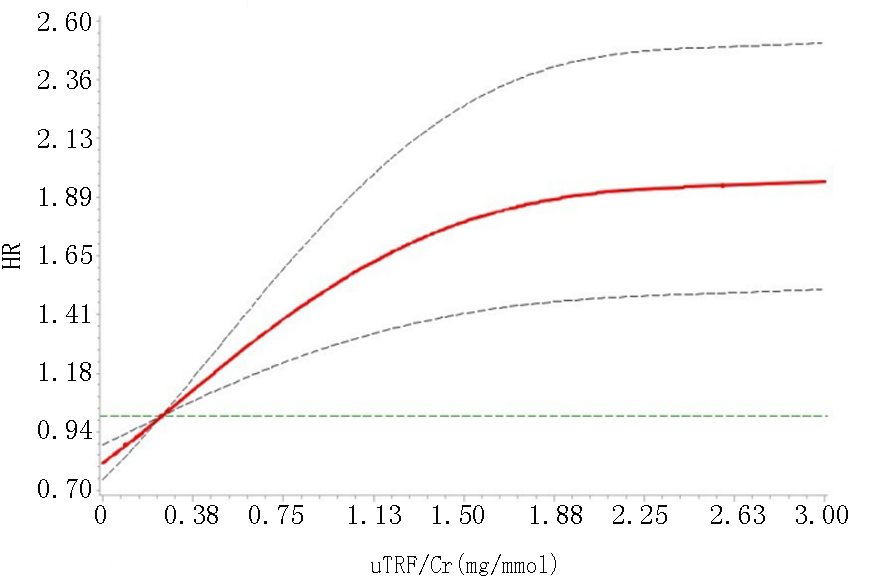
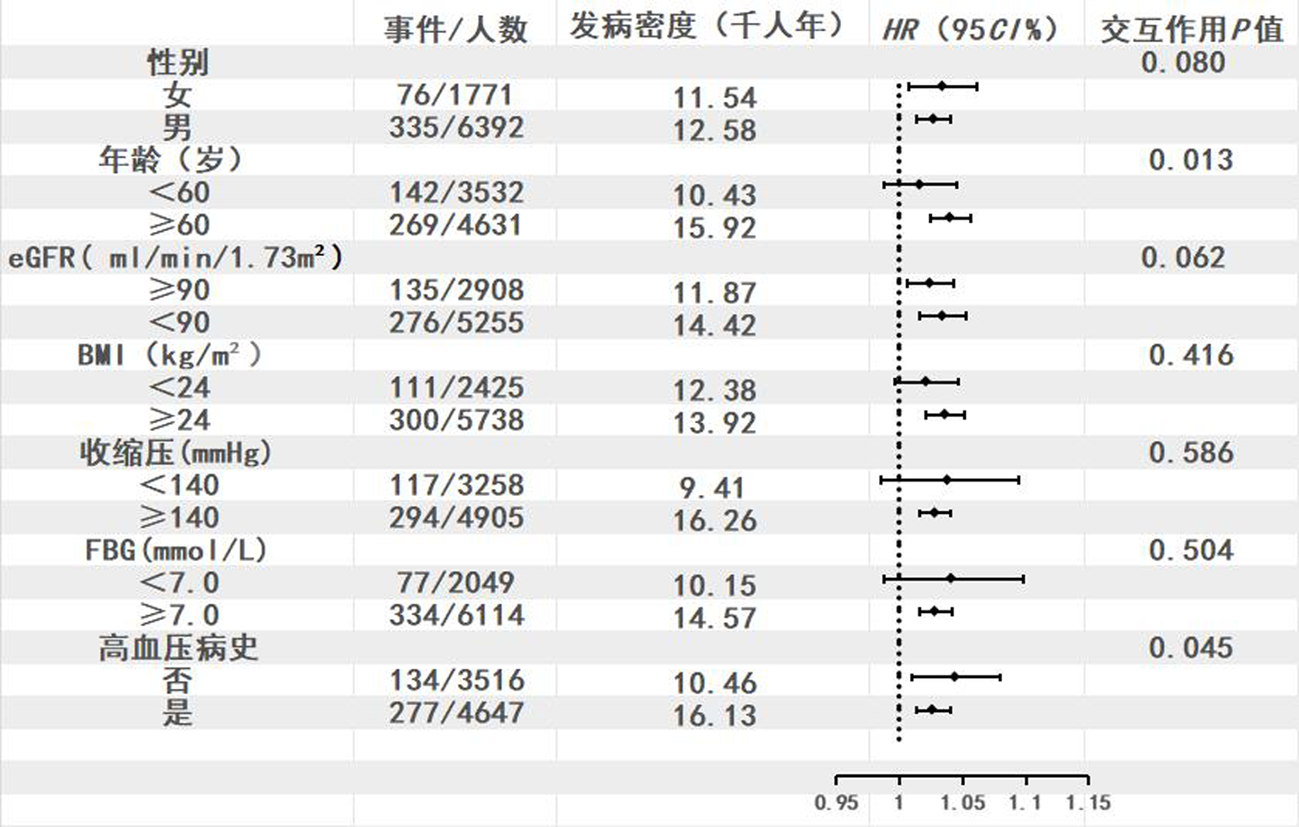
Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (8): 700-705.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.08.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association of urinary transferrin with new-onset cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ma Jiannan1, Tao Jie2, Sang Dasen2, Wu Shouling3, Zhang Qi2( )
)
- 1. Graduate School,Chengde Medical University, Chengde 067000,China
2. Department of Cardiology,Baoding No.1 Central Hospital, Baoding 071000,China
3. Department of Cardiology, Kailuan General Hospital,Tangshan 063000,China
-
Received:2024-06-13Online:2024-08-20Published:2024-09-03 -
Contact:Zhang Qi,Email: zhangqi2005a@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Jiannan, Tao Jie, Sang Dasen, Wu Shouling, Zhang Qi. Association of urinary transferrin with new-onset cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(8): 700-705.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.08.004
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 男性 [例(%)] | 收缩压 (mmHg) | 舒张压 (mmHg) | 心率 (次/min) | BMI (kg/m2) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总人群 | 8 163 | 60.46±9.96 | 6 392(78.30) | 146.08±20.60 | 82.92±10.91 | 77.47± 12.82 | 25.80±3.47 | |||||||||
| 第一分位组 | 2 721 | 58.77±9.93 | 2 326(85.48) | 141.77±19.34 | 82.07±10.48 | 58.77±9.93 | 25.73±3.34 | |||||||||
| 第二分位组 | 2 721 | 60.68±9.66 | 2 063(75.78) | 145.42±20.22 | 82.43±10.57 | 76.83±12.48 | 25.64±3.38 | |||||||||
| 第三分位组 | 2 721 | 61.92±10.03 | 2 003(73.65) | 151.03±21.15 | 84.26±11.52 | 79.06±13.14 | 26.04±3.66 | |||||||||
| 24.650 | 24.660 | 34.987 | 14.435 | 49.789 | 13.897 | |||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| 组别 | uACR (mg/mmol) | uTRF/Cr (mg/mmol) | FBG (mmol/L) | HbA1c (%) | TG (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | ||||||||||
| 总人群 | 1.67(0.81~4.50) | 0.24(0.16~0.47) | 9.11±3.17 | 7.59±1.66 | 1.54(1.05~2.34) | 3.25±0.96 | ||||||||||
| 第一分位组 | 0.98(0.65~1.54) | 0.13(0.11~0.16) | 8.38±2.60 | 7.20±1.44 | 1.44(1.01~2.16) | 3.22±0.94 | ||||||||||
| 第二分位组 | 1.50(0.79~2.71) | 0.24(0.21~0.29) | 8.82±2.93 | 7.47±1.59 | 1.49(1.01~2.28) | 3.22±0.93 | ||||||||||
| 第三分位组 | 7.46(3.10~20.00) | 0.70(0.47~1.48) | 10.12±3.67 | 8.11±1.81 | 1.70(1.15~2.63) | 3.32±1.01 | ||||||||||
| 87.580 | 33.890 | 25.340 | 37.990 | 1.479 | 39.380 | |||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.207 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| 组别 | eGFR [ml/(min·1.73 m2)] | 吸烟 [例(%)] | 高血压 [例(%)] | 降压治疗 [例(%)] | 降糖治疗 [例(%)] | |||||||||||
| 总人群 | 92.20±16.34 | 2 707(33.16) | 4 647(56.93) | 3 361(41.17) | 3 590(43.98) | |||||||||||
| 第一分位组 | 93.28±16.62 | 1 042(38.29) | 1 371(50.39) | 1 073(39.43) | 1 033(37.96) | |||||||||||
| 第二分位组 | 92.56±14.43 | 872(32.05) | 1 509(55.46) | 1 068(39.25) | 1 166(42.85) | |||||||||||
| 第三分位组 | 90.74±17.69 | 793(29.14) | 1 767(64.94) | 1 220(44.84) | 1 391(51.12) | |||||||||||
| 7.890 | 20.776 | 28.980 | 14.768 | 29.987 | ||||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||||||
Tab.1 Baseline data among the three groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 年龄(岁) | 男性 [例(%)] | 收缩压 (mmHg) | 舒张压 (mmHg) | 心率 (次/min) | BMI (kg/m2) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总人群 | 8 163 | 60.46±9.96 | 6 392(78.30) | 146.08±20.60 | 82.92±10.91 | 77.47± 12.82 | 25.80±3.47 | |||||||||
| 第一分位组 | 2 721 | 58.77±9.93 | 2 326(85.48) | 141.77±19.34 | 82.07±10.48 | 58.77±9.93 | 25.73±3.34 | |||||||||
| 第二分位组 | 2 721 | 60.68±9.66 | 2 063(75.78) | 145.42±20.22 | 82.43±10.57 | 76.83±12.48 | 25.64±3.38 | |||||||||
| 第三分位组 | 2 721 | 61.92±10.03 | 2 003(73.65) | 151.03±21.15 | 84.26±11.52 | 79.06±13.14 | 26.04±3.66 | |||||||||
| 24.650 | 24.660 | 34.987 | 14.435 | 49.789 | 13.897 | |||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| 组别 | uACR (mg/mmol) | uTRF/Cr (mg/mmol) | FBG (mmol/L) | HbA1c (%) | TG (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | ||||||||||
| 总人群 | 1.67(0.81~4.50) | 0.24(0.16~0.47) | 9.11±3.17 | 7.59±1.66 | 1.54(1.05~2.34) | 3.25±0.96 | ||||||||||
| 第一分位组 | 0.98(0.65~1.54) | 0.13(0.11~0.16) | 8.38±2.60 | 7.20±1.44 | 1.44(1.01~2.16) | 3.22±0.94 | ||||||||||
| 第二分位组 | 1.50(0.79~2.71) | 0.24(0.21~0.29) | 8.82±2.93 | 7.47±1.59 | 1.49(1.01~2.28) | 3.22±0.93 | ||||||||||
| 第三分位组 | 7.46(3.10~20.00) | 0.70(0.47~1.48) | 10.12±3.67 | 8.11±1.81 | 1.70(1.15~2.63) | 3.32±1.01 | ||||||||||
| 87.580 | 33.890 | 25.340 | 37.990 | 1.479 | 39.380 | |||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.207 | <0.001 | |||||||||||
| 组别 | eGFR [ml/(min·1.73 m2)] | 吸烟 [例(%)] | 高血压 [例(%)] | 降压治疗 [例(%)] | 降糖治疗 [例(%)] | |||||||||||
| 总人群 | 92.20±16.34 | 2 707(33.16) | 4 647(56.93) | 3 361(41.17) | 3 590(43.98) | |||||||||||
| 第一分位组 | 93.28±16.62 | 1 042(38.29) | 1 371(50.39) | 1 073(39.43) | 1 033(37.96) | |||||||||||
| 第二分位组 | 92.56±14.43 | 872(32.05) | 1 509(55.46) | 1 068(39.25) | 1 166(42.85) | |||||||||||
| 第三分位组 | 90.74±17.69 | 793(29.14) | 1 767(64.94) | 1 220(44.84) | 1 391(51.12) | |||||||||||
| 7.890 | 20.776 | 28.980 | 14.768 | 29.987 | ||||||||||||
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||||||||||
| 变量 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分组 | ||||||
| 第一分位组 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| 第二分位组 | 0.112 | 0.137 | 0.673 | 1.12 | 0.86~1.46 | 0.412 |
| 第三分位组 | 0.418 | 0.131 | 10.250 | 1.52 | 1.18~1.97 | 0.001 |
| 年龄 | 0.030 | 0.007 | 20.356 | 1.03 | 1.02~1.04 | <0.001 |
| 性别(男) | 0.125 | 0.138 | 0.815 | 1.13 | 0.86~1.49 | 0.367 |
| 收缩压 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 19.904 | 1.01 | 1.01~1.02 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -0.013 | 0.015 | 0.775 | 0.99 | 0.96~1.02 | 0.379 |
| LDL-C | 0.023 | 0.052 | 0.192 | 1.02 | 0.92~1.13 | 0.661 |
| FBG | 0.061 | 0.014 | 18.959 | 1.06 | 1.03~1.09 | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.165 | 1.00 | 0.99~1.01 | 0.685 |
| 吸烟 | 0.283 | 0.113 | 6.291 | 1.33 | 1.06~1.66 | 0.012 |
| 使用降压药 | 0.354 | 0.100 | 12.470 | 1.42 | 1.17~1.73 | <0.001 |
| 使用降糖药 | 0.029 | 0.103 | 0.078 | 1.03 | 0.84~1.26 | 0.779 |
Tab.2 Multivariate COX regression model for uTRF/Cr and newly occurred CVD
| 变量 | 回归 系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分组 | ||||||
| 第一分位组 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| 第二分位组 | 0.112 | 0.137 | 0.673 | 1.12 | 0.86~1.46 | 0.412 |
| 第三分位组 | 0.418 | 0.131 | 10.250 | 1.52 | 1.18~1.97 | 0.001 |
| 年龄 | 0.030 | 0.007 | 20.356 | 1.03 | 1.02~1.04 | <0.001 |
| 性别(男) | 0.125 | 0.138 | 0.815 | 1.13 | 0.86~1.49 | 0.367 |
| 收缩压 | 0.011 | 0.002 | 19.904 | 1.01 | 1.01~1.02 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -0.013 | 0.015 | 0.775 | 0.99 | 0.96~1.02 | 0.379 |
| LDL-C | 0.023 | 0.052 | 0.192 | 1.02 | 0.92~1.13 | 0.661 |
| FBG | 0.061 | 0.014 | 18.959 | 1.06 | 1.03~1.09 | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.165 | 1.00 | 0.99~1.01 | 0.685 |
| 吸烟 | 0.283 | 0.113 | 6.291 | 1.33 | 1.06~1.66 | 0.012 |
| 使用降压药 | 0.354 | 0.100 | 12.470 | 1.42 | 1.17~1.73 | <0.001 |
| 使用降糖药 | 0.029 | 0.103 | 0.078 | 1.03 | 0.84~1.26 | 0.779 |
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分组 | ||||||
| 第一分位组 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| 第二分位组 | 0.033 | 0.142 | 0.053 | 1.03 | 0.78~1.37 | 0.818 |
| 第三分位组 | 0.294 | 0.137 | 4.643 | 1.34 | 1.03~1.76 | 0.031 |
| 年龄 | 0.029 | 0.007 | 15.946 | 1.03 | 1.02~1.04 | <0.001 |
| 性别(男) | 0.109 | 0.150 | 0.525 | 1.12 | 0.83~1.50 | 0.367 |
| 收缩压 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 13.539 | 1.01 | 1.01~1.02 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -0.020 | 0.016 | 1.422 | 0.98 | 0.95~1.01 | 0.223 |
| LDL-C | 0.013 | 0.057 | 0.054 | 1.01 | 0.91~1.13 | 0.817 |
| FBG | 0.056 | 0.016 | 12.592 | 1.06 | 1.03~1.09 | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.323 | 1.00 | 0.99~1.01 | 0.570 |
| 吸烟 | 0.317 | 0.120 | 6.926 | 1.37 | 1.08~1.740 | 0.009 |
| 使用降压药 | 0.309 | 0.108 | 8.231 | 1.36 | 1.10~1.68 | 0.004 |
| 使用降糖药 | 0.081 | 0.111 | 0.530 | 1.08 | 0.87~1.35 | 0.467 |
Tab.3 Multivariate Cox regression model for the correlation between uTRF/Cr and newly occurred CVD after adjusting for relevant factors and excluding a large population of albuminuria
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 分组 | ||||||
| 第一分位组 | - | - | - | 1 | - | - |
| 第二分位组 | 0.033 | 0.142 | 0.053 | 1.03 | 0.78~1.37 | 0.818 |
| 第三分位组 | 0.294 | 0.137 | 4.643 | 1.34 | 1.03~1.76 | 0.031 |
| 年龄 | 0.029 | 0.007 | 15.946 | 1.03 | 1.02~1.04 | <0.001 |
| 性别(男) | 0.109 | 0.150 | 0.525 | 1.12 | 0.83~1.50 | 0.367 |
| 收缩压 | 0.010 | 0.003 | 13.539 | 1.01 | 1.01~1.02 | <0.001 |
| BMI | -0.020 | 0.016 | 1.422 | 0.98 | 0.95~1.01 | 0.223 |
| LDL-C | 0.013 | 0.057 | 0.054 | 1.01 | 0.91~1.13 | 0.817 |
| FBG | 0.056 | 0.016 | 12.592 | 1.06 | 1.03~1.09 | <0.001 |
| eGFR | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.323 | 1.00 | 0.99~1.01 | 0.570 |
| 吸烟 | 0.317 | 0.120 | 6.926 | 1.37 | 1.08~1.740 | 0.009 |
| 使用降压药 | 0.309 | 0.108 | 8.231 | 1.36 | 1.10~1.68 | 0.004 |
| 使用降糖药 | 0.081 | 0.111 | 0.530 | 1.08 | 0.87~1.35 | 0.467 |
| [1] |
Gregory A, Degu A, Kalkidan H, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10159): 1736-1788.
doi: S0140-6736(18)32203-7 pmid: 30496103 |
| [2] |
Roth G, Mensah G, Johnson C, et al. Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990-2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 76(25): 2982-3021.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010 pmid: 33309175 |
| [3] | Wang H, Zhang H, Zou Z. Changing profiles of cardiovascular disease and risk factors in China: A secondary analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2023, 136(20): 2431-2441. |
| [4] | 中国心血管健康与疾病报告编写组. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告2022》概要[J]. 中国介入心脏病学杂志, 2023, 31(7): 485-508. |
| [5] | Christine G, Bødtker M, Johnny K, et al. 10-year cardiovascular risk in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2023, 82(16): 1583-1594. |
| [6] | Wang Y, Neil A, Jiao Y, et al. Sex differences in the association between diabetes and risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 5,162,654 participants[J]. BMC Medicine, 2019, 17(1): 1-18. |
| [7] |
An Y, Zhang P, Wang P, et al. Cardiovascular and all-cause mortality over a 23-year period among Chinese with newly diagnosed diabetes in the Da Qing IGT and diabetes study[J]. Diabetes Care, 2015, 38(7): 1365-1371.
doi: 10.2337/dc14-2498 pmid: 25887356 |
| [8] |
Festa A, Agostino R. Howard Gronic. Chronic subclinical inflammation as part of the insulin resistance syndrome: The Insulin Resistance Atherosclerosis Study(IRAS)[J]. Circulation, 2000, 102(1): 42-47.
doi: 10.1161/01.cir.102.1.42 pmid: 10880413 |
| [9] | Matsushita K, Coresh J, Sang Y, et al. Estimated glomerular filtration rate and albuminuria for prediction of cardiovascular outcomes: A collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2015, 3(7): 514-525. |
| [10] |
Bernard A, Amor A, Goemaere-Vanneste J, et al. Microtransferrinuria is a more sensitive indicator of early glomerular damage in diabetes than microalbuminuria[J]. Clin Chem, 1988, 34(9):1920-1921.
pmid: 3416456 |
| [11] |
Zou L, Wang X, Guo Z, et al. Differential urinary proteomics analysis of myocardial infarction using iTRAQ quantification[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2019, 19(5): 3972-3988.
doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10088 pmid: 30942401 |
| [12] | Wu S, Huang Z, Yang X, et al. Prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health and its relationship with the 4-year cardiovascular events in a northern Chinese industrial city[J]. Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes, 2012, 5(4): 487-493. |
| [13] | Association D. Standards of medical care in diabetes-2010[J]. Diabetes Care, 2010, 33 Suppl 1(S1):S11-61. |
| [14] | Inker L, Schmid C, Tighiouart H, et al. Estimating glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine and cystatin C[J]. N Engl J Med, 2012, 367(1):20-29. |
| [15] |
Huang Z, Chen Z, Wang X, et al. Association of cardiovascular health score trajectory with incident myocardial infarction in hypertensive patients[J]. Hypertension, 2022, 79(11):2622-2630.
doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.19633 pmid: 36082672 |
| [16] | Wu J, Chen S, Zhou Y, et al. Non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol on the risks of stroke: A result from the Kailuan study[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(9): e74634. |
| [17] |
Takuma N, Mihoko H, Masafumi K, et al. Increased urinary excretions of immunoglobulin G, ceruloplasmin, and transferrin predict development of microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2006, 29(1): 142-144.
doi: 10.2337/diacare.29.1.142 pmid: 16373913 |
| [18] |
Tao J, Sang D, Zhang X, et al. An elevated urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio increases the risk of incident cardia-cerebrovascular disease in individuals with type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2024, 16(1): 30.
doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01256-5 pmid: 38291519 |
| [19] | Chen F, Yang W, Weng J, et al. Albuminuria: Prevalence, associated risk factors and relationship with cardiovascular disease[J]. J Diabetes Investig, 2014, 5(4): 464-471. |
| [20] | Juan J, Antonio J, Juan J, et al. Urine transferrin as an early endothelial dysfunction marker in type 2 diabetic patients without nephropathy: A case control study[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2021, 13(1): 128. |
| [21] |
Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu Y, et al. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis[J]. Am J Cardiol, 1972, 30(6):595-602.
doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(72)90595-4 pmid: 4263660 |
| [22] |
Fang Z, Prins J, Marwick T. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications[J]. Endocr Rev, 2004, 25(4): 543-567.
doi: 10.1210/er.2003-0012 pmid: 15294881 |
| [1] | Wu Weijun, Chen Xiao, Wang Shaodan, Bu Laijun, Wu Xinchao, Yan Chenyang, Dong Gaiqin, Jiang Lijun, Wei Wenping. Analysis of screening data of urinalysis in 1973 students in Yangzhou [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 702-705. |
| [2] | Jiang Ji, Zhu Xiaogang, Jiang Shan, Dawa Zhaba, Cen Qiang. Risk factors of proteinuria in hypertensive people living at high altitude for generations [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(12): 1086-1090. |
| [3] | Wang Lingling, Wu Jinlan, Wu Wei, Shen Shipeng, Chi Yanqing, Liu Maodong. A meta-analysis of the renal protective effects of vitamin D and its analogues in non dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1081-1088. |
| [4] | Zhang Lei, Lou Haidong, Zhi Yu, Qi Shuying. Efficacy and safety of PCSK9 inhibitors on atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(12): 1074-1080. |
| [5] | Nian Shiyana, Feng Leib. Difference of cardiovascular biochemical indicators among Dai, Hani and Yi in Yuanjiang county of Yunnan Province [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(8): 689-692. |
| [6] | Zhang Lingxia, Nie Qian, Hao Zhihua, Liu Chenghao, Wang Zhongli, Chen Feifei, Liu Huanxin. Effects of indoor and outdoor working environment on inflammatory markers of cardiovascular system [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(3): 224-227. |
| [7] | Li Yi, Yao Mahui, Liu Demin, Wang Qian, Geng Xue, Cui Wei. Prognostic value of pulse wave velocity and anklebrachial index [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(11): 986-990. |
| [8] | Niu Guochao, Yin Fengrong, Zhang Xiaolan. Clinical features and treatment of statinsinduced liver injury [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(6): 478-481. |
| [9] | Zhao Jia1, Li Gang2. Indications for statins in primary prevention of cardiovascular disease [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(6): 465-468. |
| [10] | Liang Yi1, Hu Rui2,3. The blood lipids and its clinical significance [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(6): 461-464. |
| [11] | Liu Shasha1, Chen Dan2, Zhang Jing1, Huang Yuting1, Alimila·Saiyitijiang1, Nai Zhihui1, Gao Ying1. Complement C3 level and relationship with apolipoprotein B in essential hypertension patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(9): 752-754,758. |
| [12] | Cui Xue, Yang Lin, Li Juan, Ma Lixia. Changes and significance of immunoglobulin light chain in diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(4): 305-309. |
| [13] | Wang Li, Li Mengtao,Zhang Xuan,Zeng Xiaofeng,Zhang Wen, Zhang Fengchun. Treatment comments on lupus nephritis: guidelines and advances [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(5): 470-474. |
| [14] | Zhao Zhansheng. Thyroid hormone and cardiovascular diseases [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(3): 250-253. |
| [15] | . Efficacy and safety of Evolocumab for lowering low density lipoprotein cholesterol:a meta-analysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(5): 481-485. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||