Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 324-329.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.04.006
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between serum CTRP5 and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and its diagnostic value
Li Hengnan, Huang Yan, Zhao Yajuan, Hu Guicai( )
)
- Department of Nephrology, Affiliated Hospital of Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000, China
-
Received:2022-05-17Online:2023-04-20Published:2023-06-06 -
Contact:Hu Guicai E-mail:cdguicaihu@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Hengnan, Huang Yan, Zhao Yajuan, Hu Guicai. Correlation between serum CTRP5 and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis and its diagnostic value[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 324-329.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.04.006
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 性别(例) | BMI(kg/m2) | HT(例) | DM(例) | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | 24 h腹膜透析 超滤量(ml) | 24 h尿量 (ml) | CAPD龄 (月) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 无 | ||||||||||
| NLVDD组 | 29 | 42.00±11.25 | 21 | 8 | 23.35±3.04 | 29 | 0 | 1 | 28 | 140.90±24.57 | 95.76±19.16 | 580(200, 900) | 450(0, 775) | 21(5.5, 55) | |
| LVDD组 | 85 | 53.96±11.17 | 44 | 41 | 23.83±3.25 | 82 | 3 | 24 | 61 | 152.89±24.67 | 93.81±17.08 | 650(450, 1 000) | 200(0, 600) | 32(8.5, 63) | |
| 统计值 | t=-4.972 | χ2=3.762 | t=-0.693 | χ2=7.760 | t=-2.264 | t=0.514 | Z=-1.511 | Z=-0.932 | Z=-1.087 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.000 | 0.052 | 0.490 | 0.569 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.608 | 0.131 | 0.352 | 0.277 | |||||
Tab.1 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 性别(例) | BMI(kg/m2) | HT(例) | DM(例) | SBP (mmHg) | DBP (mmHg) | 24 h腹膜透析 超滤量(ml) | 24 h尿量 (ml) | CAPD龄 (月) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 有 | 无 | 有 | 无 | ||||||||||
| NLVDD组 | 29 | 42.00±11.25 | 21 | 8 | 23.35±3.04 | 29 | 0 | 1 | 28 | 140.90±24.57 | 95.76±19.16 | 580(200, 900) | 450(0, 775) | 21(5.5, 55) | |
| LVDD组 | 85 | 53.96±11.17 | 44 | 41 | 23.83±3.25 | 82 | 3 | 24 | 61 | 152.89±24.67 | 93.81±17.08 | 650(450, 1 000) | 200(0, 600) | 32(8.5, 63) | |
| 统计值 | t=-4.972 | χ2=3.762 | t=-0.693 | χ2=7.760 | t=-2.264 | t=0.514 | Z=-1.511 | Z=-0.932 | Z=-1.087 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.000 | 0.052 | 0.490 | 0.569 | 0.005 | 0.026 | 0.608 | 0.131 | 0.352 | 0.277 | |||||
| 组别 | 例数 | HGB (g/L) | ALB (g/L) | TBIL (μmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | TCH (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLVDD组 | 29 | 115.31±15.20 | 42.40(39.60, 46.10) | 6.80(5.55, 8.51) | 1.34(0.93, 1.96) | 4.16(3.50, 5.10) | 1.08(0.94, 1.51) | ||||||||
| LVDD组 | 85 | 110.06±18.01 | 41.00(37.95, 43.65) | 6.40(4.80, 7.60) | 1.45(1.04, 2.32) | 4.39(3.94, 5.15) | 1.17(0.97, 1.47) | ||||||||
| 统计值 | t=1.407 | Z=-2.157 | Z=-1.494 | Z=-1.432 | Z=-1.113 | Z=-0.293 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.162 | 0.031 | 0.135 | 0.152 | 0.266 | 0.770 | |||||||||
| 组别 | LDL-C (mmol/L) | P (mmol/L) | Ca (mmol/L) | 钙磷乘积 (mmol2/L2) | BUN (mmol/L) | CRE (μmol/L) | |||||||||
| NLVDD组 | 2.51(2.08, 3.30) | 1.63(1.47, 1.81) | 2.24±0.22 | 3.59(3.09, 4.20) | 21.37±4.95 | 1025.56±259.73 | |||||||||
| LVDD组 | 2.68(2.19, 3.37) | 1.44(1.16, 1.82) | 2.24±0.24 | 3.19(2.60, 4.08) | 19.98±5.70 | 954.05±269.38 | |||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-0.839 | Z=-1.399 | t=0.002 | Z=-1.480 | t=1.171 | t=1.245 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.401 | 0.162 | 0.998 | 0.139 | 0.244 | 0.216 | |||||||||
| 组别 | UA (μmol/L) | Cys-c (mg/L) | FERR (ng/ml) | PTH (pg/ml) | CTRP5 (ng/ml) | BNP (pg/ml) | |||||||||
| NLVDD组 | 399.55±74.83 | 7.39(6.67, 8.33) | 247.00(84.25, 454.45) | 295.00(130.50, 471.00) | 33.45±8.77 | 656.81±143.15 | |||||||||
| LVDD组 | 400.16±86.11 | 7.64(6.65, 8.36) | 174.50(100.30, 319.50) | 249.00(133.15, 399.15) | 46.29±10.12 | 962.44±242.22 | |||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.034 | Z=-0.026 | Z=-1.067 | Z=-0.439 | t=-6.093 | t=-6.412 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.973 | 0.979 | 0.286 | 0.661 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
Tab.2 Comparison of laboratory results between the two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | HGB (g/L) | ALB (g/L) | TBIL (μmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | TCH (mmol/L) | HDL-C (mmol/L) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLVDD组 | 29 | 115.31±15.20 | 42.40(39.60, 46.10) | 6.80(5.55, 8.51) | 1.34(0.93, 1.96) | 4.16(3.50, 5.10) | 1.08(0.94, 1.51) | ||||||||
| LVDD组 | 85 | 110.06±18.01 | 41.00(37.95, 43.65) | 6.40(4.80, 7.60) | 1.45(1.04, 2.32) | 4.39(3.94, 5.15) | 1.17(0.97, 1.47) | ||||||||
| 统计值 | t=1.407 | Z=-2.157 | Z=-1.494 | Z=-1.432 | Z=-1.113 | Z=-0.293 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.162 | 0.031 | 0.135 | 0.152 | 0.266 | 0.770 | |||||||||
| 组别 | LDL-C (mmol/L) | P (mmol/L) | Ca (mmol/L) | 钙磷乘积 (mmol2/L2) | BUN (mmol/L) | CRE (μmol/L) | |||||||||
| NLVDD组 | 2.51(2.08, 3.30) | 1.63(1.47, 1.81) | 2.24±0.22 | 3.59(3.09, 4.20) | 21.37±4.95 | 1025.56±259.73 | |||||||||
| LVDD组 | 2.68(2.19, 3.37) | 1.44(1.16, 1.82) | 2.24±0.24 | 3.19(2.60, 4.08) | 19.98±5.70 | 954.05±269.38 | |||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-0.839 | Z=-1.399 | t=0.002 | Z=-1.480 | t=1.171 | t=1.245 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.401 | 0.162 | 0.998 | 0.139 | 0.244 | 0.216 | |||||||||
| 组别 | UA (μmol/L) | Cys-c (mg/L) | FERR (ng/ml) | PTH (pg/ml) | CTRP5 (ng/ml) | BNP (pg/ml) | |||||||||
| NLVDD组 | 399.55±74.83 | 7.39(6.67, 8.33) | 247.00(84.25, 454.45) | 295.00(130.50, 471.00) | 33.45±8.77 | 656.81±143.15 | |||||||||
| LVDD组 | 400.16±86.11 | 7.64(6.65, 8.36) | 174.50(100.30, 319.50) | 249.00(133.15, 399.15) | 46.29±10.12 | 962.44±242.22 | |||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.034 | Z=-0.026 | Z=-1.067 | Z=-0.439 | t=-6.093 | t=-6.412 | |||||||||
| P值 | 0.973 | 0.979 | 0.286 | 0.661 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| 项目 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 0.098 | 0.031 | 9.919 | 0.002 | 1.103 | 1.038 | 1.173 |
| ALB | -0.014 | 0.102 | 0.018 | 0.895 | 0.987 | 0.807 | 1.206 |
| DM | 0.025 | 0.016 | 2.518 | 0.113 | 1.026 | 0.994 | 1.058 |
| SBP | 1.878 | 1.221 | 2.366 | 0.124 | 6.539 | 0.598 | 71.556 |
| CTRP5 | 0.123 | 0.058 | 4.427 | 0.035 | 1.131 | 1.008 | 1.268 |
| BNP | 0.005 | 0.003 | 4.030 | 0.045 | 1.005 | 1.000 | 1.010 |
Tab.3 Multivariate Logistic regression analysis of LVDD in CAPD patients
| 项目 | B | SE | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 0.098 | 0.031 | 9.919 | 0.002 | 1.103 | 1.038 | 1.173 |
| ALB | -0.014 | 0.102 | 0.018 | 0.895 | 0.987 | 0.807 | 1.206 |
| DM | 0.025 | 0.016 | 2.518 | 0.113 | 1.026 | 0.994 | 1.058 |
| SBP | 1.878 | 1.221 | 2.366 | 0.124 | 6.539 | 0.598 | 71.556 |
| CTRP5 | 0.123 | 0.058 | 4.427 | 0.035 | 1.131 | 1.008 | 1.268 |
| BNP | 0.005 | 0.003 | 4.030 | 0.045 | 1.005 | 1.000 | 1.010 |
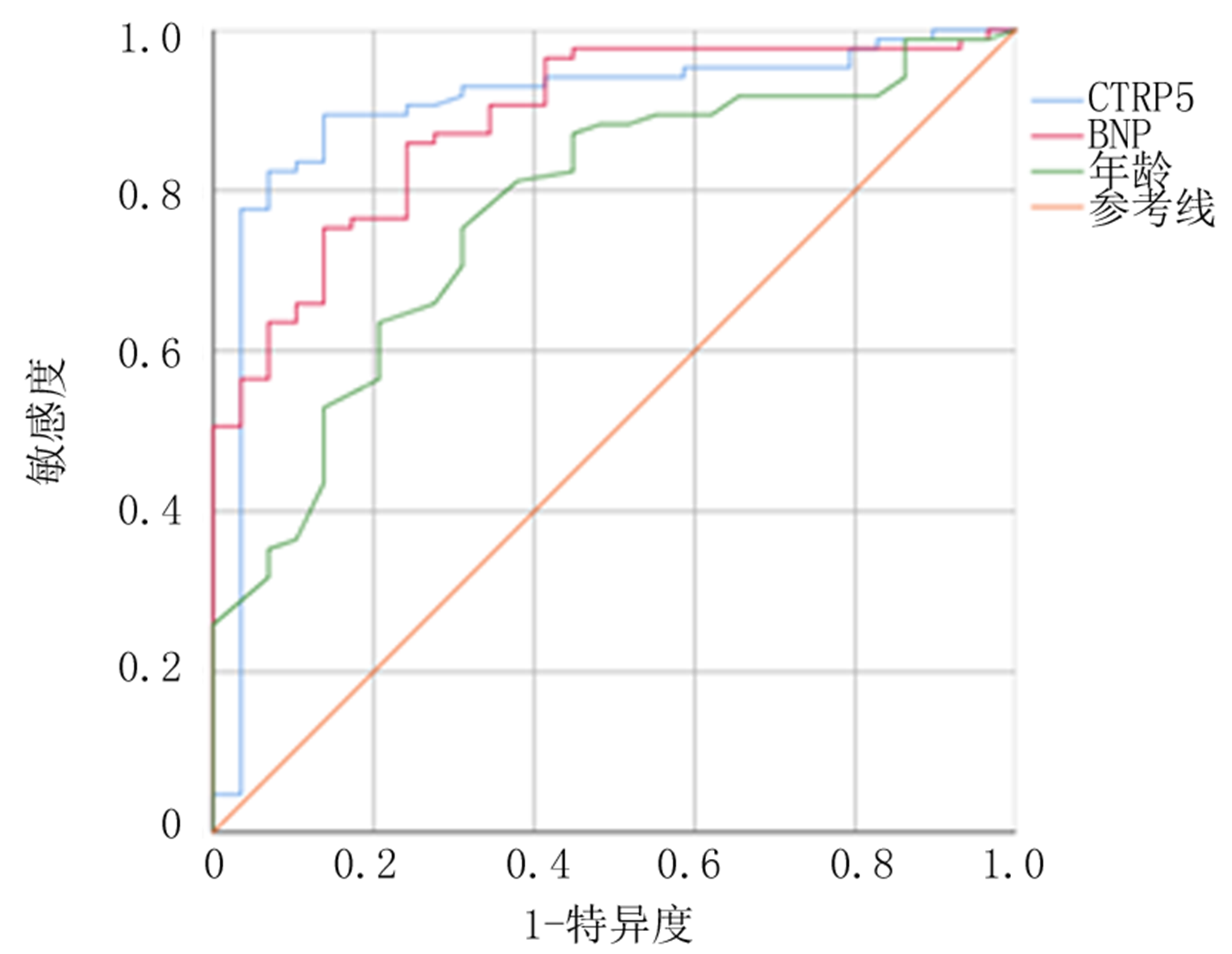
| 预测项目 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| CTRP5 | 0.902 | 0.000 | 0.828 | 0.975 | 0.894 | 0.862 | 36.78 |
| BNP | 0.886 | 0.000 | 0.821 | 0.950 | 0.859 | 0.759 | 748.22 |
| 年龄 | 0.773 | 0.000 | 0.678 | 0.868 | 0.753 | 0.690 | 47.50 |
Tab.4 Diagnostic value of each independent risk factor for LVDD in CAPD patients
| 预测项目 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| CTRP5 | 0.902 | 0.000 | 0.828 | 0.975 | 0.894 | 0.862 | 36.78 |
| BNP | 0.886 | 0.000 | 0.821 | 0.950 | 0.859 | 0.759 | 748.22 |
| 年龄 | 0.773 | 0.000 | 0.678 | 0.868 | 0.753 | 0.690 | 47.50 |
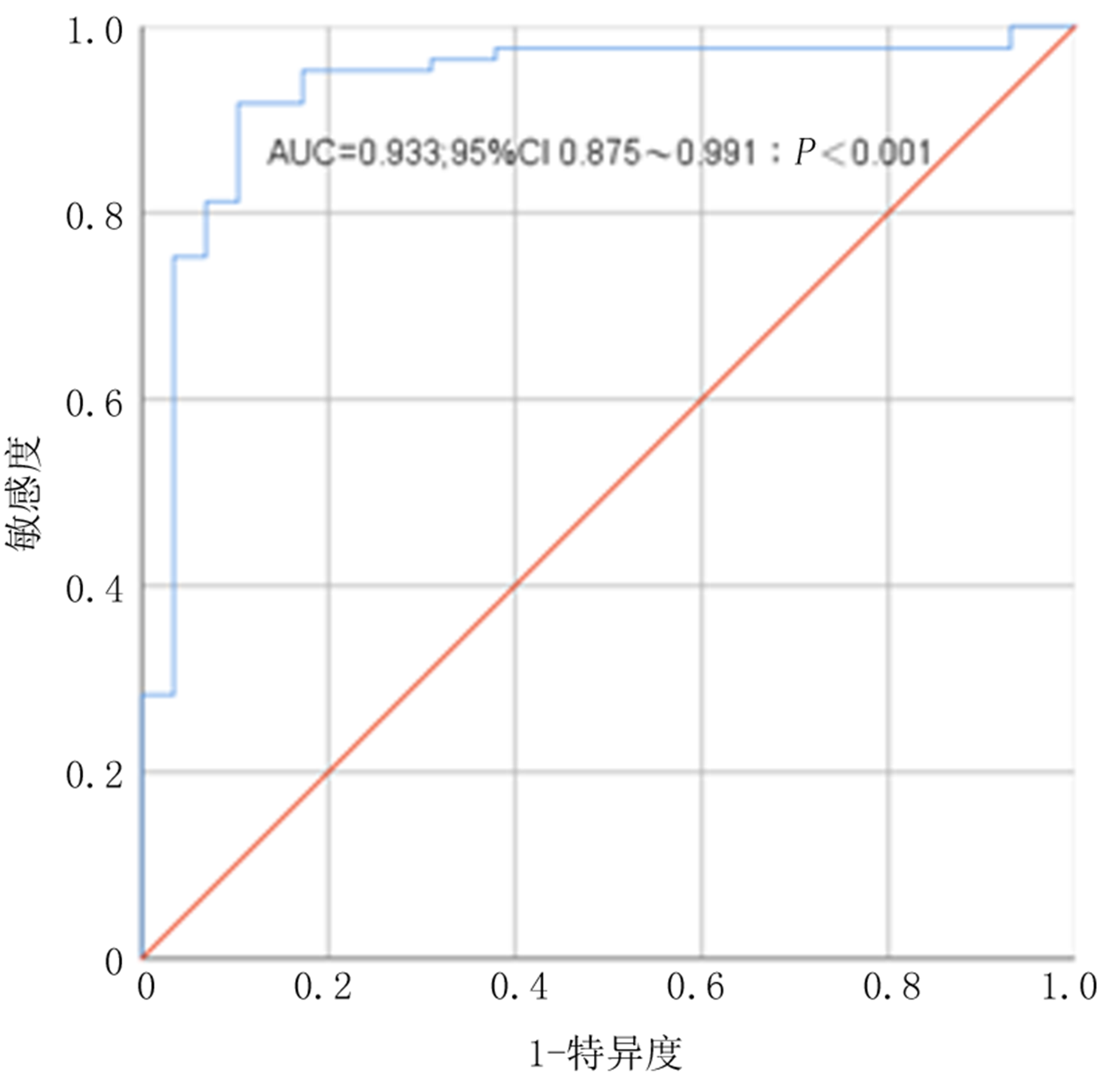
| 预测项目 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 诊断模型预测 | 0.933 | 0.000 | 0.875 | 0.991 | 0.918 | 0.897 | 0.401 |
Tab. 5 Diagnostic value of diagnostic model for LVDD in CAPD patients
| 预测项目 | AUC | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 诊断模型预测 | 0.933 | 0.000 | 0.875 | 0.991 | 0.918 | 0.897 | 0.401 |
| [1] |
Evans M, Lewis RD, Morgan AR, et al. A narrative review of chronic kidney disease in clinical practice: Current challenges and future perspectives[J]. Adv Ther, 2022, 39(1):33-43.
doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01927-z |
| [2] |
Haynes R, Zhu D, Judge PK, et al. Chronic kidney disease, heart failure and neprilysin inhibition[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2020, 35(4):558-564.
doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfz058 URL |
| [3] | Zhang L, Zhao MH, Zuo L, et al. China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2016 annual data report[J]. Kidney Int Suppl (2011), 2020, 10(2):e97-e185. |
| [4] | Han JH, Han JS, Kim EJ, et al. Diastolic dysfunction is an independent predictor of cardiovascular events in incident dialysis patients with preserved systolic function[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3):e0118694. |
| [5] |
Barberato SH, Bucharles SG, Sousa AM, et al. Prevalence and prognostic impact of diastolic dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis[J]. Arq Bras Cardiol, 2010, 94(4):457-462.
doi: S0066-782X2010005000016 pmid: 20339814 |
| [6] | 解小云, 宋艳红. CTRP5的研究进展[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2017, 30(1):27-29. |
| [7] | 韩思梁, 刘素云, 张瑞宁. 慢性心力衰竭患者血浆CTRP5水平变化[J]. 山东医药, 2017, 57(22):47-48. |
| [8] | 孙媛媛, 余其贵, 谢军. 血清CTRP3、CTRP5、CTRP9水平与老年慢性心力衰竭的临床关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2021, 41(17):3633-3636. |
| [9] |
Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, et al. Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography:An update from the American Society of Echocardiography and the European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging[J]. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging, 2016, 17(12):1321-1360.
doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jew082 URL |
| [10] |
Park M, Hsu CY, Li Y, et al. Associations between kidney function and subclinical cardiac abnormalities in CKD[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2012, 23(10):1725-1734.
pmid: 22935481 |
| [11] |
Miyajima Y, Toyama T, Mori M, et al. Relationships between kidney dysfunction and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction: A hospital-based retrospective study[J]. J Nephrol, 2021, 34(3):773-780.
doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00940-9 pmid: 33400138 |
| [12] |
'Swierblewska E, Wolf J, Kunicka K, et al. Prevalence and distribution of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in treated patients with long-lasting hypertension[J]. Blood Press, 2018, 27(6):376-384.
doi: 10.1080/08037051.2018.1484661 URL |
| [13] | Silverberg D, Wexler D, Blum M, et al. The cardio-renal anaemia syndrome: Does it exist?[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2003, 18(Suppl 8):viii7-12. |
| [14] | García-Bello JA, Ortiz-Flores J, Torres de la Riva FE, et al. Anemia and hypoalbuminemia as risk factors for left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in children with chronic kidney disease on peritoneal dialysis[J]. Nefrologia (Engl Ed), 2018, 38(4):414-419. |
| [15] |
Wang AY, Wang M, Lam CW, et al. Heart failure with preserved or reduced ejection fraction in patients treated with peritoneal dialysis[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2013, 61(6):975-983.
doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.12.030 URL |
| [16] |
van Bilsen M, Smeets PJ, Gilde AJ, et al. Metabolic remodelling of the failing heart: The cardiac burn-out syndrome?[J]. Cardiovasc Res, 2004, 61(2):218-226.
doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.014 pmid: 14736538 |
| [17] |
Park SY, Choi JH, Ryu HS, et al. C1q tumor necrosis factor alpha-related protein isoform 5 is increased in mitochondrial DNA-depleted myocytes and activates AMP-activated protein kinase[J]. J Biol Chem, 2009, 284(41):27780-27789.
doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.005611 URL |
| [18] |
Yang WM, Lee W. CTRP5 ameliorates palmitate-induced apoptosis and insulin resistance through activation of AMPK and fatty acid oxidation[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014, 452(3):715-721.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.145 URL |
| [19] |
Peng M, Liu Y, Zhang XQ, et al. CTRP5-overexpression attenuated ischemia-reperfusion associated heart injuries and improved infarction induced heart failure[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11:603322.
doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.603322 URL |
| [20] | 张城林, 冯寒, 李丽, 等. CTRP3经AMPK/PGC-1α通路促进心肌细胞线粒体生物生成[J]. 中国病理生理杂志, 2016, 32(8):1503. |
| [21] |
Schmid A, Kopp A, Aslanidis C, et al. Regulation and function of C1Q/TNF-related protein-5 (CTRP-5) in the context of adipocyte biology[J]. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes, 2013, 121(5):310-317.
doi: 10.1055/s-00000017 URL |
| [22] | Heidenreich PA, Bozkurt B, Aguilar D, et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines[J]. Circulation, 2022, 145(18):e876-e894. |
| [23] | 廖玉华, 杨杰孚, 张健, 等. 舒张性心力衰竭诊断和治疗专家共识[J]. 临床心血管病杂志, 2020, 36(1):1-10. |
| [24] | 李沛. 血浆BNP、UA、hs-CRP水平与慢性心力衰竭患者心功能及肾功能的相关性[J]. 临床医学, 2018, 38(7):81-82. |
| [1] | Wolazihan Madeniyati, Dilixiati Tuerdimaimaiti, Li Mengchen, Baihetinisha Tuerdi. Meta-analysis of the application value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 389-398. |
| [2] | Chen Xiaoting, Yan Zheng, Liu Fan, Wei Yi. Early diagnostic value of serum cystatin C and β2-microglobulin in renal function impairment after neonatal asphyxia [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(5): 437-440. |
| [3] | Jia Chengbang, Shen Lijuan, Sun Zhigang. The relationship between CEA, CA125 and NSE and the pathological characteristics of patients with NSCLC and the value of combined detection [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(11): 992-995. |
| [4] | JIA Ming-li;ZENG Bin. Diagnostic value of carotid intima-media thickness for coronary heart disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2014, 29(9): 982-984985. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||