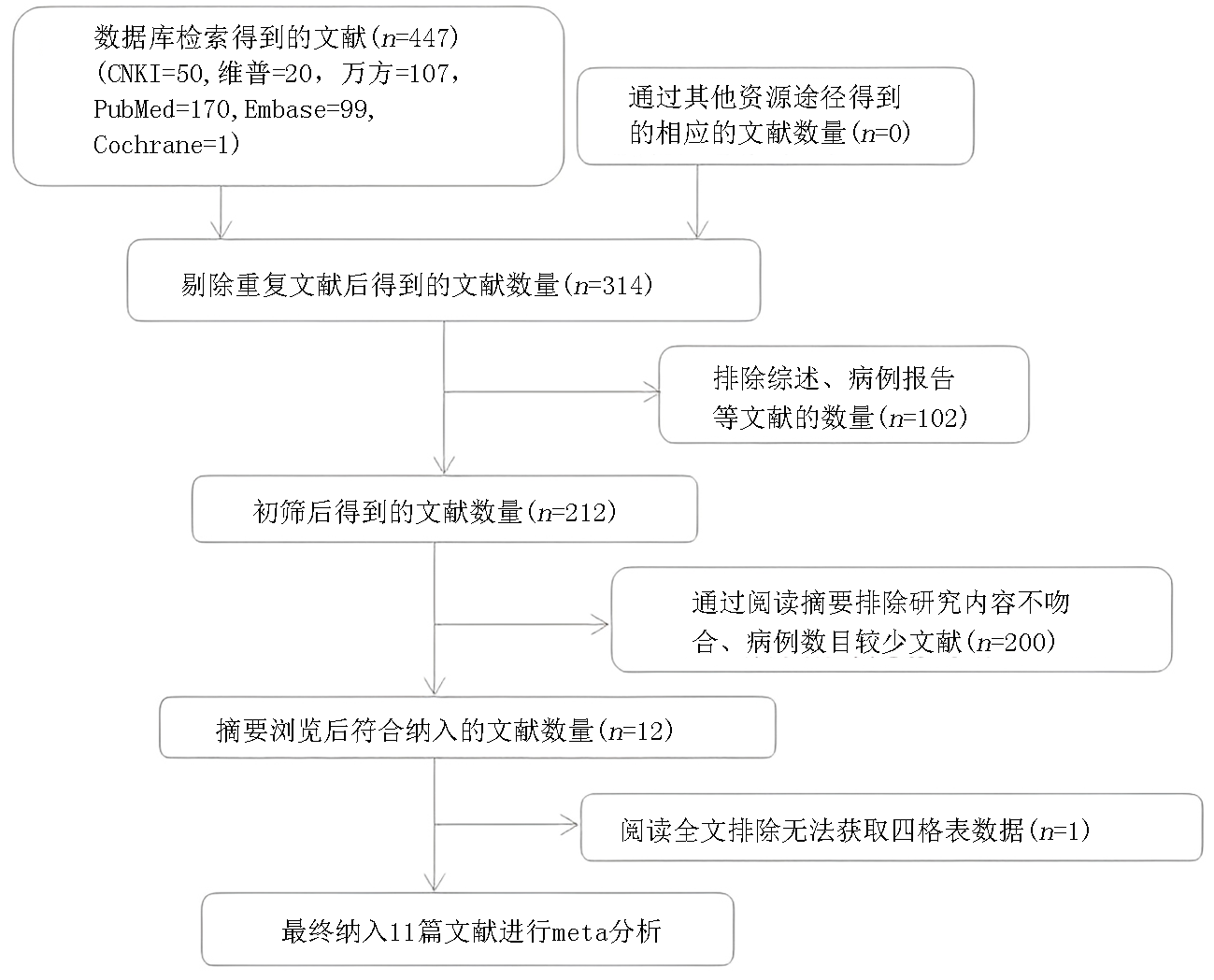
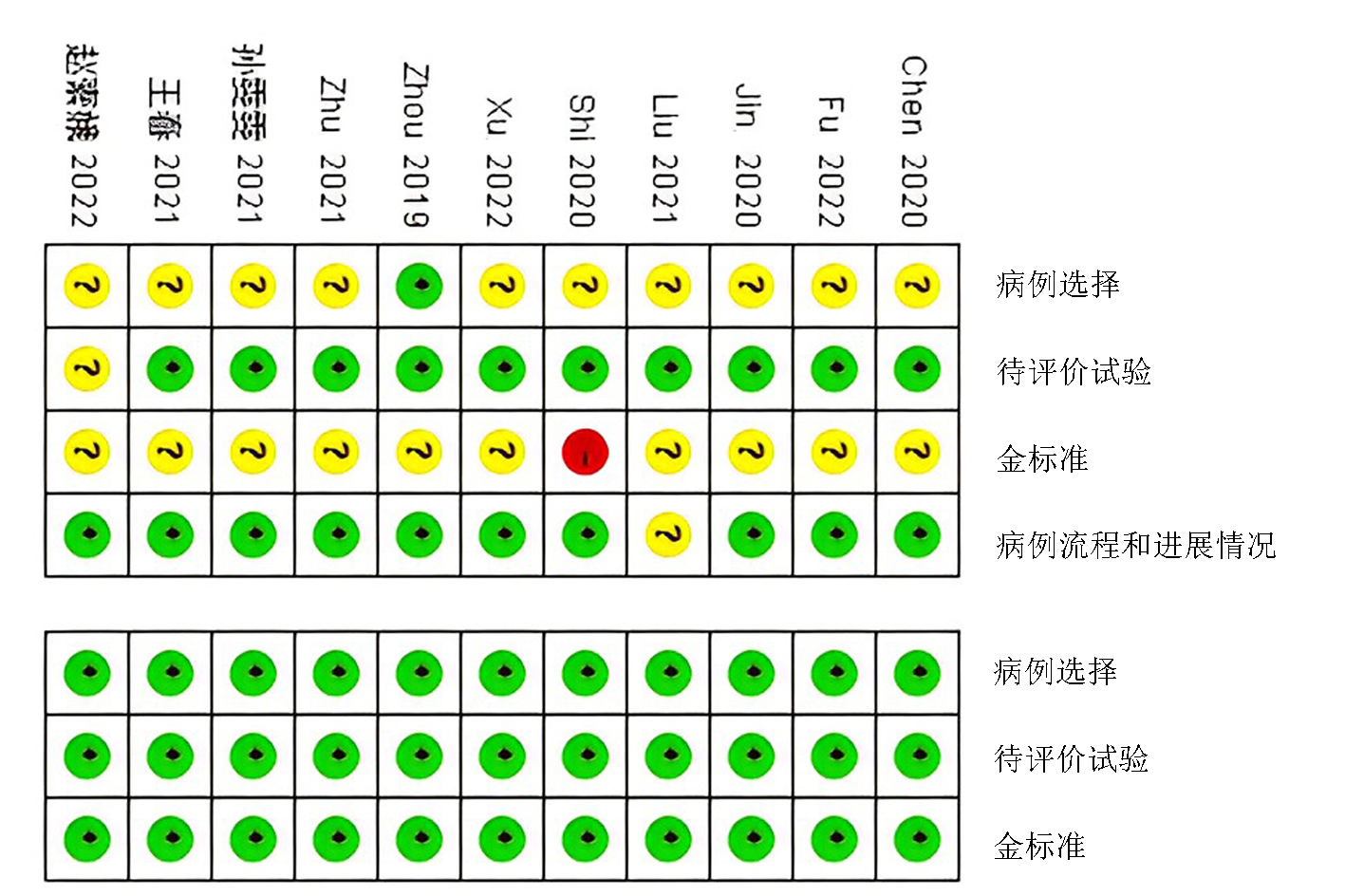
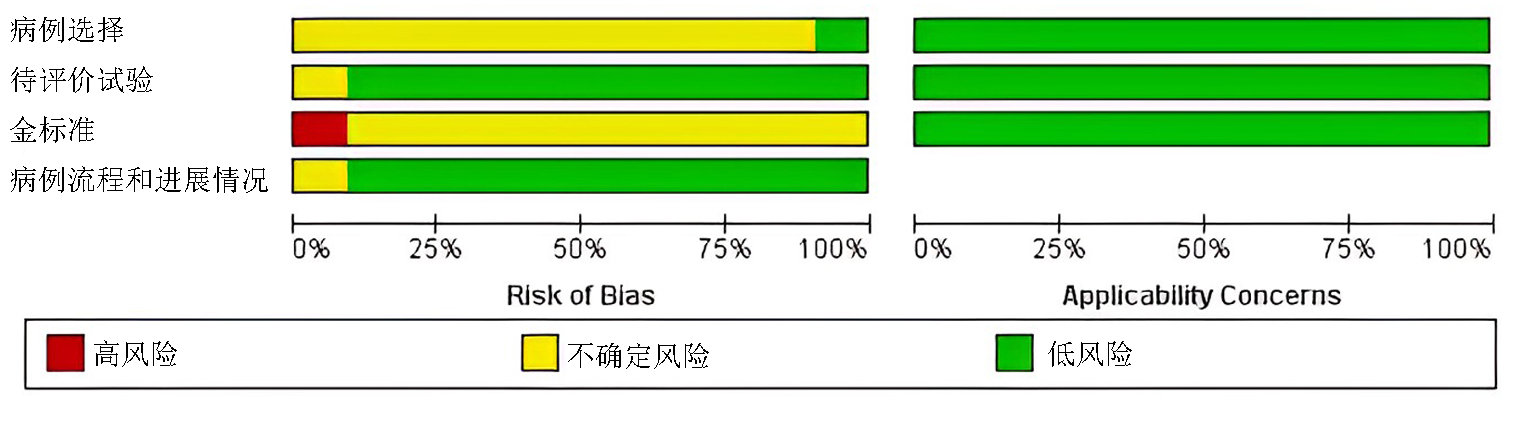
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 389-398.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.05.001
Meta-analysis of the application value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis
Wolazihan Madeniyati, Dilixiati Tuerdimaimaiti, Li Mengchen, Baihetinisha Tuerdi( )
)
- Respiratory Intensive Care Unit,the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Urumqi 830000,China
-
Received:2023-01-04Online:2023-05-20Published:2023-07-20 -
Contact:Baihetinisha Tuerdi, Email:1627971002@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wolazihan Madeniyati, Dilixiati Tuerdimaimaiti, Li Mengchen, Baihetinisha Tuerdi. Meta-analysis of the application value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 389-398.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.05.001
| 第一作者 | 年份 | PTB组(例) | 非PTB组(例) | 诊断标准 | 研究方法 | mNGS测序平台 | 标本类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou等[ | 2019 | 13 | 14 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| Shi等[ | 2020 | 48 | 62 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Chen等[ | 2020 | 17 | 20 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺标本 |
| Jin等[ | 2020 | 53 | 424 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| Liu等[ | 2021 | 142 | 111 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF |
| Zhu等[ | 2021 | 46 | 61 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 王春等[ | 2021 | 103 | 24 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 2021 | 100 | 105 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| 赵素娥等[ | 2022 | 95 | 60 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 未知 | BALF |
| Xu等[ | 2022 | 71 | 23 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Fu等[ | 2022 | 46 | 357 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | 肺标本 |
Tab.1 Characteristics of included studies
| 第一作者 | 年份 | PTB组(例) | 非PTB组(例) | 诊断标准 | 研究方法 | mNGS测序平台 | 标本类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou等[ | 2019 | 13 | 14 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| Shi等[ | 2020 | 48 | 62 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Chen等[ | 2020 | 17 | 20 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺标本 |
| Jin等[ | 2020 | 53 | 424 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| Liu等[ | 2021 | 142 | 111 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF |
| Zhu等[ | 2021 | 46 | 61 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 王春等[ | 2021 | 103 | 24 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 2021 | 100 | 105 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| 赵素娥等[ | 2022 | 95 | 60 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 未知 | BALF |
| Xu等[ | 2022 | 71 | 23 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Fu等[ | 2022 | 46 | 357 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | 肺标本 |
| 标本类型 | 作者 | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | Zhou等[ | 8 | 0 | 5 | 14 |
| Chen等[ | 14 | 0 | 3 | 20 | |
| Jin等[ | 31 | 7 | 22 | 417 | |
| Zhu等[ | 41 | 1 | 5 | 60 | |
| 王春等[ | 57 | 1 | 46 | 23 | |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 59 | 0 | 41 | 105 | |
| Fu等[ | 36 | 0 | 10 | 357 | |
| BALF | Shi等[ | 23 | 1 | 25 | 61 |
| Chen等[ | 11 | 0 | 3 | 14 | |
| Jin等[ | 11 | 2 | 10 | 108 | |
| Liu等[ | 85 | 0 | 57 | 111 | |
| Zhu等[ | 29 | 1 | 3 | 45 | |
| 王春等[ | 24 | 0 | 17 | 8 | |
| 赵素娥等[ | 55 | 0 | 40 | 60 | |
| Xu等[ | 67 | 0 | 4 | 23 | |
| 肺组织 | Jin等[ | 8 | 1 | 1 | 44 |
| Zhu等[ | 12 | 1 | 2 | 14 | |
| 王春等[ | 28 | 0 | 8 | 4 |
Tab.2 Data in four tables for the diagnosis of PTB in different clinical specimens detected by mNGS
| 标本类型 | 作者 | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | Zhou等[ | 8 | 0 | 5 | 14 |
| Chen等[ | 14 | 0 | 3 | 20 | |
| Jin等[ | 31 | 7 | 22 | 417 | |
| Zhu等[ | 41 | 1 | 5 | 60 | |
| 王春等[ | 57 | 1 | 46 | 23 | |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 59 | 0 | 41 | 105 | |
| Fu等[ | 36 | 0 | 10 | 357 | |
| BALF | Shi等[ | 23 | 1 | 25 | 61 |
| Chen等[ | 11 | 0 | 3 | 14 | |
| Jin等[ | 11 | 2 | 10 | 108 | |
| Liu等[ | 85 | 0 | 57 | 111 | |
| Zhu等[ | 29 | 1 | 3 | 45 | |
| 王春等[ | 24 | 0 | 17 | 8 | |
| 赵素娥等[ | 55 | 0 | 40 | 60 | |
| Xu等[ | 67 | 0 | 4 | 23 | |
| 肺组织 | Jin等[ | 8 | 1 | 1 | 44 |
| Zhu等[ | 12 | 1 | 2 | 14 | |
| 王春等[ | 28 | 0 | 8 | 4 |
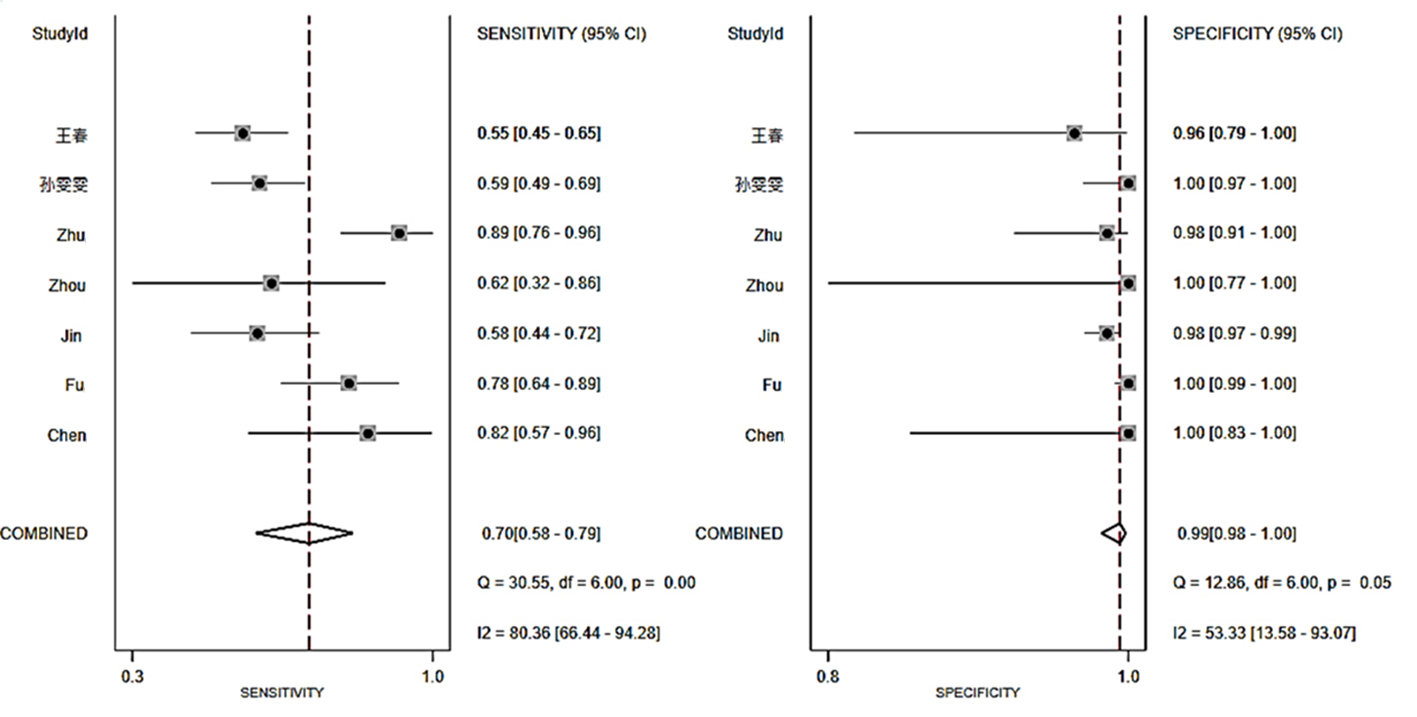
| 标本类型 | 敏感度(95% CI) | 特异度(95% CI) | PLR(95% CI) | NLR(95% CI) | DOR(95% CI) | AUC(95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
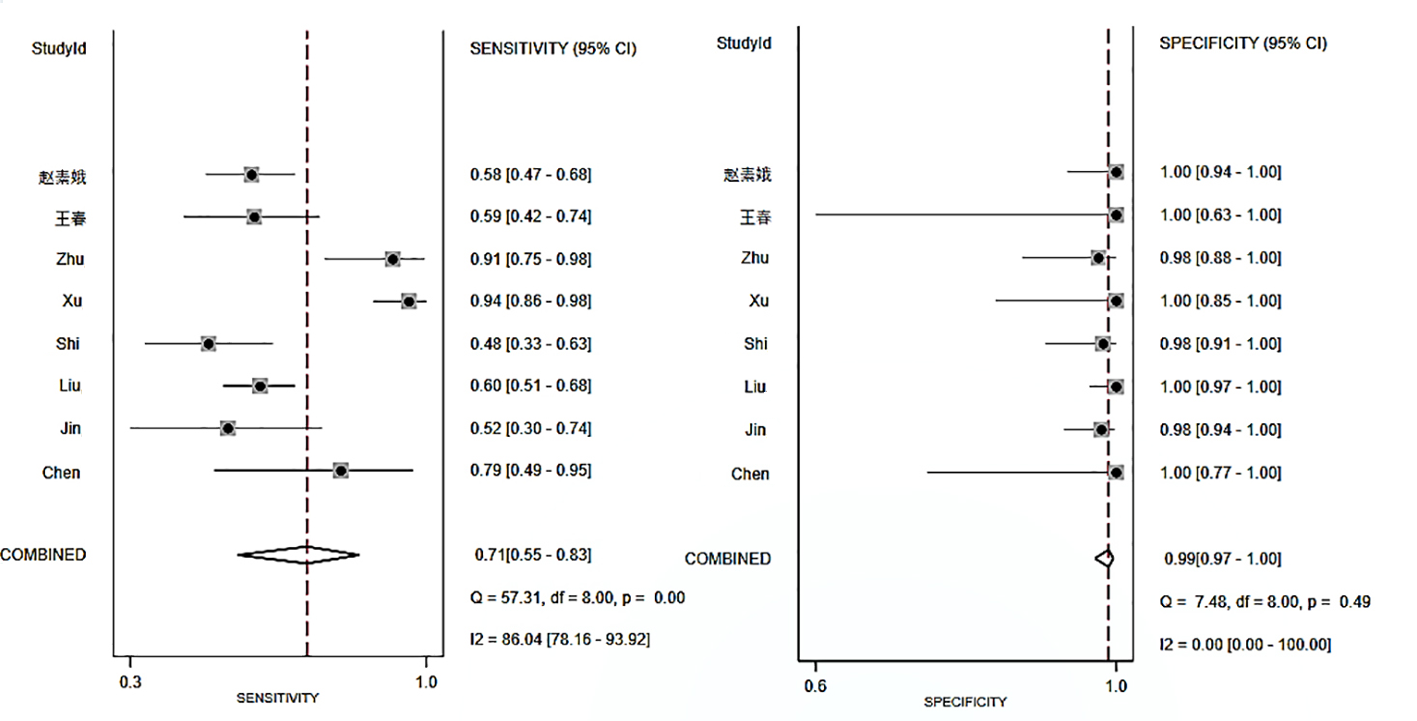
| 肺标本 | 70%(58%~79%) | 99%(98%~100%) | 106.9(31.1~366.6) | 0.31(0.21~0.43) | 350(81~1512) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
| BALF | 71%(55%~83%) | 99%(97%~100%) | 76.4(26.6~218.9) | 0.30(0.18~0.48) | 258(75~895) | 0.99(0.98~1.00) |
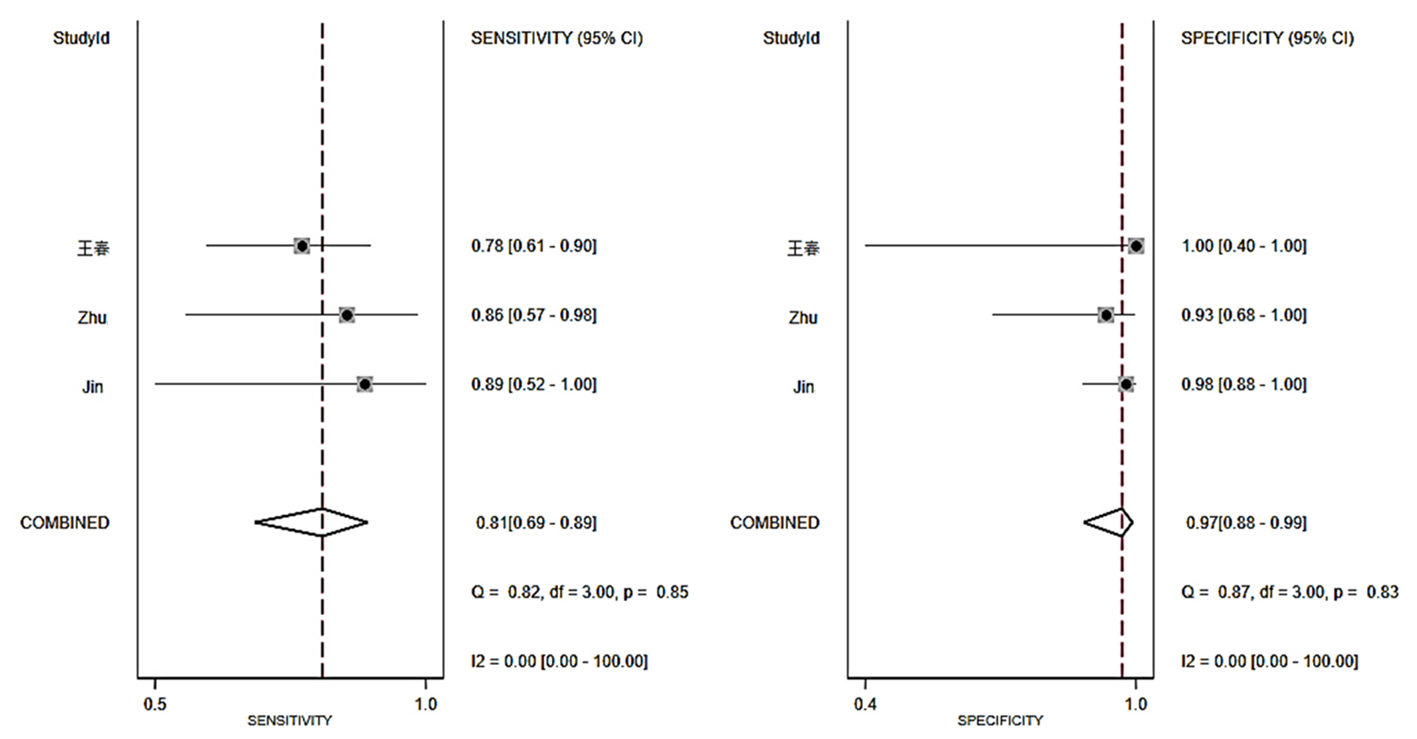
| 肺组织 | 81%(69%~89%) | 97%(88%~99%) | 26.0(6.6~102.4) | 0.19(0.11~0.33) | 135(29~639) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
Tab.3 Summary of parameters for mNGS diagnostic of PTB in different specimen types
| 标本类型 | 敏感度(95% CI) | 特异度(95% CI) | PLR(95% CI) | NLR(95% CI) | DOR(95% CI) | AUC(95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | 70%(58%~79%) | 99%(98%~100%) | 106.9(31.1~366.6) | 0.31(0.21~0.43) | 350(81~1512) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
| BALF | 71%(55%~83%) | 99%(97%~100%) | 76.4(26.6~218.9) | 0.30(0.18~0.48) | 258(75~895) | 0.99(0.98~1.00) |
| 肺组织 | 81%(69%~89%) | 97%(88%~99%) | 26.0(6.6~102.4) | 0.19(0.11~0.33) | 135(29~639) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
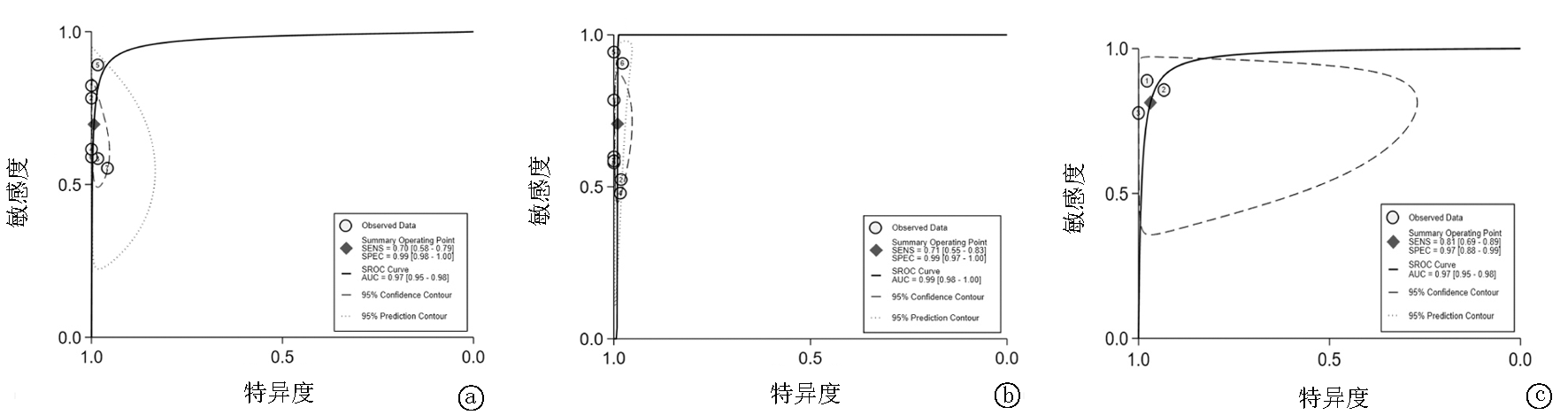
Fig.7 SROC plot of different specimens for diagnosing PTB a.SROC plot for diagnosing PTB by detecting lung samples with mNGS. b.SROC plot for diagnosing PTB by detecting BALF with mNGS. c.SROC plot for diagnosing PTB by detecting lung tissue with mNGS
| 分组 | 研究数量 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究类型 | 回顾性分析 前瞻性研究 | 7 1 | 71%(58%~83%) 67%(54%~79%) | 0.674 |
| 测序平台 | BGISEQ 其他 | 5 3 | 70%(52%~88%) 72%(47%~97%) | 0.882 |
| 痰涂片情况 | 阴性 阳性 | 2 6 | 89%(81%~97%) 64%(54%~73%) | <0.05 |
Tab.4 Subgroup analysis of mNGS detection of BALF
| 分组 | 研究数量 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究类型 | 回顾性分析 前瞻性研究 | 7 1 | 71%(58%~83%) 67%(54%~79%) | 0.674 |
| 测序平台 | BGISEQ 其他 | 5 3 | 70%(52%~88%) 72%(47%~97%) | 0.882 |
| 痰涂片情况 | 阴性 阳性 | 2 6 | 89%(81%~97%) 64%(54%~73%) | <0.05 |
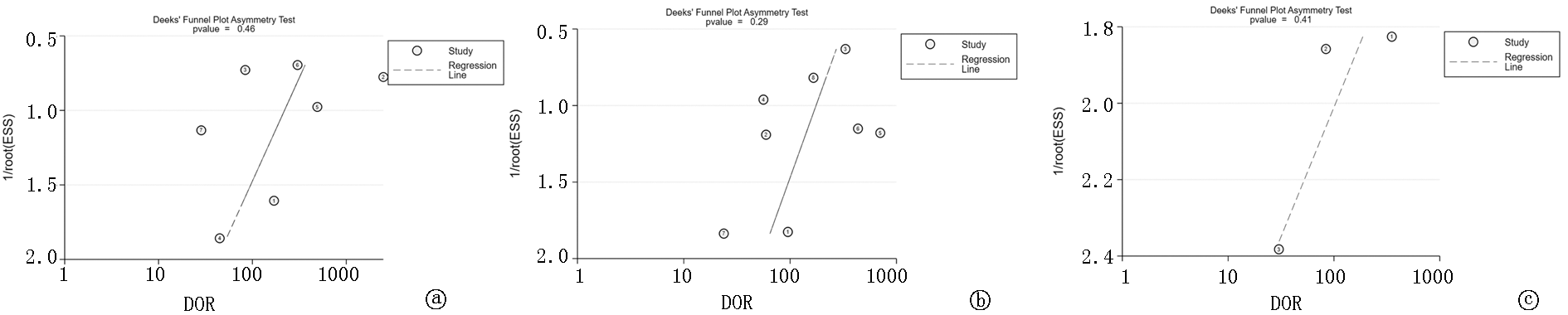
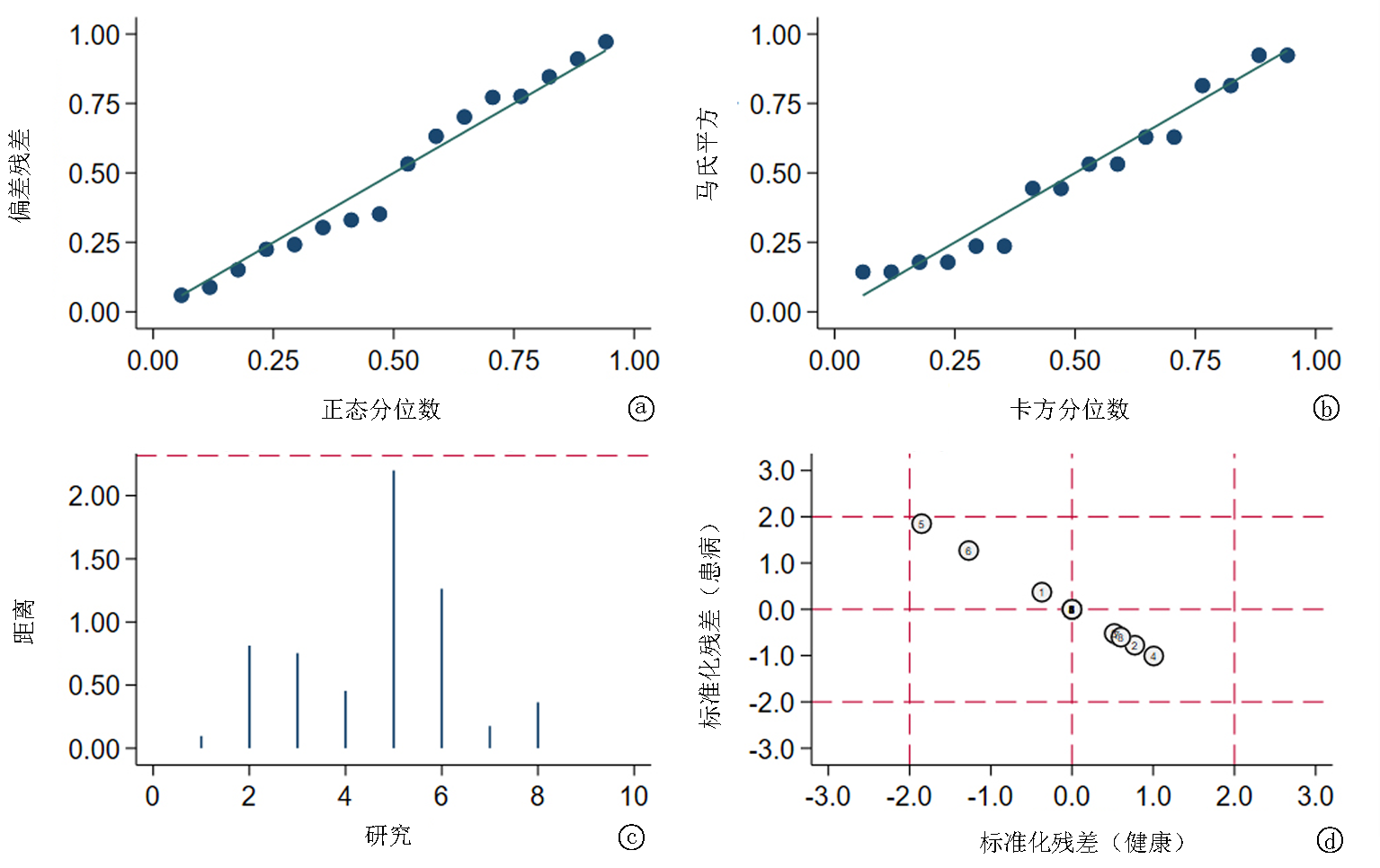
Fig.9 mNGS detects Deeks' funnel plots of 3 specimens a. Deeks' funnel diagram of mNGS detection of lung specimen for diagnosis of PTB; b. Deeks' funnel diagram of mNGS detection of BALF for diagnosis of PTB; c. Deeks' funnel diagram of mNGS detection of lung tissue for diagnosis of PTB
| [1] |
Pezzella AT. History of pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Thorac Surg Clin, 2019, 29(1): 1-17.
doi: S1547-4127(18)30128-2 pmid: 30454916 |
| [2] | 高静韬, 刘宇红. 2021年世界卫生组织全球结核病报告要点解读[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2022, 43(7): 745-749. |
| [3] |
Muttamba W, Kirenga B, Ssengooba W, et al. Prevalence of tuberculosis risk factors among bacteriologically negative and bacteriologically confirmed tuberculosis patients from five regional referral hospitals in Uganda[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2019, 100(2): 386-391.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0281 URL |
| [4] |
Suárez I, Fünger SM, Kröger S, et al. The diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2019, 116(43): 729-735.
doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0729 pmid: 31755407 |
| [5] |
Yang C, Zhang S, Yao L, et al. Evaluation of risk factors for false-negative results with an antigen-specific peripheral blood-based quantitative T cell assay (T-SPOT®. TB) in the diagnosis of active tuberculosis: A large-scale retrospective study in China[J]. J Int Med Res, 2018, 46(5): 1815-1825.
doi: 10.1177/0300060518757381 pmid: 29529901 |
| [6] | 卢春容, 房宏霞, 陆普选, 等. WHO 2021年全球结核病报告:全球与中国关键数据分析[J]. 新发传染病电子杂志, 2021, 6(4): 368-372. |
| [7] | 《中华传染病杂志》编辑委员会. 中国宏基因组学第二代测序技术检测感染病原体的临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2020, 38(11): 681-689. |
| [8] | 夏静, 陈磊, 施雨鑫, 等. 宏基因组二代测序技术在结核病诊断中的应用[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2020, 43(1): 74-76. |
| [9] |
Miao Q, Ma Y, Wang Q, et al. Microbiological diagnostic performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied to clinical practice[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2018, 67(suppl_2): S231-s240.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy693 URL |
| [10] | 张奕杰. 应用宏基因组二代测序技术诊断结核病4例并文献复习[J]. 河北医学, 2021, 27(8): 1377-1382. |
| [11] |
Zhou X, Wu H, Ruan Q, et al. Clinical evaluation of diagnosis efficacy of active mycobacterium tuberculosis complex infection via metagenomic next-generation sequencing of direct clinical samples[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2019, 9: 351.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00351 URL |
| [12] |
Shi CL, Han P, Tang PJ, et al. Clinical metagenomic sequencing for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. J Infect, 2020, 81(4): 567-574.
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.004 URL |
| [13] |
Chen P, Sun W, He Y. Comparison of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology, culture and GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay in the diagnosis of tuberculosis[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12(8): 4014-4024.
doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-1232 pmid: 32944313 |
| [14] |
Jin W, Pan J, Miao Q, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for active tuberculosis in clinical practice at a tertiary general hospital[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(17): 1065.
doi: 10.21037/atm-20-2274 pmid: 33145284 |
| [15] |
Liu X, Chen Y, Ouyang H, et al. Tuberculosis diagnosis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: A cross-sectional analysis[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2021, 104: 50-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.063 URL |
| [16] | Zhu N, Zhou D, Li S. Diagnostic accuracy of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in sputum-scarce or smear-negative cases with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 9970817. |
| [17] | 王春, 王彩英, 刘丹. 宏基因组二代测序对肺结核的诊断价值[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2021, 27(5): 489-493. |
| [18] | 孙雯雯, 顾瑾, 范琳. 宏基因组二代测序对不同类型结核病的诊断价值[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2021, 44(2): 96-100. |
| [19] | 赵素娥, 高欣, 刘胜岗, 等. 肺泡灌洗液宏基因组二代测序对疑似肺结核的诊断价值[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2022, 27(5): 722-725, 743. |
| [20] | Xu P, Yang K, Yang L, et al. Next-generation metagenome sequencing shows superior diagnostic performance in acid-fast staining sputum smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 898195. |
| [21] |
Fu M, Cao LJ, Xia HL, et al. The performance of detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in lung biopsy tissue by metagenomic next-generation sequencing[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 288.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02079-8 pmid: 35902819 |
| [22] | Mashabela GT, de Wet TJ, Warner DF. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Metabolism[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2019, 7(4). |
| [23] | Zheng Y, Qiu X, Wang T, et al. The diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in lower respiratory tract infection[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 694756. |
| [24] | 刘晓梦, 赵彩彦. 2017年感染性疾病临床进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(1): 60-65. |
| [25] | Liu HC, Gao YL, Li DF, et al. Value of xpert MTB/RIF using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2021, 59(4) :e02170-20. |
| [26] |
Wang J, Han Y, Feng J. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for mixed pulmonary infection diagnosis[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2019, 19(1): 252.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-1022-4 pmid: 31856779 |
| [27] |
Xu H, Hu X, Wang W, et al. Clinical application and evaluation of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pulmonary infection with pleural effusion[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2022, 15: 2813-2824.
doi: 10.2147/IDR.S365757 pmid: 35677528 |
| [28] |
Han D, Li Z, Li R, et al. mNGS in clinical microbiology laboratories: On the road to maturity[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 2019, 45(5-6): 668-685.
doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2019.1681933 pmid: 31691607 |
| [29] |
Wang CX, Huang Z, Fang W, et al. Preliminary assessment of nanopore-based metagenomic sequencing for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2020, 97: 54-59.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.044 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||