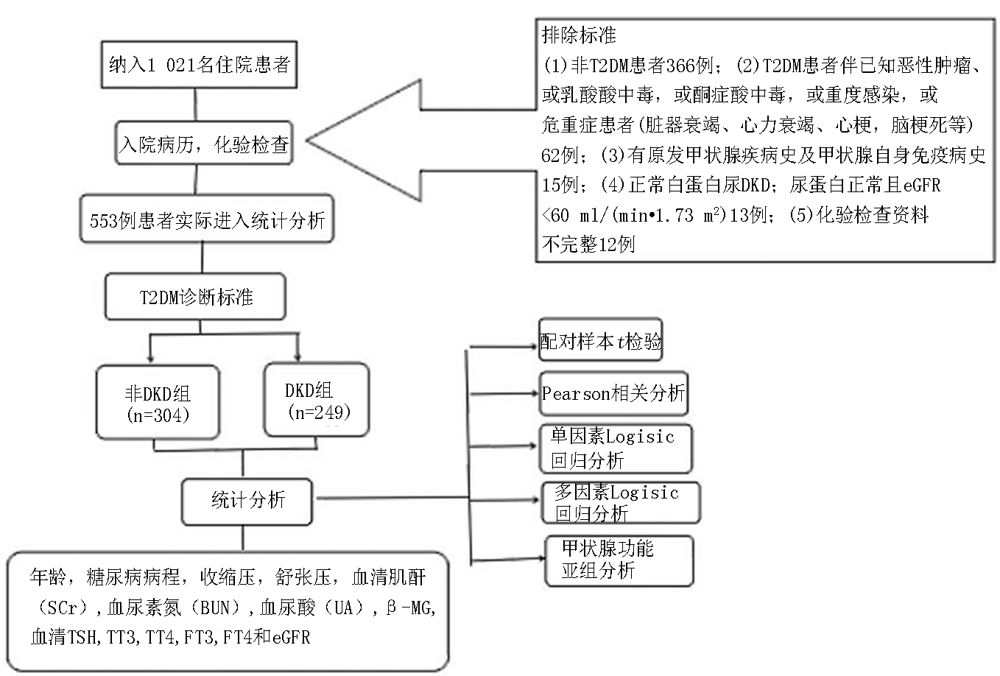
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 137-142.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.02.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prediction of thyroid hormone level on risk of type 2 diabetes nephropathy
- Department of Nephrology, Yiling Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050091, China
-
Received:2022-11-22Online:2023-02-20Published:2023-03-31 -
Contact:Li Huifang E-mail:2562754106@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Huifang, Miao Xia. Prediction of thyroid hormone level on risk of type 2 diabetes nephropathy[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 137-142.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.02.007
| 项目 | 非DKD组( | DKD组( | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 60.34±10.37 | 62.95±9.78 | 0.638 | 0.003 |
| 病程(年) | 10.27±7.068 | 12.57±7.807 | -2.287 | 0.035 |
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 141.75±18.821 | 144.79±20.843 | -1.635 | 0.102 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 80.10±11.497 | 80.84±12.162 | -0.465 | 0.634 |
| TSH(mU/L) | 2.01(1.335, 3.195) | 1.87(1.27, 3.09) | -0.993 | 0.351 |
| TT3(nmol/L) | 1.707±0.357 | 1.626±0.357 | 1.684 | 0.094 |
| TT4(nmol/L) | 104.33±20.393 | 103.247±19.768 | -0.216 | 0.839 |
| FT3(pmol/L) | 4.315±0.801 | 4.156±0.781 | 0.528 | 0.019 |
| FT4(pmol/L) | 16.55(14.995, 18.693) | 16.94(15.23, 18.895) | -1.423 | 0.155 |
| eGFR[ml/(min·1.73 m2)] | 97.766±16.396 | 86.818±22.813 | 25.032 | 0.001 |
| FT3/FT4 | 0.261±0.05 | 0.248±0.054 | 0.299 | 0.003 |
| BUN(mmol/L) | 5.025±1.376 | 5.938±2.331 | 39.697 | 0.001 |
| SCr(μmol/L) | 66.005±12.287 | 74.861±27.111 | 59.506 | 0.001 |
| UA(μmol/L) | 303.254±83.572 | 313.935±91.835 | 5.463 | 0.153 |
| β2-MG(mg/L) | 1.823±0.52 | 2.491±1.591 | 59.245 | 0.001 |
| UACR(mg/g) | 13.414±5.352 | 104.903±93.27 | 452.928 | 0.001 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 158(52.0) 146(48.0) | 122(49.0) 127(51.0) | 0.495 | 0.271 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of clinical characteristics between non-DKD and DKD patients
| 项目 | 非DKD组( | DKD组( | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 60.34±10.37 | 62.95±9.78 | 0.638 | 0.003 |
| 病程(年) | 10.27±7.068 | 12.57±7.807 | -2.287 | 0.035 |
| 收缩压(mmHg) | 141.75±18.821 | 144.79±20.843 | -1.635 | 0.102 |
| 舒张压(mmHg) | 80.10±11.497 | 80.84±12.162 | -0.465 | 0.634 |
| TSH(mU/L) | 2.01(1.335, 3.195) | 1.87(1.27, 3.09) | -0.993 | 0.351 |
| TT3(nmol/L) | 1.707±0.357 | 1.626±0.357 | 1.684 | 0.094 |
| TT4(nmol/L) | 104.33±20.393 | 103.247±19.768 | -0.216 | 0.839 |
| FT3(pmol/L) | 4.315±0.801 | 4.156±0.781 | 0.528 | 0.019 |
| FT4(pmol/L) | 16.55(14.995, 18.693) | 16.94(15.23, 18.895) | -1.423 | 0.155 |
| eGFR[ml/(min·1.73 m2)] | 97.766±16.396 | 86.818±22.813 | 25.032 | 0.001 |
| FT3/FT4 | 0.261±0.05 | 0.248±0.054 | 0.299 | 0.003 |
| BUN(mmol/L) | 5.025±1.376 | 5.938±2.331 | 39.697 | 0.001 |
| SCr(μmol/L) | 66.005±12.287 | 74.861±27.111 | 59.506 | 0.001 |
| UA(μmol/L) | 303.254±83.572 | 313.935±91.835 | 5.463 | 0.153 |
| β2-MG(mg/L) | 1.823±0.52 | 2.491±1.591 | 59.245 | 0.001 |
| UACR(mg/g) | 13.414±5.352 | 104.903±93.27 | 452.928 | 0.001 |
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 158(52.0) 146(48.0) | 122(49.0) 127(51.0) | 0.495 | 0.271 |
| TSH | ||
|---|---|---|
| SCr | 0.25 | 0.635 |
| eGFR | -0.142 | 0.001 |
| UA | 0.032 | 0.533 |
| UACR | -0.039 | 0.358 |
| β2-MG | -0.113 | 0.028 |
| BUN | 0.004 | 0.934 |
Tab. 2 Correlation analysis between TSH and renal function indexes
| TSH | ||
|---|---|---|
| SCr | 0.25 | 0.635 |
| eGFR | -0.142 | 0.001 |
| UA | 0.032 | 0.533 |
| UACR | -0.039 | 0.358 |
| β2-MG | -0.113 | 0.028 |
| BUN | 0.004 | 0.934 |
| FT4 | ||
|---|---|---|
| SCr | 0.041 | 0.333 |
| eGFR | 0.061 | 0.153 |
| UA | -0.004 | 0.934 |
| UACR | 0.01 | 0.807 |
| β2-MG | 0.037 | 0.387 |
| BUN | 0.052 | 0.221 |
Tab. 3 Correlation analysis between FT4 and renal function indexes
| FT4 | ||
|---|---|---|
| SCr | 0.041 | 0.333 |
| eGFR | 0.061 | 0.153 |
| UA | -0.004 | 0.934 |
| UACR | 0.01 | 0.807 |
| β2-MG | 0.037 | 0.387 |
| BUN | 0.052 | 0.221 |
| FT3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| SCr | -0.049 | 0.342 |
| eGFR | 0.219 | 0.001 |
| UA | 0.059 | 0.256 |
| UACR | -0.19 | 0.001 |
| β2-MG | -0.19 | 0.001 |
| BUN | -0.112 | 0.031 |
Tab. 4 Correlation analysis between FT3 and renal function indexes
| FT3 | ||
|---|---|---|
| SCr | -0.049 | 0.342 |
| eGFR | 0.219 | 0.001 |
| UA | 0.059 | 0.256 |
| UACR | -0.19 | 0.001 |
| β2-MG | -0.19 | 0.001 |
| BUN | -0.112 | 0.031 |
| Crude- | 95 | Adjusted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSH | 0.875 | 0.994 | 0.916~1.077 | ||
| FT3 | 0.712 | 0.005 | 0.564~0.901 | 0.564~0.971 | 0.005 |
| FT4 | 1.068 | 0.058 | 0.998~1.143 | 1.002~1.142 | 0.042 |
| TT3 | 0.547 | 0.094 | 0.270~1.109 | ||
| TT4 | 0.994 | 0.306 | 0.982~1.006 | ||
| FT3/FT4 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.00~0.203 |
Tab. 5 Univariate and multivariate Logistic analyses for DKD risk
| Crude- | 95 | Adjusted | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSH | 0.875 | 0.994 | 0.916~1.077 | ||
| FT3 | 0.712 | 0.005 | 0.564~0.901 | 0.564~0.971 | 0.005 |
| FT4 | 1.068 | 0.058 | 0.998~1.143 | 1.002~1.142 | 0.042 |
| TT3 | 0.547 | 0.094 | 0.270~1.109 | ||
| TT4 | 0.994 | 0.306 | 0.982~1.006 | ||
| FT3/FT4 | 0.007 | 0.004 | 0.00~0.203 |
| 组别 | 频率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TSH(mU/L) | |||
| <0.35 | 13 | - | 0.64 |
| 0.351~2.56 | 352 | 1.3969(0.448~4.35) | 0.565 |
| 2.561~4.77 | 138 | 1.093(0.34~3.513) | 0.882 |
| >4.78 | 50 | 1.477(0.424~5.142) | 0.54 |
| FT3(pmol/L) | |||
| <3.44 | 70 | - | 0.036 |
| 3.45~4.24 | 195 | 0.435(0.249~0.76) | 0.003 |
| 4.25~5.04 | 221 | 0.55(0.319~0.952) | 0.03 |
| >5.05 | 67 | 0.54(0.274~1.065) | 0.076 |
| FT4(pmol/L) | |||
| <14.5 | 83 | - | 0.552 |
| 14.16~16.94 | 217 | 1.031(0.617~1.724) | 0.906 |
| 16.95~19.73 | 178 | 1.341(0.793~2.268) | 0.274 |
| >19.731 | 80 | 1.067(0.574~1.984) | 0.838 |
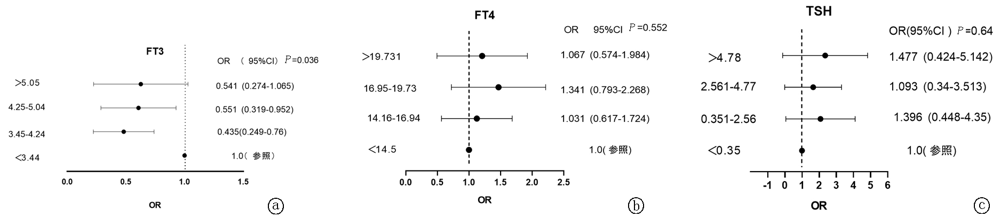
Tab. 6 TSH, FT3, FT4 stratified analyses for DKD risk
| 组别 | 频率 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TSH(mU/L) | |||
| <0.35 | 13 | - | 0.64 |
| 0.351~2.56 | 352 | 1.3969(0.448~4.35) | 0.565 |
| 2.561~4.77 | 138 | 1.093(0.34~3.513) | 0.882 |
| >4.78 | 50 | 1.477(0.424~5.142) | 0.54 |
| FT3(pmol/L) | |||
| <3.44 | 70 | - | 0.036 |
| 3.45~4.24 | 195 | 0.435(0.249~0.76) | 0.003 |
| 4.25~5.04 | 221 | 0.55(0.319~0.952) | 0.03 |
| >5.05 | 67 | 0.54(0.274~1.065) | 0.076 |
| FT4(pmol/L) | |||
| <14.5 | 83 | - | 0.552 |
| 14.16~16.94 | 217 | 1.031(0.617~1.724) | 0.906 |
| 16.95~19.73 | 178 | 1.341(0.793~2.268) | 0.274 |
| >19.731 | 80 | 1.067(0.574~1.984) | 0.838 |
| [1] |
Koye DN, Magliano DJ, Nelson RG, et al. The global epidemiology of diabetes and kidney disease[J]. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis, 2018, 25(2):121-132.
doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2017.10.011 URL |
| [2] |
Biondi B, Kahaly GJ, Robertson RP. Thyroid dysfunction and diabetes mellitus: Two closely associated disorders[J]. Endocr Rev, 2019, 40(3):789-824.
doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00163 pmid: 30649221 |
| [3] |
Narasaki Y, Sohn P, Rhee CM. The interplay between thyroid dysfunction and kidney disease[J]. Semin Nephrol, 2021, 41(2):133-143.
doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2021.03.008 pmid: 34140092 |
| [4] |
Schultheiss UT, Steinbrenner I, Nauck M, et al. GCKD investigators. Thyroid function, renal events and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients: The German Chronic Kidney Disease study[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2020, 14(3):959-968.
doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfaa052 URL |
| [5] |
Hu Y, Hu Z, Tang W, et al. Association of thyroid hormone levels with microvascular complications in euthyroid type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2022, 15:2467-2477.
doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S354872 URL |
| [6] |
Uchiyama-Matsuoka N, Tsuji K, Uchida HA, et al. Masked CKD in hyperthyroidism and reversible CKD status in hypothyroidism[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2022, 13:1048863.
doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1048863 URL |
| [7] |
Ahlqvist E, Storm P, Käräjämäki A, et al. Novel subgroups of adult-onset diabetes and their association with outcomes: A data-driven cluster analysis of six variables[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2018, 6(5):361-369.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30051-2 URL |
| [8] |
Levin A, Stevens PE. Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward[J]. Kidney Int, 2014, 85(1):49-61.
doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.444 pmid: 24284513 |
| [9] | Wu J, Li X, Tao Y, et al. Free triiodothyronine levels are associated with diabetic nephropathy in euthyroid patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Int J Endocrinol, 2015, 2015:204893. |
| [10] |
Fan J, Yan P, Wang Y, et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of low T3 syndrome in non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2016, 8, 22:1171-9.
doi: 10.12659/MSM.895953 URL |
| [11] |
Peters J, Roumeliotis S, Mertens PR, et al. Thyroid hormone status in patients with impaired kidney function[J]. Int Urol Nephrol, 2021, 53(11):2349-2358.
doi: 10.1007/s11255-021-02800-2 pmid: 33682051 |
| [12] |
Yang Z, Duan P, Li W, et al. The correlation between thyroid hormone levels and the kidney disease progression risk in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes, 2022, 15:59-67.
doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S347862 URL |
| [13] |
Hu F, Zhang T. Study on risk factors of diabetic nephropathy in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Int J Gen Med, 2020, 13:351-360.
doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S255858 pmid: 32753935 |
| [14] | Msanga D, Reis K, Kayange N, et al. Diabetic microvascular complications among children and adolescents in northwestern tanzania: A cross-sectional study[J]. Ann Glob Health, 2020, 24, 86(1):43. |
| [15] | Zou J, Tian F, Zhang Y, et al. Association between thyroid hormone levels and diabetic kidney disease in euthyroid patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 16, 8(1):4728. |
| [16] |
Das G, Taylor PN, Abusahmin H, et al. Relationship between serum thyrotropin and urine albumin excretion in euthyroid subjects with diabetes[J]. Ann Clin Biochem, 2019, 56(1):155-162.
doi: 10.1177/0004563218797979 pmid: 30114929 |
| [17] | Chen Y, Zhang W, Wang N, et al. thyroid parameters and kidney disorder in type 2 diabetes: Results from the METAL study[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2020, 2020:4798947. |
| [18] |
Feng X, Huang J, Peng Y, et al. Association between decreased thyroid stimulating hormone and hyperuricemia in type 2 diabetic patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease[J]. BMC Endocr Disord, 2021, 6, 21(1):1.
doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-6-1 URL |
| [19] |
Fei X, Xing M, Wo M, et al. Thyroid stimulating hormone and free triiodothyronine are valuable predictors for diabetic nephropathy in patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2018, 6(15):305.
doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.07.07 pmid: 30211193 |
| [20] |
Echterdiek F, Ranke MB, Schwenger V, et al. Kidney disease and thyroid dysfunction: The chicken or egg problem[J]. Pediatr Nephrol, 2022, 37(12):3031-3042.
doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05640-z pmid: 35737115 |
| [21] |
Rhee CM, Kim S, Gillen DL, et al. Association of thyroid functional disease with mortality in a national cohort of incident hemodialysis patients[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2015, 100(4):1386-1395.
doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-4311 pmid: 25632971 |
| [1] | Wang Cui, Lin Hao, Wu Pingping, Zhang Yali, Ren Jian, Xu Ting, Dong Guoyu, Zai Guotian. Correlation between hyperhomocysteinemia and early renal disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 42-45. |
| [2] | Gao Shixin, Song Bing, Shi Kexin. Diagnosis value of serum lipoprotein α, cystatin-C and uric acid on early diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 248-252. |
| [3] | He Feng, Nin Lu, Luo Gao, Yang Ruifei, Li Fanfan, Cheng Xiaoqiong, An Binbin, Li Jingjuan, Liu Yuanyuan, Guo Qian, Wang Jinyang. Correlation of Chinese visceral adipose index and visceral fat area with diabetic nephropathy and their warning values [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1089-1093. |
| [4] | Liu Meng, Hu Guicai, Yang Zongna, Guo Weiwei, Chen Wanxin. Comparative study on volume load and nutritional status in hemodialysis patients with diabetic kidney disease and non-diabetic kidney disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(4): 332-335. |
| [5] | Wang Yali, Wang Ruiying, Cui Yue. Relationship between urinary albumin and glucose increase 2 hours after glucose load in patients with type 2 diabetes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(1): 49-53. |
| [6] | Cheng Mingrong, Dai Dejian. Efficacy of Zhenqi Fuzheng Capsule combined with ursodeoxycholic acid on primary biliary cholangitis and its impact on thyroid function [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 260-263. |
| [7] | Jiang Wenwen1, Song Yawei2, Qi Meijiao1, Li Xiaojuan3, Liu Yumei1. Changes of NGAL and inflammatory cytokines in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 238-241. |
| [8] | Chen Jiaa, Xu Huab. Clinical value of serum protein electrophoresis (α2+β)/Alb ratio combined with CysC in diagnosis of early stage of diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(9): 814-818. |
| [9] | Wang Jiangli1, Liu Maodong2, Chi Yanqing2, Zhang Yimin3, Li Ying2. Urine UbA52 and urine VDBP detection and significance in patients with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(6): 541-544. |
| [10] | Cao Chong1, Fu Songbo1, Tang Xulei1, Liu Jingfang1, Ma Lihua1, Sun Weiming1, . Survey of thyroid nodules and iodine nutritional status of residents in Chengguan District of Lanzhou [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(7): 587-590. |
| [11] | Kang Yingli, Li Ying. Development of diagnosis nomenclature in kidney disease related to diabetes [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(10): 829-833. |
| [12] | Zhou Yuanyuan1, Wang Zhanjian2, Qiu Hongmei1, Li Wei1. Relationship between serum bilirubin and type 2 diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(9): 767-769,773. |
| [13] | Cui Xue, Yang Lin, Li Juan, Ma Lixia. Changes and significance of immunoglobulin light chain in diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(4): 305-309. |
| [14] | Kong Jianhua, Zhang Jie, Cui Yunjing, Hua Yingying. Comparison of two methods of nutritional assessment in elderly patients with diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(4): 301-304. |
| [15] | Hao Huiyao, Zhang Fang, Zhou Jing, Chen Yanxia, Wang Jing, Hao Yongmei. Association of diabetic kidney disease with hypertriglyceridaemic-wasit phenotype in patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(9): 964-967. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||