Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 989-992.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.11.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Monitoring of blood concentrations of isoniazid and rifampicin in different dosage forms
Wang Lin1, Wan Rong1, Liu Sha1, Liu lei2, He Jing1, Tang Libin1, Li Mingwu1( )
)
- 1. Second Department of Tuberculosis,Kunming Third People's Hospital,Kunming 650041,China
2. School of Public Health,Dali University,Dali 671003,China
-
Received:2024-04-15Online:2024-11-20Published:2024-12-04 -
Contact:Li Mingwu E-mail:ynkmlmw@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Lin, Wan Rong, Liu Sha, Liu lei, He Jing, Tang Libin, Li Mingwu. Monitoring of blood concentrations of isoniazid and rifampicin in different dosage forms[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(11): 989-992.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.11.005
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | BMI (kg/m2) | 性别[例(%)] | 治疗史[例(%)] | 结核菌培养[例(%)] | 病灶[例(%)] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 初治 | 复治 | 阳性 | 阴性 | 空洞 | 浸润 | 粟粒 | |||||||
| 口服组 | 59 | 42.7±13.5 | 23.0±3.6 | 35(59.3) | 24(40.7) | 48(81.4) | 11(18.6) | 22(37.3) | 37(62.7) | 7(11.9) | 49(83.1) | 3(5.0) | |||
| 注射组 | 64 | 43.2±13.3 | 22.5±1.8 | 41(64.1) | 23(35.9) | 55(85.9) | 9(14.1) | 20(31.3) | 44(68.7) | 9(14.1) | 49(76.6) | 6(9.3) | |||
| 0.184 | -0.980 | 2.246 | 0.526 | 0.234 | 0.339 | 0.587 | 0.324 | 1.097 | 0.790 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.854 | 0.329 | 0.134 | 0.468 | 0.629 | 0.561 | 0.444 | 0.569 | 0.295 | 0.374 | |||||
Tab.1 General information between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | BMI (kg/m2) | 性别[例(%)] | 治疗史[例(%)] | 结核菌培养[例(%)] | 病灶[例(%)] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | 初治 | 复治 | 阳性 | 阴性 | 空洞 | 浸润 | 粟粒 | |||||||
| 口服组 | 59 | 42.7±13.5 | 23.0±3.6 | 35(59.3) | 24(40.7) | 48(81.4) | 11(18.6) | 22(37.3) | 37(62.7) | 7(11.9) | 49(83.1) | 3(5.0) | |||
| 注射组 | 64 | 43.2±13.3 | 22.5±1.8 | 41(64.1) | 23(35.9) | 55(85.9) | 9(14.1) | 20(31.3) | 44(68.7) | 9(14.1) | 49(76.6) | 6(9.3) | |||
| 0.184 | -0.980 | 2.246 | 0.526 | 0.234 | 0.339 | 0.587 | 0.324 | 1.097 | 0.790 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.854 | 0.329 | 0.134 | 0.468 | 0.629 | 0.561 | 0.444 | 0.569 | 0.295 | 0.374 | |||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 用药2 h后 | 用药24 h后 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INH(mg/L) | RFP(mg/L) | INH(mg/L) | RFP(mg/L) | |||
| 口服组 | 59 | 2.18(1.47, 3.77) | 21.34(5.97, 38.64) | 1.40(0.86, 3.17) | 3.07(1.85, 9.49) | |
| 注射组 | 64 | 2.21(1.10, 4.52) | 47.95(33.49, 80.16) | 1.28(0.93, 2.51) | 5.26(1.89, 10.84) | |
| -0.013 | -5.501 | -0.856 | -0.330 | |||
| P值 | 0.990 | <0.001 | 0.392 | 0.741 | ||
Tab.2 The blood concentrations of INH and RFP at 2 hours and 24 hours of medication on the 7th day of treatment between groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 用药2 h后 | 用药24 h后 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| INH(mg/L) | RFP(mg/L) | INH(mg/L) | RFP(mg/L) | |||
| 口服组 | 59 | 2.18(1.47, 3.77) | 21.34(5.97, 38.64) | 1.40(0.86, 3.17) | 3.07(1.85, 9.49) | |
| 注射组 | 64 | 2.21(1.10, 4.52) | 47.95(33.49, 80.16) | 1.28(0.93, 2.51) | 5.26(1.89, 10.84) | |
| -0.013 | -5.501 | -0.856 | -0.330 | |||
| P值 | 0.990 | <0.001 | 0.392 | 0.741 | ||
| 组别 | 例数 | INH[例(%)] | RFP[例(%)] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <3 mg/L | 3~6 mg/L | >6 mg/L | <8 mg/L | 8~24 mg/L | >24 mg/L | |||
| 口服组 | 59 | 38(64.4) | 15(25.4) | 6(10.2) | 17(28.8) | 19(32.2) | 23(39.0) | |
| 注射组 | 64 | 41(64.1) | 17(26.6) | 6(9.3) | 5(7.8) | 3(4.7) | 56(87.5) | |
| χ2值 | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 9.219 | 15.825 | 31.452 | ||
| P值 | 0.968 | 0.886 | 0.882 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
Tab.3 The blood concentrations of INH and RFP in different dosage forms at 2 hours of medication on the 7th day of treatment
| 组别 | 例数 | INH[例(%)] | RFP[例(%)] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <3 mg/L | 3~6 mg/L | >6 mg/L | <8 mg/L | 8~24 mg/L | >24 mg/L | |||
| 口服组 | 59 | 38(64.4) | 15(25.4) | 6(10.2) | 17(28.8) | 19(32.2) | 23(39.0) | |
| 注射组 | 64 | 41(64.1) | 17(26.6) | 6(9.3) | 5(7.8) | 3(4.7) | 56(87.5) | |
| χ2值 | 0.002 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 9.219 | 15.825 | 31.452 | ||
| P值 | 0.968 | 0.886 | 0.882 | 0.002 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||
| 组别 | 例数 | 用药2 h后达目标浓度[例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| INH | RFP | ||
| 口服组 | 59 | 21(35.6) | 42(71.2) |
| 注射组 | 64 | 23(35.9) | 59(92.2) |
| χ2值 | 0.002 | 9.219 | |
| P值 | 0.968 | 0.002 | |
Tab.4 INH and RFP reaching target concentration after 2 hours of medication on the 7th day of treatment
| 组别 | 例数 | 用药2 h后达目标浓度[例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| INH | RFP | ||
| 口服组 | 59 | 21(35.6) | 42(71.2) |
| 注射组 | 64 | 23(35.9) | 59(92.2) |
| χ2值 | 0.002 | 9.219 | |
| P值 | 0.968 | 0.002 | |
| 自变量 | 偏回归系数 | 标准误 | 标准化偏 回归系数 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
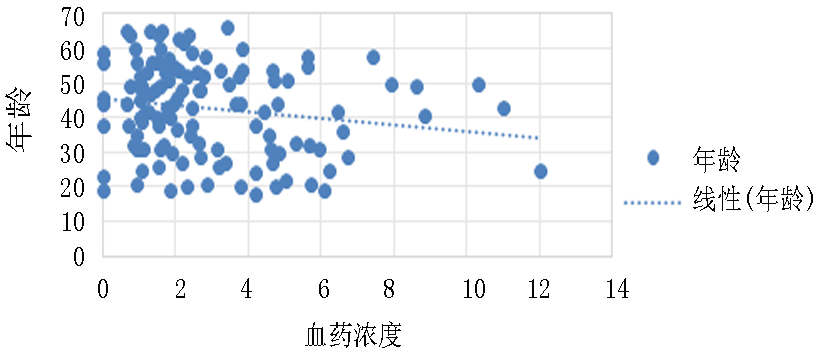
| 年龄 | -0.043 | 0.063 | -0.176 | -2.788 | 0.006 |
Tab.5 Multiple linear regression analysis results
| 自变量 | 偏回归系数 | 标准误 | 标准化偏 回归系数 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -0.043 | 0.063 | -0.176 | -2.788 | 0.006 |
| [1] | World Health Organization. Global tuberculosis report 2023[EB/OL].[2023-11-07]. https://www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/globaltuberculosis-report-2023. |
| [2] | 李亮, 李琦, 许绍发, 等. 结核病治疗学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013:22-30. |
| [3] | Alsultan A, Peloquin CA. Therapeutic drug monitoring in the treatment of tuberculosis:An update[J]. Drugs, 2014, 74(8):839-854. |
| [4] | 王黎霞, 成诗明, 周林, 等. 中华人民共和国卫生行业标准肺结核诊断: WS 288-2017[J]. 中国感染控制杂志, 2018, 17(7):642-652. |
| [5] | 国卫办疾控函[2020]279号. 中国结核病预防控制工作技术规范(2020版)[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会办公厅,2020-04-02. |
| [6] | 李明武, 赖明红, 马萌, 等. 不同剂型利福平投药后血药浓度的监测结果分析[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2019, 41(6):645-649. |
| [7] | 李明武, 万荣, 朱惠琼, 等. 不同剂型异烟肼血药浓度监测结果分析[J]. 中华临床医师杂志(电子版), 2019, 13(6):440-443. |
| [8] | 张亮, 钱智磊, 陆磊, 等. 同时测定血浆 INH、AcINH、RFP 和 PZA 的高效液相色谱法建立及其在肺结核患者中的应用[J]. 山东医药, 2015, (48):23-26. |
| [9] | 钱智磊, 张亮, 周秋云, 等. HPLC 法测定结核病患者血浆中异烟肼、吡嗪酰胺、利福平和左氧氟沙星的质量浓度[J]. 西北药学杂志, 2014, 29(6):578-581. |
| [10] | 焉学英, 张酉生. 利福平注射液治疗初治肺结核强化期疗效观察[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2011, 16(7):1119-1120. |
| [11] | 龚惠莉. 利福平注射液比较利福平胶囊治疗初治空洞型肺结核疗效分析[J]. 现代预防医学, 2012, 39(2):498-499. |
| [12] | 朱春梅. 利福平注射液与利福平胶囊治疗初治空洞型肺结核疗效分析[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2011, 16(2):219+222. |
| [13] | 李明武, 马萌, 张瑞雨, 等. 异烟肼、 利福平不同剂型对肺结核病患者的临床疗效[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2019, 40(1):105-108. |
| [14] | 张艳. 利福平治疗肺结核的血药浓度监测及对患者免疫功能的影响分析[J]. 贵州医药, 2020, 44(4):560-562. |
| [15] | 郭少晨, 朱慧, 郭超, 等. 909例结核病患者一线抗结核药物血药浓度监测结果分析[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2018, 40(7):744-749. |
| [16] | 张冰, 西娜, 陈明, 等. 274例结核病患者抗结核药物血药浓度分析及其药物安全性探究[J]. 中国药物应用与监测, 2023, 20(2):90-94. |
| [17] | 周俊, 吕小会, 刘元, 等. 三种抗结核药物血药浓度在个体及药物间的差异研究[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2017, 39(5):482-487. |
| [18] | 孙晓方, 严文, 任斐, 等. 442例异烟肼血药浓度监测结果分析[J]. 中国防痨杂志, 2015, 37(11):1136-1140. |
| [19] | 孙学智, 石丽稳, 赵丽, 等. 糖尿病对异烟肼和利福平血药浓度的影响[J]. 武汉大学学报(医学版), 2023, 44(6):764-767. |
| [20] | 张亮, 冯枭, 林霏申, 等. 异烟肼血药浓度的影响因素分析[J]. 药学与临床研究, 2018, 26(6):413-416. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||