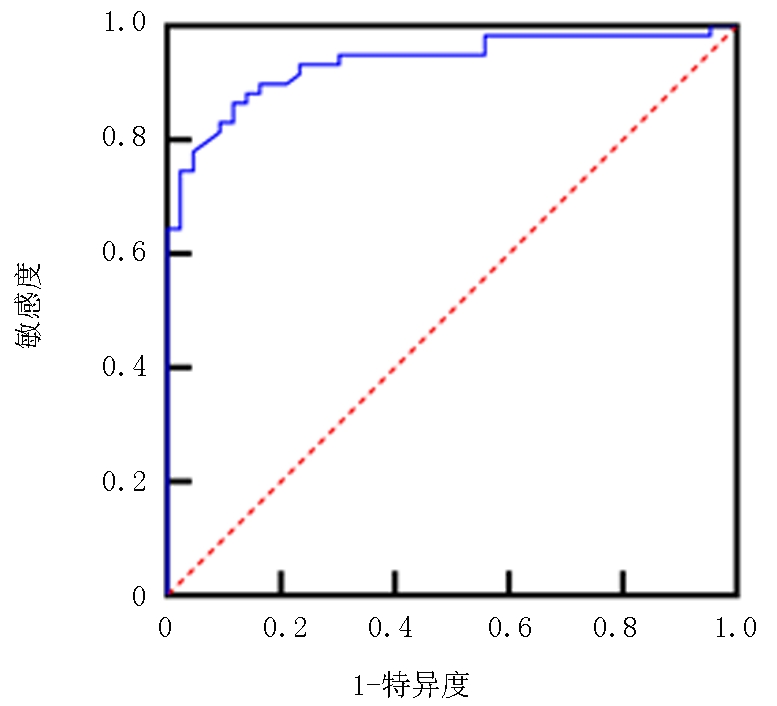
| [1] |
王玉, 张永康, 陈健飞. 早产儿支气管肺发育不良的危险因素及预后分析[J]. 海南医学, 2023, 34(1):67-70.
|
| [2] |
Abiramalatha T, Ramaswamy VV, Bandyopadhyay T, et al. Interventions to prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia in preterm neonates: An umbrella review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2022, 176(5):502-516.
doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2021.6619
pmid: 35226067
|
| [3] |
孙祎璠, 马俐, 龚小慧, 等. 基于生物信息学分析microRNA-495-5p在早产儿支气管肺发育不良中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中国当代儿科杂志, 2020, 22(1):24-30.
|
| [4] |
孙梦泽, 侯阿娜. 氨基末端脑钠肽前体在早期诊断早产儿支气管肺发育不良及合并肺动脉高压中的研究进展[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2024, 31(3):206-209.
|
| [5] |
王瑶, 徐艳, 孟令建, 等. 前B细胞集落增强因子与脂联素在支气管肺发育不良早产儿中的表达及意义[J]. 临床与病理杂志, 2021, 41(6):1286-1293.
|
| [6] |
Siffel C, Kistler KD, Lewis JFM, et al. Global incidence of bronchopulmonary dysplasia among extremely preterm infants: A systematic literature review[J]. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2021, 34(11):1721-1731.
|
| [7] |
邵肖梅, 叶鸿瑁, 丘小汕. 实用新生儿学[M]. 5版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2019.
|
| [8] |
Jian M, He SR, Liu YM, et al. The high-risk factors of different severities of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) based on the national institute of child health and human development (NICHD) diagnosis criteria in 2018[J]. J Bras Pneumol, 2021, 47(5):e20210125.
|
| [9] |
周瑞茜, 倪王平, 柯若, 等. 家庭参与式护理模式下支气管肺发育不良早产儿2岁内再入院的影响因素分析[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2022, 57(12):1481-1485.
doi: 10.3761/j.issn.0254-1769.2022.12.011
|
| [10] |
Jensen EA, Edwards EM, Greenberg LT, et al. Severity of bronchopulmonary dysplasia among very preterm infants in the United States[J]. Pediatrics, 2021, 148(1):e2020030007.
|
| [11] |
沈仙, 陈许, 卢刻羽, 等. 极早和超早产儿支气管肺发育不良的回顾性研究[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 42(10):1440-1445.
|
| [12] |
李丽丽, 李瑞, 曾月瑶, 等. 胎龄 < 32周早产儿支气管肺发育不良临床危险因素及并发症的分析与防治策略[J]. 临床医学进展, 2020, 10(4):587-594.
|
| [13] |
李俊峰. 早产极低出生体重儿支气管肺发育不良的危险因素分析探讨[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2015.
|
| [14] |
方广东, 贾贝贝, 陈长春, 等. 极低出生体重儿支气管肺发育不良的高危因素及防治[J]. 东南大学学报(医学版), 2020, 39(4):430-435.
|
| [15] |
焦冬香, 张瑜. 机械通气、肺表面活性物质联合布地奈德防治早产儿支气管肺发育不良的临床效果[J]. 临床医学研究与实践, 2023, 8(11):69-71, 182.
|
| [16] |
王彦波, 赵亮, 李丽, 等. 无创高频振荡通气联合枸橼酸咖啡因对胎龄28-32周早产儿有创机械通气撤机后呼吸支持的研究[J]. 重庆医学, 2023, 52(15):2335-2339.
|
| [17] |
张倩薇, 丁冉, 孙启斌, 等. 组织学绒毛膜羊膜炎暴露对呼吸窘迫综合征早产儿并发支气管肺发育不良的影响[J]. 中国小儿急救医学, 2021, 28(5):380-384.
|
| [18] |
王华伟, 朱雪萍. 早产儿支气管肺发育不良危险因素的研究进展[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2021, 26(11):1741-1744.
|