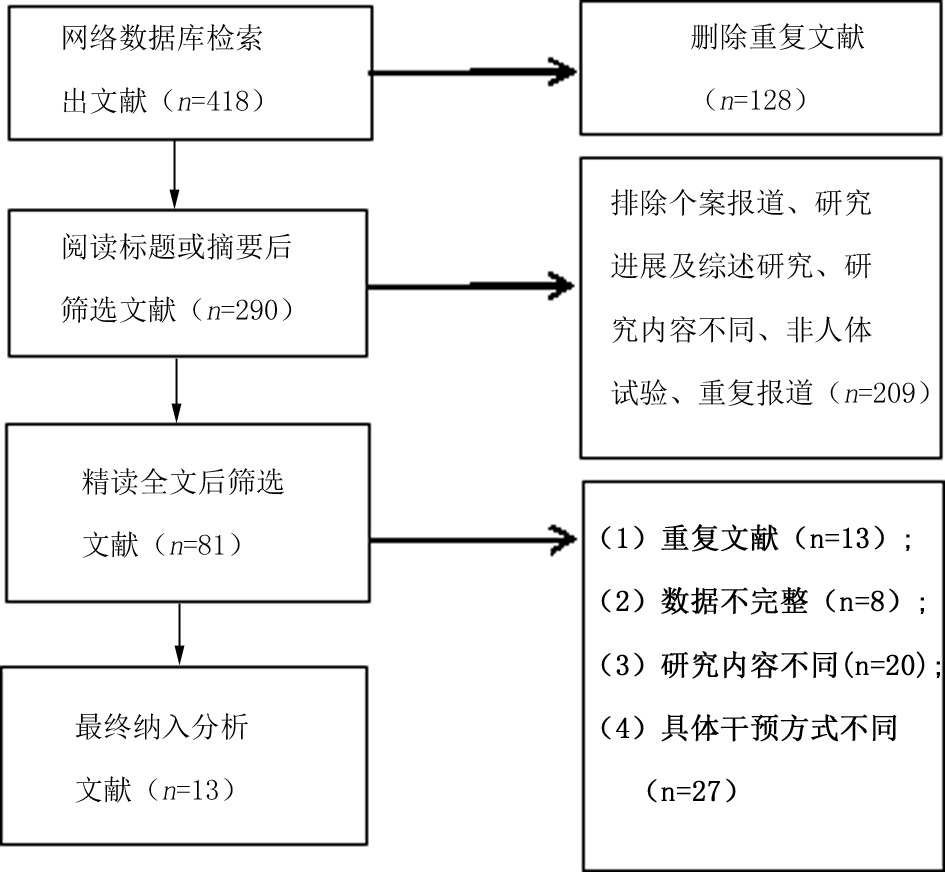
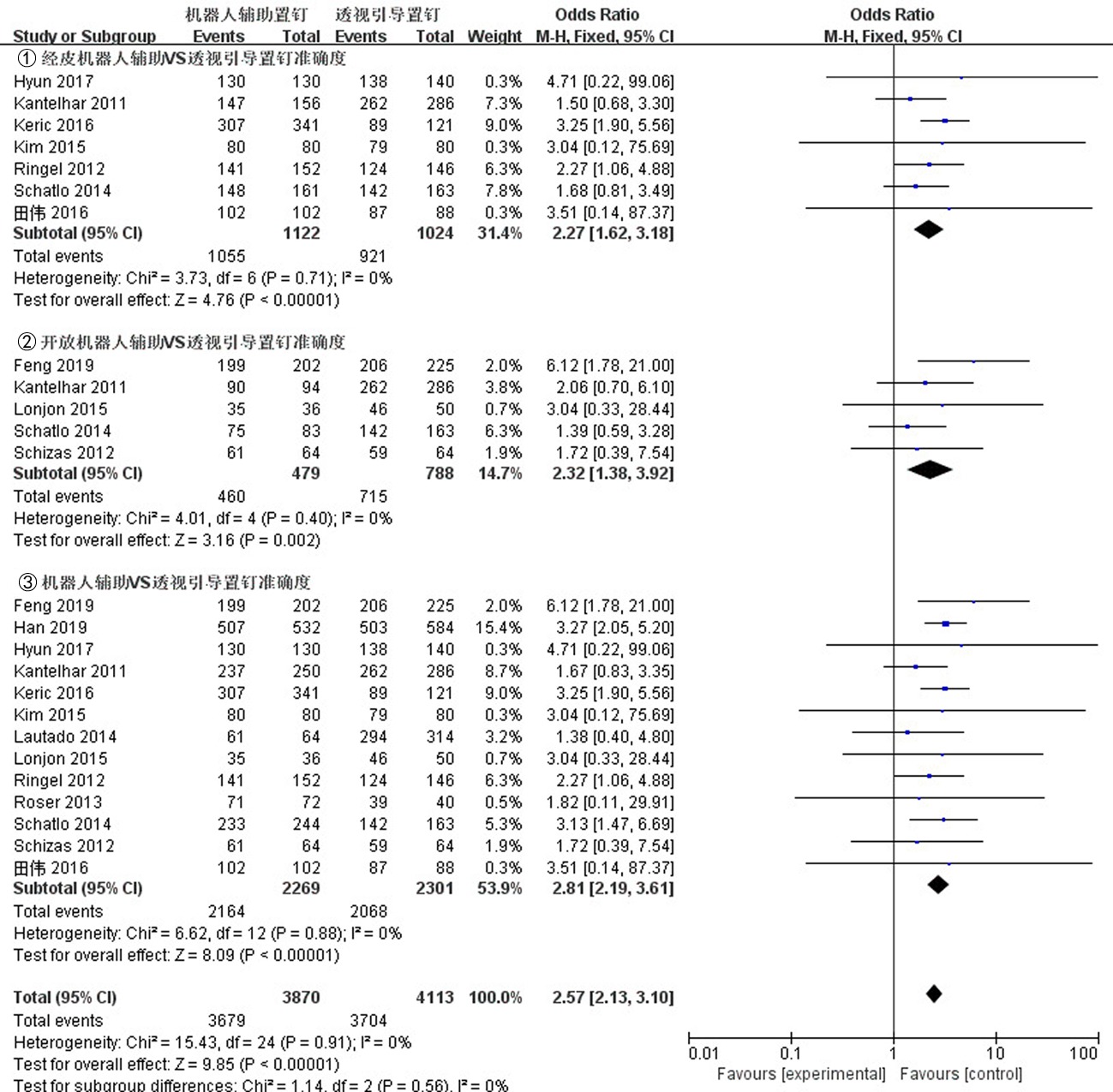
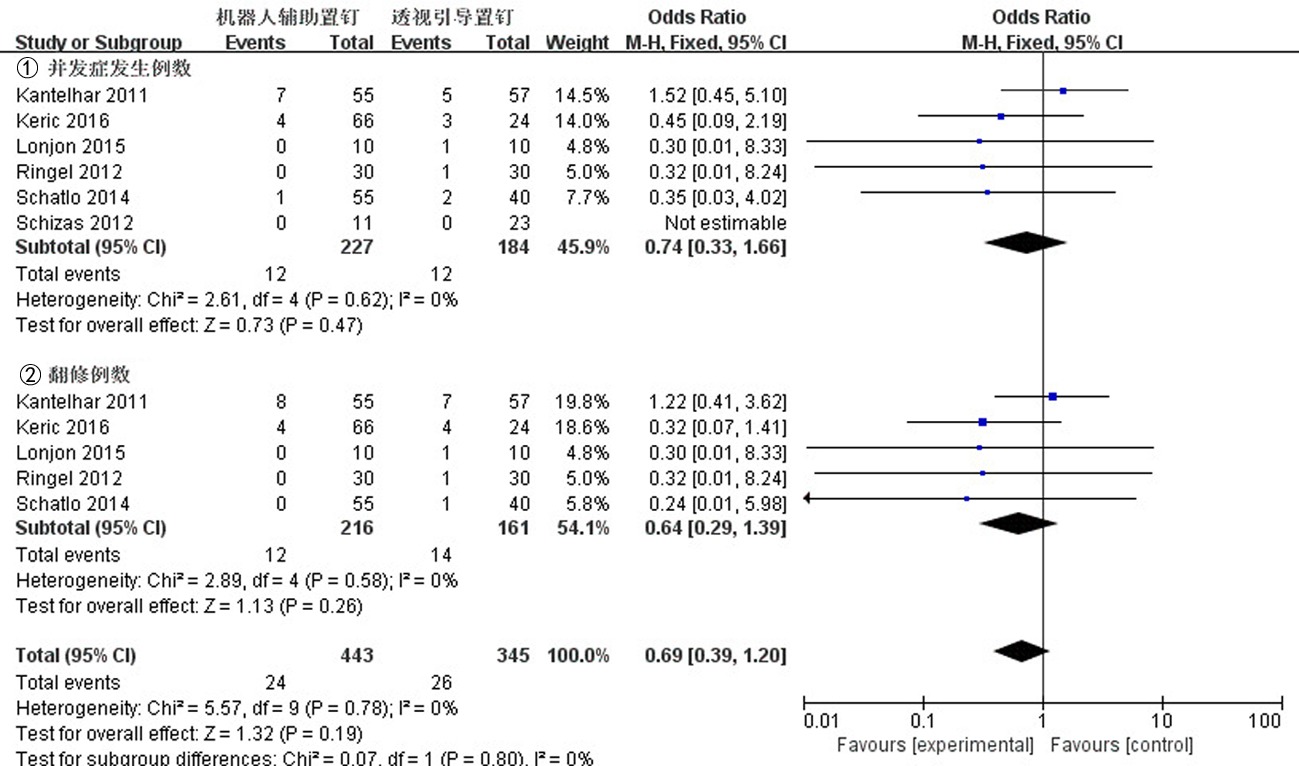
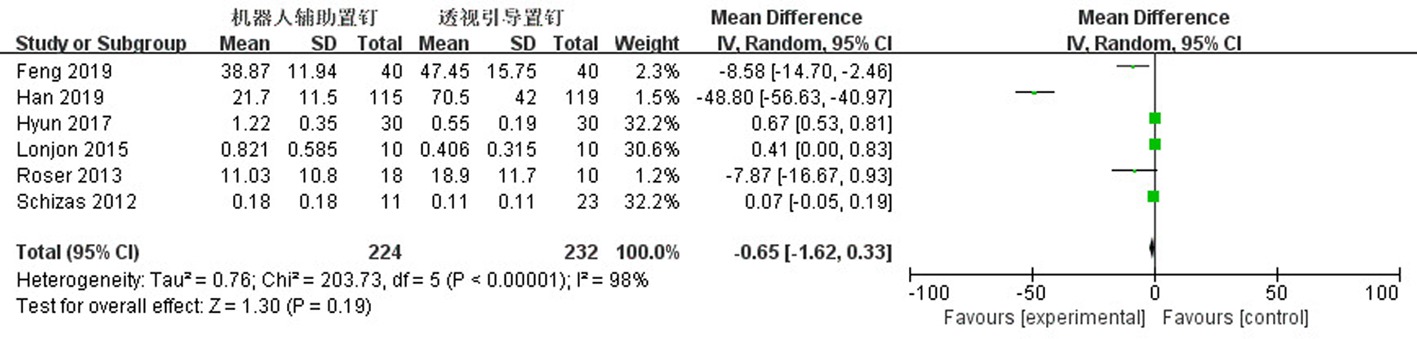
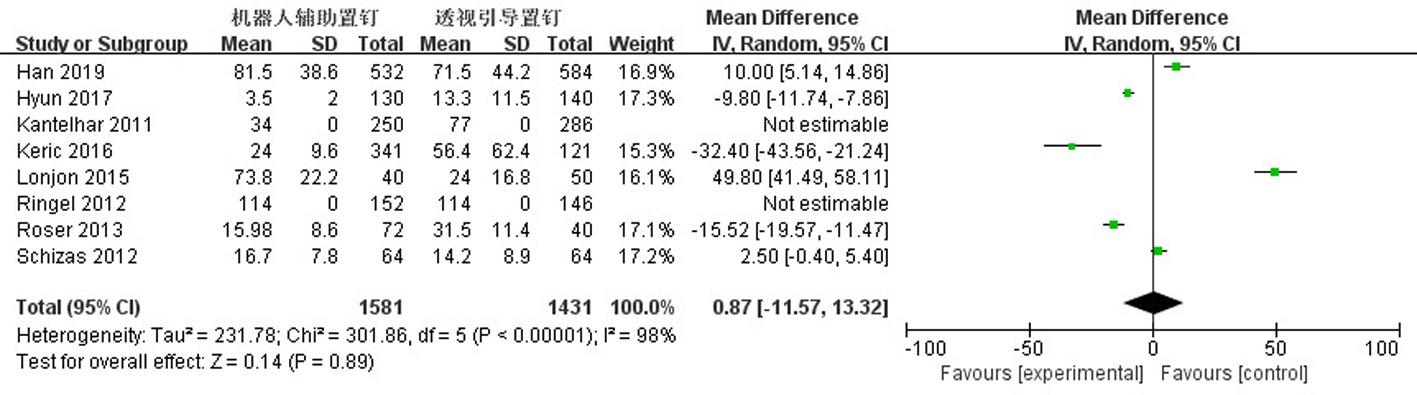
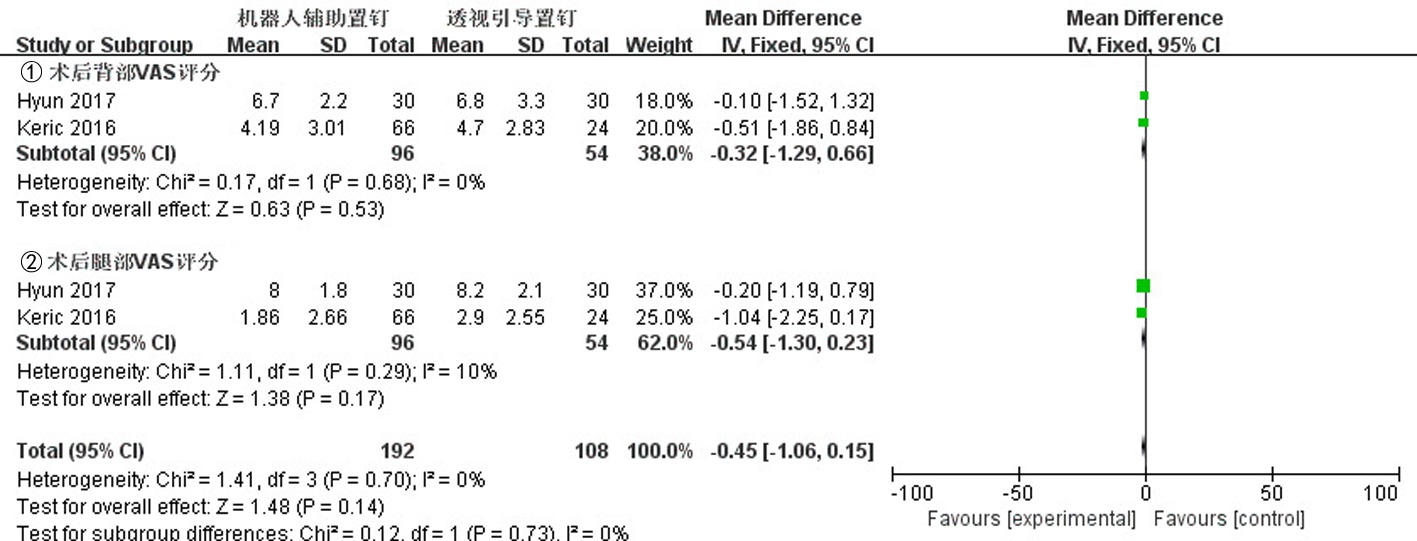
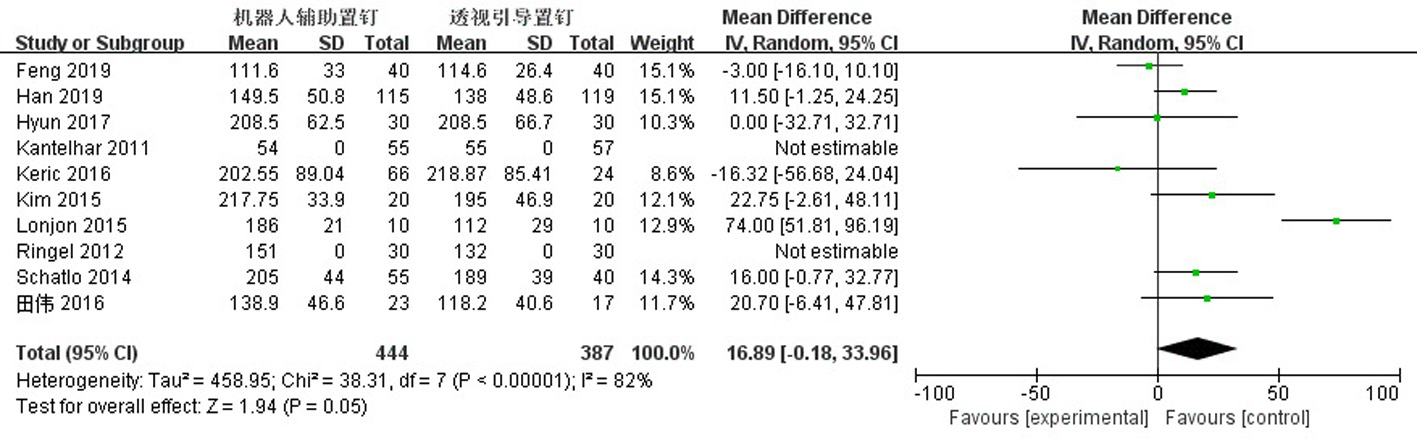
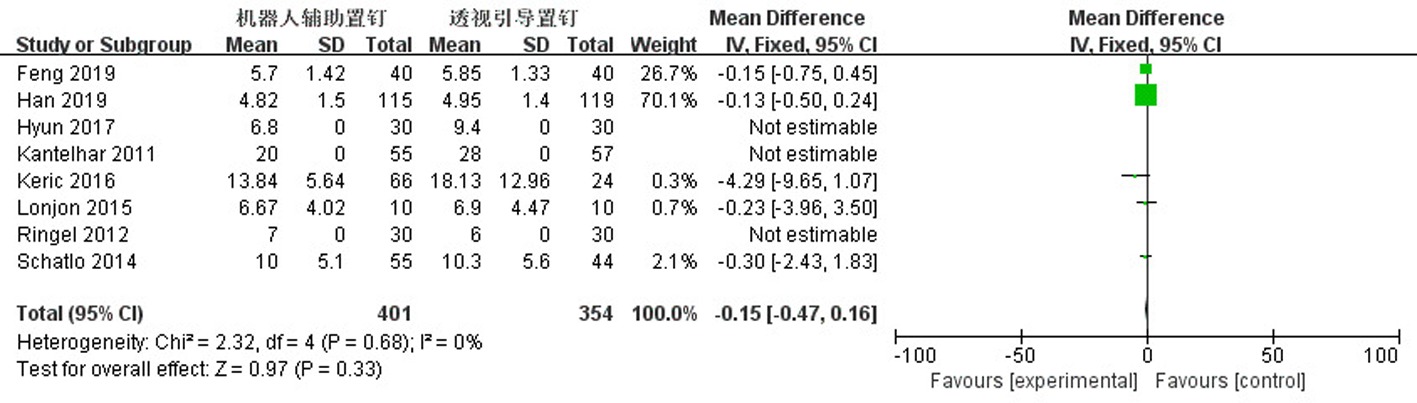
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 208-215.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of the effect of robot-assisted and free-handed pedicle screw placement in spinal diseases
- epartment of Spine Surgery,the Third Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University,Hefei 230061,Chin Da
-
Received:2022-09-06Online:2023-03-20Published:2023-05-11 -
Contact:Du Yibin E-mail:dodo1108@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Yang, Du Yibin. Meta-analysis of the effect of robot-assisted and free-handed pedicle screw placement in spinal diseases[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 208-215.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.002
| 纳入研究 | 类型 | 国家 | 年份 | 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 性别 (男/女) | 结局指标 | 改良Jadad 质量评价(分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ringel[ | 随机对照 | 德国 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 68 | 14/16 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 67 | 12/18 | ||||||
| Feng[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 40 | 67.6±6.5 | 12/28 | ①③⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 67.9±7.3 | 13/27 | ||||||
| Keric[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 72.3±11.1 | 36/30 | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 68.0±11.2 | 13/11 | ||||||
| Hyun[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 66.5 | 9/21 | ①③④⑤⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 66.8 | 8/22 | ||||||
| Kim[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2015 | 机器人辅助 | 20 | 64.4±11.9 | 11/9 | ①⑥ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 20 | 64.7±8.6 | 8/12 | ||||||
| Lautado[ | 回顾性 | 瑞士 | 2018 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | - | ① | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 48 | 60.7 | |||||||
| Schizas[ | 随机对照 | 瑞士 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | 6/5 | ①③④ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 23 | 66 | 8/15 | ||||||
| Kantelhardt[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2011 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 63.1 | 52/60 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 57 | ||||||||
| Lonjon[ | 随机对照 | 法国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 10 | 63.4±11.0 | 4/6 | ①②③④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | 4/6 | |||||||
| Han[ | 回顾性 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 54.6±11.3 | 55/60 | ①③④⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 56.1±13.4 | 58/61 | ||||||
| Schatlo[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2014 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 52(27-83) | 29/26 | ①②⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 58(23-82) | 28/12 | ||||||
| Roser[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2013 | 机器人辅助 | 18 | - | - | ①③④ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | ||||||||
| 田伟[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 23 | 54.9±11.9 | 17/23 | ①⑥ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 17 |
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of documents included
| 纳入研究 | 类型 | 国家 | 年份 | 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 性别 (男/女) | 结局指标 | 改良Jadad 质量评价(分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ringel[ | 随机对照 | 德国 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 68 | 14/16 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 67 | 12/18 | ||||||
| Feng[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 40 | 67.6±6.5 | 12/28 | ①③⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 67.9±7.3 | 13/27 | ||||||
| Keric[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 72.3±11.1 | 36/30 | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 68.0±11.2 | 13/11 | ||||||
| Hyun[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 66.5 | 9/21 | ①③④⑤⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 66.8 | 8/22 | ||||||
| Kim[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2015 | 机器人辅助 | 20 | 64.4±11.9 | 11/9 | ①⑥ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 20 | 64.7±8.6 | 8/12 | ||||||
| Lautado[ | 回顾性 | 瑞士 | 2018 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | - | ① | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 48 | 60.7 | |||||||
| Schizas[ | 随机对照 | 瑞士 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | 6/5 | ①③④ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 23 | 66 | 8/15 | ||||||
| Kantelhardt[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2011 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 63.1 | 52/60 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 57 | ||||||||
| Lonjon[ | 随机对照 | 法国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 10 | 63.4±11.0 | 4/6 | ①②③④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | 4/6 | |||||||
| Han[ | 回顾性 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 54.6±11.3 | 55/60 | ①③④⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 56.1±13.4 | 58/61 | ||||||
| Schatlo[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2014 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 52(27-83) | 29/26 | ①②⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 58(23-82) | 28/12 | ||||||
| Roser[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2013 | 机器人辅助 | 18 | - | - | ①③④ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | ||||||||
| 田伟[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 23 | 54.9±11.9 | 17/23 | ①⑥ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 17 |
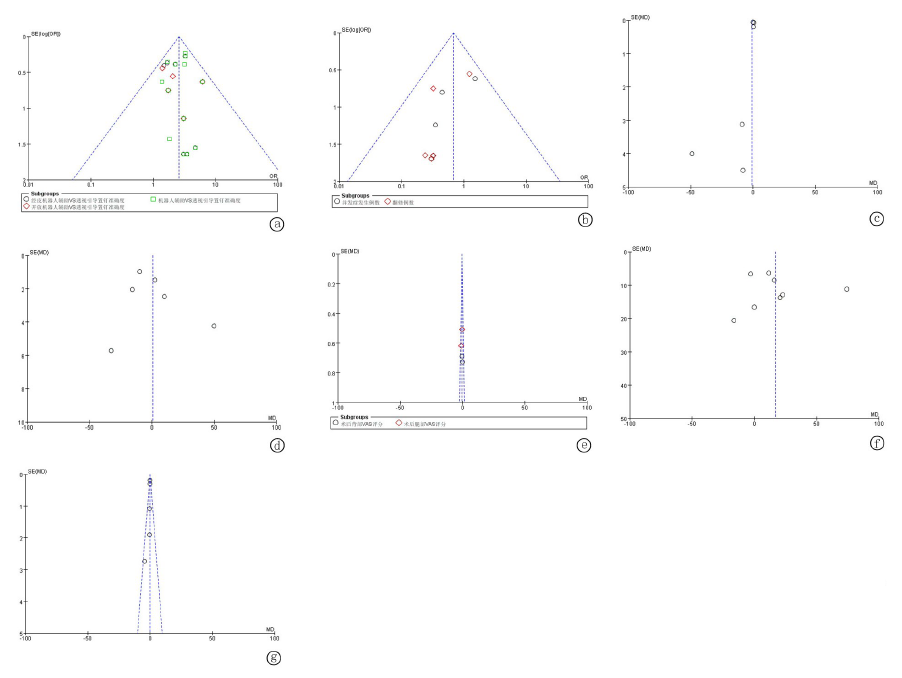
Fig.9 Publication of bias a. Funnel plot of accuracy of pedicle screw placement; b. Funnel plot of complications and revision cases; c. Funnel plot of intraoperative. radiation intensity; d. Funnel plot of intraoperative radiation time; e. Funnel plot of postoperative VAS score; f. Funnel plot of operation time; g. Funnel plot of hospitalization time
| [1] |
Nasser R, Yadla S, Maltenfort MG, et al. Complications in spine surgery[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2010, 13(2):144-157.
doi: 10.3171/2010.3.SPINE09369 URL |
| [2] | Togawa D, Kayanja MM, Reinhardt MK, et al. Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: Part 2--Evaluation of system accuracy[J]. Neurosurgery, 2007, 60(2 Suppl 1):S129-S139. |
| [3] | 田伟, 王晋超, 刘亚军, 等. 上颈椎手术方式回顾及应用机器人辅助上颈椎手术的体会[J]. 中国医疗器械信息, 2017, 23(7):9-13. |
| [4] | Joseph JR, Smith BW, Liu X, et al. Current applications of robotics in spine surgery: A systematic review of the literature[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2017, 42(5):E2. |
| [5] |
Ringel F, Stuer C, Reinke A, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: A prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012, 37(8):E496-E501.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824b7767 URL |
| [6] |
Feng S, Tian W, Sun Y, et al. Effect of robot-assisted surgery on lumbar pedicle screw internal fixation in patients with osteoporosis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 125:e1057-e1062.
doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.243 URL |
| [7] |
Keric N, Eum DJ, Afghanyar F, et al. Evaluation of surgical strategy of conventional vs. percutaneous robot-assisted spinal trans-pedicular instrumentation in spondylodiscitis[J]. J Robot Surg, 2017, 11(1):17-25.
doi: 10.1007/s11701-016-0597-5 pmid: 27277255 |
| [8] |
Hyun S, Kim K, Jahng T, et al. Minimally invasive robotic versus open fluoroscopic-guided spinal instrumented fusions: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Spine, 2017, 42(6):353-358.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001778 URL |
| [9] |
Kim H, Lee SH, Chang B, et al. Monitoring the quality of robot-assisted pedicle screw fixation in the lumbar spine by using a cumulative summation test[J]. Spine, 2015, 40(2):87-94.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000680 URL |
| [10] |
Laudato PA, Pierzchala K, Schizas C. Pedicle screw insertion accuracy using o-arm, robotic guidance, or freehand technique: A comparative study[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018, 43(6):E373-E378.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002449 URL |
| [11] |
Schizas C, Thein E, Kwiatkowski B, et al. Pedicle screw insertion: robotic assistance versus conventional C-arm fluoroscopy.[J]. Acta orthopaedica Belgica, 2012, 78(2):240-245.
pmid: 22696996 |
| [12] |
Kantelhardt SR, Martinez R, Baerwinkel S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement[J]. Eur Spine J, 2011, 20(6):860-868.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-011-1729-2 pmid: 21384205 |
| [13] |
Lonjon N, Chan-Seng E, Costalat V, et al. Robot-assisted spine surgery: Feasibility study through a prospective case-matched analysis[J]. Eur Spine J, 2016, 25(3):947-955.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3758-8 pmid: 25575857 |
| [14] | Han X, Tian W, Liu Y, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery: A prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2019:1-8. |
| [15] |
Schatlo B, Molliqaj G, Cuvinciuc V, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine: A matched cohort comparison[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2014, 20(6):636-643.
doi: 10.3171/2014.3.SPINE13714 URL |
| [16] | Roser F, Tatagiba M, Maier G. Spinal robotics: Current applications and future perspectives[J]. Neurosurgery, 2013, 72(Suppl 1):12-18. |
| [17] | 田伟, 范明星, 韩晓光, 等. 机器人辅助与传统透视辅助脊柱椎弓根螺钉内固定的临床对比研究[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志, 2016, 1(1):4-10. |
| [18] |
Bydon M, Alvi M A, Goyal A. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: Definition, natural history, conservative management, and surgical treatment[J]. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 2019, 30(3):299-304.
doi: S1042-3680(19)30016-6 pmid: 31078230 |
| [19] |
Ma XL, Zhao XW, Ma JX, et al. Effectiveness of surgery versus conservative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis: A system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Int J Surg, 2017, 44:329-338.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.07.032 URL |
| [20] |
Rustagi T, Drazin D, Oner C, et al. Fractures in spinal ankylosing disorders: A narrative review of disease and injury types, treatment techniques, and Outcomes[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2017, 31(Suppl 4):S57-S74.
doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000953 URL |
| [21] |
Aizawa T, Kokubun S, Ozawa H, et al. Increasing incidence of degenerative spinal diseases in Japan during 25 years: The registration system of spinal surgery in tohoku university spine society[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 2016, 238(2):153-163.
doi: 10.1620/tjem.238.153 pmid: 26876801 |
| [22] |
Jain A, Hassanzadeh H, Puvanesarajah V, et al. Incidence of perioperative medical complications and mortality among elderly patients undergoing surgery for spinal deformity: analysis of 3519 patients[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2017, 27(5):534-539.
doi: 10.3171/2017.3.SPINE161011 URL |
| [23] |
Mihailidis HG, Manners S, Churilov L, et al. Is spinal surgery safe in octogenarians?[J]. ANZ Journal of Surgery, 2017, 87(7-8):605-609.
doi: 10.1111/ans.13885 pmid: 28124479 |
| [24] |
Liu JM, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, et al. The effect of screw tunnels on the biomechanical stability of vertebral body after pedicle screws removal: A finite element analysis[J]. Int Orthop, 2017, 41(6):1183-1187.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3453-y URL |
| [25] |
Mac-Thiong JM, Parent S, Poitras B, et al. Neurological outcome and management of pedicle screws misplaced totally within the spinal canal[J]. Spine, 2013, 38(3):229-237.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31826980a9 pmid: 22814305 |
| [26] |
Devito DP, Kaplan L, Dietl R, et al. Clinical acceptance and accuracy assessment of spinal implants guided with SpineAssist surgical robot: Retrospective study[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010, 35(24):2109-2115.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d323ab URL |
| [27] |
Li W, Li G, Chen W, et al. The safety and accuracy of robot-assisted pedicle screw internal fixation for spine disease: A meta-analysis[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2020, 9(10):653-666.
doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.910.BJR-2020-0064.R2 pmid: 33101655 |
| [28] |
Wiesner L, Kothe R, Schulitz K P, et al. Clinical evaluation and computed tomography scan analysis of screw tracts after percutaneous insertion of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine[J]. Spine, 2000, 25(5):615-621.
doi: 10.1097/00007632-200003010-00013 pmid: 10749639 |
| [1] | Wang Jiaoyan, Zhang Yingchun, Ren Keming, Ma Guofeng, Ying Kejing. Clinical analysis of 16 cases of venous thromboembolism combined with psychiatric disorders treated with olanzapine [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1108-1113. |
| [2] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 668-672. |
| [3] | Li Hongwei, Wu Qi. Focus on venous thromboembolism during pregnancy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(4): 359-362. |
| [4] | Jiang Mingming, Yuan Yadong. Malignant neoplasms and venous thromboembolism [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(4): 373-377. |
| [5] | LIU Juan;LI Dai-hong;SONG Wen-li . Significance of monitoring thyroid function in patients after renal transplantation [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2011, 26(14): 1211-1213. |
| [6] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2011, 26(4): 317-319. |
| [7] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2010, 25(24): 2124-2124. |
| [8] | LI Yu-feng;ZHANG Sheng-li;YAO Jia-lin;FAN Yan-ling. Comparison between domestic mycophenolate mofetil dispersible tablet and imported capsule for preventing acute rejection following renal transplantation [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2010, 25(13): 1134-1137. |
| [9] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2008, 23(2): 137-138. |
| [10] | LI Yu-feng;YAO Jia-lin;ZHANG Sheng-li. Effect of rapamycin on kidney function after kidney transplanation [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2005, 20(15): 846-849. |
| [11] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2003, 18(7): 404-405. |
| [12] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2002, 17(7): 415-416. |
| [13] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2001, 16(22): 0-0. |
| [14] | . [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2001, 16(7): 336-0. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||