Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (1): 49-53.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.01.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relationship between urinary albumin and glucose increase 2 hours after glucose load in patients with type 2 diabetes
Wang Yali, Wang Ruiying( ), Cui Yue
), Cui Yue
- Department of Endocrinology, the Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050000, China
-
Received:2020-07-15Online:2021-01-20Published:2021-01-16 -
Contact:Wang Ruiying E-mail:wry0616@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yali, Wang Ruiying, Cui Yue. Relationship between urinary albumin and glucose increase 2 hours after glucose load in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(1): 49-53.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.01.010
| 指标 | N组 | A组 | B组 | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | |||||
| 男 | 23(57.5) | 37(75.5) | 18(58.1) | 3.125 | 0.073 |
| 女 | 17(42.5) | 12(24.5) | 13(41.9) | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 46(37.5, 60.5) | 36(31, 48.5)* | 53(48, 60)# | 14.817 | 0.010 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 26.4(24.5, 29.0) | 26.3(23.9, 28.7) | 24.0(22.4, 25.6)*# | 11.786 | 0.030 |
| SBP(mmol/L) | 129.5(118.3, 142.5) | 128(120.5, 141) | 128(120.5, 141) | 0.770 | 0.680 |
| DBP(mmol/L) | 83(75.3, 85) | 84(78.5, 90.5) | 83(77, 91) | 2.033 | 0.362 |
| 病程(月) | 36(6.5, 93) | 6(1, 42) | 60(6, 120)* | 9.379 | 0.009 |
| 指标 | N组 | A组 | B组 | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | |||||
| 男 | 23(57.5) | 37(75.5) | 18(58.1) | 3.125 | 0.073 |
| 女 | 17(42.5) | 12(24.5) | 13(41.9) | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 46(37.5, 60.5) | 36(31, 48.5)* | 53(48, 60)# | 14.817 | 0.010 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 26.4(24.5, 29.0) | 26.3(23.9, 28.7) | 24.0(22.4, 25.6)*# | 11.786 | 0.030 |
| SBP(mmol/L) | 129.5(118.3, 142.5) | 128(120.5, 141) | 128(120.5, 141) | 0.770 | 0.680 |
| DBP(mmol/L) | 83(75.3, 85) | 84(78.5, 90.5) | 83(77, 91) | 2.033 | 0.362 |
| 病程(月) | 36(6.5, 93) | 6(1, 42) | 60(6, 120)* | 9.379 | 0.009 |
| 指标 | N组 | A组 | B组 | χ2/F值 | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c(%) | 8.63±1.65 | 10.64±1.96* | 10.25±2.26* | 22.148 | <0.001 | ||
| FBG(mmol/L) | 5.91±1.27 | 5.65±1.57 | 5.46±1.35 | 3.305 | 0.219 | ||
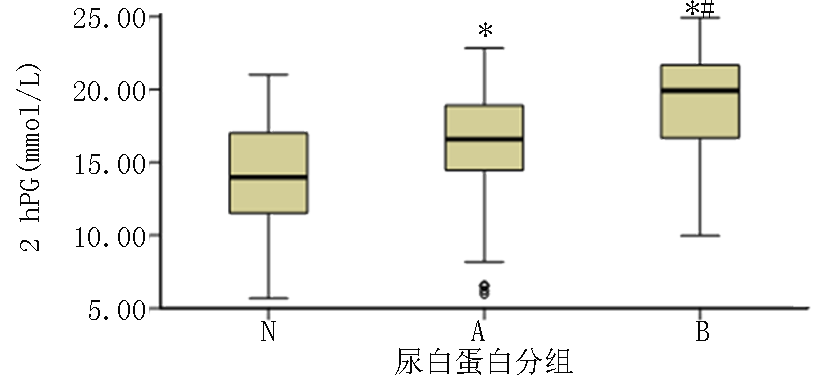
| 2 hPG(mmol/L) | 14.25±3.33 | 16.09±4.16* | 18.94±3.86*# | 24.606 | <0.001 | ||
| 2 hPG-FBG(mmol/L) | 7.99(6.08, 10.34) | 10.97(9.10, 12.54)* | 14.45(11.80, 15.91)*# | 31.880 | <0.001 | ||
| GFR ml/(min·1.73m2) | 118.2(92.2, 138.6) | 120.4(92.2, 153.4) | 103.1(93.1, 128.4) | 4.339 | 0.114 | ||
| 指标 | N组 | A组 | B组 | χ2/F值 | P值 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c(%) | 8.63±1.65 | 10.64±1.96* | 10.25±2.26* | 22.148 | <0.001 | ||
| FBG(mmol/L) | 5.91±1.27 | 5.65±1.57 | 5.46±1.35 | 3.305 | 0.219 | ||
| 2 hPG(mmol/L) | 14.25±3.33 | 16.09±4.16* | 18.94±3.86*# | 24.606 | <0.001 | ||
| 2 hPG-FBG(mmol/L) | 7.99(6.08, 10.34) | 10.97(9.10, 12.54)* | 14.45(11.80, 15.91)*# | 31.880 | <0.001 | ||
| GFR ml/(min·1.73m2) | 118.2(92.2, 138.6) | 120.4(92.2, 153.4) | 103.1(93.1, 128.4) | 4.339 | 0.114 | ||
| 指标 | r值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.042 | 0.646 |
| BMI | -0.290 | 0.001 |
| 病程 | 0.003 | 0.973 |
| HbA1c | 0.294 | 0.001 |
| 2 hPG-FBG | 0.516 | <0.001 |
| 空腹C肽 | -0.246 | 0.007 |
| 指标 | r值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.042 | 0.646 |
| BMI | -0.290 | 0.001 |
| 病程 | 0.003 | 0.973 |
| HbA1c | 0.294 | 0.001 |
| 2 hPG-FBG | 0.516 | <0.001 |
| 空腹C肽 | -0.246 | 0.007 |
| 项目 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||
| 2 hPG-FBG | 3.239 | 1.315 | 0.015 | 0.634 | 5.844 |
| 常量 | -14.039 | 14.810 | 0.345 | -4.367 | 15.289 |
| 项目 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||
| 2 hPG-FBG | 3.239 | 1.315 | 0.015 | 0.634 | 5.844 |
| 常量 | -14.039 | 14.810 | 0.345 | -4.367 | 15.289 |
| [1] |
Alicic RZ, Rooney MT, Tuttle KR. Diabetic kidney disease: challenges, progress, and possibilities[J]. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol, 2017,12(12):2032-2045.
doi: 10.2215/CJN.11491116 URL |
| [2] |
Zhang L, Long J, Jiang W, et al. Trends in chronic kidney disease in China[J]. N Engl J Med, 2016,375(9):905-906.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1602469 URL |
| [3] | 冉春华. 早期糖尿病肾病诊断中尿微量白蛋白检测价值分析[J]. 医药前沿, 2015,5(17):227. |
| [4] |
Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, Nathan DM, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus[J]. N Engl J Med, 1993,329(14):977-986.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309303291401 URL |
| [5] |
Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Atkin SL. A1C variability and the risk of microvascular complications in type 1 diabetes: data from the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial[J]. Diabetes Care, 2008,31(11):2198-2202.
doi: 10.2337/dc08-0864 pmid: 18650371 |
| [6] |
Ceriello A, De Cosmo S, Rossi MC, et al. Variability in HbA1c, blood pressure, lipid parameters and serum uric acid, and risk of development of chronic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Obes Metab, 2017,19(11):1570-1578.
doi: 10.1111/dom.2017.19.issue-11 URL |
| [7] |
Zhang XM, Li PF, Hou JN. Blood glucose profiles in East Asian and Caucasian injection-naive patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on oral medication:a pooled analysis[J]. Diabetes Metab Res Rev, 2018,34(8):e3062.
doi: 10.1002/dmrr.v34.8 URL |
| [8] |
Hou X, Wang C, Wang S, et al. Fluctuation between Fasting and 2-H Postload Glucose State Is Associated with Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Patients with HbA1c<7%[J]. PLoS One, 2014,9(7):e111173.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111173 URL |
| [9] | Zhao ZP, Zhang M, Qi JL, et al. 1520-P: All-cause mortality in Chinese adults with diabetes in association with new indicator generated by the 2-h plasma glucose level subtract fasting plasma glucose level[J]. Diabetes, 2019, 68(Supple1):1520-P. |
| [10] | 顾霖, 陆宏红, 项容. 血糖波动对2型糖尿病患者尿微量白蛋白排泄率的影响[J]. 牡丹江医学院学报, 2014,35(5):49-51. |
| [11] | Lee CL, Chen CH, Wu MJ, et al. The variability of glycated hemoglobin is associated with renal function decline in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Ther Adv Chronic Dis, 2020,3(11):1-10. |
| [12] |
Rozing MP, Møller A, Aabenhus R, et al. Changes in HbA1c during the first six years after the diagnosis of Type 2 diabetes mellitus predict long-term microvascular outcomes[J]. PLoS One, 2019,14(11):e0225230.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225230 URL |
| [13] | Chiu WC, Lai YR, Cheng BC, et al. HbA1C variability is strongly associated with development of macroalbuminuria in normal or microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A six-year follow-up study[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2020,2020:7462158. |
| [14] |
Jin SM, Kim TH, Oh S, et al. Association between the extent of urinary albumin excretion and glycaemic variability indices measured by continuous glucose monitoring[J]. Diabet Med, 2015,32(2):274-279.
doi: 10.1111/dme.12607 URL |
| [15] |
Brownlee M, Hirsch IB. Glycemic variability:a hemoglobin A1c-independent risk factor for diabetic complications[J] JAMA, 2006,295(14):1707-1708.
pmid: 16609094 |
| [16] |
Monnier L, Mas E, Ginet C, et al. Activation of oxidative stress by acute glucose fuctuations compared with sustained chronic hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. JAMA, 2006,295(14):1681-1687.
pmid: 16609090 |
| [17] |
Ying CJ, Zhou XY, Chang ZZ, et al. Blood glucose fluctuation accelerates renal injury involved to inhibit the AKT signaling pathway in diabetic rats[J]. Endocrine, 2016,53(1):81-96.
doi: 10.1007/s12020-016-0867-z URL |
| [18] |
Wu N, Shen H, Liu H, et al. Acute blood glucose fluctuation enhances rat aorta endothelial cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in vivo[J]. Cardiovasc Diabetol, 2016,15(1):109.
doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0427-0 URL |
| [19] | Oguntibeju OO. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, oxidative stress and inflammation: examining the links[J]. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol, 2019,11(3):45-63. |
| [20] |
El-Osta A, Brasacchio D, Yao DC, et al. Transient high glucose causes persistent epigenetic changes and altered gene expression during subsequent normoglycemia[J]. J Exp Med, 2008,205(10):2409-2417.
doi: 10.1084/jem.20081188 URL |
| [21] |
Costantino S, Paneni F, Battista R, et al. Impact of glycemic variability on chromatin remodeling, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes and with target HbA1c levels[J]. Diabetes, 2017,66(9):2472-2482.
doi: 10.2337/db17-0294 pmid: 28634176 |
| [22] |
Gall MA, Hougaard P, Borch-Johnsen K, et al. Risk factors for development of incipient and overt diabetic nephropathy in patients with non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: prospective, observational study[J]. BMJ, 1997,314(7083):783-788.
pmid: 9080995 |
| [23] | 邢小飞. 糖尿病肾病诊断中联合检测尿微量白蛋白、糖化血红蛋白的价值探究[J]. 药品评价, 2018,15(7):16-18. |
| [24] |
Kocak MZ, Aktas G, Duman TT, et al. Is uric acid elevation a random finding or a causative agent of diabetic nephropathy?[J]. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992), 2019,65(9):1155-1160.
doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.65.9.1156 URL |
| [25] |
Saiki A, Nagayama D, Ohhira M, et al. Effect of weight loss using formula diet on renal function in obese patients with diabetic nephropathy[J]. Int J Obes (Lond), 2005,29(9):1115-1120.
doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803009 URL |
| [26] | 朱英宁. 空腹血糖(FPG)、糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、尿微量白蛋白(um-ALB)联合检测在糖尿病肾病患者的临床应用[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2018, (14):65-67. |
| [1] | Li Huifang, Miao Xia. Prediction of thyroid hormone level on risk of type 2 diabetes nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 137-142. |
| [2] | Wang Cui, Lin Hao, Wu Pingping, Zhang Yali, Ren Jian, Xu Ting, Dong Guoyu, Zai Guotian. Correlation between hyperhomocysteinemia and early renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 42-45. |
| [3] | Gao Shixin, Song Bing, Shi Kexin. Diagnosis value of serum lipoprotein α, cystatin-C and uric acid on early diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 248-252. |
| [4] | He Feng, Nin Lu, Luo Gao, Yang Ruifei, Li Fanfan, Cheng Xiaoqiong, An Binbin, Li Jingjuan, Liu Yuanyuan, Guo Qian, Wang Jinyang. Correlation of Chinese visceral adipose index and visceral fat area with diabetic nephropathy and their warning values [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1089-1093. |
| [5] | Liu Meng, Hu Guicai, Yang Zongna, Guo Weiwei, Chen Wanxin. Comparative study on volume load and nutritional status in hemodialysis patients with diabetic kidney disease and non-diabetic kidney disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(4): 332-335. |
| [6] | Jiang Wenwen1, Song Yawei2, Qi Meijiao1, Li Xiaojuan3, Liu Yumei1. Changes of NGAL and inflammatory cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 238-241. |
| [7] | Chen Jiaa, Xu Huab. Clinical value of serum protein electrophoresis (α2+β)/Alb ratio combined with CysC in diagnosis of early stage of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(9): 814-818. |
| [8] | Wang Jiangli1, Liu Maodong2, Chi Yanqing2, Zhang Yimin3, Li Ying2. Urine UbA52 and urine VDBP detection and significance in patients with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(6): 541-544. |
| [9] | Kang Yingli, Li Ying. Development of diagnosis nomenclature in kidney disease related to diabetes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(10): 829-833. |
| [10] | Zhou Yuanyuan1, Wang Zhanjian2, Qiu Hongmei1, Li Wei1. Relationship between serum bilirubin and type 2 diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(9): 767-769,773. |
| [11] | Cui Xue, Yang Lin, Li Juan, Ma Lixia. Changes and significance of immunoglobulin light chain in diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(4): 305-309. |
| [12] | Kong Jianhua, Zhang Jie, Cui Yunjing, Hua Yingying. Comparison of two methods of nutritional assessment in elderly patients with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(4): 301-304. |
| [13] | Hao Huiyao, Zhang Fang, Zhou Jing, Chen Yanxia, Wang Jing, Hao Yongmei. Association of diabetic kidney disease with hypertriglyceridaemic-wasit phenotype in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(9): 964-967. |
| [14] | Fu Shuxia;Li Shaomei;Yu Lianying. Clinical advances in kidney disease researches during 2014 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(2): 161-166173. |
| [15] | Wang Chunhua. Effect of alprostadil combined with Sanqi Panax Notoginseng Injection on proteinuria in early diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(12): 1410-1412. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||