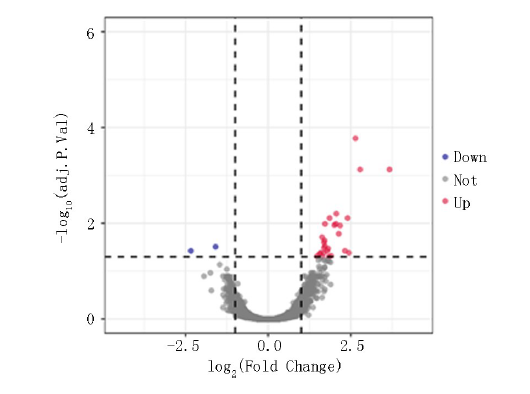
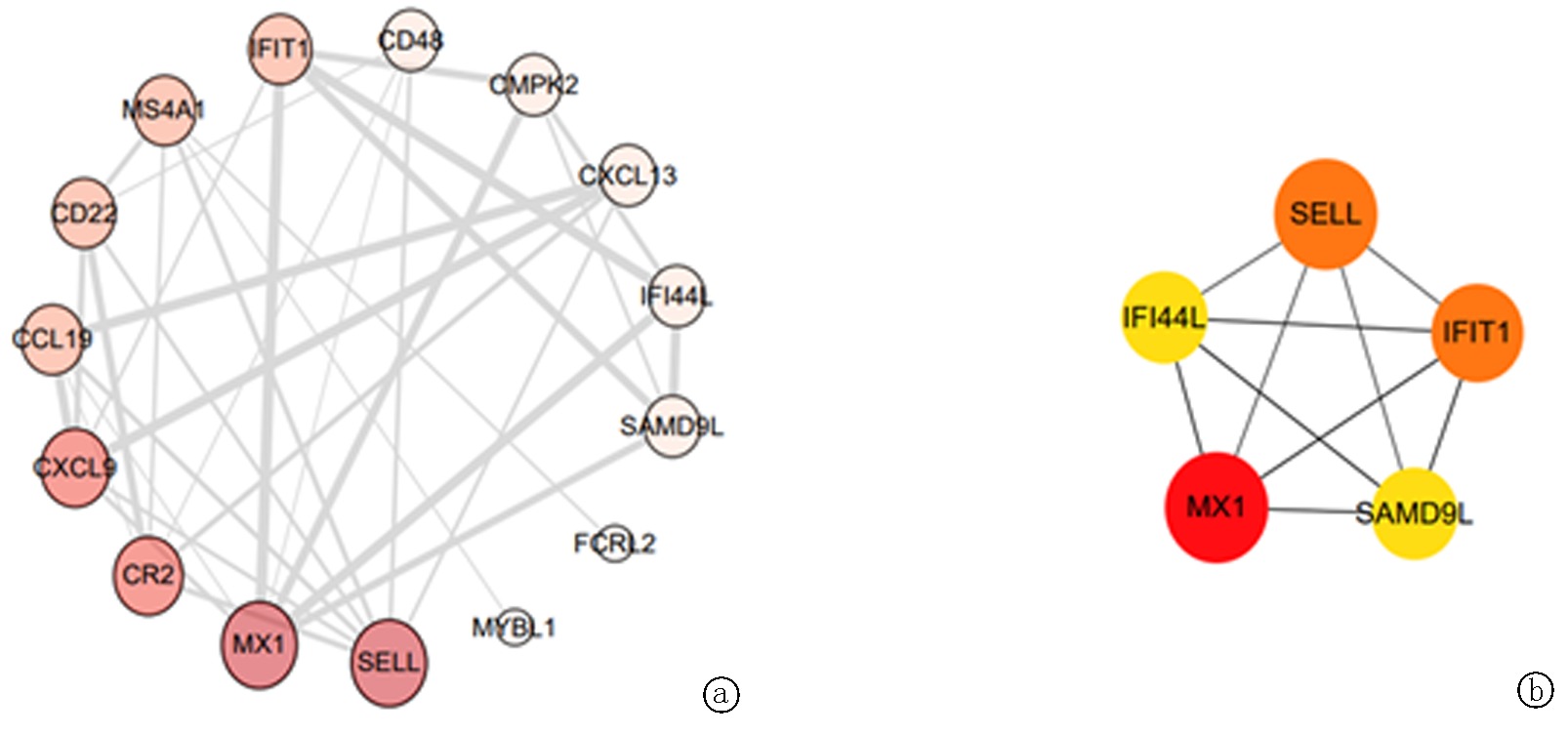
Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 792-797.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.09.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed genes of primary Sjögren's syndrome
- Department of Rheumatology and Immunology,the Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School,Nanjing 210008,China
-
Received:2022-07-11Online:2024-09-20Published:2024-09-24 -
Contact:Wang Dandan E-mail:dandanwang2007@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yun, Wang Dandan. Bioinformatic analysis of differentially expressed genes of primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 792-797.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.09.004
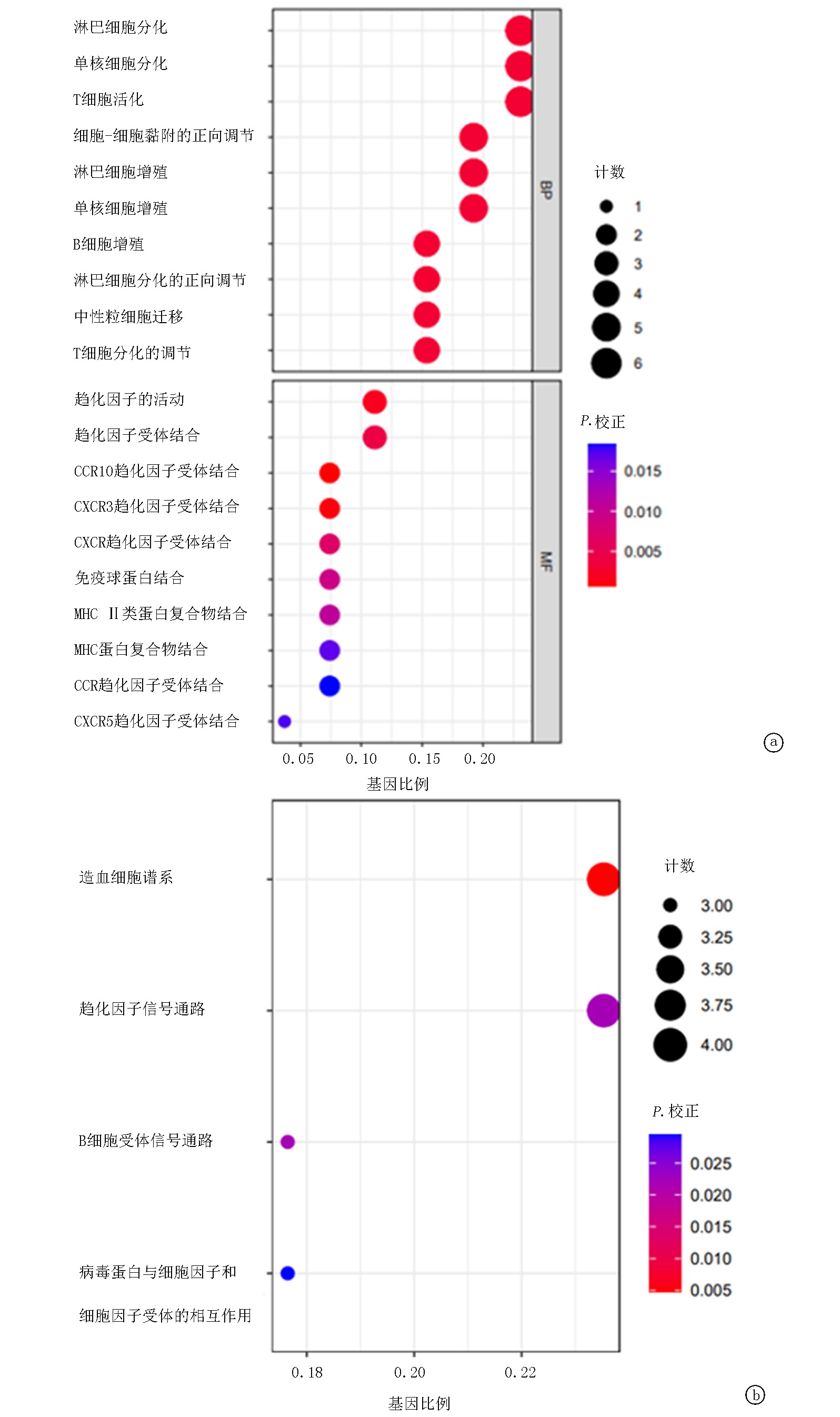
Tab.1 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis
| 分类 | ID | 功能 | P值 | 基因 数目 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO-BP | GO:0030098 | 淋巴细胞分化 | 1.00E-05 | 6 |
| GO:0042100 | B细胞增殖 | 1.01E-05 | 4 | |
| GO:0045621 | 淋巴细胞分化的正向调节 | 1.22E-05 | 4 | |
| GO:1903131 | 单核细胞分化 | 2.10E-05 | 6 | |
| GO:1990266 | 中性粒细胞迁移 | 2.30E-05 | 4 | |
| GO:0022409 | 细胞-细胞黏附的正向调节 | 3.93E-05 | 5 | |
| GO:0046651 | 淋巴细胞增殖 | 4.20E-05 | 5 | |
| GO:0032943 | 单核细胞增殖 | 4.41E-05 | 5 | |
| GO:0042110 | T细胞活化 | 4.44E-05 | 6 | |
| GO:0045580 | T细胞分化的调节 | 4.64E-05 | 4 | |
| GO-MF | GO:0031735 | CCR10趋化因子受体结合 | 6.24E-06 | 2 |
| GO:0048248 | CXCR3趋化因子受体结合 | 2.08E-05 | 2 | |
| GO:0008009 | 趋化因子的活动 | 4.99E-05 | 3 | |
| GO:0042379 | 趋化因子受体结合 | 0.000158 | 3 | |
| GO:0045236 | CXCR趋化因子受体结合 | 0.000314 | 2 | |
| GO:0019865 | 免疫球蛋白结合 | 0.000517 | 2 | |
| GO:0023026 | MHC II类蛋白复合物结合 | 0.000714 | 2 | |
| GO:0023023 | MHC蛋白复合物结合 | 0.001271 | 2 | |
| GO:0031724 | CXCR5趋化因子受体结合 | 0.00147 | 1 | |
| GO:0048020 | CCR趋化因子受体结合 | 0.002251 | 2 | |
| KEGG | hsa04640 | 造血细胞谱系 | 4.34E-05 | 4 |
| hsa04062 | 趋化因子信号通路 | 0.000561 | 4 | |
| hsa04662 | B细胞受体信号通路 | 0.000605 | 3 | |
| hsa04061 | 病毒蛋白与细胞因子和细胞因子受体的相互作用 | 0.001079 | 3 |
Tab.1 GO and KEGG enrichment analysis
| 分类 | ID | 功能 | P值 | 基因 数目 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO-BP | GO:0030098 | 淋巴细胞分化 | 1.00E-05 | 6 |
| GO:0042100 | B细胞增殖 | 1.01E-05 | 4 | |
| GO:0045621 | 淋巴细胞分化的正向调节 | 1.22E-05 | 4 | |
| GO:1903131 | 单核细胞分化 | 2.10E-05 | 6 | |
| GO:1990266 | 中性粒细胞迁移 | 2.30E-05 | 4 | |
| GO:0022409 | 细胞-细胞黏附的正向调节 | 3.93E-05 | 5 | |
| GO:0046651 | 淋巴细胞增殖 | 4.20E-05 | 5 | |
| GO:0032943 | 单核细胞增殖 | 4.41E-05 | 5 | |
| GO:0042110 | T细胞活化 | 4.44E-05 | 6 | |
| GO:0045580 | T细胞分化的调节 | 4.64E-05 | 4 | |
| GO-MF | GO:0031735 | CCR10趋化因子受体结合 | 6.24E-06 | 2 |
| GO:0048248 | CXCR3趋化因子受体结合 | 2.08E-05 | 2 | |
| GO:0008009 | 趋化因子的活动 | 4.99E-05 | 3 | |
| GO:0042379 | 趋化因子受体结合 | 0.000158 | 3 | |
| GO:0045236 | CXCR趋化因子受体结合 | 0.000314 | 2 | |
| GO:0019865 | 免疫球蛋白结合 | 0.000517 | 2 | |
| GO:0023026 | MHC II类蛋白复合物结合 | 0.000714 | 2 | |
| GO:0023023 | MHC蛋白复合物结合 | 0.001271 | 2 | |
| GO:0031724 | CXCR5趋化因子受体结合 | 0.00147 | 1 | |
| GO:0048020 | CCR趋化因子受体结合 | 0.002251 | 2 | |
| KEGG | hsa04640 | 造血细胞谱系 | 4.34E-05 | 4 |
| hsa04062 | 趋化因子信号通路 | 0.000561 | 4 | |
| hsa04662 | B细胞受体信号通路 | 0.000605 | 3 | |
| hsa04061 | 病毒蛋白与细胞因子和细胞因子受体的相互作用 | 0.001079 | 3 |
| [1] | Nocturne G, Virone A, Ng WF, et al. Rheumatoid factor and disease activity are independent predictors of lymphoma in primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2016, 68(4):977-985. |
| [2] | 中华医学会风湿病学分会. 干燥综合征诊断及治疗指南[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2010, 14(11):766-768. |
| [3] | Greenwell-Wild T, Moutsopoulos NM, Gliozzi M, et al. Chitinases in the salivary glands and circulation of patients with Sjögren's syndrome: Macrophage harbingers of disease severity[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2011, 63(10):3103-3115. |
| [4] | Horvath S, Nazmul-Hossain AN, Pollard RP, et al. Systems analysis of primary Sjögren's syndrome pathogenesis in salivary glands identifies shared pathways in human and a mouse model[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2012, 14(6):R238. |
| [5] |
Leek JT, Johnson WE, Parker HS, et al. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments[J]. Bioinformatics, 2012, 28(6):882-883.
doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts034 pmid: 22257669 |
| [6] | Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, et al. Limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2015, 43(7):e47. |
| [7] |
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y, et al. ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters[J]. OMICS, 2012, 16(5):284-287.
doi: 10.1089/omi.2011.0118 pmid: 22455463 |
| [8] |
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, et al. STRING: A database of predicted functional associations between proteins[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2003, 31(1):258-261.
doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg034 pmid: 12519996 |
| [9] |
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks[J]. Genome Res, 2003, 13(11):2498-2504.
doi: 10.1101/gr.1239303 pmid: 14597658 |
| [10] | Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, et al. CytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome[J]. BMC Syst Biol, 2014, 8:S11. |
| [11] |
Kang HI, Fei HM, Saito I, et al. Comparison of HLA class II genes in Caucasoid, Chinese, and Japanese patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. J Immunol, 1993, 150:3615-3623.
pmid: 8468491 |
| [12] | Ishimaru N, Arakaki R, Yoshida S, et al. Expression of the retinoblastoma protein RbAp48 in exocrine glands leads to Sjögren's syndrome-like autoimmune exocrinopathy[J]. J Exp Med, 2008, 205(12):2915-2927. |
| [13] |
Saito I, Servenius B, Compton T, et al. Detection of epstein-Barr virus DNA by polymerase chain reaction in blood and tissue biopsies from patients with Sjogren's syndrome[J]. J Exp Med, 1989, 169(6):2191-2198.
doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2191 pmid: 2543732 |
| [14] |
Moriyama M, Hayashida JN, Toyoshima T, et al. Cytokine/chemokine profiles contribute to understanding the pathogenesis and diagnosis of primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 2012, 169(1):17-26.
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2012.04587.x pmid: 22670774 |
| [15] |
McArthur C, Wang Y, Veno P, et al. Intracellular trafficking and surface expression of SS-A (Ro), SS-B (La), poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and alpha-fodrin autoantigens during apoptosis in human salivary gland cells induced by tumour necrosis factor-alpha[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2002, 47(6):443-448.
doi: 10.1016/s0003-9969(02)00025-0 pmid: 12102760 |
| [16] |
Naito Y, Matsumoto I, Wakamatsu E, et al. Altered peptide ligands regulate muscarinic acetylcholine receptor reactive T cells of patients with Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2006, 65(2):269-271.
pmid: 16410534 |
| [17] | Kong L, Ogawa N, Nakabayashi T, et al. Fas and fas ligand expression in the salivary glands of patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1997, 40(1):87-97. |
| [18] |
Nakamura H, Koji T, Tominaga M, et al. Apoptosis in labial salivary glands from Sjögren's syndrome (SS) patients: Comparison with human T lymphotropic virus-I (HTLV-I)-seronegative and -seropositive SS patients[J]. Clin Exp Immunol, 1998, 114(1):106-112.
pmid: 9764611 |
| [19] |
Nakamura H, Kawakami A, Izumi M, et al. Detection of the soluble form of Fas ligand (sFasL) and sFas in the saliva from patients with Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2005, 23(6):915.
pmid: 16396719 |
| [20] |
Tsubota K, Saito I, Miyasaka N. Granzyme A and perforin expressed in the lacrimal glands of patients with Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Am J Ophthalmol, 1994, 117(1):120-121.
pmid: 7904795 |
| [21] |
Fujihara T, Fujita H, Tsubota K, et al. Preferential localization of CD8+ alpha E beta 7+ T cells around acinar epithelial cells with apoptosis in patients with Sjögren's syndrome[J]. J Immunol, 1999, 163(4):2226-2235.
pmid: 10438965 |
| [22] |
Carsons SE, Vivino FB, Parke A, et al. Treatment guidelines for rheumatologic manifestations of Sjögren's syndrome: Use of biologic agents, management of fatigue, and inflammatory musculoskeletal Pain[J]. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken), 2017, 69(4):517-527.
doi: 10.1002/acr.22968 pmid: 27390247 |
| [23] |
Fensterl V, Sen GC. Interferon-induced Ifit proteins: Their role in viral pathogenesis[J]. J Virol, 2015, 89(5):2462-2468.
doi: 10.1128/JVI.02744-14 pmid: 25428874 |
| [24] | Jiang H, Tsang L, Wang H, et al. IFI44L as a forward regulator enhancing host antituberculosis responses[J]. J Immunol Res, 2021, 2021:5599408. |
| [25] | Haller O, Kochs G. Human MxA protein: An interferon-induced dynamin-like GTPase with broad antiviral activity[J]. J Interferon Cytokine Res, 2011, 31(1):79-87. |
| [26] |
Imgenberg-Kreuz J, Sandling JK, Almlöf JC, et al. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis in multiple tissues in primary Sjögren's syndrome reveals regulatory effects at interferon-induced genes[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2016, 75(11):2029-2036.
doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208659 pmid: 26857698 |
| [27] | Bodewes ILA, Versnel MA. Interferon activation in primary Sjögren's syndrome: Recent insights and future perspective as novel treatment target[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2018, 14(10):817-829. |
| [28] | Jhamnani RD, Rosenzweig SD. An update on gain-of-function mutations in primary immunodeficiency diseases[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2017, 17(6):391-397. |
| [29] |
Sahoo SS, Pastor VB, Goodings C, et al. Clinical evolution, genetic landscape and trajectories of clonal hematopoiesis in SAMD9/SAMD9L syndromes[J]. Nat Med, 2021, 27(10):1806-1817.
doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01511-6 pmid: 34621053 |
| [30] | Allenspach EJ, Soveg F, Finn LS, et al. Germline SAMD9L truncation variants trigger global translational repression[J]. J Exp Med, 2021, 218(5):e20201195. |
| [31] |
Wedepohl S, Beceren-Braun F, Riese S, et al. L-selectin--a dynamic regulator of leukocyte migration[J]. Eur J Cell Biol, 2012, 91(4):257-264.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2011.02.007 pmid: 21546114 |
| [32] |
Sarraj B, Ludányi K, Glant TT, et al. Expression of CD44 and L-selectin in the innate immune system is required for severe joint inflammation in the proteoglycan-induced murine model of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Immunol, 2006, 177(3):1932-1940.
pmid: 16849507 |
| [33] |
Kabeerdoss J, Sandhya P, Mandal SK, et al. High salivary soluble L-selectin and interleukin-7 levels in Asian Indian patients with primary Sjögren's syndrome[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2016, 35(12):3063-3067.
pmid: 27620619 |
| [34] |
Mikulowska-Mennis A, Xu B, Berberian JM, et al. Lymphocyte migration to inflamed lacrimal glands is mediated by vascular cell adhesion molecule-1/alpha(4)beta(1) integrin, peripheral node addressin/l-selectin, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 adhesion pathways[J]. Am J Pathol, 2001, 159(2):671-681.
pmid: 11485925 |
| [1] | Xie Jianli, Wang Junxiang, Chen Haiying. Application of musculoskeletal ultrasound in ankylosing spondylitis with peripheral osteophytes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 787-791. |
| [2] | Han Kaiyang, Feng Tongtong, Bao Ying. Analysis of clinical characteristics and risk factors of lupus nephritis combined with neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(9): 812-815. |
| [3] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(8): 763-768. |
| [4] | Song Yijing, Li Jian, Song Qin, Shao Li. Predictive value of C-reactive protein combined with triglyceride glucose index for coronary heart disease risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(6): 506-511. |
| [5] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(5): 475-480. |
| [6] | Zhu Suhua, Xu Shengqiu. Review: efficacy and pharmacogenomics of leflunomide plus methotrexate versus iguratimod plus methotrexate in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(4): 304-313. |
| [7] | Zhang Xiaoyang, Zang Meirong, Suo Jing, Meng Jianbo, Song Xiaoning, Wang Jinkai. Ankylosing spondylitis combined with acute promyelocytic leukaemia and disseminated intravascular coagulation: A case report and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(4): 342-346. |
| [8] | Gong Sijing, Yang Yushu, Guo Huifang, Ding Meng, Wang Wei, Gao Lixia. Analysis of the clinical value for anti-Ro52 and anti-Ro60 antibodies in connective tissue disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(3): 227-233. |
| [9] | Song Jialiang, Jiang Yingjie, Kong Ruina, Cai Qing, Gao Jie. IgG4-related diseases characterized by increased IgE level and eosinophil count with multiple lymphadenopathy: A case report [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 57-60. |
| [10] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 92-96. |
| [11] | He Peihua, Zhou Xingfu, Hong Weihong, Wang Lichun, Liu Sujun, Jin Yuyan, Zeng Jiahao, Liu Lichang. Clinical analysis of 4 cases of IgG4-related kidney disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 1016-1021. |
| [12] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(10): 944-948. |
| [13] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 753-756. |
| [14] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(7): 663-667. |
| [15] | . [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 279-284. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||