Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 524-530.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.06.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive value of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 in cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke
- Department of Neurology, Shanghai Baoshan District Wusong Central Hospital, Shanghai 201900, China
-
Received:2023-11-30Online:2024-06-20Published:2024-07-18 -
Contact:Shen Tao, Email:xuchenglong1616@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yuping, Shen Tao. Predictive value of milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor 8 in cognitive impairment after ischemic stroke[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(6): 524-530.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.06.007
| 项目 | 认知障碍组(n=52) | 认知正常组(n=78) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 32(61.5) 20(38.5) | 45(57.7) 33(42.3) | χ2=0.191 | 0.662 |
| 年龄(岁) | 61.35±3.44 | 60.72±3.54 | t=1.002 | 0.318 |
| 发病至入院治疗时间(h) | 48.63±4.85 | 47.50±4.76 | t=1.321 | 0.189 |
| 入院时NIHSS评分(分) | 14.00(12.00,16.00) | 13.50(12.00,15.00) | Z=1.225 | 0.220 |
| 糖尿病[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 15(28.8) 37(71.2) | 19(24.4) 59(75.6) | χ2=0.325 | 0.568 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 26(50.0) 26(50.0) | 43(55.1) 35(44.9) | χ2=0.329 | 0.566 |
| 高血脂症[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 7(13.5) 45(86.5) | 7(9.0) 71(91.0) | χ2=0.654 | 0.419 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 16(30.8) 36(69.2) | 17(21.8) 61(78.2) | χ2=1.327 | 0.249 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 14(26.9) 38(73.1) | 16(20.5) 62(79.5) | χ2=0.772 | 0.395 |
| 脑梗死部位[例(%)] | ||||
| 基底节 | 9(17.3) | 19(24.4) | ||
| 额叶 | 19(36.5) | 10(12.8) | ||
| 顶叶 | 9(17.3) | 12(15.4) | ||
| 脑干 | 4(7.7) | 12(15.4) | χ2=11.119 | 0.078 |
| 颞叶 | 7(13.5) | 14(17.9) | ||
| 小脑 | 2(3.9) | 5(6.4) | ||
| 丘脑 | 2(3.9) | 6(7.7) | ||
| 梗死面积[例(%)] | ||||
| 大面积 | 3(5.8) | 1(1.3) | ||
| 中面积 | 23(44.2) | 24(30.8)* | Z=2.163 | 0.031 |
| 小面积 | 26(50.0) | 53(67.9) | ||
| 出院后用药情况[例(%)] | ||||
| 阿司匹林 | 48(92.3) | 74(94.9) | χ2=0.355 | 0.551 |
| 氯呲格雷 | 42(80.8) | 65(83.3) | χ2=0.141 | 0.707 |
| 他汀类药物 | 35(67.3) | 49(62.8) | χ2=0.275 | 0.633 |
| 入院时空腹血糖(mmol/L) | 6.25±1.25 | 6.14±1.18 | t=0.509 | 0.611 |
| 入院时TC(mmol/L) | 4.18±0.74 | 4.06±0.65 | t=0.978 | 0.330 |
| 入院时TG(mmol/L) | 1.63±0.35 | 1.52±0.38 | t=1.785 | 0.077 |
| 入院时HDL-C(mmol/L) | 0.92±0.24 | 0.96±0.28 | t=1.033 | 0.304 |
| 入院时LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.71±0.75 | 2.63±0.61 | t=0.593 | 0.554 |
Tab.1 Clinical data between normal cognition group and impaired cognition group
| 项目 | 认知障碍组(n=52) | 认知正常组(n=78) | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 性别[例(%)] | ||||
| 男 女 | 32(61.5) 20(38.5) | 45(57.7) 33(42.3) | χ2=0.191 | 0.662 |
| 年龄(岁) | 61.35±3.44 | 60.72±3.54 | t=1.002 | 0.318 |
| 发病至入院治疗时间(h) | 48.63±4.85 | 47.50±4.76 | t=1.321 | 0.189 |
| 入院时NIHSS评分(分) | 14.00(12.00,16.00) | 13.50(12.00,15.00) | Z=1.225 | 0.220 |
| 糖尿病[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 15(28.8) 37(71.2) | 19(24.4) 59(75.6) | χ2=0.325 | 0.568 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 26(50.0) 26(50.0) | 43(55.1) 35(44.9) | χ2=0.329 | 0.566 |
| 高血脂症[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 7(13.5) 45(86.5) | 7(9.0) 71(91.0) | χ2=0.654 | 0.419 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 16(30.8) 36(69.2) | 17(21.8) 61(78.2) | χ2=1.327 | 0.249 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | ||||
| 是 否 | 14(26.9) 38(73.1) | 16(20.5) 62(79.5) | χ2=0.772 | 0.395 |
| 脑梗死部位[例(%)] | ||||
| 基底节 | 9(17.3) | 19(24.4) | ||
| 额叶 | 19(36.5) | 10(12.8) | ||
| 顶叶 | 9(17.3) | 12(15.4) | ||
| 脑干 | 4(7.7) | 12(15.4) | χ2=11.119 | 0.078 |
| 颞叶 | 7(13.5) | 14(17.9) | ||
| 小脑 | 2(3.9) | 5(6.4) | ||
| 丘脑 | 2(3.9) | 6(7.7) | ||
| 梗死面积[例(%)] | ||||
| 大面积 | 3(5.8) | 1(1.3) | ||
| 中面积 | 23(44.2) | 24(30.8)* | Z=2.163 | 0.031 |
| 小面积 | 26(50.0) | 53(67.9) | ||
| 出院后用药情况[例(%)] | ||||
| 阿司匹林 | 48(92.3) | 74(94.9) | χ2=0.355 | 0.551 |
| 氯呲格雷 | 42(80.8) | 65(83.3) | χ2=0.141 | 0.707 |
| 他汀类药物 | 35(67.3) | 49(62.8) | χ2=0.275 | 0.633 |
| 入院时空腹血糖(mmol/L) | 6.25±1.25 | 6.14±1.18 | t=0.509 | 0.611 |
| 入院时TC(mmol/L) | 4.18±0.74 | 4.06±0.65 | t=0.978 | 0.330 |
| 入院时TG(mmol/L) | 1.63±0.35 | 1.52±0.38 | t=1.785 | 0.077 |
| 入院时HDL-C(mmol/L) | 0.92±0.24 | 0.96±0.28 | t=1.033 | 0.304 |
| 入院时LDL-C(mmol/L) | 2.71±0.75 | 2.63±0.61 | t=0.593 | 0.554 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 治疗前 | 入院7 d | 出院时 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 认知障碍组 | 52 | 181.63±10.36☆ | 248.55±21.60*☆ | 356.75±29.66*#☆ |
| 认知正常组 | 78 | 201.67±12.47 | 279.22±20.49* | 432.15±30.41*# |
| 组间 | F=300.539, P<0.01 | |||
| 不同时点 | F=2831.796, P<0.01 | |||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=57.829, P<0.01 | |||
Tab.2 Serum MFG-E8 levels in normal cognition group and impaired cognition group at different time points(ng/L)
| 组别 | 例数 | 治疗前 | 入院7 d | 出院时 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 认知障碍组 | 52 | 181.63±10.36☆ | 248.55±21.60*☆ | 356.75±29.66*#☆ |
| 认知正常组 | 78 | 201.67±12.47 | 279.22±20.49* | 432.15±30.41*# |
| 组间 | F=300.539, P<0.01 | |||
| 不同时点 | F=2831.796, P<0.01 | |||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=57.829, P<0.01 | |||
| 组别 | 例数 | 治疗前 | 入院7 d | 出院时 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中重度组 | 18 | 176.79±13.12☆ | 240.25±17.93*☆ | 345.42±33.16*#☆ |
| 轻度组 | 34 | 184.20±7.61 | 252.94±22.32* | 362.74±26.20*# |
| 组间 | F=10.888, P=0.002 | |||
| 不同时点 | F=848.083, P<0.01 | |||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=0.676,P=0.551 | |||
Tab. 3 Serum MFG-E8 levels of cognition impairment in subgroups at different time points (ng/L)
| 组别 | 例数 | 治疗前 | 入院7 d | 出院时 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中重度组 | 18 | 176.79±13.12☆ | 240.25±17.93*☆ | 345.42±33.16*#☆ |
| 轻度组 | 34 | 184.20±7.61 | 252.94±22.32* | 362.74±26.20*# |
| 组间 | F=10.888, P=0.002 | |||
| 不同时点 | F=848.083, P<0.01 | |||
| 组间·不同时点 | F=0.676,P=0.551 | |||
| 组别 | 例数 | △1MFG-E8 | △2MFG-E8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 认知障碍组 | 52 | 66.91±22.07 | 175.11±28.84 |
| 认知正常组 | 78 | 77.55±26.68 | 230.47±32.48 |
| t值 | 2.383 | 9.946 | |
| P值 | 0.019 | <0.001 |
Tab.4 Changes in serum MFG-E8 levels between normal cognition group and impaired cognition group(ng/L)
| 组别 | 例数 | △1MFG-E8 | △2MFG-E8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 认知障碍组 | 52 | 66.91±22.07 | 175.11±28.84 |
| 认知正常组 | 78 | 77.55±26.68 | 230.47±32.48 |
| t值 | 2.383 | 9.946 | |
| P值 | 0.019 | <0.001 |
| 项目 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 治疗前MFG-E8 | -0.362 | 0.097 | 14.089 | <0.001 | 0.696 | 0.576 | 0.841 |
| 入院7 dMFG-E8 | -0.068 | 0.021 | 10.478 | 0.001 | 0.934 | 0.879 | 0.974 |
| 出院时MFG-E8 | -0.090 | 0.022 | 17.067 | <0.001 | 0.914 | 0.876 | 0.954 |
| △1MFG-E8 | -0.086 | 0.031 | 7.925 | 0.005 | 0.917 | 0.864 | 0.974 |
| △2MFG-E8 | -0.079 | 0.025 | 10.287 | 0.001 | 0.924 | 0.880 | 0.970 |
| 梗死面积 | - | - | 3.902 | 0.142 | - | - | - |
| 中面积 | 1.634 | 0.831 | 3.867 | 0.049 | 5.126 | 1.005 | 26.130 |
| 大面积 | 0.372 | 1.322 | 0.079 | 0.778 | 1.451 | 0.109 | 19.376 |
Tab.5 Analysis of risk factors for cognitive impairment after IS using multivariate logistic regression analysis
| 项目 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Waldχ2值 | P值 | OR值 | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 治疗前MFG-E8 | -0.362 | 0.097 | 14.089 | <0.001 | 0.696 | 0.576 | 0.841 |
| 入院7 dMFG-E8 | -0.068 | 0.021 | 10.478 | 0.001 | 0.934 | 0.879 | 0.974 |
| 出院时MFG-E8 | -0.090 | 0.022 | 17.067 | <0.001 | 0.914 | 0.876 | 0.954 |
| △1MFG-E8 | -0.086 | 0.031 | 7.925 | 0.005 | 0.917 | 0.864 | 0.974 |
| △2MFG-E8 | -0.079 | 0.025 | 10.287 | 0.001 | 0.924 | 0.880 | 0.970 |
| 梗死面积 | - | - | 3.902 | 0.142 | - | - | - |
| 中面积 | 1.634 | 0.831 | 3.867 | 0.049 | 5.126 | 1.005 | 26.130 |
| 大面积 | 0.372 | 1.322 | 0.079 | 0.778 | 1.451 | 0.109 | 19.376 |
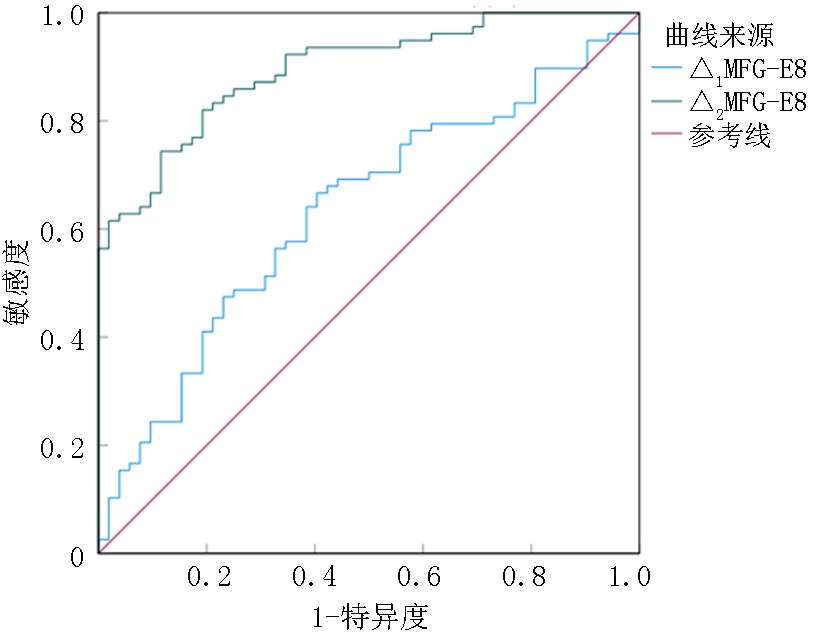
| 项目 | AUC | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||||
| △1MFG-E8 | 0.632 | 0.049 | 0.011 | 0.536 | 0.729 | 0.667 | 0.596 | 67.125 ng/L |
| △2MFG-E8 | 0.895 | 0.026 | <0.001 | 0.843 | 0.947 | 0.744 | 0.885 | 196.87 ng/L |
Tab.6 The predictive value of serum MFG-E8 changes in cognitive dysfunction after IS
| 项目 | AUC | 标准误 | P值 | 95%CI | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 界值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | |||||||
| △1MFG-E8 | 0.632 | 0.049 | 0.011 | 0.536 | 0.729 | 0.667 | 0.596 | 67.125 ng/L |
| △2MFG-E8 | 0.895 | 0.026 | <0.001 | 0.843 | 0.947 | 0.744 | 0.885 | 196.87 ng/L |
| [1] | Qu Y, Zhuo L, Li N, et al. Prevalence of post-stroke cognitive impairment in china:A community-based,cross-sectional study[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4):e0122864. |
| [2] | Lo JW, Crawford JD, Desmond DW, et al. Profile of and risk factors for poststroke cognitive impairment in diverse ethnoregional groups[J]. Neurology, 2019, 93(24):e2257-e2271. |
| [3] | Merriman NA, Sexton E, McCabe G, et al. Addressing cognitive impairment following stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis of non-randomised controlled studies of psychological interventions[J]. BMJ Open, 2019, 9(2):e024429. |
| [4] | 刘美霞, 周龙. 缺血性脑卒中患者血清Pannexin1水平及其临床意义[J]. 中国现代医学杂志, 2020, 30(8):110-113. |
| [5] | 朱子煜, 王磊, 王祖华, 等. 血清Lp-PLA2、PARK7、EPO水平变化与急性缺血性脑卒中患者NIHSS评分、CIMT的关系[J]. 中国医师杂志, 2020, 22(8):1204-1207. |
| [6] | 张晓雯, 姜金兰, 吴晓冬. 小胶质细胞对大脑认知障碍的研究进展[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2023, 27(4):498-500. |
| [7] | Fang YY, Zhang JH. MFG-E8 alleviates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal cell apoptosis by STAT3 regulating the selective polarization of microglia[J]. Int J Neurosci, 2021, 131(1):15-24. |
| [8] | Tzioras M, Daniels MJD, Davies C, et al. Human astrocytes and microglia show augmented ingestion of synapses in Alzheimer's disease via MFG-E8[J]. Cell Rep Med, 2023, 4(9):101175. |
| [9] | 中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国缺血性脑卒中和短暂性脑缺血发作二级预防指南2014[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2015, 48(4):258-273. |
| [10] |
Villalobos E, Barnes SR, Qureshi IA, et al. Spanish version of the National Institutes of health stroke scale: Awareness and use in United States. A survey study[J]. J Vasc Interv Neurol, 2017, 9(3):1-6.
pmid: 28243343 |
| [11] | 王慧云, 郭安娜. 简易精神状态检查量表的汉化及在脑外伤病人中的信效度研究[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(24):4488-4490. |
| [12] | Wong A, Yiu S, Nasreddine Z, et al. Validity and reliability of two alternate versions of the Montreal cognitive assessment (Hong Kong version) for screening of mild neurocognitive disorder[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(5):e0196344. |
| [13] | 谢琪, 钟娟平, 裴菊红, 等. 卒中后认知功能障碍评估工具的应用与选择研究进展[J]. 广西医学, 2022, 44(18):2167-2171. |
| [14] |
柳正, 王朝晖, 周春亭. MFGE8在缺血性脑损伤中表达及对巨噬细胞极化的调控作用[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2021, 38(10):1065-1069.
doi: 10.19845/j.cnki.zfysjjbzz.2021.0233 |
| [15] | 王迪, 韦传东. MFG-E8与冠心病的关系研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2020, 26(2):219-223. |
| [16] | 李铭麟, 崔檬, 王佳贺. 巨噬细胞与阿尔茨海默病相关性的研究进展[J]. 实用老年医学, 2022, 36(1):95-99. |
| [17] | Wagner J, Degenhardt K, Veit M, et al. Medin co-aggregates with vascular amyloid-β in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Nature, 2022, 612(7938):123-131. |
| [18] | Choi JI, Kang HY, Han C, et al. Milk fat globule-epidermal growth factor VIII ameliorates brain injury in the subacute phase of cerebral ischemia in an animal model[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2020, 63(2):163-170. |
| [19] | Gao YY, Zhang ZH, Zhuang Z, et al. Recombinant milk fat globule-EGF factor-8 reduces apoptosis via integrin β3/FAK/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats after traumatic brain injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(9):845. |
| [20] | Brissette MJ, Lepage S, Lamonde AS, et al. MFG-E8 released by apoptotic endothelial cells triggers anti-inflammatory macrophage reprogramming[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(4):e36368. |
| [21] | 黄伟. MFG-E8调控系统性红斑狼疮内中性粒细胞免疫反应及组织损伤的作用机制研究[D]. 湖北: 华中科技大学, 2017. |
| [22] | 王雪颖, 孟海宁, 王松梅, 等. CXC趋化因子受体7对缺血性脑卒中神经元细胞周期的影响[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2022, 34(2):151-155. |
| [23] | 贾莉子, 李晓燕, 杜宁. 缺血性脑卒中病人定量脑电图参数与梗死面积、NIHSS评分的相关性[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 21(1):161-164. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||