Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 412-416.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.05.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive value of a combiniton detection of serum resistin, malondialdehyde and IL-6 tests in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis
Yu Xuehua1,2, Zhang Ning2,3, Wu Jing2, Sun Hui2, Zhao Yunhong2, Liu Gaifang2( )
)
- 1. Graduate School of Hebei North University,Zhangjiakou 075132,China
2. Department of Gastroenterology,Hebei General Hospital,Shijiazhuang 050057,China
3. Graduate School of Hebei Medical University,Shijiazhuang 050017,China
-
Received:2023-04-07Online:2023-05-20Published:2023-07-20 -
Contact:Liu Gaifang, Email:liugaifang65@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yu Xuehua, Zhang Ning, Wu Jing, Sun Hui, Zhao Yunhong, Liu Gaifang. Predictive value of a combiniton detection of serum resistin, malondialdehyde and IL-6 tests in predicting the severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 412-416.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.05.004
| 指标 | MAP(n=66) | MSAP(n=30) | SAP(n=24) | χ2/F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(例) | 0.45 | 0.799 | |||
| 男性 | 51 | 22 | 17 | ||
| 女性 | 15 | 8 | 7 | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 44.73±14.64 | 46.00±13.99 | 45.79±16.02 | 0.71 | 0.708 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 26.31±4.22 | 27.32±4.17 | 27.18±4.40 | 2.25 | 0.338 |
| 病因(例) | 3.20 | 0.806 | |||
| 胆源性 | 22 | 11 | 6 | ||
| 酒精性 | 11 | 3 | 5 | ||
| 高脂血症性 | 31 | 15 | 11 | ||
| 特发性 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of general indicators of AP with different degrees
| 指标 | MAP(n=66) | MSAP(n=30) | SAP(n=24) | χ2/F值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别(例) | 0.45 | 0.799 | |||
| 男性 | 51 | 22 | 17 | ||
| 女性 | 15 | 8 | 7 | ||
| 年龄(岁) | 44.73±14.64 | 46.00±13.99 | 45.79±16.02 | 0.71 | 0.708 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 26.31±4.22 | 27.32±4.17 | 27.18±4.40 | 2.25 | 0.338 |
| 病因(例) | 3.20 | 0.806 | |||
| 胆源性 | 22 | 11 | 6 | ||
| 酒精性 | 11 | 3 | 5 | ||
| 高脂血症性 | 31 | 15 | 11 | ||
| 特发性 | 2 | 1 | 2 |
| 指标 | MAP组(n=66) | MSAP组(n=30) | SAP组(n=24) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抵抗素(ng/ml) | 462.87(251.20, 680.92) | 854.25(654.39, 1116.56) | 1167.60(762.01, 2055.89) | 45.97 | 0.000 |
| 丙二醛(ng/ml) | 261.80(160.24, 555.60) | 507.55(361.50, 702.17) | 863.41(522.13, 1096.78) | 31.07 | 0.000 |
| IL-6(pg/ml) | 14.58(8.12, 27.64) | 35.43(14.69, 42.98) | 46.55(36.05, 65.97) | 43.42 | 0.000 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.84(4.07, 6.50) | 5.44(4.59, 7.37) | 5.28(4.06, 11.81) | 3.53 | 0.173 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 2.93(1.09, 6.99) | 2.53(1.14, 8.18) | 5.36(0.87, 21.66) | 1.40 | 0.492 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 37.58(21.60, 102.06) | 86.50(64.74, 181.01) | 239.83(77.97, 334.70) | 36.32 | 0.000 |
| PCT(ng/ml) | 0.11(0.06, 0.36) | 0.33(0.18, 1.57) | 1.19(0.75, 3.06) | 28.09 | 0.000 |
Tab. 2 Comparison of serum resistin, MDA, IL-6 in AP patients with different degrees
| 指标 | MAP组(n=66) | MSAP组(n=30) | SAP组(n=24) | χ2值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抵抗素(ng/ml) | 462.87(251.20, 680.92) | 854.25(654.39, 1116.56) | 1167.60(762.01, 2055.89) | 45.97 | 0.000 |
| 丙二醛(ng/ml) | 261.80(160.24, 555.60) | 507.55(361.50, 702.17) | 863.41(522.13, 1096.78) | 31.07 | 0.000 |
| IL-6(pg/ml) | 14.58(8.12, 27.64) | 35.43(14.69, 42.98) | 46.55(36.05, 65.97) | 43.42 | 0.000 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 4.84(4.07, 6.50) | 5.44(4.59, 7.37) | 5.28(4.06, 11.81) | 3.53 | 0.173 |
| TG(mmol/L) | 2.93(1.09, 6.99) | 2.53(1.14, 8.18) | 5.36(0.87, 21.66) | 1.40 | 0.492 |
| CRP(mg/L) | 37.58(21.60, 102.06) | 86.50(64.74, 181.01) | 239.83(77.97, 334.70) | 36.32 | 0.000 |
| PCT(ng/ml) | 0.11(0.06, 0.36) | 0.33(0.18, 1.57) | 1.19(0.75, 3.06) | 28.09 | 0.000 |
| 指标 | 抵抗素 | 丙二醛 | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抵抗素 | 1.000 | 0.437* | 0.574* |
| 丙二醛 | 0.437* | 1.000 | 0.343* |
| IL-6 | 0.574* | 0.343* | 1.000 |
| CRP | 0.373* | 0.146 | 0.356* |
| PCT | 0.342* | 0.283* | 0.370* |
| BMI | 0.164 | 0.396* | 0.037 |
| TC | -0.002 | -0.102 | 0.026 |
| TG | 0.038 | -0.072 | 0.061 |
Tab. 3 Correlation analysis of resistin, MDA, IL-6
| 指标 | 抵抗素 | 丙二醛 | IL-6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 抵抗素 | 1.000 | 0.437* | 0.574* |
| 丙二醛 | 0.437* | 1.000 | 0.343* |
| IL-6 | 0.574* | 0.343* | 1.000 |
| CRP | 0.373* | 0.146 | 0.356* |
| PCT | 0.342* | 0.283* | 0.370* |
| BMI | 0.164 | 0.396* | 0.037 |
| TC | -0.002 | -0.102 | 0.026 |
| TG | 0.038 | -0.072 | 0.061 |
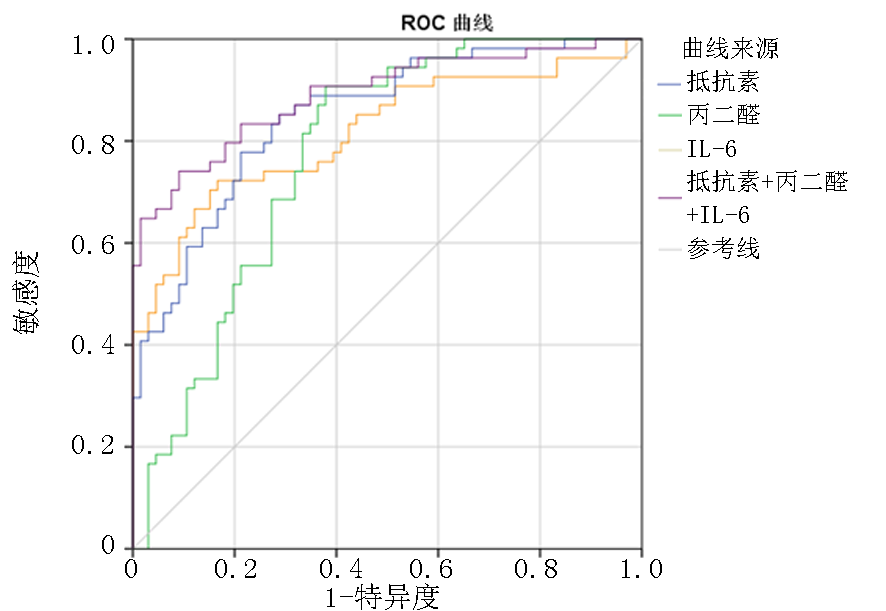
| 指标 | AUC(95%置信区间) | 界值 | 敏感度 (%) | 特异度 (%) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抵抗素(ng/ml) | 0.850(0.782~0.917) | 693.99 | 77.80 | 78.80 | <0.05 |
| 丙二醛 (ng/ml) | 0.774(0.690~0.857) | 314.36 | 90.70 | 62.10 | <0.05 |
| IL-6(pg/ml) | 0.817(0.738~0.897) | 31.86 | 72.20 | 83.30 | <0.05 |
| 联合检测 | 0.890(0.830~0.951) | 0.55 | 74.10 | 90.90 | <0.05 |
Tab. 4 Predictive value of serum resistin, MDA, IL-6 and their combined detection on SAP (MSAP+SAP)
| 指标 | AUC(95%置信区间) | 界值 | 敏感度 (%) | 特异度 (%) | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 抵抗素(ng/ml) | 0.850(0.782~0.917) | 693.99 | 77.80 | 78.80 | <0.05 |
| 丙二醛 (ng/ml) | 0.774(0.690~0.857) | 314.36 | 90.70 | 62.10 | <0.05 |
| IL-6(pg/ml) | 0.817(0.738~0.897) | 31.86 | 72.20 | 83.30 | <0.05 |
| 联合检测 | 0.890(0.830~0.951) | 0.55 | 74.10 | 90.90 | <0.05 |
| [1] |
Dobszai D, Mátrai P, Gyöngyi Z, et al. Body-mass index correlates with severity and mortality in acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2019, 25(6): 729-43.
doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i6.729 URL |
| [2] |
Hong S, Qiwen B, Ying J, et al. Body mass index and the risk and prognosis of acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2011, 23(12): 1136-43.
doi: 10.1097/MEG.0b013e32834b0e0e URL |
| [3] |
Longo M, Zatterale F, Naderi J, et al. Adipose tissue dysfunction as determinant of obesity-associated metabolic complications[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(9):2358.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20092358 URL |
| [4] |
Kuan LL, Dennison AR, Garcea G. Association of visceral adipose tissue on the incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis: A systematic review[J]. Pancreatology, 2020, 20(6): 1056-1061.
doi: S1424-3903(20)30204-0 pmid: 32768177 |
| [5] |
Xie J, Xu L, Pan Y, et al. Impact of visceral adiposity on severity of acute pancreatitis: a propensity score-matched analysis[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2019, 19(1): 87.
doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-1015-z pmid: 31195984 |
| [6] | Navina S, Acharya C, DeLany JP, et al. Lipotoxicity causes multisystem organ failure and exacerbates acute pancreatitis in obesity[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2011, 3(107): 107ra10. |
| [7] |
Acharya C, Navina S, Singh VP. Role of pancreatic fat in the outcomes of pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2014, 14(5): 403-438.
doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2014.06.004 pmid: 25278311 |
| [8] |
Karpavicius A, Dambrauskas Z, Gradauskas A, et al. The clinical value of adipokines in predicting the severity and outcome of acute pancreatitis[J]. BMC Gastroenterol, 2016, 16(1): 99.
doi: 10.1186/s12876-016-0514-4 pmid: 27549125 |
| [9] |
Kibar YI, Albayrak F, Arabul M, et al. Resistin: New serum marker for predicting severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. J Int Med Res, 2016, 44(2): 328-337.
doi: 10.1177/0300060515605428 pmid: 26857860 |
| [10] |
Xue LN, Wang XY, Tan Y, et al. Significance of resistin expression in acute pancreatitis[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 9(4): 1438-1442.
doi: 10.3892/etm.2015.2270 URL |
| [11] |
Schäffler A, Hamer O, Dickopf J, et al. Admission resistin levels predict peripancreatic necrosis and clinical severity in acute pancreatitis[J]. Am J Gastroenterol, 2010, 105(11): 2474-2484.
doi: 10.1038/ajg.2010.278 pmid: 20648005 |
| [12] | Langmead C, Lee PJ, Paragomi P, et al. A novel 5-cytokine panel outperforms conventional predictive markers of persistent organ failure in acute pancreatitis[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2021, 12(5): e00351. |
| [13] |
Yu P, Wang S, Qiu Z, et al. Efficacy of resistin and leptin in predicting persistent organ failure in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Pancreatology, 2016, 16(6): 952-957.
doi: S1424-3903(16)31183-8 pmid: 27654573 |
| [14] | Yang J, Liu M, Wang S, et al. Alteration of peripheral resistin and the severity of acute pancreatitis: A meta-analysis[J]. Front Med (Lausanne), 2022, 9: 915152. |
| [15] | Piao X, Sui X, Liu B, et al. Picroside ii improves severe acute pancreatitis-induced hepatocellular injury in rats by affecting JAK2/STAT3 phosphorylation signaling[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021: 9945149. |
| [16] |
杜奕奇, 李维勤, 毛恩强. 中国急性胰腺炎多学科诊治(MDT)共识意见(草案)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2015, 35(12): 1004-1010.
doi: 10.7504/nk2015110301 |
| [17] |
Sternby H, Hartman H, Thorlacius H, et al. The initial course of IL1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12, IFN-γ and TNF-α with regard to severity grade in acute pancreatitis[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(4):591.
doi: 10.3390/biom11040591 URL |
| [18] | 中华医学会外科学分会胰腺外科学组. 中国急性胰腺炎诊治指南(2021)[J]. 浙江实用医学, 2021, 26(6): 511-19+35. |
| [19] |
Sbeit W, Khoury T. Fatty pancreas represents a risk factor for acute pancreatitis: A pilot study[J]. Pancreas, 2021, 50(7): 990-993.
doi: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001867 URL |
| [20] |
Xie J, Xu L, Pan Y, et al. Nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease is related independently to the severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2019, 31(8): 973-978.
doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001477 URL |
| [21] | Kwak MS, Lim JW, Kim H. Astaxanthin Inhibits Interleukin-6 Expression in Cerulein/Resistin-Stimulated Pancreatic Acinar Cells[J]. Mediators Inflamm, 2021: 5587297. |
| [22] | Taouis M, Benomar Y. Is resistin the master link between inflammation and inflammation-related chronic diseases?[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2021, 533: 111341. |
| [23] |
Jiang CY, Wang W. Resistin aggravates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines in cerulein-stimulated AR42J pancreatic acinar cells[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2017, 15(1): 502-506.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6027 URL |
| [24] |
Jiang CY, Wang W, Tang J X, et al. The adipocytokine resistin stimulates the production of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 in pancreatic acinar cells via NF-κB activation[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2013, 36(11): 986-992.
doi: 10.3275/9002 pmid: 23765438 |
| [25] |
Burnett MS, Lee CW, Kinnaird TD, et al. The potential role of resistin in atherogenesis[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2005, 182(2): 241-248.
pmid: 16159596 |
| [26] | Gaweł S, Wardas M, Niedworok E, et al. Malondialdehyde (MDA) as a lipid peroxidation marker[J]. Wiad Lek, 2004, 57(9-10): 453-455. |
| [27] |
Del Rio D, Stewart AJ, Pellegrini N. A review of recent studies on malondialdehyde as toxic molecule and biological marker of oxidative stress[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2005, 15(4): 316-328.
doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2005.05.003 URL |
| [28] |
Hernández V, Miranda M, Pascual I, et al. Malondialdehyde in early phase of acute pancreatitis[J]. Rev Esp Enferm Dig, 2011, 103(11): 563-569.
pmid: 22149557 |
| [29] | Abu-Hilal M, McPhail M J, Marchand L, et al. Malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase as potential markers of severity in acute pancreatitis[J]. JOP, 2006, 7(2): 185-192. |
| [30] | Cho IR, Do MY, Han SY, et al. Comparison of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, procalcitonin, and the computed tomography severity index for early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis[J]. Gut Liver, 2023 Feb 15. Epub ahead of print. |
| [31] | Kumar RB, Karim T, Jain A, et al. Role of serum interleukin-6 and c-reactive protein in early prediction of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. J West Afr Coll Surg, 2022, 12(4): 20-26. |
| [32] | Cui H, Mei C, Cui M, et al. Predictive value of serum chlorine and interleukin-6 combined with coagulation indexes on severity of severe acute pancreatitis[J]. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue, 2022, 34(12): 1301-1304. |
| [33] | Li J, Chen Z, Li L, et al. Interleukin-6 is better than C-reactive protein for the prediction of infected pancreatic necrosis and mortality in patients with acute pancreatitis[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2022, 12: 933221. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||