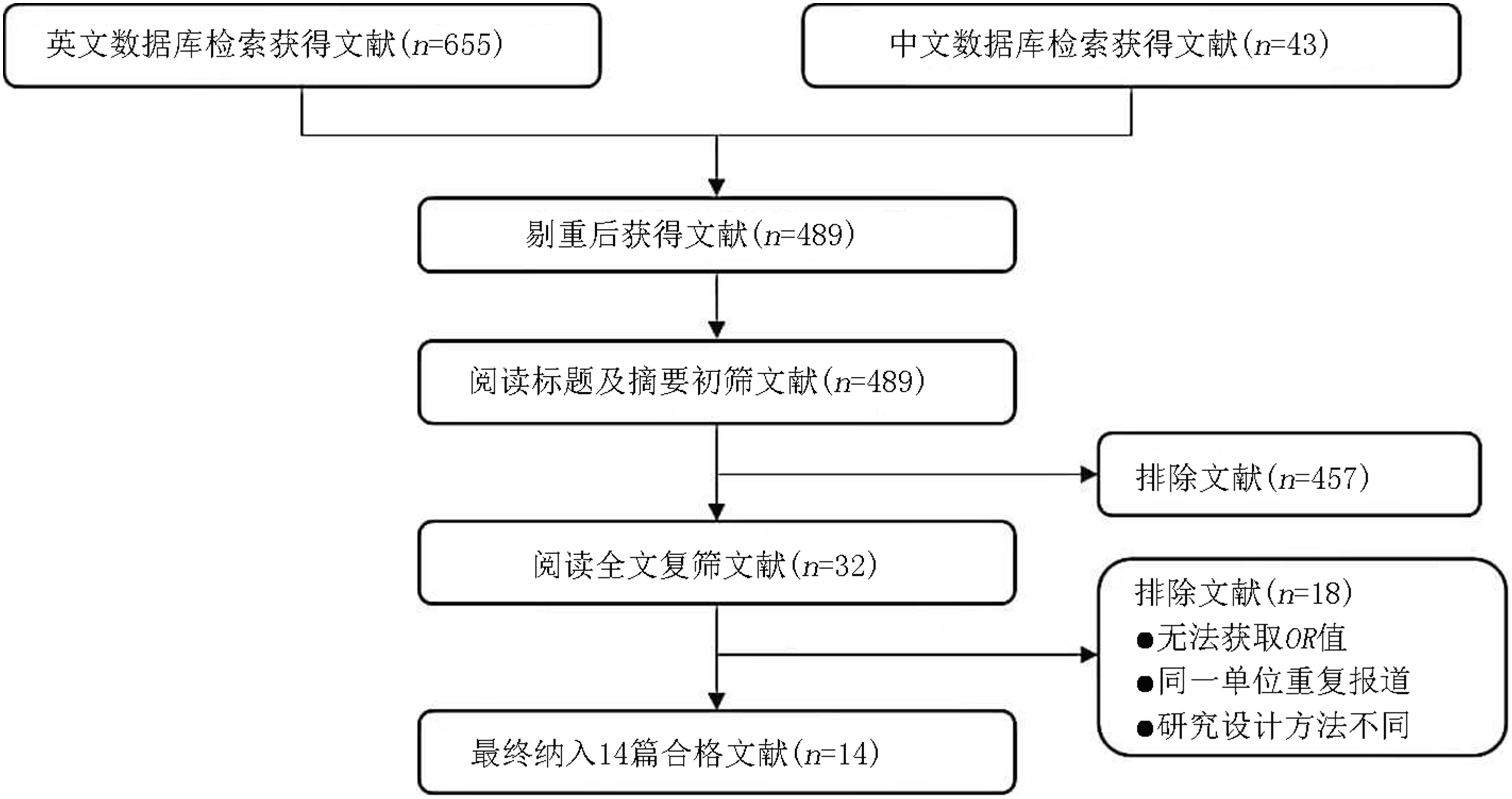
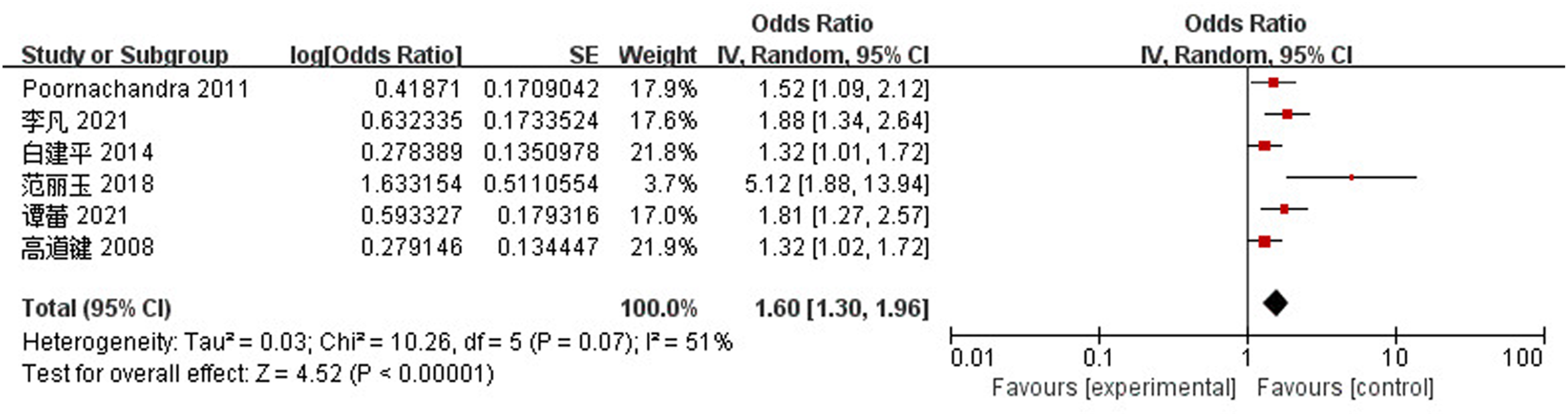
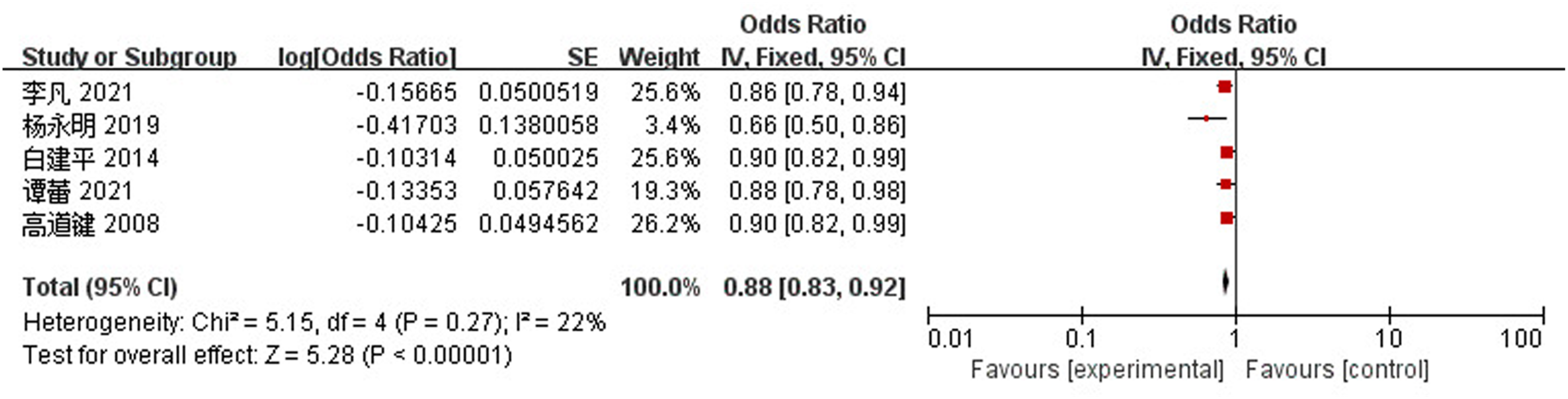
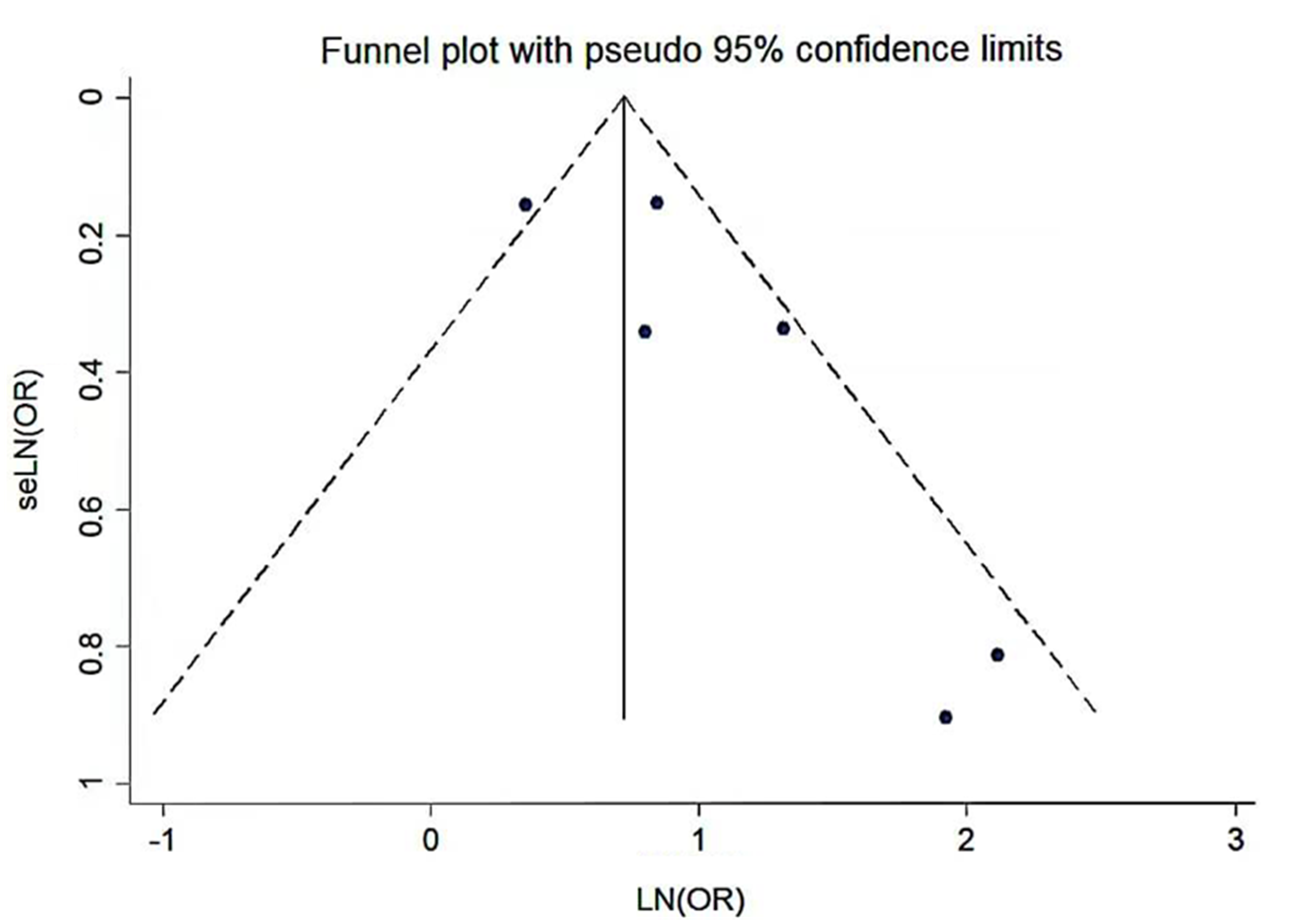
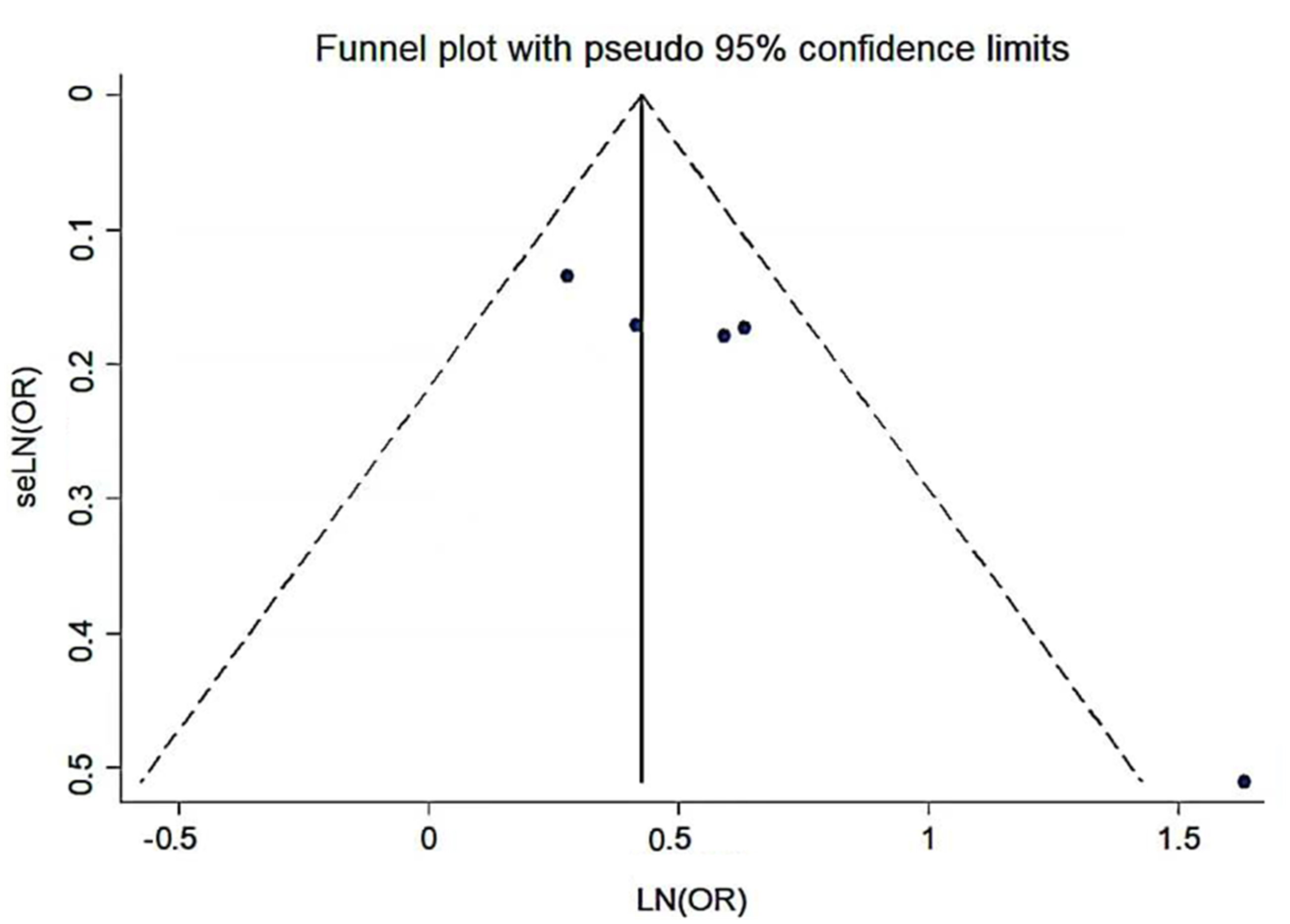
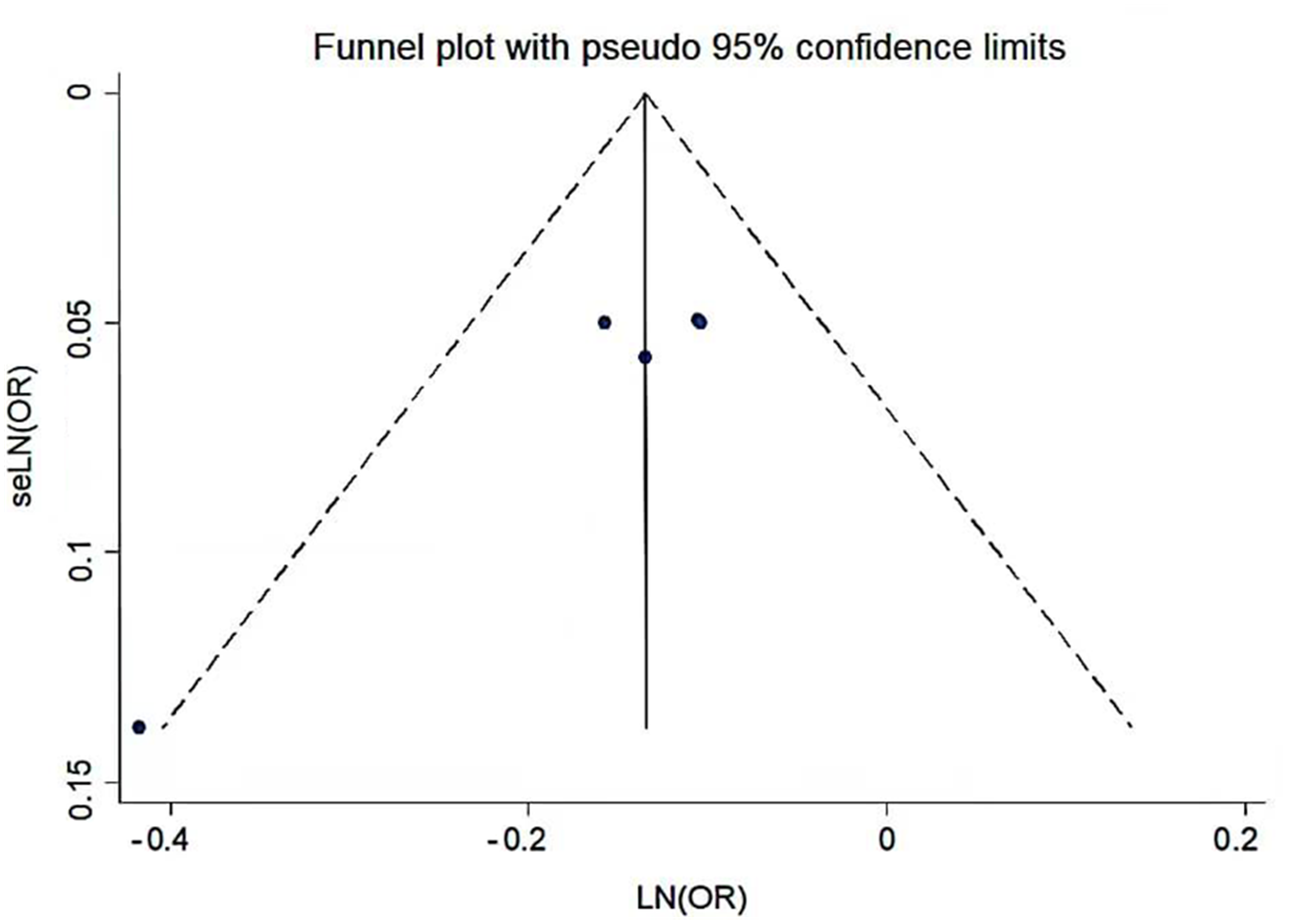
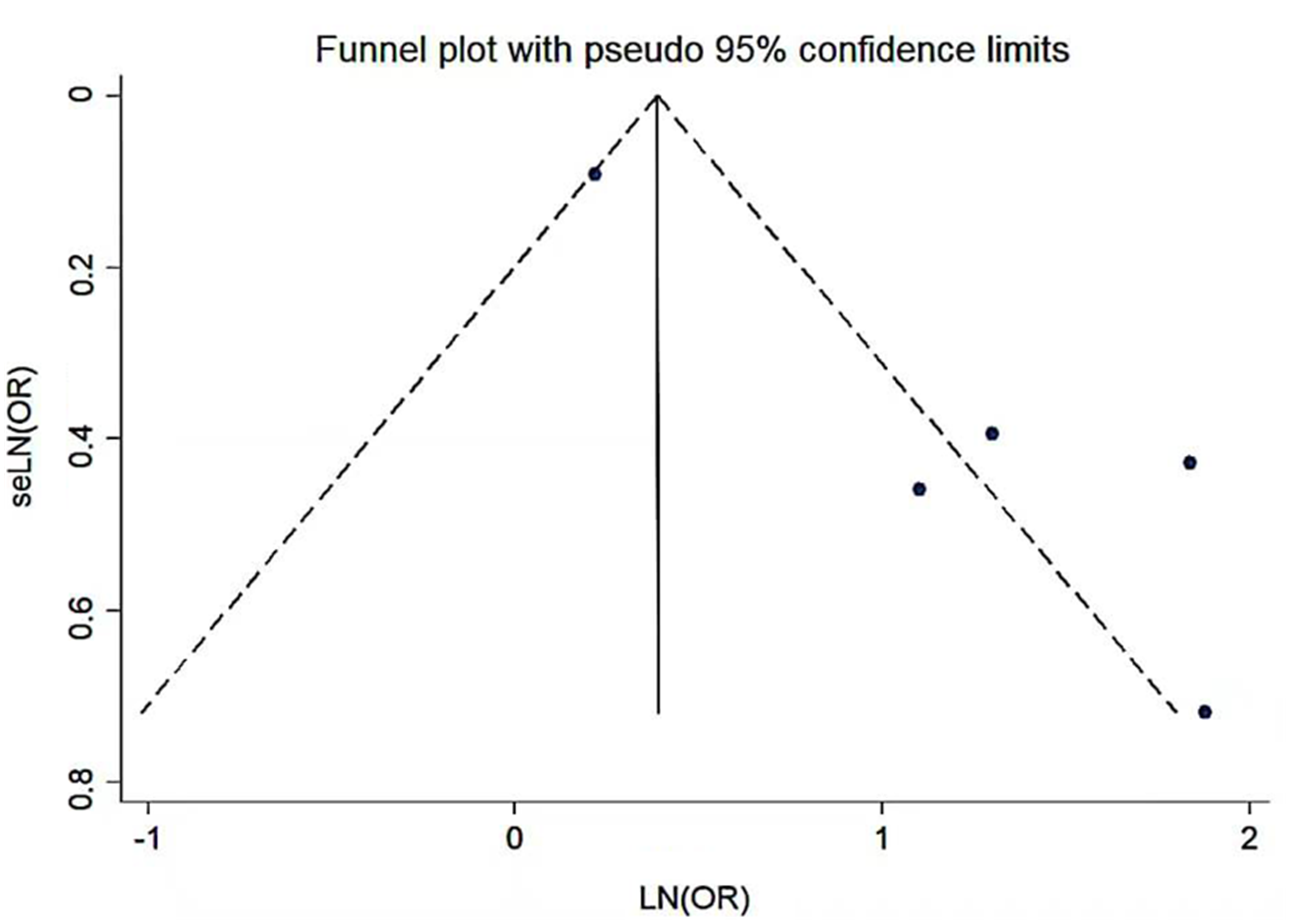
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 293-301.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.04.001
Meta-analysis of risk factors for pancreatic pseudocyst in acute pancreatitis
Ma Mingfu, Wei Zhiguo, He Tieying( )
)
- Department of Pancreatic Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830011, China
-
Received:2022-11-29Online:2023-04-20Published:2023-06-06 -
Contact:He Tieying E-mail:tietie5309@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Mingfu, Wei Zhiguo, He Tieying. Meta-analysis of risk factors for pancreatic pseudocyst in acute pancreatitis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 293-301.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.04.001
Tab.1 NOS score of finally included studies
| 纳入研究 | 研究对象 选择 | 组间 可比性 | 暴露或 结果评价 | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范丽玉[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 高道键[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| 李凡[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 谭蕾[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| 徐太军[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| 杨永明[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| 杨子云[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Maringhini[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Cui[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Diculescu[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Kim[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Poornachandra[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Tan[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 白建平[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
Tab.1 NOS score of finally included studies
| 纳入研究 | 研究对象 选择 | 组间 可比性 | 暴露或 结果评价 | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范丽玉[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 高道键[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| 李凡[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 谭蕾[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| 徐太军[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| 杨永明[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| 杨子云[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Maringhini[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
| Cui[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Diculescu[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Kim[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| Poornachandra[ | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 |
| Tan[ | 4 | 2 | 3 | 9 |
| 白建平[ | 4 | 1 | 3 | 8 |
Tab. 2 Basic characteristics of included literatures
| 第一作者 | 发表 年份 | 国家 | 研究类型 | 病例组 | 对照组 | 危险因素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范丽玉[ | 2018 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 143 | 317 | ①②④⑤⑥ |
| 高道键[ | 2008 | 中国 | 队列研究 | 30 | 70 | ⑥⑦ |
| 李凡[ | 2021 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 70 | 646 | ②⑥⑦⑧⑨ |
| 谭蕾[ | 2021 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 48 | 94 | ⑥⑦⑩11 |
| 徐太军[ | 2022 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 58 | 342 | ②11121314 |
| 杨永明[ | 2019 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 51 | 75 | ①②⑦14 |
| 杨子云[ | 2020 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 78 | 493 | ②⑧121516 |
| Maringhini[ | 1996 | 意大利 | 队列研究 | 16 | 84 | ②③④ |
| Cui[ | 2014 | 韩国 | 队列研究 | 19 | 90 | 17 |
| Diculescu[ | 2005 | 罗马尼亚 | 队列研究 | 13 | 49 | 1218 |
| Kim[ | 2012 | 韩国 | 病例对照 | 51 | 350 | 121519 |
| Poornachandra[ | 2011 | 印度 | 队列研究 | 34 | 31 | ①③⑤⑥ |
| Tan[ | 2018 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 654 | 3 233 | 121520 |
| 白建平[ | 2014 | 中国 | 队列研究 | 40 | 80 | ⑥⑦ |
Tab. 2 Basic characteristics of included literatures
| 第一作者 | 发表 年份 | 国家 | 研究类型 | 病例组 | 对照组 | 危险因素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范丽玉[ | 2018 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 143 | 317 | ①②④⑤⑥ |
| 高道键[ | 2008 | 中国 | 队列研究 | 30 | 70 | ⑥⑦ |
| 李凡[ | 2021 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 70 | 646 | ②⑥⑦⑧⑨ |
| 谭蕾[ | 2021 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 48 | 94 | ⑥⑦⑩11 |
| 徐太军[ | 2022 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 58 | 342 | ②11121314 |
| 杨永明[ | 2019 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 51 | 75 | ①②⑦14 |
| 杨子云[ | 2020 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 78 | 493 | ②⑧121516 |
| Maringhini[ | 1996 | 意大利 | 队列研究 | 16 | 84 | ②③④ |
| Cui[ | 2014 | 韩国 | 队列研究 | 19 | 90 | 17 |
| Diculescu[ | 2005 | 罗马尼亚 | 队列研究 | 13 | 49 | 1218 |
| Kim[ | 2012 | 韩国 | 病例对照 | 51 | 350 | 121519 |
| Poornachandra[ | 2011 | 印度 | 队列研究 | 34 | 31 | ①③⑤⑥ |
| Tan[ | 2018 | 中国 | 病例对照 | 654 | 3 233 | 121520 |
| 白建平[ | 2014 | 中国 | 队列研究 | 40 | 80 | ⑥⑦ |
| [1] |
Wang GJ, Gao CF, Wei D, et al. Acute pancreatitis: Etiology and common pathogenesis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2009, 15(12): 1427-1430.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.15.1427 URL |
| [2] | Hines OJ, Pandol SJ. Management of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. BMJ, 2019, 367: 16227. |
| [3] |
Pitchumoni CS, Agarwal N. Pancreatic pseudocysts. When and how should drainage be performed?[J]. Gastroenterol Clin North Am, 1999, 28(3): 615-639.
doi: 10.1016/S0889-8553(05)70077-7 URL |
| [4] | Khanna AK, Tiwary SK, Kumar P. Pancreatic pseudocyst: Therapeutic dilemma[J]. Int J Inflam, 2012, 2012: 279476. |
| [5] |
Redwan AA, Hamad MA, Omar MA. Pancreatic pseudocyst dilemma: Cumulative multicenter experience in ma nagement using endoscopy, laparoscopy, and open surgery[J]. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A, 2017, 27(10): 1022-1030.
doi: 10.1089/lap.2017.0006 pmid: 28459653 |
| [6] |
Magyar A, Tihanyi T, Szlávik R, et al. Pancreatic pseudocysts causing compression symptoms[J]. Acta Chir Hung, 1994, 34(1-2): 59-67.
pmid: 7604630 |
| [7] |
Vignesh S, Brugge WR. Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic cysts[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2008, 42(5): 493-506.
doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181616159 pmid: 18344889 |
| [8] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9): 603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z pmid: 20652370 |
| [9] | 范丽玉. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿形成的危险因素分析[D]. 青岛大学, 2018. |
| [10] | 高道键, 李兆申, 张文俊, 等. 重症急性胰腺炎后假性囊肿形成的早期危险因素分析[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2008, 8(4):243-245. |
| [11] | 李凡. 急性胰腺炎后并发胰腺假性囊肿的危险因素及预测分析[D]. 兰州大学, 2021. |
| [12] | 谭蕾, 高青. 重症急性胰腺炎患者胰腺假性囊肿形成的相关因素分析[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2021, 21(4):266-270. |
| [13] | 徐太军, 王翔, 徐蕊, 等. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿常见危险因素分析[J]. 河北医药, 2022, 44(8):1215-1217. |
| [14] | 杨永明. 急性胰腺炎后并发胰腺假性囊肿形成的相关危险因素分析[D]. 昆明医科大学, 2019. |
| [15] |
杨子云, 张海蓉, 何佳薇, 等. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿危险因素分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(29):3682-3689.
doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.013 |
| [16] |
Maringhini A, Ciambra M, Patti R, et al. Ascites, pleural, and pericardial effusions in acute pancreatitis. A prospective study of incidence, natural history, and prognostic role[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 1996, 41(5): 848-852.
doi: 10.1007/BF02091521 URL |
| [17] |
Cui ML, Kim KH, Kim HG, et al. Incidence, risk factors and clinical course of pancreatic fluid collections in acute pancreatitis[J]. Dig Dis Sci, 2014, 59(5): 1055-1062.
doi: 10.1007/s10620-013-2967-4 URL |
| [18] |
Diculescu M, Ciocîrlan M, Ciocîrlan M, et al. Predictive factors for pseudocysts and peripancreatic collections in acute pancreatitis[J]. Rom J Gastroenterol, 2005, 14(2): 129-134.
pmid: 15990931 |
| [19] |
Kim KO, Kim TN. Acute pancreatic pseudocyst: Incidence, risk factors, and clinical outcomes[J]. Pancreas, 2012, 41(4): 577-581.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182374def URL |
| [20] |
Poornachandra KS, Bhasin DK, Nagi B, et al. Clinical, biochemical, and radiologic parameters at admission predicting formation of a pseudocyst in acute pancreatitis[J]. J Clin Gastroenterol, 2011, 45(2): 159-163.
doi: 10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181dd9d14 pmid: 20628310 |
| [21] |
Tan JH, Zhou L, Cao RC, et al. Identification of risk factors for pancreatic pseudocysts formation, intervention and recurrence: A 15-year retrospective analysis in a tertiary hospital in China[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2018, 18(1):143.
doi: 10.1186/s12876-018-0874-z |
| [22] | 白建平. 急性重症胰腺炎后假性囊肿形成早期危险因素分析[J]. 中外医疗, 2014, 33(2): 40-41. |
| [23] |
Hamada S, Masamune A, Kikuta K, et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of acute pancreatitis in Japan[J]. Pancreas, 2014, 43(8): 1244-1248.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000000200 URL |
| [24] |
Kristiansen L, Grønbaek M, Becker U, et al. Risk of pancreatitis according to alcohol drinking habits: A population-based cohort study[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2008, 168(8): 932-937.
doi: 10.1093/aje/kwn222 pmid: 18779386 |
| [25] | Criddle DN. The role of fat and alcohol in acute pancreatitis: A dangerous liaison[J]. Pancreatology, 2015, 15(< W>4 Suppl): S6-S12. |
| [26] |
Pandol SJ, Lugea A, Mareninova OA, et al. Investigating the pathobiology of alcoholic pancreatitis[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 2011, 35(5): 830-837.
doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2010.01408.x pmid: 21284675 |
| [27] | Zhang XP, Li ZJ, Zhang J. Inflammatory mediators and microcirculatory disturbance in acute pancreatitis[J]. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int, 2009, 8(4): 351-357. |
| [28] | 高鸿亮, 王磊, 廖如奕. 体质量指数、 血糖水平与急性胰腺炎相关性分析[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2012, 26(1): 27-28. |
| [29] |
Martínez J, Sánchez-Payá J, Palazón JM, et al. Is obesity a risk factor in acute pancreatitis? A meta-analysis[J]. Pancreatology, 2004, 4(1): 42-48.
doi: 10.1159/000077025 pmid: 14988657 |
| [30] |
Shen HN, Chang YH, Chen HF, et al. Increased risk of severe acute pancreatitis in patients with diabetes[J]. Diabet Med, 2012, 29(11): 1419-1424.
doi: 10.1111/dme.2012.29.issue-11 URL |
| [31] |
张冰, 朱国玲, 孙秋, 等. 基线空腹血糖水平与急性胰腺炎发病风险的前瞻性队列研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2021, 24(1): 60-64.
doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.602 |
| [32] | 袁琳, 李学良. 急性胰腺炎与新发糖尿病的关系[J]. 胃肠病学, 2015, 20(8): 500-502. |
| [33] |
Sun YF, Song Y, Liu CS, et al. Correlation between the glucose level and the development of acute pancreatitis[J]. Saudi J Biol Sci, 2019, 26(2): 427-430.
doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2018.11.012 URL |
| [34] | 蒋丽丽, 李兆申. 急性胰腺炎复发诱因及内镜治疗[J]. 中华胰腺病杂志, 2010, 10(2):75-78. |
| [35] | Rehan A, Shabbir Z, Shaukat A, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of modified CT severity index in assessing severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak, 2016, 26(12): 967-970. |
| [36] |
Lee WS, Huang JF, Chuang WL. Outcome assessment in acute pancreatitis patients[J]. Kaohsiung J Med Sci, 2013, 29(9): 469-477.
doi: 10.1016/j.kjms.2012.10.007 URL |
| [37] |
Vincent JL, Russell JA, Jacob M, et al. Albumin administration in the acutely ill: What is new and where next?[J]. Crit Care, 2014, 18(4): 231.
doi: 10.1186/cc13991 URL |
| [38] | Zhang W, Hu J, Yao B, et al. Evaluation of early prognostic factors of mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis: A retrospective study[J]. Gastroenterol Res Pract, 2017, 2017: 8363561. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||