380) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=0.041 | Z=-1.386 | t=-0.382 | t=-3.206 | Z=0.594 | Z=-0.084 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.967 | 0.166 | 0.704 | 0.003 | 0.553 | 0.993 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | LDL-C(mmol/L) | HDL-C(mmol/L) | 血糖(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 2.501±0.717 | 2.632±0.873 | 1.160(0.890, 1.283) | 1.120(0.890,1.535) | 5.660(4.415, 8.783) | 7.755(4.790,10.190) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 2.658±1.028 | 2.523±0.824 | 1.180(1.010, 1.280) | 1.085(0.943,1.275) | 6.010(5.183, 7.795) | 6.340(5.323,8.295) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.530 | t=0.415 | Z=-0.360 | Z=-0.842 | Z=-0.152 | Z=-0.776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.599 | 0.680 | 0.719 | 0.400 | 0.879 | 0.438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | DD(μg/L) | CRP(mg/L) | 白细胞计数(×109/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 580.000 (265.000, 1180.000) | 450.000 (317.500,542.500) | 6.430 (2.245, 19.760) | 2.030 (0.500,7.750) | 6.010 (5.285, 8.960) | 5.975 (4.513,7.308) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 850.000 (530.000, 1222.000) | 845.000 (405.000,1360.000) | 9.670 (1.770, 38.270) | 14.920 (1.323,41.463) | 7.895 (6.248, 10.095) | 7.410 (6.633,8.623) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-1.290 | Z=-2.244 | Z=-0.145 | Z=-2.784 | Z=-1.354 | Z=-2.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.197 | 0.025 | 0.885 | 0.005 | 0.176 | 0.021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 血小板计数(×109/L) | 血红蛋白(g/L) | 尿酸(μmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 170.130±60.650 | 193.00±59.754 | 100.310±22.123 | 97.940±18.580 | 414.944±102.891 | 362.513±98.781 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 183.540±71.768 | 148.92±63.082 | 97.580±23.204 | 91.310±21.346 | 397.808±118.975 | 384.042±165.014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.615 | t=2.292 | t=0.371 | t=1.068 | t=0.470 | t=-0.515 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.542 | 0.027 | 0.713 | 0.292 | 0.641 | 0.609 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PTH(pmol/L) | BNP(pg/ml) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 204.350(90.005, 281.625) | 210.650(148.475,519.975) | 1454.850(393.600, 3978.750) | 265.200(102.475, 627.600) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 199.100(137.200, 334.500) | 195.960(118.300,526.400) | 375.050(144, 325, 804.325) | 617.300(195.400, 930.900) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-0.675 | Z=-0.605 | Z=-2.620 | Z=-1.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.511 | 0.545 | 0.009 | 0.189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 项目 | 生存组(n=34) | 死亡组(n=10) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 139.760±14.794 | 166.200±29.657 | t=-2.721 | 0.021 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 83.060±11.478 | 80.200±26.607 | t=0.215 | 0.834 |
| 钠(mmol/L) | 140.162±3.184 | 134.590±3.060 | t=4.905 | 0.000 |
| 钙(mmol/L) | 2.072±0.269 | 2.289±0.217 | t=-2.326 | 0.025 |
| 磷(mmol/L) | 1.729±0.553 | 2.353±0.735 | t=-2.877 | 0.006 |
| 钾(mmol/L) | 4.539±0.663 | 4.958±0.691 | t=-1.742 | 0.089 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 665.588±297.093 | 659.660±349.388 | t=0.053 | 0.958 |
| 尿素氮(mmol/L) | 21.950(16.575,32.338) | 20.655(16.975,41.823) | Z=-0.224 | 0.823 |
| ALT(U/L) | 18.250(9.500,24.300) | 27.150(15.775,35.425) | Z=-1.933 | 0.053 |
| AST(U/L) | 15.750(10.950,21.733) | 21.950(15.175,26.825) | Z=-1.723 | 0.085 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 35.356±5.034 | 31.460±3.760 | t=2.261 | 0.029 |
| 总蛋白(g/L) | 61.678±5.876 | 59.510±11.336 | t=0.581 | 0.573 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 1.230(0.920,1.820) | 2.500(0.638,3.433) | Z=-1.030 | 0.303 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.334±1.239 | 5.437±1.744 | t=-2.248 | 0.030 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.525±0.754 | 2.355±0.560 | t=0.524 | 0.603 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.100(0.958,1.428) | 0.895(0.750,1.238) | Z=-1.743 | 0.081 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 6.630(4.858,10.088) | 6.755(5.573,7.980) | Z=-0.168 | 0.867 |
| DD(μg/L) | 465.000(245.000,712.500) | 2290.000(887.500,5370.000) | Z=-3.194 | 0.001 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 2.010(0.623,10.153) | 44.025(17.148,82.225) | t=-3.926 | 0.000 |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 6.717±2.138 | 12.535±6.053 | t=-2.986 | 0.014 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 179.030±60.215 | 108.300±63.477 | t=3.227 | 0.002 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 96.650±19.602 | 85.800±19.702 | t=1.537 | 0.132 |
| BNP(pg/ml) | 473.350(225.800,732.125) | 1177.300(928.375,1717.175) | Z=-4.257 | 0.000 |
| PTH(pmol/L) | 194.860(107.625,324.150) | 108.350(51.400,258.750) | Z=-1.432 | 0.152 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 396.294±140.248 | 392.540±237.481 | t=0.047 | 0.963 |
| 项目 | 生存组(n=34) | 死亡组(n=10) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 139.760±14.794 | 166.200±29.657 | t=-2.721 | 0.021 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 83.060±11.478 | 80.200±26.607 | t=0.215 | 0.834 |
| 钠(mmol/L) | 140.162±3.184 | 134.590±3.060 | t=4.905 | 0.000 |
| 钙(mmol/L) | 2.072±0.269 | 2.289±0.217 | t=-2.326 | 0.025 |
| 磷(mmol/L) | 1.729±0.553 | 2.353±0.735 | t=-2.877 | 0.006 |
| 钾(mmol/L) | 4.539±0.663 | 4.958±0.691 | t=-1.742 | 0.089 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 665.588±297.093 | 659.660±349.388 | t=0.053 | 0.958 |
| 尿素氮(mmol/L) | 21.950(16.575,32.338) | 20.655(16.975,41.823) | Z=-0.224 | 0.823 |
| ALT(U/L) | 18.250(9.500,24.300) | 27.150(15.775,35.425) | Z=-1.933 | 0.053 |
| AST(U/L) | 15.750(10.950,21.733) | 21.950(15.175,26.825) | Z=-1.723 | 0.085 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 35.356±5.034 | 31.460±3.760 | t=2.261 | 0.029 |
| 总蛋白(g/L) | 61.678±5.876 | 59.510±11.336 | t=0.581 | 0.573 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 1.230(0.920,1.820) | 2.500(0.638,3.433) | Z=-1.030 | 0.303 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.334±1.239 | 5.437±1.744 | t=-2.248 | 0.030 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.525±0.754 | 2.355±0.560 | t=0.524 | 0.603 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.100(0.958,1.428) | 0.895(0.750,1.238) | Z=-1.743 | 0.081 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 6.630(4.858,10.088) | 6.755(5.573,7.980) | Z=-0.168 | 0.867 |
| DD(μg/L) | 465.000(245.000,712.500) | 2290.000(887.500,5370.000) | Z=-3.194 | 0.001 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 2.010(0.623,10.153) | 44.025(17.148,82.225) | t=-3.926 | 0.000 |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 6.717±2.138 | 12.535±6.053 | t=-2.986 | 0.014 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 179.030±60.215 | 108.300±63.477 | t=3.227 | 0.002 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 96.650±19.602 | 85.800±19.702 | t=1.537 | 0.132 |
| BNP(pg/ml) | 473.350(225.800,732.125) | 1177.300(928.375,1717.175) | Z=-4.257 | 0.000 |
| PTH(pmol/L) | 194.860(107.625,324.150) | 108.350(51.400,258.750) | Z=-1.432 | 0.152 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 396.294±140.248 | 392.540±237.481 | t=0.047 | 0.963 |
| [1] | 杜静, 王训, 高宗良. 脑出血合并维持性血液透析24例临床分析[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2018, 21(14):1572-1576. |
| [2] | Rabindranath K, Adams J, Macleod AM, et al. Intermittent versus continuous renal replacement therapy for acute renal failure in adults[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2007, (3):CD003773. |
| [3] |
Srisawat N, Lawsin L, Uchino S, et al. Cost of acute renal replacement therapy in the intensive care unit: Results from The Beginning and Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney (BEST Kidney) study[J]. Crit Care, 2010, 14(2):R46.
doi: 10.1186/cc8933 URL |
| [4] |
Brandenburger T, Dimski T, et al. Renal replacement therapy and anticoagulation[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol, 2017, 31(3):387-401.
doi: S1521-6896(17)30053-8 pmid: 29248145 |
| [5] | 张鑫, 张文博, 李莹, 等. 连续性血液净化中阿加曲班与枸橼酸钠的抗凝效果及安全性比较[J]. 武警医学, 2020, 31(2):103-106. |
| [6] |
Liu C, Mao Z, Kang H, et al. Regional citrate versus heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20(1):144.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1299-0 URL |
| [7] |
Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Kellum JA, Bellomo R. Clinical review: Anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy--heparin or citrate?[J]. Crit Care, 2011, 15(1):202.
doi: 10.1186/cc9358 pmid: 21345279 |
| [8] | Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2012, 120(4):c179-c184. |
| [9] | 高晓琴, 孙小鹉, 任小军, 等. 枸橼酸钠抗凝法行血液透析治疗的临床应用价值[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2017, 17(11):1661-1663. |
| [10] | 杨松涛, 赵娜, 胡军, 等. 应用普通含钙血液透析液局部枸橼酸抗凝血液透析的临床观察[J]. 中国血液净化, 2017, 16(7):474-476+487. |
| [11] | 庞娟. 枸橼酸抗凝在血液透析高危出血患者中的应用[J]. 中国当代医药, 2018, 25(14):38-40. |
| [12] | 邵汉权, 杨雪, 邓勇进, 等. 枸橼酸抗凝在肾衰竭合并脑出血患者血液滤过治疗中的应用研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2018, 15(14):130-133. |
| [13] |
Slowinski T, Morgera S, Joannidis M, et al. Safety and efficacy of regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemodialysis in the presence of liver failure: The Liver Citrate Anticoagulation Threshold (L-CAT) observational study[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19:349.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1066-7 pmid: 26415638 |
| [14] | Ricci D, Panicali L, Facchini MG, et al. Citrate anticoagulation during continuous renal replacement therapy[J]. Contrib Nephrol, 2017, 190:19-30. |
| [15] |
Waikar SS, Curhan GC, Brunelli SM. Mortality associated with low serum sodium concent ration in maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Am J Med, 2011, 124(1):77-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.07.029 URL |
| [16] |
O’Neill WC. Targeting serum calcium in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: Is normal too high?[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 89(1):40-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.10.001 URL |
| [17] | 许明杰, 洪大情, 王莉. 局部枸橼酸钠抗凝在普通血液透析中的应用进展[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2020, 17(3):251-255. |
| [18] |
Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Ostermann M. Bench-to-bedside review: Citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy, from science to practice[J]. Crit Care, 2012, 16(6):249.
doi: 10.1186/cc11645 pmid: 23216871 |
| [19] |
Ding F, Song JH, Jung JY, et al. A biomimetic membrane device that modulates the excessive inflammatory response to sepsis[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(4):e18584.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018584 URL |
| [20] |
Strobl K, Harm S, Weber V, et al. The role of ionized calcium and magnesium in regional citrate anticoagulation and its impact on inflammatory parameters[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2017, 40(1):15-21.
doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000558 pmid: 28218351 |
| [21] |
Huguet M, Rodas L, Blasco M, et al. Clinical impact of regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2017, 40(12):676-682.
doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000633 pmid: 28862718 |
| [1] | Tao Yang, Pan Qingquan, Li Yan. Evaluation of hemoperfusion and continuous renal replacement therapy in paraquat poisoning patients complicated with MODS [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 330-334. |
| [2] | Dai Jing, Chen Huaqian. Wunderlich syndrome in a patient on haemodialysis with a review of the literature [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(12): 1107-1111. |
| [3] | Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Tian Fen, Li Jun, Cui Li, Xing Guangqun. Risk factors of cerebral hemorrhage in uremic patients on regular hemodialysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(1): 20-25. |
| [4] | Lin Na, Liu Chuan, Wu Tianyu, Cao Lei. A case of acute hemorrhagic cerebral infarction caused by infective endocarditis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(1): 66-69. |
| [5] | Huang Junyue, Ma Zhigang, Li Yingping, Xue Rong, Huang Wenhui, Jing Xiaojiang. Effects of high-flux hemodialysis combined with L-carnitine treatment on lipid metabolism in uremic patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(3): 253-256. |
| [6] | Zhang Zhenzhou, Wu Shengxiang, Zhang Guolong. Correlation between serum calcium concentration and prognosis in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(2): 120-123. |
| [7] | Ding Hong;Pan Jieping;Zhu Jinhua;Tian Ying;Song Lei;Shen Minning. Five cases of scleroderma renal crisis combined with literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(9): 1013-1018. |
| [8] | Yu Qin;Xing Guangqun;Zhou Quan. Effects of neutrophil extracellular traps and contact system in uremic patients with acute coronary syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(5): 540-543544. |
| [9] | Wang Huiling;Jiang Yuantao;Zhang Hong;Song Yueping;Li Haihui;Ran Xiaofang;Li Zhenzhong;Zhang Haijing;Su Yanchao. Functional changes of intestinal mucosal barrier in patients with severe stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(5): 529-531532. |
| [10] | He Lianyi. Application effect of different dialysis frequencies in uremic patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(11): 1292-1.29513e+007. |
| [11] | Liu Zhengqing;Guo Lili. Curative effect of hemoperfusion combined with hemodialysis on uremic nervous system damage [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(1): 64-6667. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||