Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 20-25.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.01.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Risk factors of cerebral hemorrhage in uremic patients on regular hemodialysis
Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Tian Fen, Li Jun, Cui Li, Xing Guangqun( )
)
- Department of Nephropathy, The Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao 266555, China
-
Received:2021-06-24Online:2022-01-20Published:2022-01-20 -
Contact:Xing Guangqun E-mail:gqx99monash@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Tian Fen, Li Jun, Cui Li, Xing Guangqun. Risk factors of cerebral hemorrhage in uremic patients on regular hemodialysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(1): 20-25.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.01.003
| 项目 | 脑出血组(n=44) | 对照组(n=224) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 26(59.1) 18(40.9) | 133(59.4) 91(40.6) | χ2=0.001 | 0.972 |
| 年龄(岁) | 54(45, 64) | 54(43, 64) | Z=-0.535 | 0.593 |
| 高血压病史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 41(93.2) 3(6.8) | 70(31.3) 154(68.7) | χ2=58.135 | <0.05 |
| 脑出血事件前收缩压(mmHg) | 184.810±24.081 | 147.400±19.887 | t=-10.91 | <0.05 |
| 脑出血事件前舒张压(mmHg) | 103.930±14.608 | 82.780±13.349 | t=-9.376 | <0.05 |
| 日常血液透析时收缩压(mmHg) | 159.120±22.343 | 146.970±20.056 | t=-3.57 | <0.05 |
| 日常血液透析时舒张压(mmHg) | 88.910±13.425 | 83.130±13.106 | t=-2.639 | <0.05 |
| 糖尿病病史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 23(52.3) 21(47.7) | 31(13.8) 193(86.2) | χ2=33.763 | <0.05 |
| 脑血管事件史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 32(72.8) 12(27.2) | 43(19.2) 181(80.8) | χ2=52.291 | <0.05 |
| 透析时肝素使用[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 40(90.9) 4(9.1) | 216(96.4) 8(3.6) | χ2=2.619 | 0.106 |
| 原发病为多囊肾[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 4(9.1) 40(90.9) | 2(0.9) 222(99.1) | χ2=11.293 | <0.05 |
| 初始透析方式是否为血液透析[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 40(90.9) 4(9.1) | 213(95.1) 11(4.9) | χ2=1.216 | 0.270 |
| 日常应用华法林[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 18(40.9) 26(59.1) | 5(2.2) 219(97.8) | χ2=70.121 | <0.05 |
| 日常应用阿司匹林[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 12(27.3) 32(72.7) | 89(39.7) 135(60.3) | χ2=2.431 | 0.119 |
| 项目 | 脑出血组(n=44) | 对照组(n=224) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 26(59.1) 18(40.9) | 133(59.4) 91(40.6) | χ2=0.001 | 0.972 |
| 年龄(岁) | 54(45, 64) | 54(43, 64) | Z=-0.535 | 0.593 |
| 高血压病史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 41(93.2) 3(6.8) | 70(31.3) 154(68.7) | χ2=58.135 | <0.05 |
| 脑出血事件前收缩压(mmHg) | 184.810±24.081 | 147.400±19.887 | t=-10.91 | <0.05 |
| 脑出血事件前舒张压(mmHg) | 103.930±14.608 | 82.780±13.349 | t=-9.376 | <0.05 |
| 日常血液透析时收缩压(mmHg) | 159.120±22.343 | 146.970±20.056 | t=-3.57 | <0.05 |
| 日常血液透析时舒张压(mmHg) | 88.910±13.425 | 83.130±13.106 | t=-2.639 | <0.05 |
| 糖尿病病史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 23(52.3) 21(47.7) | 31(13.8) 193(86.2) | χ2=33.763 | <0.05 |
| 脑血管事件史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 32(72.8) 12(27.2) | 43(19.2) 181(80.8) | χ2=52.291 | <0.05 |
| 透析时肝素使用[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 40(90.9) 4(9.1) | 216(96.4) 8(3.6) | χ2=2.619 | 0.106 |
| 原发病为多囊肾[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 4(9.1) 40(90.9) | 2(0.9) 222(99.1) | χ2=11.293 | <0.05 |
| 初始透析方式是否为血液透析[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 40(90.9) 4(9.1) | 213(95.1) 11(4.9) | χ2=1.216 | 0.270 |
| 日常应用华法林[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 18(40.9) 26(59.1) | 5(2.2) 219(97.8) | χ2=70.121 | <0.05 |
| 日常应用阿司匹林[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 12(27.3) 32(72.7) | 89(39.7) 135(60.3) | χ2=2.431 | 0.119 |
| 项目 | 脑出血组(n=44) | 对照组(n=244) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 血清钠(mmol/L) | 136.553±6.230 | 141.487±3.498 | t=5.043 | <0.05 |
| 血清钙(mmol/L) | 2.244±0.330 | 1.958±0.272 | t=-6.075 | <0.05 |
| 血清磷(mmol/L) | 1.560(1.333,2.225) | 1.920(1.578,2.283) | Z=-1.977 | 0.058 |
| 血清钾(mmol/L) | 4.867±0.850 | 4.524±0.769 | t=-2.636 | <0.05 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 760.819±299.471 | 803.496±254.091 | t=0.980 | 0.328 |
| 尿素氮(mmol/L) | 25.410(17.300,37.770) | 28.220(21.625,34.935) | Z=-0.694 | 0.488 |
| 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) | 14.700(10.500,20.400) | 12.100(7.850,18.950) | Z=-2.113 | <0.05 |
| 谷草转氨酶(U/L) | 14.800(11.400,21.600) | 13.000(10.150,17.250) | Z=-1.780 | 0.075 |
| 血清白蛋白(g/L) | 33.900 (28.300,38.000) | 34.900(29.950,39.350) | Z=-0.963 | 0.335 |
| 血清总蛋白(g/L) | 59.345±9.146 | 60.651±8.943 | t=0.874 | 0.383 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 1.890(1.410,2.860) | 1.360(1.020,1.820) | Z=-4.437 | <0.05 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.570(3.730,5.400) | 4.040(3.435,4.980) | Z=-1.930 | 0.054 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.470(1.980,3.340) | 2.270(1.825,2.845) | Z=-2.251 | <0.05 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.100(0.970,1.270) | 1.070(0.955,1.320) | Z=-0.216 | 0.829 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 5.945(4.893,8.423) | 4.870(4.283,6.115) | Z=-2.866 | <0.05 |
| D-二聚体(μg/L) | 720.000(340.000,1180.000) | 380.000(230.000,577.500) | Z=-4.945 | <0.05 |
| 活化部分凝血活酶时间(s) | 32.600(28.200,34.400) | 31.150(28.125,34.000) | Z=-1.063 | 0.268 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 12.100(11.400,13.400) | 11.800(10.700,12.675) | Z=-1.670 | 0.095 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 8.900(2.200,20.000) | 2.510(0.515,9.460) | Z=-4.325 | <0.05 |
| PCT(ng/ml) | 0.410(0.175,2.010) | 0.270(0.070,0.600) | Z=-2.675 | <0.05 |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 7.445(5.550,9.863) | 5.890(5.005,7.180) | Z=-3.496 | <0.05 |
| 中性粒细胞(×109/L) | 5.530(3.638,6.590) | 4.200(3.270,5.230) | Z=-3.049 | <0.05 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 178.175±67.057 | 186.349±68.026 | t=0.702 | 0.483 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 98.000(75.000,113.000) | 88.000(74.000,105.000) | Z=-1.945 | 0.052 |
| BNP(pg/ml) | 604.400(248.075,1558.625) | 236.800(104.700,495.500) | Z=-3.873 | <0.05 |
| 甲状旁腺素(pmol/L) | 171.300(95.620,288.300) | 239.700(134.100,355.100) | Z=-1.841 | 0.066 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 404.663±111.767 | 414.434±137.255 | t=0.425 | 0.671 |
| 血沉(mm/h) | 30.000(11.700,94.800) | 20.900(13.575,34.425) | Z=-1.077 | 0.593 |
| 项目 | 脑出血组(n=44) | 对照组(n=244) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 血清钠(mmol/L) | 136.553±6.230 | 141.487±3.498 | t=5.043 | <0.05 |
| 血清钙(mmol/L) | 2.244±0.330 | 1.958±0.272 | t=-6.075 | <0.05 |
| 血清磷(mmol/L) | 1.560(1.333,2.225) | 1.920(1.578,2.283) | Z=-1.977 | 0.058 |
| 血清钾(mmol/L) | 4.867±0.850 | 4.524±0.769 | t=-2.636 | <0.05 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 760.819±299.471 | 803.496±254.091 | t=0.980 | 0.328 |
| 尿素氮(mmol/L) | 25.410(17.300,37.770) | 28.220(21.625,34.935) | Z=-0.694 | 0.488 |
| 谷丙转氨酶(U/L) | 14.700(10.500,20.400) | 12.100(7.850,18.950) | Z=-2.113 | <0.05 |
| 谷草转氨酶(U/L) | 14.800(11.400,21.600) | 13.000(10.150,17.250) | Z=-1.780 | 0.075 |
| 血清白蛋白(g/L) | 33.900 (28.300,38.000) | 34.900(29.950,39.350) | Z=-0.963 | 0.335 |
| 血清总蛋白(g/L) | 59.345±9.146 | 60.651±8.943 | t=0.874 | 0.383 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 1.890(1.410,2.860) | 1.360(1.020,1.820) | Z=-4.437 | <0.05 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.570(3.730,5.400) | 4.040(3.435,4.980) | Z=-1.930 | 0.054 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.470(1.980,3.340) | 2.270(1.825,2.845) | Z=-2.251 | <0.05 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.100(0.970,1.270) | 1.070(0.955,1.320) | Z=-0.216 | 0.829 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 5.945(4.893,8.423) | 4.870(4.283,6.115) | Z=-2.866 | <0.05 |
| D-二聚体(μg/L) | 720.000(340.000,1180.000) | 380.000(230.000,577.500) | Z=-4.945 | <0.05 |
| 活化部分凝血活酶时间(s) | 32.600(28.200,34.400) | 31.150(28.125,34.000) | Z=-1.063 | 0.268 |
| 凝血酶原时间(s) | 12.100(11.400,13.400) | 11.800(10.700,12.675) | Z=-1.670 | 0.095 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 8.900(2.200,20.000) | 2.510(0.515,9.460) | Z=-4.325 | <0.05 |
| PCT(ng/ml) | 0.410(0.175,2.010) | 0.270(0.070,0.600) | Z=-2.675 | <0.05 |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 7.445(5.550,9.863) | 5.890(5.005,7.180) | Z=-3.496 | <0.05 |
| 中性粒细胞(×109/L) | 5.530(3.638,6.590) | 4.200(3.270,5.230) | Z=-3.049 | <0.05 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 178.175±67.057 | 186.349±68.026 | t=0.702 | 0.483 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 98.000(75.000,113.000) | 88.000(74.000,105.000) | Z=-1.945 | 0.052 |
| BNP(pg/ml) | 604.400(248.075,1558.625) | 236.800(104.700,495.500) | Z=-3.873 | <0.05 |
| 甲状旁腺素(pmol/L) | 171.300(95.620,288.300) | 239.700(134.100,355.100) | Z=-1.841 | 0.066 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 404.663±111.767 | 414.434±137.255 | t=0.425 | 0.671 |
| 血沉(mm/h) | 30.000(11.700,94.800) | 20.900(13.575,34.425) | Z=-1.077 | 0.593 |
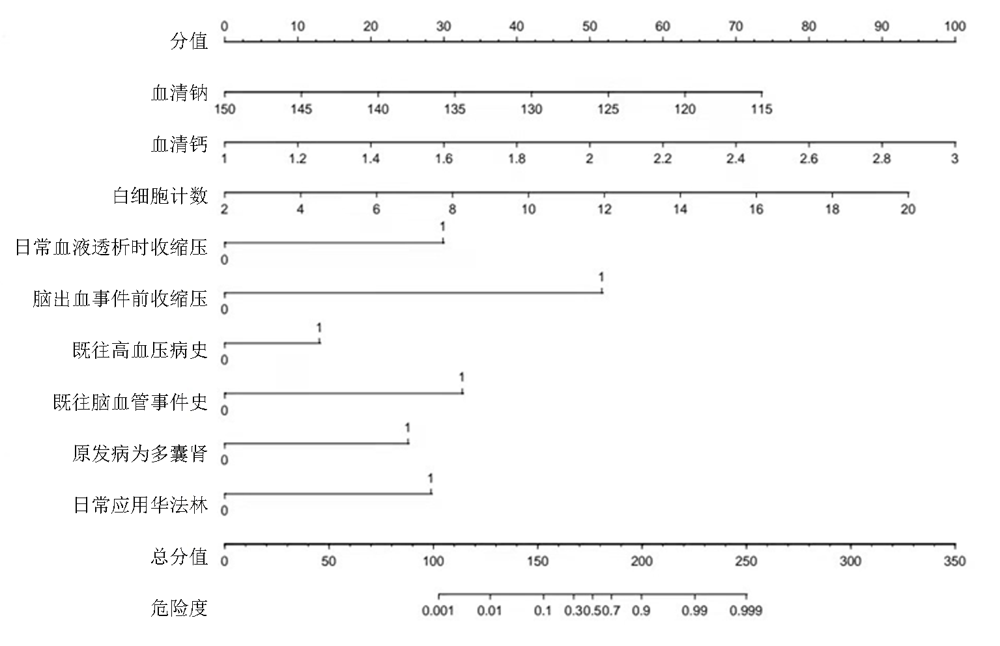
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 脑出血事件前收缩压 | 3.206 | 0.729 | 4.40 | <0.01 | 24.667 | 5.907 | 103.020 |
| 日常血液透析时收缩压 | 2.818 | 0.850 | 3.32 | <0.01 | 16.746 | 3.165 | 88.615 |
| 血清钠 | -0.217 | 0.057 | -3.83 | <0.01 | 0.334 | 0.191 | 0.585 |
| 血清钙 | 3.432 | 0.874 | 3.93 | <0.01 | 3.212 | 1.795 | 5.749 |
| D-二聚体 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.51 | <0.01 | 2.216 | 1.422 | 3.453 |
| 白细胞计数 | 0.238 | 0.086 | 2.78 | 0.005 | 1.792 | 1.188 | 2.702 |
| 既往高血压病史 | 3.010 | 0.869 | 3.46 | <0.01 | 20.279 | 3.690 | 111.440 |
| 既往脑血管事件史 | 1.855 | 0.636 | 2.92 | 0.004 | 6.393 | 1.837 | 22.244 |
| 原发病为多囊肾 | 2.416 | 0.950 | 2.54 | 0.011 | 11.204 | 1.740 | 72.162 |
| 日常应用华法林 | 3.269 | 0.904 | 3.62 | <0.01 | 26.280 | 4.472 | 154.430 |
| 因素 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 脑出血事件前收缩压 | 3.206 | 0.729 | 4.40 | <0.01 | 24.667 | 5.907 | 103.020 |
| 日常血液透析时收缩压 | 2.818 | 0.850 | 3.32 | <0.01 | 16.746 | 3.165 | 88.615 |
| 血清钠 | -0.217 | 0.057 | -3.83 | <0.01 | 0.334 | 0.191 | 0.585 |
| 血清钙 | 3.432 | 0.874 | 3.93 | <0.01 | 3.212 | 1.795 | 5.749 |
| D-二聚体 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 3.51 | <0.01 | 2.216 | 1.422 | 3.453 |
| 白细胞计数 | 0.238 | 0.086 | 2.78 | 0.005 | 1.792 | 1.188 | 2.702 |
| 既往高血压病史 | 3.010 | 0.869 | 3.46 | <0.01 | 20.279 | 3.690 | 111.440 |
| 既往脑血管事件史 | 1.855 | 0.636 | 2.92 | 0.004 | 6.393 | 1.837 | 22.244 |
| 原发病为多囊肾 | 2.416 | 0.950 | 2.54 | 0.011 | 11.204 | 1.740 | 72.162 |
| 日常应用华法林 | 3.269 | 0.904 | 3.62 | <0.01 | 26.280 | 4.472 | 154.430 |
| [1] |
Toyoda K, Ninomiya T. Stroke and cerebrovascular diseases in patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2014, 13(8):823-833.
doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70026-2 URL |
| [2] |
Thomé FS, Sesso RC, Lopes AA, et al. Brazilian chronic dialysis survey 2017[J]. J Bras Nefrol, 2019, 41(2):208-214.
doi: 10.1590/2175-8239-jbn-2018-0178 URL |
| [3] |
Wakasugi M, Matsuo K, Kazama JJ, et al. Higher mortality due to intracerebral hemorrhage in dialysis patients: A comparison with the general population in Japan[J]. Ther Apher Dial, 2015, 19(1):45-49.
doi: 10.1111/1744-9987.12192 URL |
| [4] |
Lee M, Saver JL, Chang KH, et al. Low glomerular filtration rate and risk of stroke: Meta-analysis[J]. BMJ, 2010, 341:c4249.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.c4249 URL |
| [5] | Cherng YG, Lin CS, Shih CC, et al. Stroke risk and outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease or end-stage renal disease: Two nationwide studies[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(1):e0191155. |
| [6] |
Dad T, Weiner DE. Stroke and chronic kidney disease: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management across kidney disease stages[J]. Semin Nephrol, 2015, 35(4):311-322.
doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2015.06.003 URL |
| [7] |
Tonelli M, Karumanchi SA, Thadhani R. Epidemiology and mechanisms of uremia-related cardiovascular disease[J]. Circulation, 2016, 133(5):518-536.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018713 URL |
| [8] |
Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, et al. Erratum regarding “US Renal Data System 2017 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States”[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2018, 71(4):501.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.03.001 URL |
| [9] |
Arnold J, Sims D, Ferro CJ. Modulation of stroke risk in chronic kidney disease[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2016, 9(1):29-38.
doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfv136 pmid: 26798458 |
| [10] |
Kitamura M, Tateishi Y, Sato S, et al. Association between serum calcium levels and prognosis, hematoma volume, and onset of cerebral hemorrhage in patients undergoing hemodialysis[J]. BMC Nephrol, 2019, 20(1):210.
doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1400-4 pmid: 31174486 |
| [11] | Howarth C. The contribution of astrocytes to the regulation of cerebral blood flow[J]. Front Neurosci, 2014, 8:103. |
| [12] |
Shroff RC, McNair R, Skepper JN, et al. Chronic mineral dysregulation promotes vascular smooth muscle cell adaptation and extracellular matrix calcification[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 21(1):103-112.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009060640 URL |
| [13] |
Beierwaltes WH. The role of calcium in the regulation of renin secretion[J]. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol, 2010, 298(1):F1-F11.
doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00143.2009 URL |
| [14] |
Smajilovic S, Yano S, Jabbari R, et al. The calcium-sensing receptor and calcimimetics in blood pressure modulation[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2011, 164(3):884-893.
doi: 10.1111/bph.2011.164.issue-3 URL |
| [15] |
Eisner DA, Caldwell JL, Kistamás K, Trafford AW. Calcium and excitation-contraction coupling in the heart[J]. Circ Res, 2017, 121(2):181-195.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310230 pmid: 28684623 |
| [16] |
O'Neill WC. Targeting serum calcium in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: Is normal too high?[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 89(1):40-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.10.001 URL |
| [17] |
Abdullahi W, Tripathi D, Ronaldson PT. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: Targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2018, 315(3):C343-C356.
doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00095.2018 URL |
| [18] |
Cortina G, Hansford JR, Duke T. Central diabetes insipidus and cisplatin-induced renal salt wasting syndrome: A challenging combination[J]. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 2016, 63(5):925-927.
doi: 10.1002/pbc.25910 pmid: 26928867 |
| [19] | 刘颖, 张艳, 莫颖. 对接受维持性血液透析患者预后影响因素的研究[J]. 当代医药论丛, 2020, 18(10):103-104. |
| [20] |
Cohen G, Raupachova J, Borchhardt K, et al. Cinacalcet effect on polymorphonuclear leucocytes of kidney transplant patients[J]. Eur J Clin Invest 43 (5):476-482.
doi: 10.1111/eci.2013.43.issue-5 URL |
| [21] |
Yamada S, Tsuruya K, Taniguchi M, et al. Association between serum phosphate levels and stroke risk in patients undergoing hemodialysis: The Q-cohort study[J]. Stroke, 2016, 47(9):2189-2196.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.013195 URL |
| [22] |
Naganuma T, Takemoto Y, Shoji T, et al. Cerebral microbleeds predict intracerebral hemorrhage in hemodialysis patients[J]. Stroke, 2015, 46(8):2107-2112.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.009324 URL |
| [23] |
Wilkinson DA, Heung M, Deol A, et al. Cerebral aneurysms in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: A comparison of management approaches[J]. Neurosurgery, 2019 84(6):E352-E361.
doi: 10.1093/neuros/nyy336 |
| [24] | 肖文颖. 多囊肾伴高血压1例[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2015, 3(21):197-198. |
| [25] | Xiao M, Li Q, Feng H, et al. Neural vascular mechanism for the cerebral blood flow autoregulation after hemorrhagic stroke[J]. Neural Plast, 2017, 2017:5819514. |
| [1] | Yu Zeyu, Lin Xi, Chen Zhanghua, Yang Wei, Chen Zhimin, Zhang Hai. Analysis of risk factors for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 43-46. |
| [2] | Liu Lili, Yuan Yuting, Lai Gengliang, Tian Chuan, Lan Xiang, Ye Zhonglv. The relationship between minimal residual disease on day 15 and prognosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 47-52. |
| [3] | Wei Zeng, Cao Ling, She Dunmin, Liu Yan, Wang Yan, Zhang Zhenwen. The causes of death in 54 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(9): 806-812. |
| [4] | Wang Yingnan, Zhao Qi, Bai Haiwei, Wu Danna, Wei Jinmei, Li Shengjiang, Li Ruiling, Zhang Ruixing. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of gastric cancer-related stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 417-422. |
| [5] | Ma Mingfu, Wei Zhiguo, He Tieying. Meta-analysis of risk factors for pancreatic pseudocyst in acute pancreatitis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [6] | Leng Wantong, Tao Jie. Risk factors of postoperative venous thromboembolism in patients with multiple myeloma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 340-345. |
| [7] | Ma Hongli, Lu Hao, Wang Dan, Jiao Haixing, Li Yike, Li Siyu, Lu Jing. Meta-analysis of disability risk factors in stroke patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| [8] | Du Jiayi, Liu Lili, He Yongzhong, Tian Chuan, Lan Xiang, Ye Zhonglyu. Clinical observation of serious adverse events in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia during chemotherapy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 149-154. |
| [9] | Liang Bingsong, Li Yuying, Zhang Qiping, Chen Yingdao, Li jian. Analysis of factors affecting clinical efficacy of Tirofiban in treating branch atheromatous disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(12): 1091-1094. |
| [10] | Ding Siqi, Liu Shihua, Zhang Chao, Zhong Ping, Cao Li. Risk factors for epilepsy after delayed post-stroke epilepsy and its clinical correlation with blood Hcy, hs-CRP and D-D [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(10): 893-897. |
| [11] | Yao Huajun, Zhou Jun, Yin Xue, Zhang Haie, Zhang Haiyan. Analysis on congenital cytomegalovirus infection rate and risk factors of high viral load of high-risk newborns in Xiaogan City Single Center [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(6): 530-533. |
| [12] | Li Ya, Qiu Shixiang, Chen Chao, Zhong Liming. Depression-related factors and corresponding correlations with quality of life in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(6): 539-543. |
| [13] | Song Siping, Jiang Qixia, Liu Xiaoqing. Risk factors of intraoperative acquired pressure injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 211-219. |
| [14] | Zheng Lihua, Du Runsen, Zhao Yaheng, Liu Peng. Influencing factors and predictive indicators of vascular calcification [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(2): 114-118. |
| [15] | Guo Yanzhen, Wang Nuojin, Ma Junji. Risk factors for colorectal adenoma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(2): 137-140. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||