

临床荟萃 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 425-431.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.05.008
李文哲, 商进春, 李春梅, 李君, 田芬, 崔莉, 陈怿鹏, 张小凡, 邢广群( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-24
出版日期:2021-05-20
发布日期:2021-06-09
通讯作者:
邢广群
E-mail:gqx99monash@163.com
基金资助:
Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Li Jun, Tian Fen, Cui Li, Chen Yipeng, Zhang Xiaofan, Xing Guangqun( )
)
Received:2021-03-24
Online:2021-05-20
Published:2021-06-09
Contact:
Xing Guangqun
E-mail:gqx99monash@163.com
摘要:
目的 探讨枸橼酸钠抗凝连续性肾脏替代治疗(continuous renal replacement therapy, CRRT)在救治尿毒症脑出血患者中的优势。方法 2012年1月至2020年6月尿毒症脑出血患者44例,根据抗凝方式分为枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组(n=17)和无肝素CRRT组(n=27),比较两组生存率及各指标之间的差异;根据结局事件分为生存组(n=34)和死亡组(n=10),比较、分析枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT在救治尿毒症脑出血患者中的价值。结果 经过枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT治疗的脑出血患者生存率为100.0%,而经过无肝素CRRT治疗的患者生存率为63.0%(χ2=8.148,P=0.004)。两组在血清钠、钙、钾、血小板计数、白细胞计数、C反应蛋白(CRP)、D-二聚体、甘油三酯方面差异有统计学意义。生存组B型钠尿肽、钙、CRP、D-二聚体、磷、白细胞计数较死亡组显著减低,而血清白蛋白、钠、血小板计数较死亡组显著升高。结论 尿毒症患者脑出血发生后,枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT治疗具有比无肝素CRRT治疗更为明显的优势,既能保证充分血液透析,又能改善尿毒症脑出血患者的低血钠、高血钙,减轻炎症状态,保证救治成功率。
中图分类号:
李文哲, 商进春, 李春梅, 李君, 田芬, 崔莉, 陈怿鹏, 张小凡, 邢广群. 枸橼酸钠抗凝连续性肾脏替代治疗救治尿毒症脑出血患者的优势[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(5): 425-431.
Li Wenzhe, Shang Jinchun, Li Chunmei, Li Jun, Tian Fen, Cui Li, Chen Yipeng, Zhang Xiaofan, Xing Guangqun. Effect of sodium citrate anticoagulation in continuous renal replacement therapy on uremic patients with cerebral hemorrhage[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(5): 425-431.
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄(岁) | 既往高血压 病史 [例(%)] | 既往糖尿 病史 [例(%)] | 既往脑血管 病史 [例(%)] | 既往多囊肾 病史 [例(%)] | 脑出血前常规 血液透析使用 肝素/低分子 肝素[例(%)] | 日常使用 华法林 [例(%)] | 日常使用 阿司匹林 [例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 6(35.2) | 55.31±12.24 | 15(88.2) | 6(35.3) | 12(70.6) | 2(11.8) | 17(100) | 7(41.2) | 4(23.5) |
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 15(55.6) | 12(44.4) | 55.15±13.62 | 26(96.3) | 17(63.0) | 20(74.1) | 2(7.4) | 27(100) | 11(40.7) | 8(29.6) |
| 统计值 | χ2= 0.361 | t=-0.040 | χ2=1.067 | χ2=3.201 | χ2=0.064 | χ2=0.202 | χ2=0.000 | χ2=0.001 | χ2=0.196 | ||
| P值 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||
表1 两组一般资料比较
| 组别 | 例数 | 性别[例(%)] | 年龄(岁) | 既往高血压 病史 [例(%)] | 既往糖尿 病史 [例(%)] | 既往脑血管 病史 [例(%)] | 既往多囊肾 病史 [例(%)] | 脑出血前常规 血液透析使用 肝素/低分子 肝素[例(%)] | 日常使用 华法林 [例(%)] | 日常使用 阿司匹林 [例(%)] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 男 | 女 | ||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 11(64.7) | 6(35.2) | 55.31±12.24 | 15(88.2) | 6(35.3) | 12(70.6) | 2(11.8) | 17(100) | 7(41.2) | 4(23.5) |
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 15(55.6) | 12(44.4) | 55.15±13.62 | 26(96.3) | 17(63.0) | 20(74.1) | 2(7.4) | 27(100) | 11(40.7) | 8(29.6) |
| 统计值 | χ2= 0.361 | t=-0.040 | χ2=1.067 | χ2=3.201 | χ2=0.064 | χ2=0.202 | χ2=0.000 | χ2=0.001 | χ2=0.196 | ||
| P值 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | >0.05 | ||
| 项目 | 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组(n=17) | 无肝素CRRT组(n=27) | Z值/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出血量(ml) | 31.690(15.549,39.061) | 17.298(6.756,51.687) | -0.845 | 0.398 |
| 格拉斯哥评分(分) | 10.000(4.000,15.000) | 10.000(3.750,13.250) | -0.328 | 0.743 |
| 破入脑室[例(%)] | 3(6.8) | 2(4.6) | 1.086 | 0.297 |
| 脑出血部位[例(%)] | 4.475 | 0.929 | ||
| 基底节区 | 4(23.5) | 8(29.6) | 0.196 | 0.658 |
| 额顶颞枕叶 | 4(23.5) | 7(25.9) | 0.032 | 0.858 |
| 蛛网膜下腔 | 3(17.6) | 3(11.1) | 0.378 | 0.538 |
| 脑干 | 1(5.9) | 4(14.8) | 0.826 | 0.363 |
| 丘脑 | 2(11.8) | 2(7.4) | 0.240 | 0624 |
| 放射冠区 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.736 |
| 小脑 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.735 |
| 硬膜下血肿 | 0 | 1(3.7) | 0.644 | 0.422 |
| 脑室旁 | 1(5.9) | 0 | 1.625 | 0.202 |
表2 两组出血量、GCS及破入脑室比较
| 项目 | 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组(n=17) | 无肝素CRRT组(n=27) | Z值/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 出血量(ml) | 31.690(15.549,39.061) | 17.298(6.756,51.687) | -0.845 | 0.398 |
| 格拉斯哥评分(分) | 10.000(4.000,15.000) | 10.000(3.750,13.250) | -0.328 | 0.743 |
| 破入脑室[例(%)] | 3(6.8) | 2(4.6) | 1.086 | 0.297 |
| 脑出血部位[例(%)] | 4.475 | 0.929 | ||
| 基底节区 | 4(23.5) | 8(29.6) | 0.196 | 0.658 |
| 额顶颞枕叶 | 4(23.5) | 7(25.9) | 0.032 | 0.858 |
| 蛛网膜下腔 | 3(17.6) | 3(11.1) | 0.378 | 0.538 |
| 脑干 | 1(5.9) | 4(14.8) | 0.826 | 0.363 |
| 丘脑 | 2(11.8) | 2(7.4) | 0.240 | 0624 |
| 放射冠区 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.736 |
| 小脑 | 1(5.9) | 1(3.7) | 0.114 | 0.735 |
| 硬膜下血肿 | 0 | 1(3.7) | 0.644 | 0.422 |
| 脑室旁 | 1(5.9) | 0 | 1.625 | 0.202 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 钠(mmol/L) | 钙(mmol/L) | 磷(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 135.725±6.064 | 141.289±3.382 | 2.217±0.218 | 2.155±0.219 | 1.460(1.345, 2.315) | 1.745(1.485, 2.103) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 138.548±4.678 | 138.415±4.061 | 2.082±0.293 | 2.438±0.296 | 1.560(1.320, 2.230) | 1.960(1.530, 2.420) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-1.712 | t=2.466 | t=0.163 | t=-3.603 | Z=-0.274 | Z=-1.299 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.095 | 0.018 | 0.103 | 0.001 | 0.784 | 0.194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 钾(mmol/L) | 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 尿素氮(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 4.908±0.987 | 4.327±0.507 | 821.050±337.104 | 570.378±186.234 | 25.205(16.800, 34.013) | 21.310(14.590,28.183) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 4.706±0.703 | 4.771±0.643 | 635.562±309.111 | 698.715±337.762 | 22.560(15.815, 36.775) | 21.135(17.460,33.510) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.756 | t=-2.445 | t=1.793 | t=-1.462 | Z=-0.428 | Z=-1.098 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.454 | 0.019 | 0.081 | 0.151 | 0.669 | 0.272 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | ALT(U/L) | AST(U/L) | 白蛋白(g/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 16.119±2.611 | 20.069±2.362 | 13.300(9.350, 15.700) | 15.750(12.275,23.923) | 35.994±5.104 | 35.006±4.868 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 14.676±1.484 | 24.402±4.285 | 15.200(11.650, 21.625) | 18.700(12.150,25.375) | 32.610±6.642 | 31.339±7.922 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=0.516 | t=-0.784 | Z=-1.657 | Z=-0.418 | t=1.724 | t=1.899 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.609 | 0.437 | 0.098 | 0.676 | 0.093 | 0.065 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 总蛋白(g/L) | 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 60.150(53.550, 67.050) | 60.500(57.675,64.025) | 2.270±0.439 | 1.391±0.604 | 4.080(3.533, 4.258) | 4.110(3.223,5.193) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 61.215(52.325, 67.775) | 62.550(58.300,69.200) | 2.480±0.338 | 2.215±1.060 | 4.585(3.743, 5.335) | 3.990(3.775,4.380) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=0.041 | Z=-1.386 | t=-0.382 | t=-3.206 | Z=0.594 | Z=-0.084 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.967 | 0.166 | 0.704 | 0.003 | 0.553 | 0.993 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | LDL-C(mmol/L) | HDL-C(mmol/L) | 血糖(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 2.501±0.717 | 2.632±0.873 | 1.160(0.890, 1.283) | 1.120(0.890,1.535) | 5.660(4.415, 8.783) | 7.755(4.790,10.190) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 2.658±1.028 | 2.523±0.824 | 1.180(1.010, 1.280) | 1.085(0.943,1.275) | 6.010(5.183, 7.795) | 6.340(5.323,8.295) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.530 | t=0.415 | Z=-0.360 | Z=-0.842 | Z=-0.152 | Z=-0.776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.599 | 0.680 | 0.719 | 0.400 | 0.879 | 0.438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | DD(μg/L) | CRP(mg/L) | 白细胞计数(×109/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 580.000 (265.000, 1180.000) | 450.000 (317.500,542.500) | 6.430 (2.245, 19.760) | 2.030 (0.500,7.750) | 6.010 (5.285, 8.960) | 5.975 (4.513,7.308) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 850.000 (530.000, 1222.000) | 845.000 (405.000,1360.000) | 9.670 (1.770, 38.270) | 14.920 (1.323,41.463) | 7.895 (6.248, 10.095) | 7.410 (6.633,8.623) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-1.290 | Z=-2.244 | Z=-0.145 | Z=-2.784 | Z=-1.354 | Z=-2.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.197 | 0.025 | 0.885 | 0.005 | 0.176 | 0.021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 血小板计数(×109/L) | 血红蛋白(g/L) | 尿酸(μmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 170.130±60.650 | 193.00±59.754 | 100.310±22.123 | 97.940±18.580 | 414.944±102.891 | 362.513±98.781 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 183.540±71.768 | 148.92±63.082 | 97.580±23.204 | 91.310±21.346 | 397.808±118.975 | 384.042±165.014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.615 | t=2.292 | t=0.371 | t=1.068 | t=0.470 | t=-0.515 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.542 | 0.027 | 0.713 | 0.292 | 0.641 | 0.609 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PTH(pmol/L) | BNP(pg/ml) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 204.350(90.005, 281.625) | 210.650(148.475,519.975) | 1454.850(393.600, 3978.750) | 265.200(102.475, 627.600) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 199.100(137.200, 334.500) | 195.960(118.300,526.400) | 375.050(144, 325, 804.325) | 617.300(195.400, 930.900) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-0.675 | Z=-0.605 | Z=-2.620 | Z=-1.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.511 | 0.545 | 0.009 | 0.189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
表3 两组实验室指标比较
| 组别 | 例数 | 钠(mmol/L) | 钙(mmol/L) | 磷(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 135.725±6.064 | 141.289±3.382 | 2.217±0.218 | 2.155±0.219 | 1.460(1.345, 2.315) | 1.745(1.485, 2.103) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 138.548±4.678 | 138.415±4.061 | 2.082±0.293 | 2.438±0.296 | 1.560(1.320, 2.230) | 1.960(1.530, 2.420) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-1.712 | t=2.466 | t=0.163 | t=-3.603 | Z=-0.274 | Z=-1.299 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.095 | 0.018 | 0.103 | 0.001 | 0.784 | 0.194 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 钾(mmol/L) | 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 尿素氮(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 4.908±0.987 | 4.327±0.507 | 821.050±337.104 | 570.378±186.234 | 25.205(16.800, 34.013) | 21.310(14.590,28.183) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 4.706±0.703 | 4.771±0.643 | 635.562±309.111 | 698.715±337.762 | 22.560(15.815, 36.775) | 21.135(17.460,33.510) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.756 | t=-2.445 | t=1.793 | t=-1.462 | Z=-0.428 | Z=-1.098 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.454 | 0.019 | 0.081 | 0.151 | 0.669 | 0.272 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | ALT(U/L) | AST(U/L) | 白蛋白(g/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 16.119±2.611 | 20.069±2.362 | 13.300(9.350, 15.700) | 15.750(12.275,23.923) | 35.994±5.104 | 35.006±4.868 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 14.676±1.484 | 24.402±4.285 | 15.200(11.650, 21.625) | 18.700(12.150,25.375) | 32.610±6.642 | 31.339±7.922 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=0.516 | t=-0.784 | Z=-1.657 | Z=-0.418 | t=1.724 | t=1.899 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.609 | 0.437 | 0.098 | 0.676 | 0.093 | 0.065 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 总蛋白(g/L) | 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 60.150(53.550, 67.050) | 60.500(57.675,64.025) | 2.270±0.439 | 1.391±0.604 | 4.080(3.533, 4.258) | 4.110(3.223,5.193) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 61.215(52.325, 67.775) | 62.550(58.300,69.200) | 2.480±0.338 | 2.215±1.060 | 4.585(3.743, 5.335) | 3.990(3.775,4.380) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=0.041 | Z=-1.386 | t=-0.382 | t=-3.206 | Z=0.594 | Z=-0.084 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.967 | 0.166 | 0.704 | 0.003 | 0.553 | 0.993 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | LDL-C(mmol/L) | HDL-C(mmol/L) | 血糖(mmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 2.501±0.717 | 2.632±0.873 | 1.160(0.890, 1.283) | 1.120(0.890,1.535) | 5.660(4.415, 8.783) | 7.755(4.790,10.190) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 2.658±1.028 | 2.523±0.824 | 1.180(1.010, 1.280) | 1.085(0.943,1.275) | 6.010(5.183, 7.795) | 6.340(5.323,8.295) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.530 | t=0.415 | Z=-0.360 | Z=-0.842 | Z=-0.152 | Z=-0.776 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.599 | 0.680 | 0.719 | 0.400 | 0.879 | 0.438 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | DD(μg/L) | CRP(mg/L) | 白细胞计数(×109/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 580.000 (265.000, 1180.000) | 450.000 (317.500,542.500) | 6.430 (2.245, 19.760) | 2.030 (0.500,7.750) | 6.010 (5.285, 8.960) | 5.975 (4.513,7.308) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 850.000 (530.000, 1222.000) | 845.000 (405.000,1360.000) | 9.670 (1.770, 38.270) | 14.920 (1.323,41.463) | 7.895 (6.248, 10.095) | 7.410 (6.633,8.623) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-1.290 | Z=-2.244 | Z=-0.145 | Z=-2.784 | Z=-1.354 | Z=-2.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.197 | 0.025 | 0.885 | 0.005 | 0.176 | 0.021 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | 血小板计数(×109/L) | 血红蛋白(g/L) | 尿酸(μmol/L) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 170.130±60.650 | 193.00±59.754 | 100.310±22.123 | 97.940±18.580 | 414.944±102.891 | 362.513±98.781 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 183.540±71.768 | 148.92±63.082 | 97.580±23.204 | 91.310±21.346 | 397.808±118.975 | 384.042±165.014 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | t=-0.615 | t=2.292 | t=0.371 | t=1.068 | t=0.470 | t=-0.515 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.542 | 0.027 | 0.713 | 0.292 | 0.641 | 0.609 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PTH(pmol/L) | BNP(pg/ml) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 治疗前 | 治疗后 | 治疗前 | 治疗后 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT组 | 17 | 204.350(90.005, 281.625) | 210.650(148.475,519.975) | 1454.850(393.600, 3978.750) | 265.200(102.475, 627.600) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 无肝素CRRT组 | 27 | 199.100(137.200, 334.500) | 195.960(118.300,526.400) | 375.050(144, 325, 804.325) | 617.300(195.400, 930.900) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 统计值 | Z=-0.675 | Z=-0.605 | Z=-2.620 | Z=-1.313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| P值 | 0.511 | 0.545 | 0.009 | 0.189 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
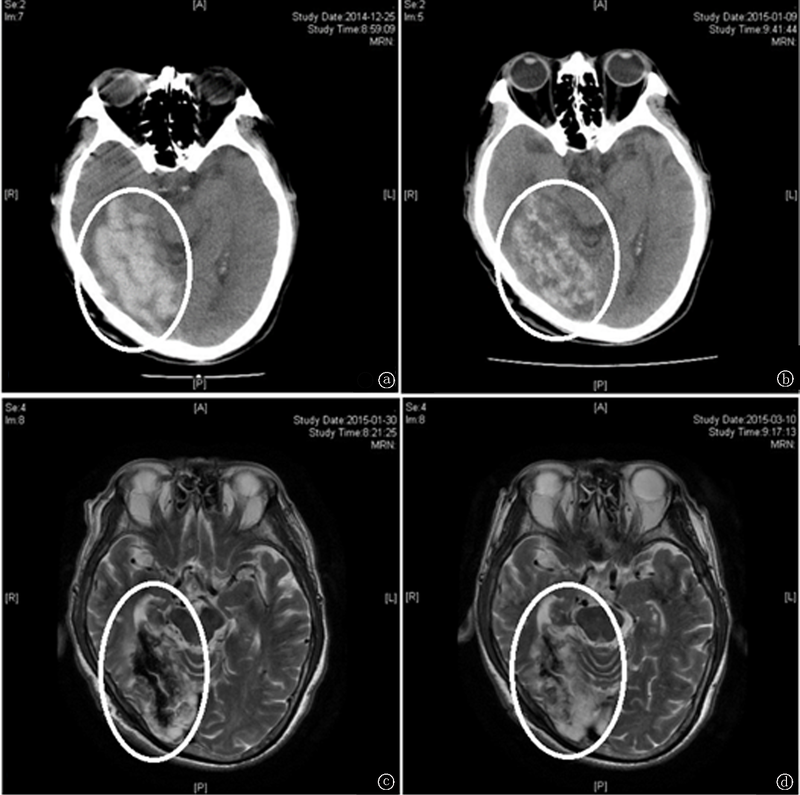
图2 尿毒症患者1例,脑出血后经过12次枸橼酸钠抗凝CRRT救治前后颅脑影像学改变 a.患者出血时颅脑CT,可见右侧枕叶见团片状高密度影,边界清楚;b治疗后2周时颅脑CT,可见右侧枕叶团片状高低混杂密度影,边界欠清,密度较治疗前密度减低,血肿较前吸收;c治疗后1月余复查颅脑MR,右侧枕叶可见不规则形长短混杂T1长短混杂T2信号影,符合出血性脑梗死,范围较治疗后2周减小,血肿进一步吸收转化;d治疗后2月余复查颅脑MR,右侧枕叶可见不规则形等长混杂T1长短混杂T2信号影,与治疗后1月相比再次吸收减轻,转化为陈旧性出血性脑梗死表现
| 项目 | 生存组(n=34) | 死亡组(n=10) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 139.760±14.794 | 166.200±29.657 | t=-2.721 | 0.021 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 83.060±11.478 | 80.200±26.607 | t=0.215 | 0.834 |
| 钠(mmol/L) | 140.162±3.184 | 134.590±3.060 | t=4.905 | 0.000 |
| 钙(mmol/L) | 2.072±0.269 | 2.289±0.217 | t=-2.326 | 0.025 |
| 磷(mmol/L) | 1.729±0.553 | 2.353±0.735 | t=-2.877 | 0.006 |
| 钾(mmol/L) | 4.539±0.663 | 4.958±0.691 | t=-1.742 | 0.089 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 665.588±297.093 | 659.660±349.388 | t=0.053 | 0.958 |
| 尿素氮(mmol/L) | 21.950(16.575,32.338) | 20.655(16.975,41.823) | Z=-0.224 | 0.823 |
| ALT(U/L) | 18.250(9.500,24.300) | 27.150(15.775,35.425) | Z=-1.933 | 0.053 |
| AST(U/L) | 15.750(10.950,21.733) | 21.950(15.175,26.825) | Z=-1.723 | 0.085 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 35.356±5.034 | 31.460±3.760 | t=2.261 | 0.029 |
| 总蛋白(g/L) | 61.678±5.876 | 59.510±11.336 | t=0.581 | 0.573 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 1.230(0.920,1.820) | 2.500(0.638,3.433) | Z=-1.030 | 0.303 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.334±1.239 | 5.437±1.744 | t=-2.248 | 0.030 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.525±0.754 | 2.355±0.560 | t=0.524 | 0.603 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.100(0.958,1.428) | 0.895(0.750,1.238) | Z=-1.743 | 0.081 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 6.630(4.858,10.088) | 6.755(5.573,7.980) | Z=-0.168 | 0.867 |
| DD(μg/L) | 465.000(245.000,712.500) | 2290.000(887.500,5370.000) | Z=-3.194 | 0.001 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 2.010(0.623,10.153) | 44.025(17.148,82.225) | t=-3.926 | 0.000 |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 6.717±2.138 | 12.535±6.053 | t=-2.986 | 0.014 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 179.030±60.215 | 108.300±63.477 | t=3.227 | 0.002 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 96.650±19.602 | 85.800±19.702 | t=1.537 | 0.132 |
| BNP(pg/ml) | 473.350(225.800,732.125) | 1177.300(928.375,1717.175) | Z=-4.257 | 0.000 |
| PTH(pmol/L) | 194.860(107.625,324.150) | 108.350(51.400,258.750) | Z=-1.432 | 0.152 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 396.294±140.248 | 392.540±237.481 | t=0.047 | 0.963 |
表4 两组治疗后相关资料比较
| 项目 | 生存组(n=34) | 死亡组(n=10) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 139.760±14.794 | 166.200±29.657 | t=-2.721 | 0.021 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 83.060±11.478 | 80.200±26.607 | t=0.215 | 0.834 |
| 钠(mmol/L) | 140.162±3.184 | 134.590±3.060 | t=4.905 | 0.000 |
| 钙(mmol/L) | 2.072±0.269 | 2.289±0.217 | t=-2.326 | 0.025 |
| 磷(mmol/L) | 1.729±0.553 | 2.353±0.735 | t=-2.877 | 0.006 |
| 钾(mmol/L) | 4.539±0.663 | 4.958±0.691 | t=-1.742 | 0.089 |
| 血肌酐(μmol/L) | 665.588±297.093 | 659.660±349.388 | t=0.053 | 0.958 |
| 尿素氮(mmol/L) | 21.950(16.575,32.338) | 20.655(16.975,41.823) | Z=-0.224 | 0.823 |
| ALT(U/L) | 18.250(9.500,24.300) | 27.150(15.775,35.425) | Z=-1.933 | 0.053 |
| AST(U/L) | 15.750(10.950,21.733) | 21.950(15.175,26.825) | Z=-1.723 | 0.085 |
| 白蛋白(g/L) | 35.356±5.034 | 31.460±3.760 | t=2.261 | 0.029 |
| 总蛋白(g/L) | 61.678±5.876 | 59.510±11.336 | t=0.581 | 0.573 |
| 甘油三酯(mmol/L) | 1.230(0.920,1.820) | 2.500(0.638,3.433) | Z=-1.030 | 0.303 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.334±1.239 | 5.437±1.744 | t=-2.248 | 0.030 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.525±0.754 | 2.355±0.560 | t=0.524 | 0.603 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.100(0.958,1.428) | 0.895(0.750,1.238) | Z=-1.743 | 0.081 |
| 血糖(mmol/L) | 6.630(4.858,10.088) | 6.755(5.573,7.980) | Z=-0.168 | 0.867 |
| DD(μg/L) | 465.000(245.000,712.500) | 2290.000(887.500,5370.000) | Z=-3.194 | 0.001 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 2.010(0.623,10.153) | 44.025(17.148,82.225) | t=-3.926 | 0.000 |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 6.717±2.138 | 12.535±6.053 | t=-2.986 | 0.014 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 179.030±60.215 | 108.300±63.477 | t=3.227 | 0.002 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 96.650±19.602 | 85.800±19.702 | t=1.537 | 0.132 |
| BNP(pg/ml) | 473.350(225.800,732.125) | 1177.300(928.375,1717.175) | Z=-4.257 | 0.000 |
| PTH(pmol/L) | 194.860(107.625,324.150) | 108.350(51.400,258.750) | Z=-1.432 | 0.152 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 396.294±140.248 | 392.540±237.481 | t=0.047 | 0.963 |
| [1] | 杜静, 王训, 高宗良. 脑出血合并维持性血液透析24例临床分析[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2018, 21(14):1572-1576. |
| [2] | Rabindranath K, Adams J, Macleod AM, et al. Intermittent versus continuous renal replacement therapy for acute renal failure in adults[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2007, (3):CD003773. |
| [3] |
Srisawat N, Lawsin L, Uchino S, et al. Cost of acute renal replacement therapy in the intensive care unit: Results from The Beginning and Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney (BEST Kidney) study[J]. Crit Care, 2010, 14(2):R46.
doi: 10.1186/cc8933 URL |
| [4] |
Brandenburger T, Dimski T, et al. Renal replacement therapy and anticoagulation[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol, 2017, 31(3):387-401.
doi: S1521-6896(17)30053-8 pmid: 29248145 |
| [5] | 张鑫, 张文博, 李莹, 等. 连续性血液净化中阿加曲班与枸橼酸钠的抗凝效果及安全性比较[J]. 武警医学, 2020, 31(2):103-106. |
| [6] |
Liu C, Mao Z, Kang H, et al. Regional citrate versus heparin anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients: A meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Crit Care, 2016, 20(1):144.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1299-0 URL |
| [7] |
Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Kellum JA, Bellomo R. Clinical review: Anticoagulation for continuous renal replacement therapy--heparin or citrate?[J]. Crit Care, 2011, 15(1):202.
doi: 10.1186/cc9358 pmid: 21345279 |
| [8] | Khwaja A. KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury[J]. Nephron Clin Pract, 2012, 120(4):c179-c184. |
| [9] | 高晓琴, 孙小鹉, 任小军, 等. 枸橼酸钠抗凝法行血液透析治疗的临床应用价值[J]. 中国药物与临床, 2017, 17(11):1661-1663. |
| [10] | 杨松涛, 赵娜, 胡军, 等. 应用普通含钙血液透析液局部枸橼酸抗凝血液透析的临床观察[J]. 中国血液净化, 2017, 16(7):474-476+487. |
| [11] | 庞娟. 枸橼酸抗凝在血液透析高危出血患者中的应用[J]. 中国当代医药, 2018, 25(14):38-40. |
| [12] | 邵汉权, 杨雪, 邓勇进, 等. 枸橼酸抗凝在肾衰竭合并脑出血患者血液滤过治疗中的应用研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2018, 15(14):130-133. |
| [13] |
Slowinski T, Morgera S, Joannidis M, et al. Safety and efficacy of regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous venovenous hemodialysis in the presence of liver failure: The Liver Citrate Anticoagulation Threshold (L-CAT) observational study[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19:349.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1066-7 pmid: 26415638 |
| [14] | Ricci D, Panicali L, Facchini MG, et al. Citrate anticoagulation during continuous renal replacement therapy[J]. Contrib Nephrol, 2017, 190:19-30. |
| [15] |
Waikar SS, Curhan GC, Brunelli SM. Mortality associated with low serum sodium concent ration in maintenance hemodialysis[J]. Am J Med, 2011, 124(1):77-84.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2010.07.029 URL |
| [16] |
O’Neill WC. Targeting serum calcium in chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease: Is normal too high?[J]. Kidney Int, 2016, 89(1):40-45.
doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2015.10.001 URL |
| [17] | 许明杰, 洪大情, 王莉. 局部枸橼酸钠抗凝在普通血液透析中的应用进展[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2020, 17(3):251-255. |
| [18] |
Oudemans-van Straaten HM, Ostermann M. Bench-to-bedside review: Citrate for continuous renal replacement therapy, from science to practice[J]. Crit Care, 2012, 16(6):249.
doi: 10.1186/cc11645 pmid: 23216871 |
| [19] |
Ding F, Song JH, Jung JY, et al. A biomimetic membrane device that modulates the excessive inflammatory response to sepsis[J]. PLoS One, 2011, 6(4):e18584.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018584 URL |
| [20] |
Strobl K, Harm S, Weber V, et al. The role of ionized calcium and magnesium in regional citrate anticoagulation and its impact on inflammatory parameters[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2017, 40(1):15-21.
doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000558 pmid: 28218351 |
| [21] |
Huguet M, Rodas L, Blasco M, et al. Clinical impact of regional citrate anticoagulation in continuous renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients[J]. Int J Artif Organs, 2017, 40(12):676-682.
doi: 10.5301/ijao.5000633 pmid: 28862718 |
| [1] | 陶阳, 潘清泉, 李岩. 血液灌流和连续性肾脏替代治疗对百草枯中毒并发MODS患者的应用评价[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 330-334. |
| [2] | 郭晓翠, 赖碧红. 慢性肾功能衰竭患者血液透析后生活质量的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(11): 1038-1041. |
| [3] | 李姮, 李永辉, 孙小强, 王琳, 何峰. 窦性心律慢性心力衰竭患者抗凝治疗安全性及有效性系统评价[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(5): 406-411. |
| [4] | 李文哲, 商进春, 李春梅, 田芬, 李君, 崔莉, 邢广群. 尿毒症规律血液透析患者脑出血危险因素分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(1): 20-25. |
| [5] | 史晓英, 何洪真, 郭星, 吕佩源. 脑白质高信号与自发性脑出血[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(6): 562-565. |
| [6] | 吝娜, 刘川, 吴天宇, 曹磊. 感染性心内膜炎致急性出血性脑梗死1例[J]. 临床荟萃, 2021, 36(1): 66-69. |
| [7] | 耿彦平,王立立,谷剑,齐鹏,陈淑霞. 抗凝治疗量表中文版效度及信度分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(9): 788-791. |
| [8] | 李贵友,刘伦志. 蛋白质结合的尿毒症毒素与血液透析患者认知功能的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(4): 380-384. |
| [9] | 孙如梦, 李英. 抗凝相关性肾病研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2020, 35(12): 1148-1152. |
| [10] | 黄军悦,马志刚,李莹屏,薛嵘,黄文辉,荆晓江. 高通量血液透析联合左卡尼汀对尿毒症患者血脂代谢的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2019, 34(3): 253-256. |
| [11] | 张振洲, 吴生祥, 张国龙. 血清钙浓度与高血压性脑出血患者预后的相关性研究[J]. 临床荟萃, 2019, 34(2): 120-123. |
| [12] | 饶明月,王亚玲,张国茹,王梅. 急性冠脉综合征抗凝治疗进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(9): 761-766. |
| [13] | 李亮,王梅. 急性冠脉综合征部分特殊人群抗血小板治疗研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(9): 767-770. |
| [14] | 牛国超, 尹凤荣, 张晓岚. 他汀类药物致肝损伤的临床特征及其防治[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(6): 478-481. |
| [15] | 徐炳东,麦鸿成,吴正懂,朱培植,梁宇彬,张玉生. 不明原因栓塞性卒中的诊治进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(3): 185-188,193. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||