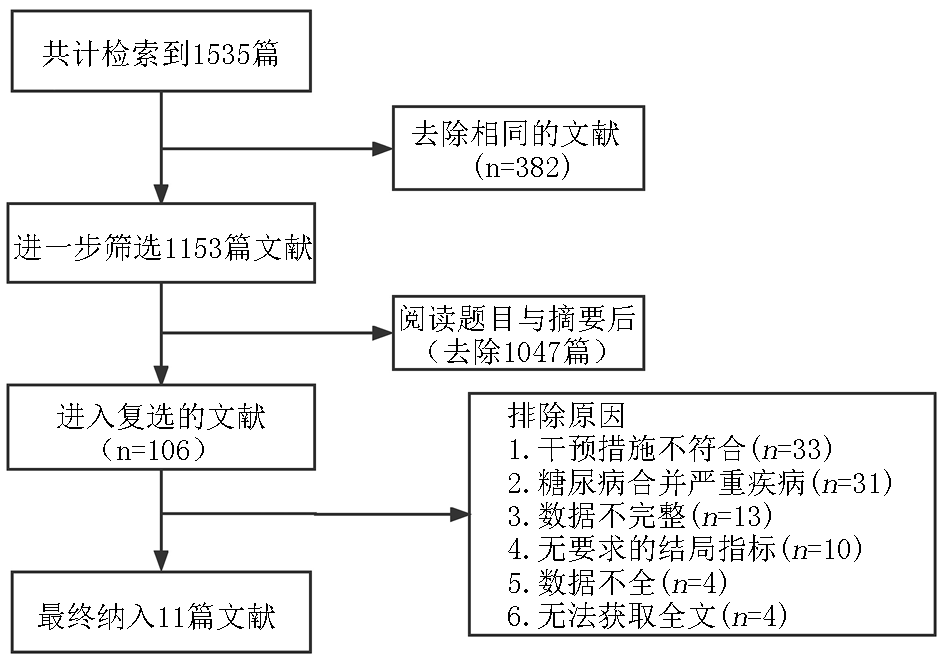
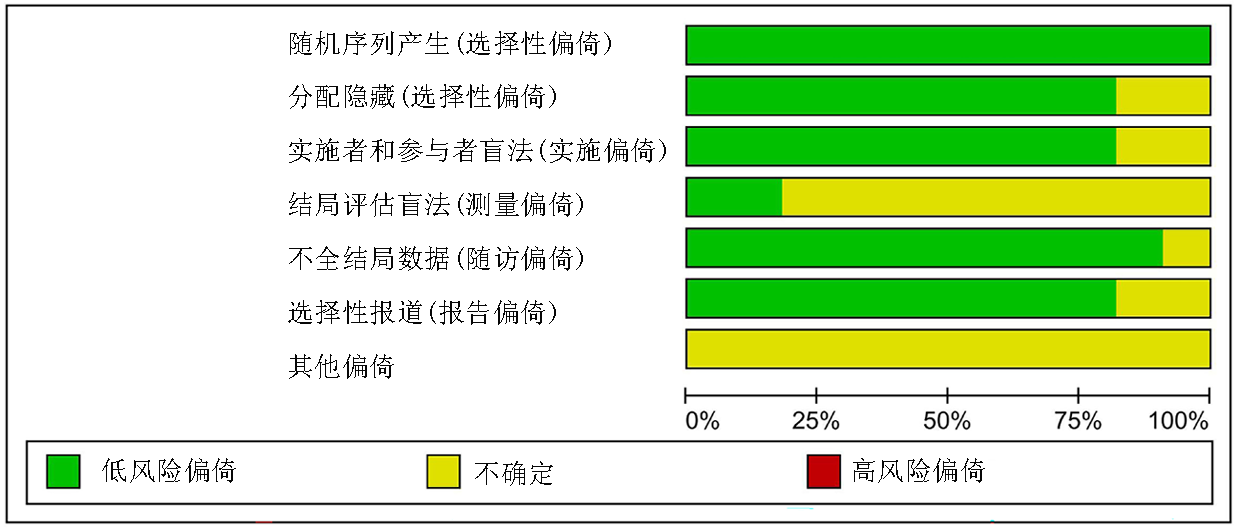
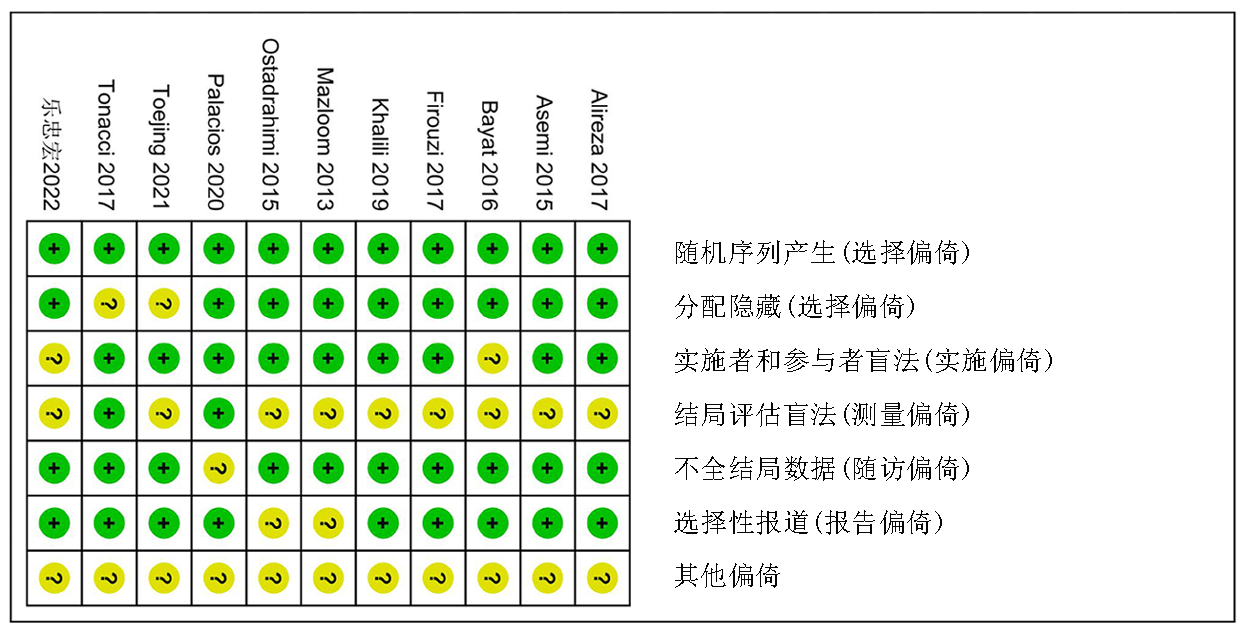
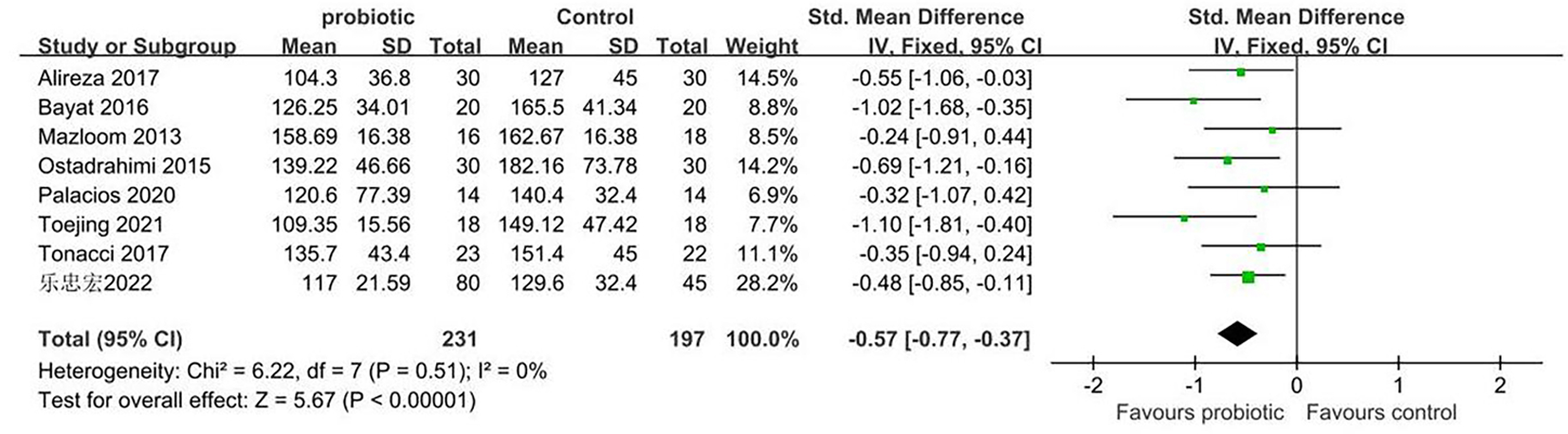
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 581-587.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.07.001
Probiotic supplementation on improving glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Jin Jiahui1, Yang Yang2, Qin Tong1, He Yuxin1, Su Meihua1( )
)
- 1. Physical Education Institute of Jimei University, Xiamen 361021, China
2. Graduate School of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 301617, China
-
Received:2023-01-03Online:2023-07-20Published:2023-09-01 -
Contact:Su Meihua E-mail:sumh1234@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jin Jiahui, Yang Yang, Qin Tong, He Yuxin, Su Meihua. Probiotic supplementation on improving glucose metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(7): 581-587.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.07.001
| #1 2型糖尿病 | #7 #1 and #3 in主题 |
| #2益生菌 | #8 #4 and #2 in主题 |
| #3双歧杆菌 | #9 #4 and #3 in主题 |
| #4糖耐量受损 | #10 (#1 or #4) and (#2 and #3) in主题 |
| #6 #1 and #2 in主题 | #11 (#1 or #4) and (#2 and #3) in摘要 |
Tab. 1 Search strategies of CNKI database
| #1 2型糖尿病 | #7 #1 and #3 in主题 |
| #2益生菌 | #8 #4 and #2 in主题 |
| #3双歧杆菌 | #9 #4 and #3 in主题 |
| #4糖耐量受损 | #10 (#1 or #4) and (#2 and #3) in主题 |
| #6 #1 and #2 in主题 | #11 (#1 or #4) and (#2 and #3) in摘要 |
| 作者与年限 | 国家 | 干预组 | 对照组 | 干预方案 | 干预 周期 | 结局 指标 | Cochrane 评分 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本量 (例) | 年龄 (岁) | 样本量 (例) | 年龄 (岁) | 干预组 | 对照组 | |||||||||
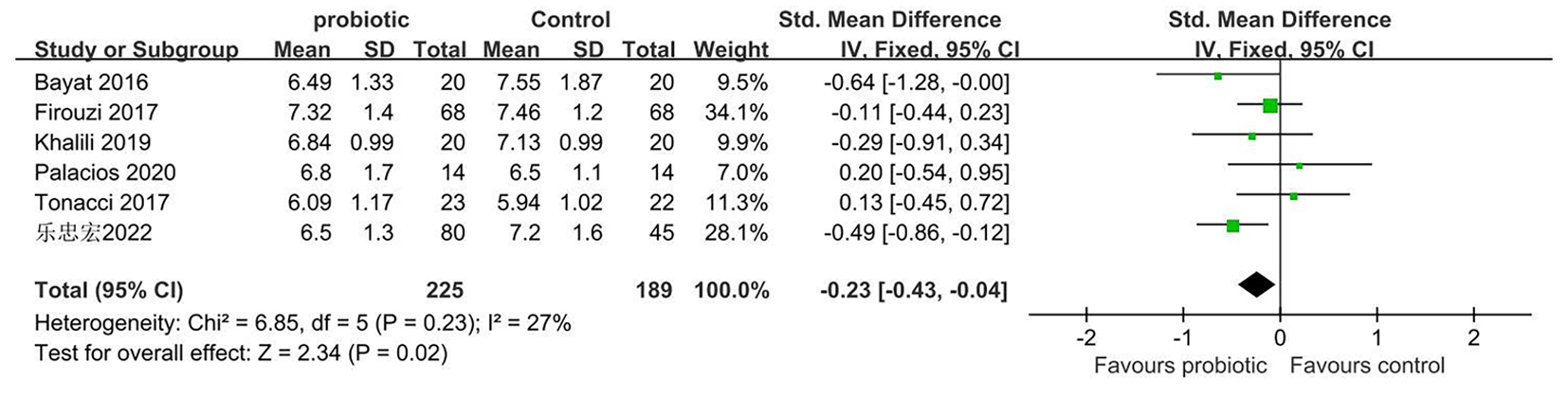
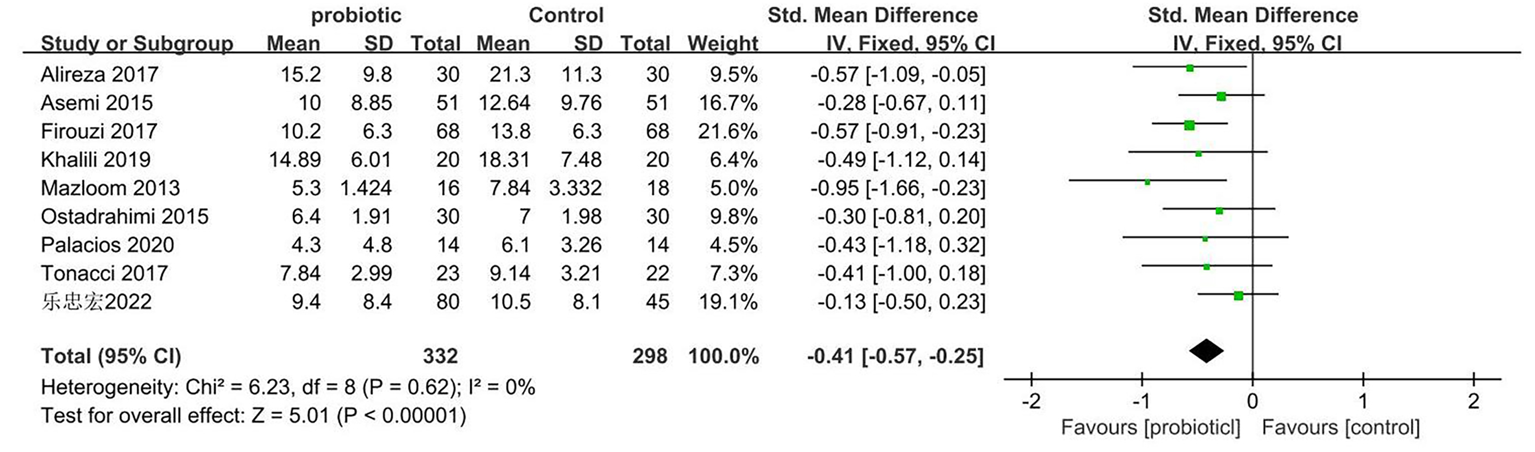
| 乐忠宏[ | 中国 | 80 | 59.4±6.1 | 45 | 58.1±5.3 | 二甲双胍+双歧杆菌四联活菌片 (3片/次,3次/d) | 二甲双胍+保持饮食 结构不变 | 12周 | ①②③ | 4分 | ||||
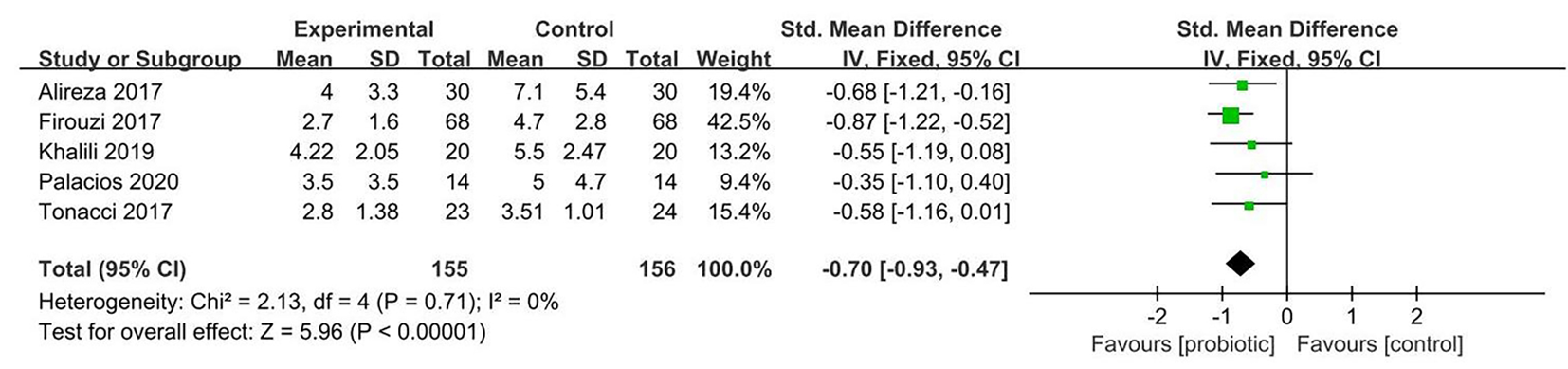
| Palacios[ | 澳大 利亚 | 14 | 61.4±8.9 | 14 | 56.1±12.3 | 二甲双胍+益生菌胶囊(含有植物乳杆菌Lp-115、保加利亚乳杆菌Lb-64、加氏乳杆菌Lg-36短双歧杆菌Bb-03、动物双歧杆菌lactisBi-07、双歧杆菌Bb-06、嗜热链球菌St-21、布拉氏酵母DBVPG 6763的胶囊) | 二甲双胍+安慰剂(微晶纤维素,二氧化硅和硬脂酸镁) | 12周 | ①②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Tonucci[ | 巴西 | 24 | 51.40±6.80 | 24 | 50.21±8.7 | 患者补充含有嗜酸乳杆菌La-5(6×107 CFU/g)、乳酸双歧杆菌BB-12(2×107CFU/g)的牛奶 | 补充安慰剂(牛奶) | 6周 | ①②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Toejing[ | 泰国 | 18 | 61.78±7.73 | 18 | 63.50±5.94 | 补充含有益生菌的胶囊(副干酪乳杆菌HII01 50×109CFU/g) | 补充安慰剂(玉米淀粉) | 12周 | ①② | 4分 | ||||
| Khalili[ | 伊朗 | 20 | 43.95±8.14 | 20 | 45±5.37 | 补充含有108CFU/g干酪乳杆菌的胶囊 | 补充安慰剂(含有麦芽糖糊精) | 8周 | ②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Firouzi[ | 伊朗 | 68 | 52.9±9.2 | 68 | 54.2±8.3 | 每包提供3×1010 CFU/g活微生物制剂粉末(其中每包粉末含有嗜酸乳杆菌,乳酸杆菌,双歧杆菌,长双歧杆菌) | 补充安慰剂 | 12周 | ②③ | 5分 | ||||
| Alireza[ | 伊朗 | 30 | 36~75 | 30 | 36~75 | 补充含有2×109 CFU/g嗜酸乳杆菌、干酪乳杆菌、双歧双歧杆菌的胶囊 | 补充安慰剂 | 12周 | ①②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Bayat[ | 伊朗 | 20 | 46.95±9.34 | 20 | 54.1±9.54 | 补充含有益生菌的酸奶 | 饮食指导,保持饮食结 构不变 | 8周 | ①② | 4分 | ||||
| Asemi[ | 伊朗 | 51 | 52.9±8.1 | 51 | 52.9±8.1 | 补充益生元的食品,其含有产孢乳杆菌1×107 CFU/g | 补充对照食品(不含益生菌) | 6周 | ③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Mazloom[ | 伊朗 | 16 | 55.4±8 | 18 | 51.8±10.2 | 补充含有嗜酸乳杆菌、保加利亚乳杆菌、双歧乳杆菌和干酪乳杆菌的胶囊 | 补充含有硬脂酸镁的 胶囊 | 6周 | ①③ | 4分 | ||||
| Ostadrahimi[ | 伊朗 | 30 | 48.29±11.71 | 30 | 51.4±8.6 | 补充600 ml有益生菌的发酵乳(其含有嗜酸乳杆菌、干酪乳杆菌、双歧杆菌) | 补充600 ml普通乳品 | 8周 | ①③ | 4分 | ||||
Tab. 2 Basic characteristics of the included studies
| 作者与年限 | 国家 | 干预组 | 对照组 | 干预方案 | 干预 周期 | 结局 指标 | Cochrane 评分 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 样本量 (例) | 年龄 (岁) | 样本量 (例) | 年龄 (岁) | 干预组 | 对照组 | |||||||||
| 乐忠宏[ | 中国 | 80 | 59.4±6.1 | 45 | 58.1±5.3 | 二甲双胍+双歧杆菌四联活菌片 (3片/次,3次/d) | 二甲双胍+保持饮食 结构不变 | 12周 | ①②③ | 4分 | ||||
| Palacios[ | 澳大 利亚 | 14 | 61.4±8.9 | 14 | 56.1±12.3 | 二甲双胍+益生菌胶囊(含有植物乳杆菌Lp-115、保加利亚乳杆菌Lb-64、加氏乳杆菌Lg-36短双歧杆菌Bb-03、动物双歧杆菌lactisBi-07、双歧杆菌Bb-06、嗜热链球菌St-21、布拉氏酵母DBVPG 6763的胶囊) | 二甲双胍+安慰剂(微晶纤维素,二氧化硅和硬脂酸镁) | 12周 | ①②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Tonucci[ | 巴西 | 24 | 51.40±6.80 | 24 | 50.21±8.7 | 患者补充含有嗜酸乳杆菌La-5(6×107 CFU/g)、乳酸双歧杆菌BB-12(2×107CFU/g)的牛奶 | 补充安慰剂(牛奶) | 6周 | ①②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Toejing[ | 泰国 | 18 | 61.78±7.73 | 18 | 63.50±5.94 | 补充含有益生菌的胶囊(副干酪乳杆菌HII01 50×109CFU/g) | 补充安慰剂(玉米淀粉) | 12周 | ①② | 4分 | ||||
| Khalili[ | 伊朗 | 20 | 43.95±8.14 | 20 | 45±5.37 | 补充含有108CFU/g干酪乳杆菌的胶囊 | 补充安慰剂(含有麦芽糖糊精) | 8周 | ②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Firouzi[ | 伊朗 | 68 | 52.9±9.2 | 68 | 54.2±8.3 | 每包提供3×1010 CFU/g活微生物制剂粉末(其中每包粉末含有嗜酸乳杆菌,乳酸杆菌,双歧杆菌,长双歧杆菌) | 补充安慰剂 | 12周 | ②③ | 5分 | ||||
| Alireza[ | 伊朗 | 30 | 36~75 | 30 | 36~75 | 补充含有2×109 CFU/g嗜酸乳杆菌、干酪乳杆菌、双歧双歧杆菌的胶囊 | 补充安慰剂 | 12周 | ①②③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Bayat[ | 伊朗 | 20 | 46.95±9.34 | 20 | 54.1±9.54 | 补充含有益生菌的酸奶 | 饮食指导,保持饮食结 构不变 | 8周 | ①② | 4分 | ||||
| Asemi[ | 伊朗 | 51 | 52.9±8.1 | 51 | 52.9±8.1 | 补充益生元的食品,其含有产孢乳杆菌1×107 CFU/g | 补充对照食品(不含益生菌) | 6周 | ③④ | 5分 | ||||
| Mazloom[ | 伊朗 | 16 | 55.4±8 | 18 | 51.8±10.2 | 补充含有嗜酸乳杆菌、保加利亚乳杆菌、双歧乳杆菌和干酪乳杆菌的胶囊 | 补充含有硬脂酸镁的 胶囊 | 6周 | ①③ | 4分 | ||||
| Ostadrahimi[ | 伊朗 | 30 | 48.29±11.71 | 30 | 51.4±8.6 | 补充600 ml有益生菌的发酵乳(其含有嗜酸乳杆菌、干酪乳杆菌、双歧杆菌) | 补充600 ml普通乳品 | 8周 | ①③ | 4分 | ||||
| [1] | World Health Organization Global Reports on Diabetes[R]. Geneva:WHO, 2016. |
| [2] |
Barko PC, McMichael MA, Swanson KS, et al. The gastrointestinal microbiome: A review[J]. J Vet Intern Med, 2018, 32(1):9-25.
doi: 10.1111/jvim.14875 pmid: 29171095 |
| [3] |
Larsen N, Vogensen FK, van den Berg FW, et al. Gut microbiota in human adults with type 2 diabetes differs from non-diabetic adults[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(2):e9085.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009085 URL |
| [4] |
Lee S, Kirkland R, Grunewald ZI, et al. Beneficial effects of non-encapsulated or encapsulated probiotic supplementation on microbiota composition, intestinal barrier functions, inflammatory profiles, and glucose tolerance in high fat fed rats[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(9):1975.
doi: 10.3390/nu11091975 URL |
| [5] | 乐忠宏, 崔婷婷, 王朏朏, 等. 益生菌对2型糖尿病患者肠道菌群及胰岛素敏感性的影响[J]. 中国糖尿病杂志, 2022, 30(7):491-495. |
| [6] |
Palacios T, Vitetta L, Coulson S, et al. Targeting the intestinal microbiota to prevent type 2 diabetes and enhance the effect of metformin on glycaemia: A randomised controlled pilot study[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(7):2041.
doi: 10.3390/nu12072041 URL |
| [7] |
Tonucci LB, Olbrich Dos Santos KM, Licursi de Oliveira L, et al. Clinical application of probiotics in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study[J]. Clin Nutr. 2017, 36(1):85-92.
doi: S0261-5614(15)00331-3 pmid: 26732026 |
| [8] |
Toejing P, Khampithum N, Sirilun S, et al. Influence of lactobacillus paracasei HII01 supplementation on glycemia and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes: A randomized clinical trial[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(7):1455.
doi: 10.3390/foods10071455 URL |
| [9] |
Khalili L, Alipour B, Asghari Jafar-Abadi M, et al. The effects of lactobacillus casei on glycemic response, serum sirtuin1 and fetuin-a levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Iran Biomed J, 2019, 23(1):68-77.
pmid: 29803203 |
| [10] |
Firouzi S, Majid HA, Ismail A, et al. Effect of multi-strain probiotics (multi-strain microbial cell preparation) on glycemic control and other diabetes-related outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Eur J Nutr, 2017, 56(4):1535-1550.
doi: 10.1007/s00394-016-1199-8 pmid: 26988693 |
| [11] |
Soleimani A, Zarrati Mojarrad M, Bahmani F, et al. Probiotic supplementation in diabetic hemodialysis patients has beneficial metabolic effects[J]. Kidney Int, 2017, 91(2):435-442.
doi: S0085-2538(16)30592-0 pmid: 27927601 |
| [12] |
Bayat A, Azizi-Soleiman F, Heidari-Beni M, et al. Effect of cucurbita ficifolia and probiotic yogurt consumption on blood glucose, lipid profile, and inflammatory marker in type 2 diabetes[J]. Int J Prev Med, 2016, 7:30.
doi: 10.4103/2008-7802.175455 pmid: 26955460 |
| [13] |
Asemi Z, Alizadeh SA, Ahmad K, et al. Effects of beta-carotene fortified synbiotic food on metabolic control of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A double-blind randomized cross-over controlled clinical trial[J]. Clin Nutr, 2016, 35(4):819-825.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.07.009 pmid: 26209256 |
| [14] | Mazloom Z, Yousefinejad A, Dabbaghmanesh MH. Effect of probiotics on lipid profile, glycemic control, insulin action, oxidative stress, and inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes: A clinical trial[J]. Iran J Med Sci, 2013, 38(1):38-43. |
| [15] |
Ostadrahimi A, Taghizadeh A, Mobasseri M, et al. Effect of probiotic fermented milk (kefir) on glycemic control and lipid profile in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial[J]. Iran J Public Health, 2015, 44(2):228-237.
pmid: 25905057 |
| [16] |
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, et al. The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials[J]. BMJ, 2011, 343:d5928.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928 URL |
| [17] |
Sebastián Domingo JJ, Sánchez Sánchez C. From the intestinal flora to the microbiome[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2018, 110(1):51-56.
doi: 10.17235/reed.2017.4947/2017 pmid: 29271225 |
| [18] | 梁家琪, 刘恒旭, 阳金鑫, 等. 运动与肠道菌健康效益的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [19] |
Vrieze A, Van NE, Holleman F, et al. Transfer of intestinal microbiota from lean donors increasesinsulin sensitivity in individuals with metabolic syndrome[J]. Gastroenterology, 2012, 143(4):913-916.
doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.031 pmid: 22728514 |
| [20] |
Newgard CB, An J, Bain JR, et al. A branched-chain amino acid-related metabolic signature that differentiates obese and lean humans and contributes to insulin resistance[J]. Cell Metab, 2009, 9(4):311-326.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.02.002 pmid: 19356713 |
| [21] |
Asghari G, Farhadnejad H, Teymoori F, et al. High dietary intake of branched-chain amino acids is associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance in adults[J]. J Diabetes, 2018, 10(5):357-364.
doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12639 pmid: 29281182 |
| [22] |
Koh A, Molinaro A, Ståhlman M, et al. Microbially Produced Imidazole Propionate Impairs Insulin Signaling through mTORC1[J]. Cell, 2018, 175(4):947-961.
doi: S0092-8674(18)31306-0 pmid: 30401435 |
| [23] |
Zheng X, Chen T, Jiang RI. Hyocholic acid species improve gluo se homeostasis through a distinct TGR5 and FXR signaling mechanism[J]. Cell Metab, 2021, 33(4):791-803.
doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.017 URL |
| [24] | Salamon D, Sroka-Oleksiak A, Kapusta P, et al. Characteristics of gut microbiota in adult patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes based on next-generation sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene fragment[J]. Pol Arch Intern Med, 2018, 128(6):336-343. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||