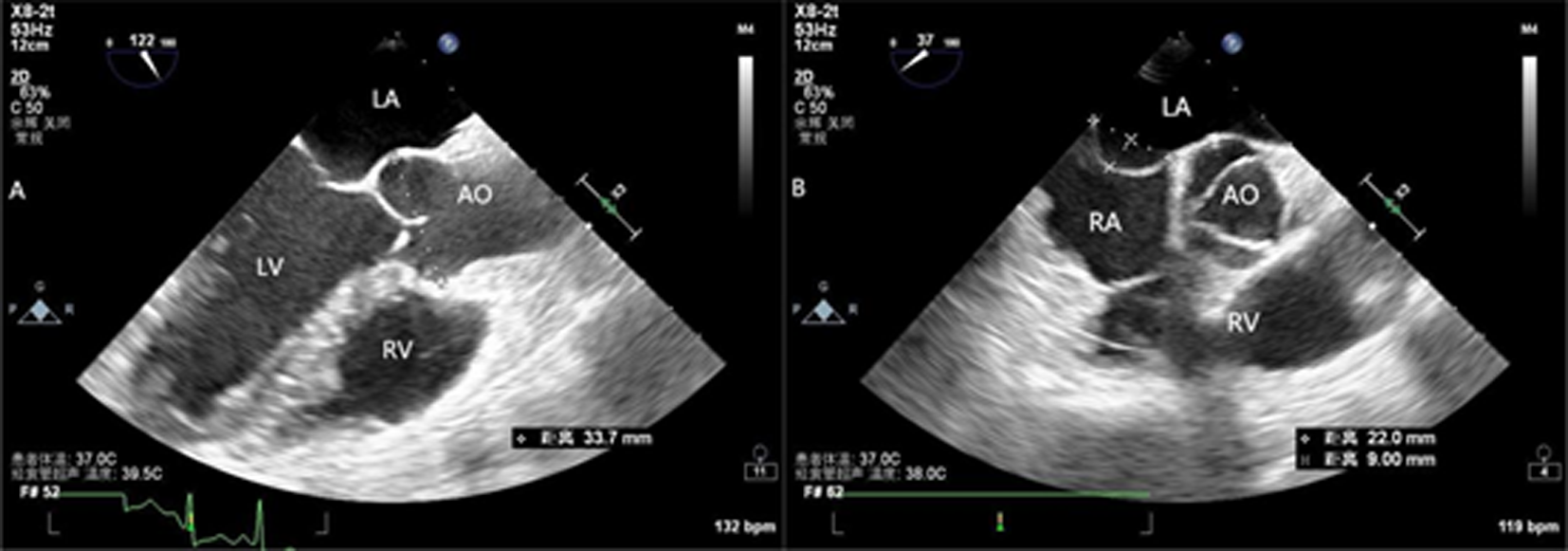
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1012-1015.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.11.009
Previous Articles Next Articles
Aortic root anatomy and atrial septal mobility analyzed by transesophageal echocardiography
Li Lisha1,2, Shen Xianghui2( ), Liu Yanhui2, Ren Yanbin2
), Liu Yanhui2, Ren Yanbin2
- 1. Department of Postgraduate,Chengde Medical University,Chengde 067000,China
2. Department of Ultrasound Medicine,Handan Centre Hospital,Handan 056002,China
-
Received:2023-05-16Online:2023-11-20Published:2024-01-17 -
Contact:Shen Xianghui E-mail:63945852@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Lisha, Shen Xianghui, Liu Yanhui, Ren Yanbin. Aortic root anatomy and atrial septal mobility analyzed by transesophageal echocardiography[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 1012-1015.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.11.009
| 项目 | 数据 |
|---|---|
| 经食管超声图像 | |
| 主动脉根部直径(mm) | 32.2±3.5 |
| 主动脉瓣[例(%)] | |
| 正常 | 92(89.3) |
| 钙化 | 10(9.7) |
| 狭窄 | 1(1.0) |
| 房间隔直径(mm) | 25.6±5.1 |
| 房间隔活动度(mm) | 4.3±3.1 |
| ASA[例(%)] | 10(9.7) |
| PFO[例(%)] | 46(44.7) |
| 经胸超声图像 | |
| 左房前后径(mm) | 35.7±6.5 |
| LVEF[例(%)] | |
| ≤50% | 12(11.7) |
| >50% | 91(88.3) |
| 舒张功能[例(%)] | |
| 正常 | 63(61.2) |
| 功能受限 | 40(38.8) |
Tab.1 Transesophageal echocardiographic measurements and findings of patients with clinically indicated studies( n=103)
| 项目 | 数据 |
|---|---|
| 经食管超声图像 | |
| 主动脉根部直径(mm) | 32.2±3.5 |
| 主动脉瓣[例(%)] | |
| 正常 | 92(89.3) |
| 钙化 | 10(9.7) |
| 狭窄 | 1(1.0) |
| 房间隔直径(mm) | 25.6±5.1 |
| 房间隔活动度(mm) | 4.3±3.1 |
| ASA[例(%)] | 10(9.7) |
| PFO[例(%)] | 46(44.7) |
| 经胸超声图像 | |
| 左房前后径(mm) | 35.7±6.5 |
| LVEF[例(%)] | |
| ≤50% | 12(11.7) |
| >50% | 91(88.3) |
| 舒张功能[例(%)] | |
| 正常 | 63(61.2) |
| 功能受限 | 40(38.8) |
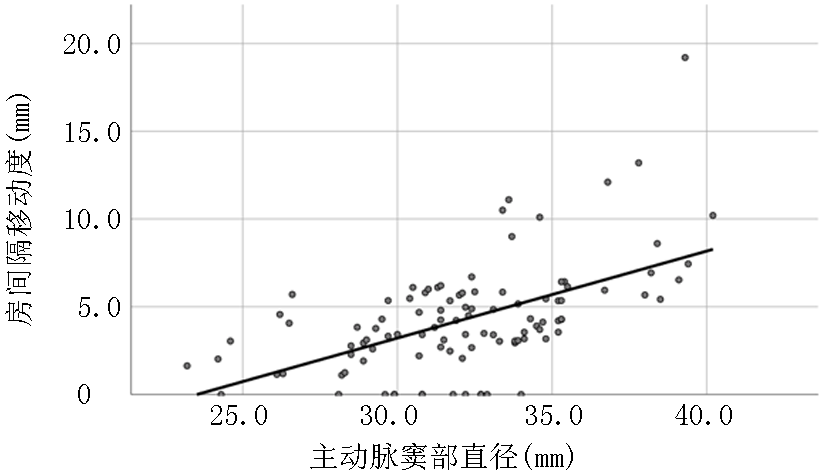
| 主动脉直径 | B系数 | 95% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未调整 | 0.50 | 0.349~0.642 | <0.01 |
| 调整后 | |||
| 年龄 | 0.013 | -0.024~0.051 | 0.487 |
| 性别 | 4.184 | 2.754~5.613 | <0.01 |
| 体重 | -0.036 | -0.095~0.025 | 0.226 |
| 身高 | 0.17 | 0.044~0.297 | <0.01 |
| 左房前后径 | -0.30 | -0.116~0.057 | 0.501 |
| 多变量调整* | 0.63 | 0.477~0.784 | <0.01 |
Tab. 2 Crude and adjusted linear regression coeffificients between aortic root diameter and ASM
| 主动脉直径 | B系数 | 95% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 未调整 | 0.50 | 0.349~0.642 | <0.01 |
| 调整后 | |||
| 年龄 | 0.013 | -0.024~0.051 | 0.487 |
| 性别 | 4.184 | 2.754~5.613 | <0.01 |
| 体重 | -0.036 | -0.095~0.025 | 0.226 |
| 身高 | 0.17 | 0.044~0.297 | <0.01 |
| 左房前后径 | -0.30 | -0.116~0.057 | 0.501 |
| 多变量调整* | 0.63 | 0.477~0.784 | <0.01 |
| 组别 | 例数 | PFO |
|---|---|---|
| 无偏移 | 13 | 2(15.4) |
| 右偏移 | 80 | 37(46.2)* |
| 左偏及左右偏移 | 10 | 7(70.0)* |
| χ2值 | 7.188 | |
| 0.027 |
Tab. 3 Direction of atrial septal excursion and prevalence of patent foramen ovale (n[%])
| 组别 | 例数 | PFO |
|---|---|---|
| 无偏移 | 13 | 2(15.4) |
| 右偏移 | 80 | 37(46.2)* |
| 左偏及左右偏移 | 10 | 7(70.0)* |
| χ2值 | 7.188 | |
| 0.027 |
| [1] |
Amarenco P, Bogousslavsky J, Caplan LR, et al. Classification of stroke subtypes[J]. Cerebrovasc Dis, 2009, 27(5):493-501.
doi: 10.1159/000210432 pmid: 19342825 |
| [2] |
Feske SK. Ischemic stroke[J]. Am J Med, 2021, 134(12):1457-64.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.07.027 pmid: 34454905 |
| [3] |
Mas JL, Derumeaux G, Guillon B, et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Anticoagulation vs. Antiplatelets after Stroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(11):1011-1021.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1705915 URL |
| [4] |
Abdelaziz HK, Saad M, Abuomara HZ, et al. Long-term outcomes of patent foramen ovale closure or medical therapy after cryptogenic stroke: A meta-analysis of randomized trials[J]. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv, 2018, 92(1):176-186.
doi: 10.1002/ccd.v92.1 URL |
| [5] |
Søndergaard L, Kasner SE, Rhodes JF, et al. Patent foramen ovale closure or antiplatelet therapy for cryptogenic stroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(11):1033-1042.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707404 URL |
| [6] |
Reed D, Reed C, Stemmermann G, et al. Are aortic aneurysms caused by atherosclerosis?[J]. Circulation, 1992, 85(1):205-211.
doi: 10.1161/01.cir.85.1.205 pmid: 1728451 |
| [7] |
Yu S, Guo X, Li G, et al. Gender discrepancy in the predictive effect of aortic root diameter on incidence of cardiovascular events among rural Northeast Chinese[J]. BMJ Open, 2022; 12(9):e039207.
doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039207 URL |
| [8] |
Rudoy AS, Bova AA, Nekhaichik TA. Atrial septal aneurysm: evolution of diagnostic and clinical judgements[J]. Ter Arkh, 2017, 89(9): 104-108.
doi: 10.17116/terarkh2017899104-108 pmid: 29039838 |
| [9] |
Silvestry FE, Cohen MS, Armsby LB, et al. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessme nt of atrial septal defect and patent forameno vale: From the American Society of Echocardiog raphy and Society for Cardiac Angiography an d Interventions[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2015, 28(8):910-958.
doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2015.05.015 URL |
| [10] |
Chopard R, Meneveau N. Right-to-left atrial shunting associated with aortic root aneurysm: a case report of a rare cause of platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome[J]. Heart Lung Circ, 2013, 22(1):71-75.
doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2012.08.007 pmid: 22999442 |
| [11] |
Hasegawa M, Nagai T, Murakami T, et al. Platypnoea-orthodeoxia syndrome due to deformation of the patent foramen ovale caused by a dilated ascending aorta: a case report[J]. Eur Heart J Case Rep, 2020, 4(2):1-4.
doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaa045 pmid: 32352045 |
| [12] |
Blanche C, Noble S, Roffi M, et al. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome in the elderly treated by percutaneous patent foramen ovale closure: A case series and literature review[J]. Eur J Intern Med, 2013, 24(8):813-817.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2013.08.698 pmid: 24007641 |
| [13] |
Eicher JC, Bonniaud P, Baudouin N, et al. Hypoxaemia associated with an enlarged aortic root: A new syndrome?[J]. Heart, 2005, 91(8):1030-1035.
doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.027839 pmid: 15761046 |
| [14] |
Othman F, Bailey B, Collins N, et al. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome in the setting of patent foramen ovale without pulmonary hypertension or major lung disease[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2022, 11(15):e024609.
doi: 10.1161/JAHA.121.024609 URL |
| [15] |
Heidemann A Jr, Dall'Oglio L, Bertoldi EG, et al. Increased mobility of the atrial septum in aortic root dilation: an observational study on transesophageal echocardiography[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12:701399.
doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.701399 URL |
| [16] |
Bertaux G, Eicher JC, Petit A, et al. Anotomic interaction between the aortic root and the atrial septum: A prospective echocardiographic study[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2007, 20(4): 409-414.
doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2006.09.008 URL |
| [17] |
Kazawa S, Enomoto T, Suzuki N, et al. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome in a patient with an atrial septal defect: The diagnosis and choice of treatment[J]. Intern Med, 2017, 56(2):169-173.
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7728 URL |
| [18] |
Gardin JM, Arnold AM, Polak J, et al. Usefulness of aortic root dimension in persons > or = 65 years of age in predicting heart failure, stroke, cardiovascular mortality, all-cause mortality and acute myocardial infarction (from the Cardiovascular Health Study)[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2006, 97(2):270-275.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.08.039 URL |
| [19] |
Kamimura D, Suzuki T, Musani SK, et al. Increased proximal aortic diameter is associated with risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in blacks the jackson heart study[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2017, 6(6):e005005.
doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005005 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 14
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 101
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||