Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 248-252.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.03.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Diagnosis value of serum lipoprotein α, cystatin-C and uric acid on early diabetic nephropathy
Gao Shixin1, Song Bing2( ), Shi Kexin3
), Shi Kexin3
- 1. Graduate School of Jinzhou Medical University, Huludao Central Hospital, Huludao 125000, China
2. Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, The First Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, China
3. Department of Endocrine, Huludao Central Hospital, Huludao 125000, China
-
Received:2021-12-02Online:2022-03-20Published:2022-04-02 -
Contact:Song Bing E-mail:13634965277@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Gao Shixin, Song Bing, Shi Kexin. Diagnosis value of serum lipoprotein α, cystatin-C and uric acid on early diabetic nephropathy[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 248-252.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.03.009
| 指标 | NA组(n=50) | MA组(n=51) | CA组(n=49) | F/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(男/女)] | 27/23 | 31/20 | 29/20 | 0.515 | 0.77 |
| 年龄(岁) | 57.32±9.85 | 60.13±12.81 | 61.09±9.14 | 2.20 | 0.11 |
| 身高(cm) | 165.44±13.79 | 168.17±8.25 | 167.96±7.65 | 1.46 | 0.23 |
| 体重(kg) | 72.14±11.91 | 71.09±12.16 | 69.46±9.15 | 1.32 | 0.27 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 7(3, 14) | 10(4,18) | 9(6,9) | 2.17 | 0.34 |
| 高血压病程(年) | 0(0,6) | 0(0,8) | 0(0,5) | 0.53 | 0.77 |
| 身体质量指数BMI(kg/m2) | 25.89±3.39 | 25.09±3.72 | 24.61±2.62 | 1.92 | 0.15 |
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 129.5±15.14 | 134.4±18.37 | 158.32±24.36 | 46.01 | 0.00 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 81.42±9.20 | 83.66±11.99 | 87.85±11.95 | 6.55 | 0.00 |
| 指标 | NA组(n=50) | MA组(n=51) | CA组(n=49) | F/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(男/女)] | 27/23 | 31/20 | 29/20 | 0.515 | 0.77 |
| 年龄(岁) | 57.32±9.85 | 60.13±12.81 | 61.09±9.14 | 2.20 | 0.11 |
| 身高(cm) | 165.44±13.79 | 168.17±8.25 | 167.96±7.65 | 1.46 | 0.23 |
| 体重(kg) | 72.14±11.91 | 71.09±12.16 | 69.46±9.15 | 1.32 | 0.27 |
| 糖尿病病程(年) | 7(3, 14) | 10(4,18) | 9(6,9) | 2.17 | 0.34 |
| 高血压病程(年) | 0(0,6) | 0(0,8) | 0(0,5) | 0.53 | 0.77 |
| 身体质量指数BMI(kg/m2) | 25.89±3.39 | 25.09±3.72 | 24.61±2.62 | 1.92 | 0.15 |
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 129.5±15.14 | 134.4±18.37 | 158.32±24.36 | 46.01 | 0.00 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 81.42±9.20 | 83.66±11.99 | 87.85±11.95 | 6.55 | 0.00 |
| 指标 | NA组(n=50) | MA组(n=51) | CA组(n=49) | F/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UACR(mg/mmol) | 0.89(0.52, 1.6725) | 5.6(3.6,12.61) | 70(44.175, 101.5)*# | 204.58 | 0.00 |
| SCr(μmol/L) | 66.49±15.36 | 67.24±15.87 | 381.36±150.9*# | 239.01 | 0.00 |
| eGFR[ml/(min·1.73 m2)] | 106.17±27.40 | 113.27±30.139 | 31.57±20.48*# | 329.50 | 0.00 |
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.08(7.3,9.35) | 9.12(7.61,12.89) | 9.94(7.5,11.1)*# | 13.79 | 0.01 |
| HbA1c(%) | 8.15(7.08,10) | 9.6(7.8,11) | 8.4(6.40,9.55)*# | 9.25 | 0.01 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 2.29±1.61 | 2.42±1.68 | 2.13±0.88 | 1.31 | 0.27 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.62±1.12 | 4.70±1.34 | 4.38±1.12 | 1.98 | 0.14 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.01±0.27 | 0.99±0.30 | 0.97±0.25 | 0.52 | 0.60 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.72±0.91 | 2.71±0.75 | 2.83±0.74 | 0.68 | 0.51 |
| Cys-C(mg/L) | 0.91±0.24 | 2.03±2.03 | 4.67±2.50*# | 67.64 | 0.00 |
| UA(μmol/L) | 291.72±3.06 | 318.86±96.059 | 415.71±142.82*# | 24.52 | 0.00 |
| LP(α)(nmol/L) | 8.05±3.06 | 57.83±14.47* | 139.71±47.00*# | 269.78 | 0.00 |
| 指标 | NA组(n=50) | MA组(n=51) | CA组(n=49) | F/χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UACR(mg/mmol) | 0.89(0.52, 1.6725) | 5.6(3.6,12.61) | 70(44.175, 101.5)*# | 204.58 | 0.00 |
| SCr(μmol/L) | 66.49±15.36 | 67.24±15.87 | 381.36±150.9*# | 239.01 | 0.00 |
| eGFR[ml/(min·1.73 m2)] | 106.17±27.40 | 113.27±30.139 | 31.57±20.48*# | 329.50 | 0.00 |
| FPG(mmol/L) | 8.08(7.3,9.35) | 9.12(7.61,12.89) | 9.94(7.5,11.1)*# | 13.79 | 0.01 |
| HbA1c(%) | 8.15(7.08,10) | 9.6(7.8,11) | 8.4(6.40,9.55)*# | 9.25 | 0.01 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 2.29±1.61 | 2.42±1.68 | 2.13±0.88 | 1.31 | 0.27 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.62±1.12 | 4.70±1.34 | 4.38±1.12 | 1.98 | 0.14 |
| HDL-C(mmol/L) | 1.01±0.27 | 0.99±0.30 | 0.97±0.25 | 0.52 | 0.60 |
| LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.72±0.91 | 2.71±0.75 | 2.83±0.74 | 0.68 | 0.51 |
| Cys-C(mg/L) | 0.91±0.24 | 2.03±2.03 | 4.67±2.50*# | 67.64 | 0.00 |
| UA(μmol/L) | 291.72±3.06 | 318.86±96.059 | 415.71±142.82*# | 24.52 | 0.00 |
| LP(α)(nmol/L) | 8.05±3.06 | 57.83±14.47* | 139.71±47.00*# | 269.78 | 0.00 |
| 指标 | UACR | SCr | eGFR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cys-C | 0.204(0.012) | 0.736(0.000) | -0.548(0.000) |
| UA | 0.261(0.001) | 0.377(0.000) | -0.460(0.000) |
| Lp(α) | 0.455(0.000) | 0.75(0.000) | -0.641(0.000) |
| 指标 | UACR | SCr | eGFR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cys-C | 0.204(0.012) | 0.736(0.000) | -0.548(0.000) |
| UA | 0.261(0.001) | 0.377(0.000) | -0.460(0.000) |
| Lp(α) | 0.455(0.000) | 0.75(0.000) | -0.641(0.000) |
| 指标 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| LP(α) | 0.022 | 0.008 | 7.923 | 0.005 | 1.023 | 1.007 | 1.039 |
| Cys-C | 3.459 | 0.903 | 14.680 | 0.000 | 31.773 | 5.416 | 186.395 |
| 指标 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| LP(α) | 0.022 | 0.008 | 7.923 | 0.005 | 1.023 | 1.007 | 1.039 |
| Cys-C | 3.459 | 0.903 | 14.680 | 0.000 | 31.773 | 5.416 | 186.395 |
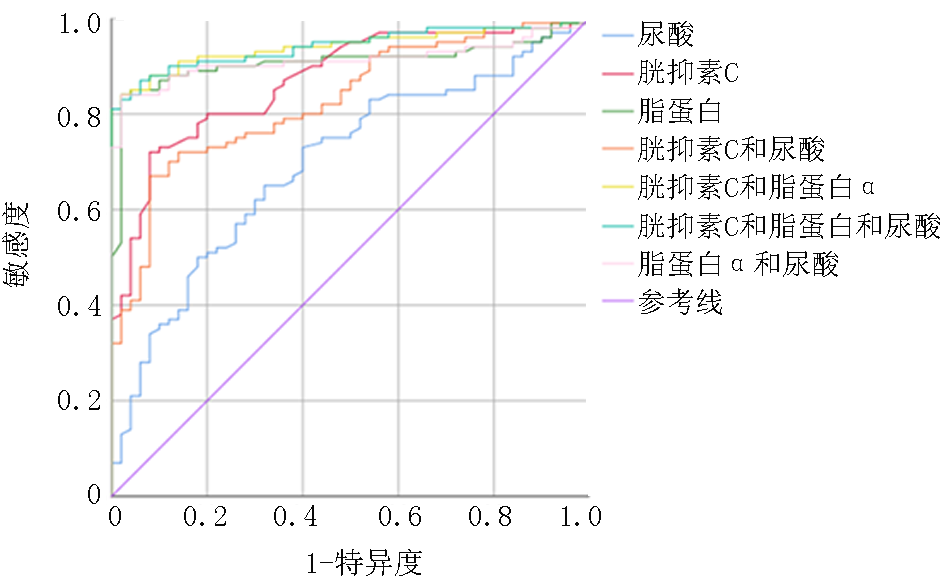
| 检验变量 | AUC | SE | P值 | 95%CI | 切割值 | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) | 约登指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA | 0.697 | 0.044 | 0.000 | 0.610-0.783 | 297.5 | 65 | 68 | 0.33 |
| Cys-C | 0.871 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.814-0.928 | 1.15 | 72 | 92 | 0.64 |
| LP(α) | 0.909 | 0.026 | 0.000 | 0.858-0.959 | 30.6 | 84 | 98 | 0.82 |
| Cys-C+UA | 0.828 | 0.033 | 0.000 | 0.763-0.894 | 0.70 | 67 | 92 | 0.59 |
| Cys-C+ Lp(α) | 0.940 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.902-0.978 | 0.57 | 84 | 98 | 0.82 |
| Lp(α)+UA | 0.912 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.864-0.961 | 0.59 | 84 | 98 | 0.82 |
| Cys-C+ Lp(α)+UA | 0.941 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.903-0.978 | 0.45 | 87 | 94 | 0.81 |
| 检验变量 | AUC | SE | P值 | 95%CI | 切割值 | 敏感度(%) | 特异度(%) | 约登指数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UA | 0.697 | 0.044 | 0.000 | 0.610-0.783 | 297.5 | 65 | 68 | 0.33 |
| Cys-C | 0.871 | 0.029 | 0.000 | 0.814-0.928 | 1.15 | 72 | 92 | 0.64 |
| LP(α) | 0.909 | 0.026 | 0.000 | 0.858-0.959 | 30.6 | 84 | 98 | 0.82 |
| Cys-C+UA | 0.828 | 0.033 | 0.000 | 0.763-0.894 | 0.70 | 67 | 92 | 0.59 |
| Cys-C+ Lp(α) | 0.940 | 0.020 | 0.000 | 0.902-0.978 | 0.57 | 84 | 98 | 0.82 |
| Lp(α)+UA | 0.912 | 0.025 | 0.000 | 0.864-0.961 | 0.59 | 84 | 98 | 0.82 |
| Cys-C+ Lp(α)+UA | 0.941 | 0.019 | 0.000 | 0.903-0.978 | 0.45 | 87 | 94 | 0.81 |
| [1] | 毛维维. 血清胱抑素C水平对糖尿病视网膜病变合并糖尿病肾病的诊断价值[J]. 医学临床研究, 2021, 38(4):619-621. |
| [2] |
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB . Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(2):88-98.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151 pmid: 29219149 |
| [3] | Sagoo MK, Gnudi L. Diabetic nephropathy: An overview[J]. Methods Mol Biol, 2020, 2067:3-7. |
| [4] | 周蓓蓓, 杨帆. 糖尿病肾病损伤标志物的研究进展[J]. 华夏医学, 2019, 32(1):162-165. |
| [5] |
Fineberg D, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Cooper ME. Diabetic nephropathy: Diagnosis and treatment[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2013, 9(12):713-723.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.184 pmid: 24100266 |
| [6] | 崔娇娇, 雷根平, 董盛. 早期诊断糖尿病肾病生化指标的研究进展[J], 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2021, 35(5)538-540. |
| [7] | Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: National cross sectional study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369:m997. |
| [8] | Zhang XX, Kong J, Yun K. Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in China: A meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020: 2315607. |
| [9] |
Ghys L, Paepe D, Smets P, et al. Cystatin C: A new renal marker and its potential use in small animal medicine[J]. J Vet Intern Med, 2014, 28(4):1152-1164.
doi: 10.1111/jvim.12366 pmid: 24814357 |
| [10] |
Ren X, Zhang Z, Yan Z. Association Between Lipoprotein(A) and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12:633529.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.633529 URL |
| [11] |
Xuan L, Wang T, Dai H, et al. Serum lipoprotein (a) associates with a higher risk of reduced renal function: A prospective investigation[J]. J Lipid Res, 2020, 61(10):1320-1327.
doi: 10.1194/jlr.RA120000771 URL |
| [12] |
Lin J, Reilly MP, Terembula K, et al. Plasma lipoprotein(a) levels are associated with mild renal impairment in type 2 diabetics independent of albuminuria[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(12):e114397.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114397 URL |
| [13] |
Kim J, Lee CM, Kim HJ. Biomarkers for chronic kidney disease in dogs: a comparison study[J]. J Vet Med Sci, 2020, 82(8):1130-1137.
doi: 10.1292/jvms.20-0125 URL |
| [14] |
Hu Y, Zhao H, Lu J, et al. High uric acid promotes dysfunction in pancreatic β cells by blocking IRS2/AKT signaling[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2020, 520:111070.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.111070 URL |
| [15] | 白慧华, 周铸, 邓楠. 2型糖尿病患者发生血管并发症的危险因素分析[J]. 海南医学, 2018, 29(13):1802-1804. |
| [16] |
Lanaspa MA, Ishimoto T, Cicerchi C, et al. Endogenous fructose production and fructokinase activation mediate renal injury in diabetic nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2014, 25(11):2526-2538.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013080901 pmid: 24876114 |
| [17] |
Cirillo P, Gersch MS, Mu W, et al. Ketohexokinase-dependent metabolism of fructose induces proinflammatory mediators in proximal tubular cells[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2009, 20(3):545-553.
doi: 10.1681/ASN.2008060576 pmid: 19158351 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||