Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 43-46.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.01.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of risk factors for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children
Yu Zeyu( ), Lin Xi, Chen Zhanghua, Yang Wei, Chen Zhimin, Zhang Hai
), Lin Xi, Chen Zhanghua, Yang Wei, Chen Zhimin, Zhang Hai
- Department of Paediatrics, Luoyuan County Hospital, Luoyuan 350600, China
-
Received:2023-10-19Online:2024-01-20Published:2024-03-22
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Zeyu, Lin Xi, Chen Zhanghua, Yang Wei, Chen Zhimin, Zhang Hai. Analysis of risk factors for refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 43-46.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.01.007
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 女性 [例(%)] | 肝功能损害 [例(%)] | 皮疹 [例(%)] | 肺部影像学 进行性加重 [例(%)] | 发热持续时间 ≥7 d[例(%)] | 发热持续时间 ≥10 d[例(%)] | 发热峰值≥39 ℃ [例(%)] | 发热峰值≥40 ℃ [例(%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例组 | 67 | 2.10(0.8,10.0) | 23(34.3) | 10(14.9) | 8(11.9) | 5(7.5) | 67(100.0) | 28(41.8) | 67(100.0) | 50(74.6) |
| 对照组 | 134 | 2.35(0.75,10.0) | 50(37.3) | 22(16.4) | 18(13.4) | 0 | 60(44.8) | 23(17.2) | 85(63.4) | 20(14.9) |
| 统计值 | χ2=0.172 | χ2=0.172 | χ2=0.088 | χ2=7.409 | χ2=58.559 | χ2=14.306 | χ2=32.398 | χ2=70.142 | ||
| 0.057 | 0.678 | 0.668 | 0.356 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Tab.1 Comparison of general information between two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 女性 [例(%)] | 肝功能损害 [例(%)] | 皮疹 [例(%)] | 肺部影像学 进行性加重 [例(%)] | 发热持续时间 ≥7 d[例(%)] | 发热持续时间 ≥10 d[例(%)] | 发热峰值≥39 ℃ [例(%)] | 发热峰值≥40 ℃ [例(%)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例组 | 67 | 2.10(0.8,10.0) | 23(34.3) | 10(14.9) | 8(11.9) | 5(7.5) | 67(100.0) | 28(41.8) | 67(100.0) | 50(74.6) |
| 对照组 | 134 | 2.35(0.75,10.0) | 50(37.3) | 22(16.4) | 18(13.4) | 0 | 60(44.8) | 23(17.2) | 85(63.4) | 20(14.9) |
| 统计值 | χ2=0.172 | χ2=0.172 | χ2=0.088 | χ2=7.409 | χ2=58.559 | χ2=14.306 | χ2=32.398 | χ2=70.142 | ||
| 0.057 | 0.678 | 0.668 | 0.356 | 0.005 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 肺部影像学呈 大叶性肺炎 [例(%)] | 异常心电图 [例(%)] | 异常尿常规 (血尿、蛋白尿) [例(%)] | 白细胞计数 (×109/L) | 中性粒细胞 计数(×109/L) | 血小板计数 (×109/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例组 | 67 | 64(95.5) | 3(4.5) | 10(14.9) | 17.54(6.58,32.44) | 9.56(0.85,25.67) | 94.51(62.47,130.69) | |||||||
| 对照组 | 134 | 52(38.8) | 6(4.5) | 18(13.4) | 13.69(4.85,20.42) | 7.85(0.76,17.44) | 250.35(118.32,480.87) | |||||||
| 统计值 | χ2=58.870 | χ2=0. 130 | χ2=0.080 | |||||||||||
| 0.000 | 0.718 | 0. 773 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 血清铁蛋白 (μg/L) | D-二聚体 (mg/L) | C反应蛋白 (mg/L) | 乳酸脱氢酶 ( U/L) | 谷丙转氨酶 ( U/L) | 白蛋白 (g/L) | ||||||||
| 病例组 | 428.26(108.47,554.62) | 3.14(0.42,6.54) | 52.28(0.50,185.25) | 408.58(190.55,1439) | 48.25(15.32,205.86) | 36.85(26.53,47.27) | ||||||||
| 对照组 | 307.85(80.67,486.43) | 2.33(0.38,4.22) | 16.58(0.50,80.54) | 306.15(154.63,608.21) | 18.54(6.42,68.92) | 41.85(36.0,43.24) | ||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||
| 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 血清钠(mmol/L) | 血清钙(mmol/L) | 总胆红素(μmol/L) | 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 肌酸激酶同工酶( U/L) | |||||||||
| 病例组 | 135.83±2.47 | 2.48±0.21 | 7.28(2.18,36.22) | 1.07(0.17,3.43) | 30.70(6.69,144.69) | |||||||||
| 对照组 | 136.34±2.27 | 2.44±0.17 | 6.61(2.01,25.29) | 1.13(0.15,8.53) | 30.38(0.20,99.69) | |||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||
| 0.150 | 0.165 | 0.096 | 0.101 | 0.105 | ||||||||||
Tab.2 Comparison of clinical data between two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 肺部影像学呈 大叶性肺炎 [例(%)] | 异常心电图 [例(%)] | 异常尿常规 (血尿、蛋白尿) [例(%)] | 白细胞计数 (×109/L) | 中性粒细胞 计数(×109/L) | 血小板计数 (×109/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病例组 | 67 | 64(95.5) | 3(4.5) | 10(14.9) | 17.54(6.58,32.44) | 9.56(0.85,25.67) | 94.51(62.47,130.69) | |||||||
| 对照组 | 134 | 52(38.8) | 6(4.5) | 18(13.4) | 13.69(4.85,20.42) | 7.85(0.76,17.44) | 250.35(118.32,480.87) | |||||||
| 统计值 | χ2=58.870 | χ2=0. 130 | χ2=0.080 | |||||||||||
| 0.000 | 0.718 | 0. 773 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 血清铁蛋白 (μg/L) | D-二聚体 (mg/L) | C反应蛋白 (mg/L) | 乳酸脱氢酶 ( U/L) | 谷丙转氨酶 ( U/L) | 白蛋白 (g/L) | ||||||||
| 病例组 | 428.26(108.47,554.62) | 3.14(0.42,6.54) | 52.28(0.50,185.25) | 408.58(190.55,1439) | 48.25(15.32,205.86) | 36.85(26.53,47.27) | ||||||||
| 对照组 | 307.85(80.67,486.43) | 2.33(0.38,4.22) | 16.58(0.50,80.54) | 306.15(154.63,608.21) | 18.54(6.42,68.92) | 41.85(36.0,43.24) | ||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||
| 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.018 | 0.000 | 0.000 | |||||||||
| 组别 | 血清钠(mmol/L) | 血清钙(mmol/L) | 总胆红素(μmol/L) | 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 肌酸激酶同工酶( U/L) | |||||||||
| 病例组 | 135.83±2.47 | 2.48±0.21 | 7.28(2.18,36.22) | 1.07(0.17,3.43) | 30.70(6.69,144.69) | |||||||||
| 对照组 | 136.34±2.27 | 2.44±0.17 | 6.61(2.01,25.29) | 1.13(0.15,8.53) | 30.38(0.20,99.69) | |||||||||
| 统计值 | ||||||||||||||
| 0.150 | 0.165 | 0.096 | 0.101 | 0.105 | ||||||||||
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 白蛋白下降 | -0.125 | 0.041 | 7.326 | 0.008 | 0.765 | 0.723 | 0.951 |
| 乳酸脱氢酶≥500 U/L | 0.009 | 0.003 | 5.654 | 0.015 | 1.001 | 1.001 | 1.018 |
| 热峰≥40 ℃ | 2.953 | 1.032 | 8.095 | 0.003 | 19.364 | 2.507 | 149.071 |
| 影像学呈大叶性肺炎 | 3.380 | 1.213 | 7.663 | 0.005 | 29.673 | 2.685 | 326.841 |
| 血小板计数下降 | -0.408 | 0.130 | 8.804 | 0.002 | 0.646 | 0.487 | 0.856 |
Tab.3 Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for RMPP
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 白蛋白下降 | -0.125 | 0.041 | 7.326 | 0.008 | 0.765 | 0.723 | 0.951 |
| 乳酸脱氢酶≥500 U/L | 0.009 | 0.003 | 5.654 | 0.015 | 1.001 | 1.001 | 1.018 |
| 热峰≥40 ℃ | 2.953 | 1.032 | 8.095 | 0.003 | 19.364 | 2.507 | 149.071 |
| 影像学呈大叶性肺炎 | 3.380 | 1.213 | 7.663 | 0.005 | 29.673 | 2.685 | 326.841 |
| 血小板计数下降 | -0.408 | 0.130 | 8.804 | 0.002 | 0.646 | 0.487 | 0.856 |
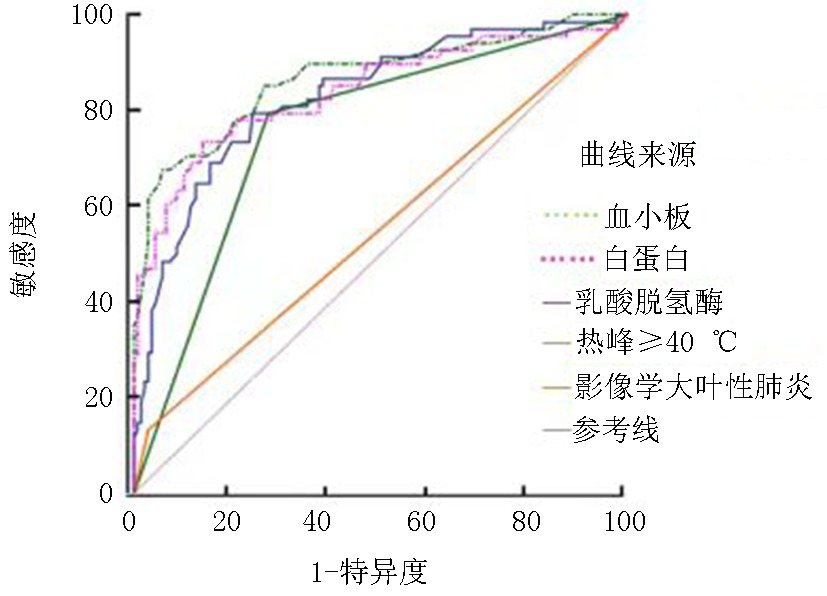
| 变量 | 曲线下 面积 | 标准误 | 界值 | 95% | 敏感度 (%) | 特异度 (%) | 约登指数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| 白蛋白下降 | 0.765 | 0.028 | <40 g/L | <0.01 | 0.803 | 0.901 | 67.64 | 94.13 | 0.620 |
| 乳酸脱氢酶≥500 U/L | 0.753 | 0.032 | ≥500 U/L | <0.01 | 0.772 | 0.877 | 73.42 | 86.01 | 0.590 |
| 热峰≥40 ℃ | 0.750 | 0.030 | - | <0.01 | 0.685 | 0.807 | 79.31 | 72.38 | 0.520 |
| 血小板计数下降 | 0.821 | 0.030 | <120×109/L | <0.01 | 0.761 | 0.868 | 79.32 | 75.63 | 0.550 |
| 影像学呈大叶性肺炎 | 0.541 | 0.021 | - | 0.019 | 0.469 | 0.611 | 13.13 | 97.15 | 0.100 |
Tab.4 Predictive potentials of risk factors for RMPP
| 变量 | 曲线下 面积 | 标准误 | 界值 | 95% | 敏感度 (%) | 特异度 (%) | 约登指数 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||||
| 白蛋白下降 | 0.765 | 0.028 | <40 g/L | <0.01 | 0.803 | 0.901 | 67.64 | 94.13 | 0.620 |
| 乳酸脱氢酶≥500 U/L | 0.753 | 0.032 | ≥500 U/L | <0.01 | 0.772 | 0.877 | 73.42 | 86.01 | 0.590 |
| 热峰≥40 ℃ | 0.750 | 0.030 | - | <0.01 | 0.685 | 0.807 | 79.31 | 72.38 | 0.520 |
| 血小板计数下降 | 0.821 | 0.030 | <120×109/L | <0.01 | 0.761 | 0.868 | 79.32 | 75.63 | 0.550 |
| 影像学呈大叶性肺炎 | 0.541 | 0.021 | - | 0.019 | 0.469 | 0.611 | 13.13 | 97.15 | 0.100 |
| [1] | Guo DX, Hu WJ, Wei R, et al. Epidemiology and mechanism of drug resistance of in Beijing, China: A multicenter study[J]. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2019, 19(3): 288-296. |
| [2] | Søndergaard MJ, Friis MB, Hansen DS, et al. Clinical manifestations in infants and children with Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(4): e0195288. |
| [3] |
Liu JR, Lu J, Dong F, et al. Low bacterial co-infection invalidates the early use of non-anti-Mycoplasma pneumoniae antibiotics in pediatric refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia patients[J]. Front Pediatr, 2018, 6(3): 296.
doi: 10.3389/fped.2018.00296 URL |
| [4] | 刘建华, 刘金荣, 唐晓蕾, 等. 难治性肺炎支原体肺炎患儿遗留闭塞性支气管炎的预测因素分析[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2023, 61(4):317-321. |
| [5] | 蓝引乐, 杨德华, 陈志敏, 等. 甲泼尼龙治疗儿童难治性肺炎支原体肺炎的效果及患儿肺泡灌洗细胞因子变化[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2015, 53(10):779-783. |
| [6] | 张大炜, 李鑫, 孙桂凤. 2021年成都地区肺炎支原体感染流行病学分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3):237-240. |
| [7] | 周鹏, 周旭, 张葆清. 儿童难治性支原体肺炎发病机制研究进[J]. 山东医药, 2016, 56(42):103-105. |
| [8] | 陈钦, 王程毅, 刘光华, 等. 110例儿童重症肺炎支原体肺炎临床特点分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2017, 32(6):503-506. |
| [9] | 农光民. 肺炎支原体肺炎临床及影像学特点[J]. 中国实用儿科杂志, 2015, 30(3):173-176. |
| [10] | 邹映雪. 肺炎支原体肺炎炎症指标异常的临床意义[J]. 中华实用儿科临床杂志, 2021, 36(16):1209-1214. |
| [11] | 赵顺英, 钱素云, 陈志敏, 等. 儿童肺炎支原体肺炎诊疗指南.2023年版[J]. 国际流行病学传染病学杂志, 2023, 50(2):79-85. |
| [12] | 郑雪香, 林继雷, 代继宏, 等. 基于决策曲线和剂量反应分析评估乳酸脱氢酶对儿童难治性肺炎支原体肺炎的预测价值[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2020, 22(2):112-117. |
| [13] |
Lee E, Lee YY. Predictive factors of the responses to treatmengt of Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(6): 1154.
doi: 10.3390/jcm10061154 URL |
| [14] | 郭轲, 张瑜, 陈若才, 等. 血小板参数、CRP、LHD联合影像学表现在儿童难治性支原体肺炎诊断和预后中的价值研究[J]. 湖南师范大学学报(医学版), 2020, 17(5):179-182. |
| [15] | 江载芳, 申昆玲, 沈颖, 等. 诸福棠实用儿科学[M]. 第8版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2015:1896-1897. |
| [16] | 贺宇杉, 杨梅, 钱素云, 等. 细胞因子对难治性肺炎支原体肺炎的预测作用[J]. 中华儿科杂志, 2021, 59(5):422-425. |
| [17] | 程婷婷, 齐彩英, 张雪莲, 等. 重症肺炎支原体肺炎与血清IgE和C反应蛋白水平的相关性及临床特点[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5):433-437. |
| [18] | 尹延凤, 雷飞飞, 张刚, 等. 血清蛋白成分及炎性细胞因子与支原体肺炎患儿病情严重程度的相关性研究[J]. 实用预防医学, 2019, 5(26):528-531. |
| [1] | Liu Lili, Yuan Yuting, Lai Gengliang, Tian Chuan, Lan Xiang, Ye Zhonglv. The relationship between minimal residual disease on day 15 and prognosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 47-52. |
| [2] | Wei Zeng, Cao Ling, She Dunmin, Liu Yan, Wang Yan, Zhang Zhenwen. The causes of death in 54 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(9): 806-812. |
| [3] | Wu Weijun, Chen Xiao, Wang Shaodan, Bu Laijun, Wu Xinchao, Yan Chenyang, Dong Gaiqin, Jiang Lijun, Wei Wenping. Analysis of screening data of urinalysis in 1973 students in Yangzhou [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 702-705. |
| [4] | Chen Congshui, Li Yuan, Chen Shufang. Concerning the diagnosis and integrated Chinese and Western medicine treatment of acute biliary pancreatitis in children: A case report [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 726-730. |
| [5] | Sun Xingxing, Lin Hai. Changes in immune function and prognostic risk factors for severe pneumonia in children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 521-525. |
| [6] | Xiao Meng, Cheng Tingting, Ma Qiange, Feng Xiaoying, Li Lihua, Li Tao. Clinical characteristics and laboratory examination of Epstein-Barr virus infection and infectious mononucleosis in Chengde [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 526-531. |
| [7] | Song Jinfang, Song Hang, Song Shiyi, Tian Xin. Childhood eosinophilic gastroenteritis with multiple serous cavity effusion: A case report and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(6): 544-549. |
| [8] | Wang Yingnan, Zhao Qi, Bai Haiwei, Wu Danna, Wei Jinmei, Li Shengjiang, Li Ruiling, Zhang Ruixing. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of gastric cancer-related stroke [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 417-422. |
| [9] | Ma Mingfu, Wei Zhiguo, He Tieying. Meta-analysis of risk factors for pancreatic pseudocyst in acute pancreatitis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [10] | Leng Wantong, Tao Jie. Risk factors of postoperative venous thromboembolism in patients with multiple myeloma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(4): 340-345. |
| [11] | Ma Hongli, Lu Hao, Wang Dan, Jiao Haixing, Li Yike, Li Siyu, Lu Jing. Meta-analysis of disability risk factors in stroke patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| [12] | Du Jiayi, Liu Lili, He Yongzhong, Tian Chuan, Lan Xiang, Ye Zhonglyu. Clinical observation of serious adverse events in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia during chemotherapy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 149-154. |
| [13] | Liang Bingsong, Li Yuying, Zhang Qiping, Chen Yingdao, Li jian. Analysis of factors affecting clinical efficacy of Tirofiban in treating branch atheromatous disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(12): 1091-1094. |
| [14] | Wang Siyuan, Wang Li, Wen Xinran, Li Xiaoqing. Multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2(SARS-CoV-2) infection: Two cases report and literature review [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(12): 1112-1116. |
| [15] | Ding Siqi, Liu Shihua, Zhang Chao, Zhong Ping, Cao Li. Risk factors for epilepsy after delayed post-stroke epilepsy and its clinical correlation with blood Hcy, hs-CRP and D-D [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(10): 893-897. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||