Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 1067-1072.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.12.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Safety of lumbar drainage on aneurysm subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients: a meta-analysis
Ma Hongmeia( ), Li Yuemeib, Li Xiaofangb, Pan Shiqinc
), Li Yuemeib, Li Xiaofangb, Pan Shiqinc
- a. Department of Neurology;b. Department of Nursing;c. Intensive Care Unit, Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital, Xining 810007, China
-
Received:2021-04-27Online:2021-12-20Published:2021-12-24 -
Contact:Ma Hongmei E-mail:hmma@alu.suda.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Ma Hongmei, Li Yuemei, Li Xiaofang, Pan Shiqin. Safety of lumbar drainage on aneurysm subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients: a meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(12): 1067-1072.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.12.002
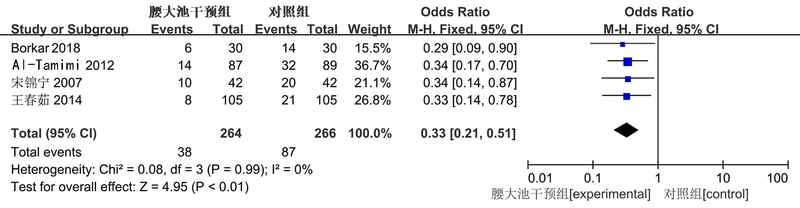
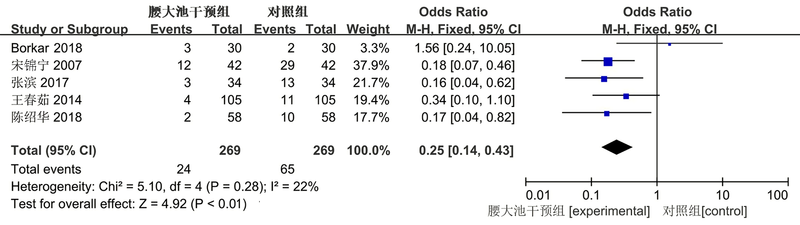
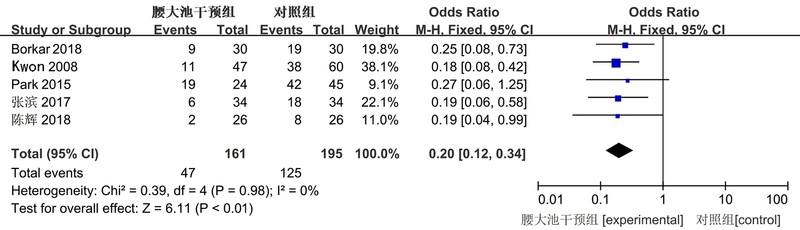
| 作者 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 人种 | 临床特征 | 例数 | 干预方法 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | 对照组 | 干预组 | |||||||
| Ochiai [ | 2001 | 美国 | 高加索 | Fisher分级Ⅰ-Ⅴ级 | 33 | 17 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ⑤ | |
| Kwon[ | 2008 | 印度 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 30 | 30 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②⑤⑥ | |
| Al-Tamimi[ | 2012 | 德国 | 高加索 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 105 | 105 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①④⑤ | |
| Park[ | 2015 | 韩国 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 126 | 108 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②⑤⑥ | |
| Borkar [ | 2018 | 印度 | 亚裔 | Hunt-Hess分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 30 | 30 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①②④⑤ | |
| 宋锦宁[ | 2007 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Hunt-Hess分级Ⅰ-Ⅴ级 | 42 | 42 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①③ | |
| 肖胜[ | 2013 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Hunt-Hess分级Ⅰ-Ⅳ级 | 39 | 33 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ⑤ | |
| 王春茹[ | 2014 | 中国 | 亚裔 | 未说明 | 105 | 105 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①③⑤ | |
| 张滨[ | 2017 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 34 | 34 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②③ | |
| 陈辉[ | 2018 | 中国 | 亚裔 | 未说明 | 26 | 26 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ② | |
| 陈绍华[ | 2018 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅰ-Ⅲ | 58 | 58 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②③⑤ | |
| 作者 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 人种 | 临床特征 | 例数 | 干预方法 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干预组 | 对照组 | 对照组 | 干预组 | |||||||
| Ochiai [ | 2001 | 美国 | 高加索 | Fisher分级Ⅰ-Ⅴ级 | 33 | 17 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ⑤ | |
| Kwon[ | 2008 | 印度 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 30 | 30 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②⑤⑥ | |
| Al-Tamimi[ | 2012 | 德国 | 高加索 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 105 | 105 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①④⑤ | |
| Park[ | 2015 | 韩国 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 126 | 108 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②⑤⑥ | |
| Borkar [ | 2018 | 印度 | 亚裔 | Hunt-Hess分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 30 | 30 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①②④⑤ | |
| 宋锦宁[ | 2007 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Hunt-Hess分级Ⅰ-Ⅴ级 | 42 | 42 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①③ | |
| 肖胜[ | 2013 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Hunt-Hess分级Ⅰ-Ⅳ级 | 39 | 33 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ⑤ | |
| 王春茹[ | 2014 | 中国 | 亚裔 | 未说明 | 105 | 105 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ①③⑤ | |
| 张滨[ | 2017 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅱ-Ⅳ级 | 34 | 34 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②③ | |
| 陈辉[ | 2018 | 中国 | 亚裔 | 未说明 | 26 | 26 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ② | |
| 陈绍华[ | 2018 | 中国 | 亚裔 | Fisher分级Ⅰ-Ⅲ | 58 | 58 | 常规治疗 | 腰大池引流 | ②③⑤ | |
| [1] |
Lawton MT, Vates GE. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage[J]. N Engl J Med, 2017, 377(3):257-266.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp1605827 URL |
| [2] |
Connolly ES Jr, Rabinstein AA, Carhuapoma JR, et al. Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association[J]. Stroke, 2012, 43(6):1711-1737.
doi: 10.1161/STR.0b013e3182587839 pmid: 22556195 |
| [3] |
Qian C, Yu X, Chen J, et al. Effect of the drainage of cerebrospinal fluid in patients with aneurismal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A meta-analysis[J]. Medicine, 2016, 95(41):e5140.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005140 URL |
| [4] | Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0[EB/OL](2011-03-01) [2014-07-12]. |
| [5] |
Ochiai H, Yamakawa Y. Continuous lumbar drainage for the preoperative management of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Neurol Med Chir, 2001, 41(12):576-580.
doi: 10.2176/nmc.41.576 URL |
| [6] |
Kwon OY, Kim YJ, Kim YJ, et al. The utility and benefits of external lumbar CSF drainage after endovascular coiling on aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2008, 43(6):281-287.
doi: 10.3340/jkns.2008.43.6.281 URL |
| [7] |
Al-Tamimi YZ, Bhargava D, Feltbower RG, et al. Lumbar drainage of cerebrospinal fluid after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial (LUMAS)[J]. Stroke, 2012, 43(3):677-682.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.111.625731 pmid: 22282887 |
| [8] |
Park S, Yang N, Seo E. The effectiveness of lumbar cerebrospinal fluid drainage to reduce the cerebral vasospasm after surgical clipping for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. J Korean Neurosurg Soc, 2015, 57(3):167-173.
doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.57.3.167 URL |
| [9] |
Borkar SA, Singh M, Kale SS, et al. Spinal cerebrospinal fluid drainage for prevention of vasospasm in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A prospective, randomized controlled study[J]. Asian J Neurosurg, 2018, 13(2) :238-246.
doi: 10.4103/1793-5482.228512 URL |
| [10] | 宋锦宁, 刘守勋, 王拓, 等. 动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血早期病因治疗与保守治疗效果的对照研究[J]. 中国急救医学, 2007, 27(1):12-14. |
| [11] | 肖胜, 王鸿生, 武永康. 腰大池置管外引流术在动脉瘤术后早期应用分析[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2013, 18(1):52-53. |
| [12] | 王春茹, 陈念, 王立平. 动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血腰大池引流的疗效分析[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2014, 17(18):74-76. |
| [13] | 张滨. 腰大池置管持续引流对动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血并发脑积水的防治效果[J]. 中国药物经济学, 2017, 12(7):112-114. |
| [14] | 陈辉, 赖琴, 贾映海, 等. PICC管持续腰大池引流联合尼莫地平鞘内注射治疗动脉瘤性蛛网膜下腔出血的临床研究[J]. 中国老年保健医学, 2018, 83(2):54-56. |
| [15] | 陈绍华. 动脉瘤夹闭术后腰大池引流联合3H治疗蛛网膜下腔出血的效果及对血管活性因子的影响[J]. 医学临床研究, 2018, 35(9):1723-1726. |
| [16] | Chowdhury T, Petropolis A, Wilkinson M, et al. Controversies in the anesthetic management of intraoperative rupture of intracranial aneurysm[J]. Anesthesiol Res Pract, 2014: 595837. |
| [17] | Chowdhury T, Cappellani RB, Sandu N, et al. Perioperative variables contributing to the rupture of intracranial aneurysm: An update[J]. Scient World J, 2013: 396404. |
| [18] |
Ibrahim GM, Macdonald RL. The effects of flfluid balance and colloid administration on outcomes in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A propensity score-matched analysis[J]. Neurocrit Care, 2013 19(2):140-149.
doi: 10.1007/s12028-013-9860-z pmid: 23715669 |
| [19] |
Maeda Y, Shirao S, Yoneda H, et al. Comparison of lumbar drainage and external ventricular drainage for clearance of subarachnoid clots after Guglielmi detachable coil embolization for aneurysmal subarachnoid Hemorrhage[J]. Clin Neurol Neurosurg, 2013, 115(7):965-970.
doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2012.10.001 URL |
| [20] | Chen S, Li Q, Wu H, et al. The harmful effects of subarachnoid hemorrhage on extracerebral organs[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2014: 858496. |
| [21] |
Mrozek S, Constantin JM, Geeraerts T. Brain lung crosstalk: Implications for neurocritical care patients[J]. World J Crit Care Med, 2015, 4(3):163-178.
doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v4.i3.163 URL |
| [22] |
Van Donkelaar CE, Bakker NA, Veeger NJ, et al. Predictive factors for rebleeding after aneutysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Rebleeding aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage study[J]. Stroke, 2015, 46(8):2100-2106.
doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010037 pmid: 26069261 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||