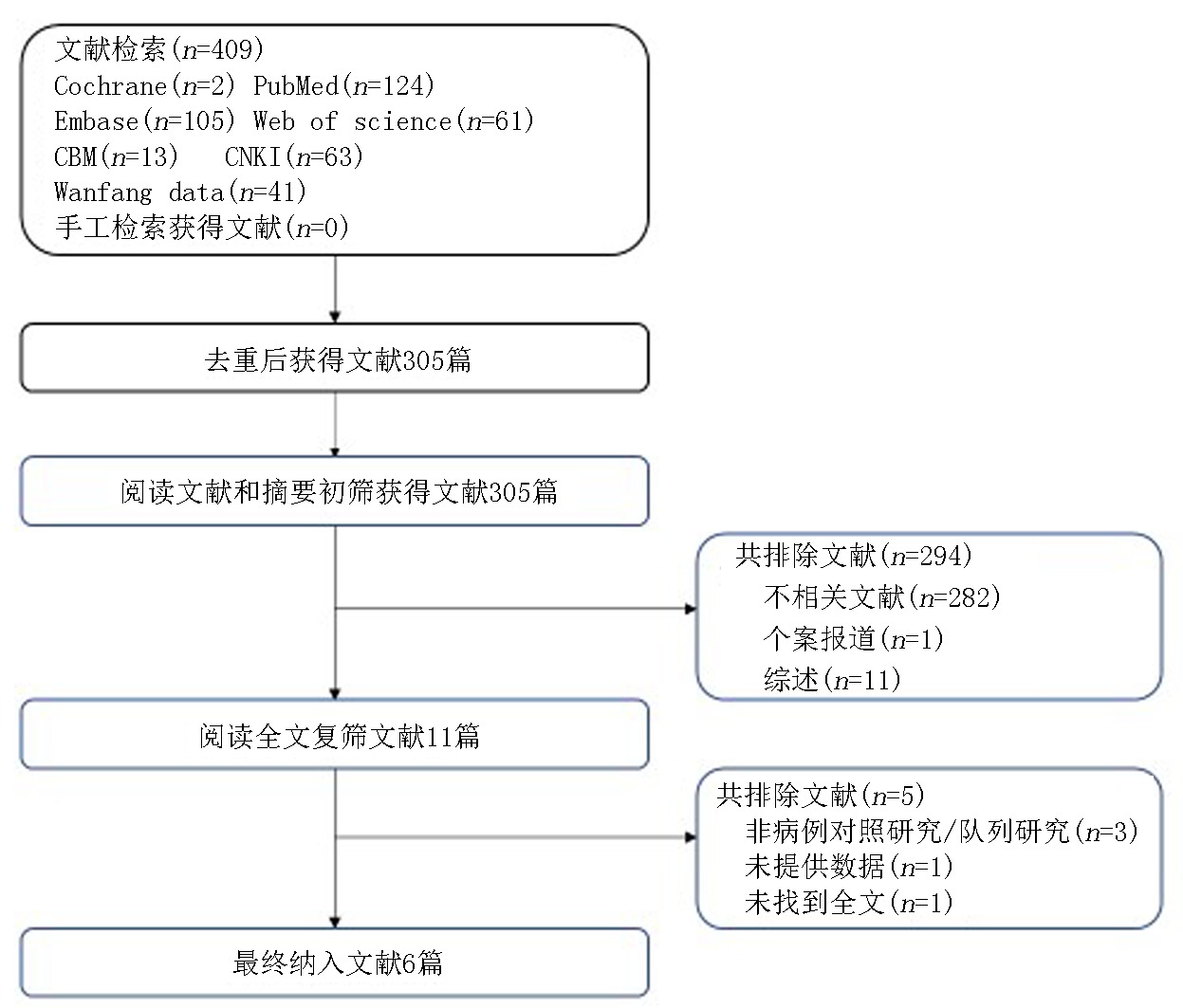
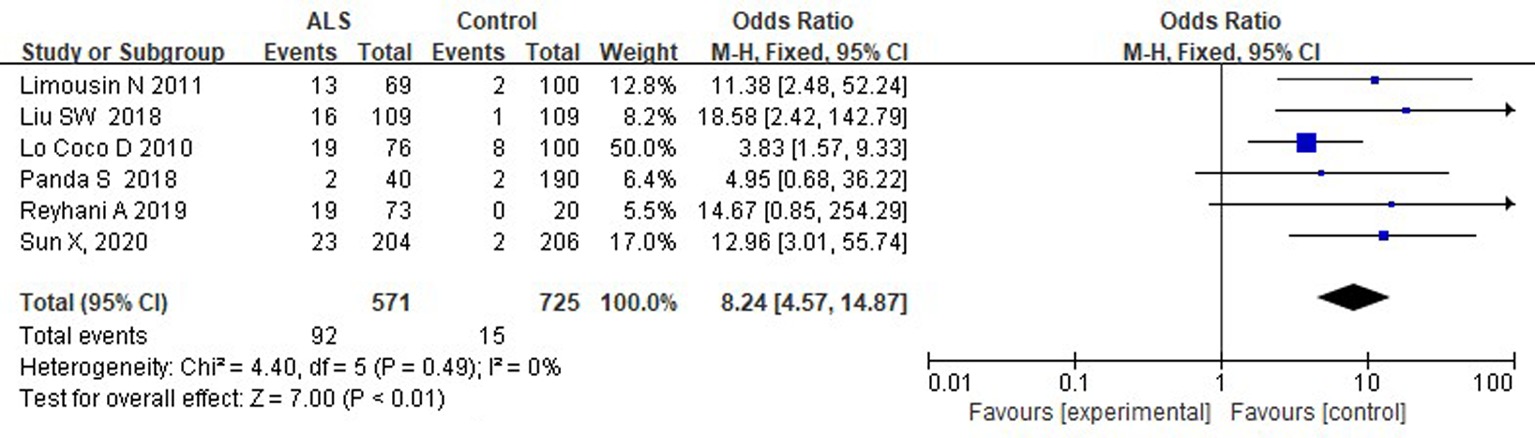
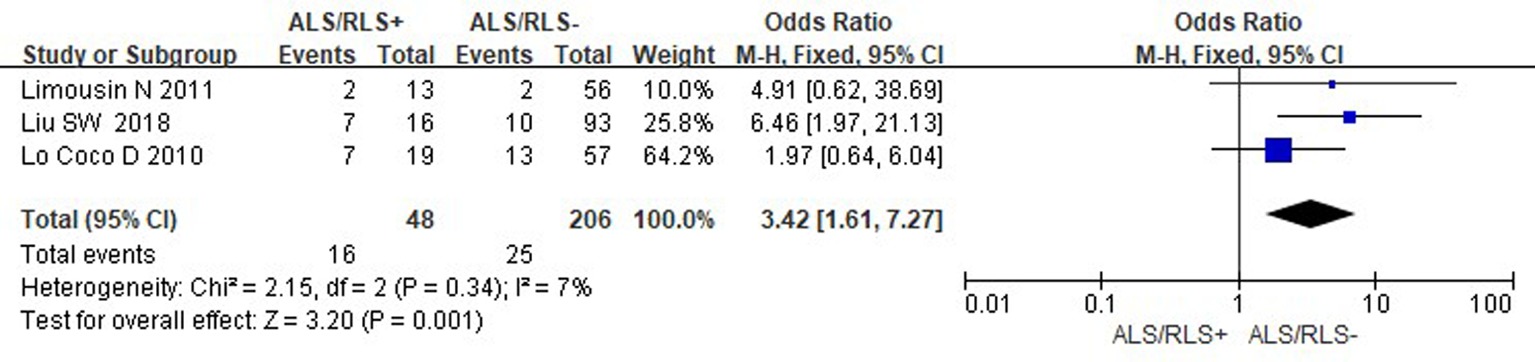
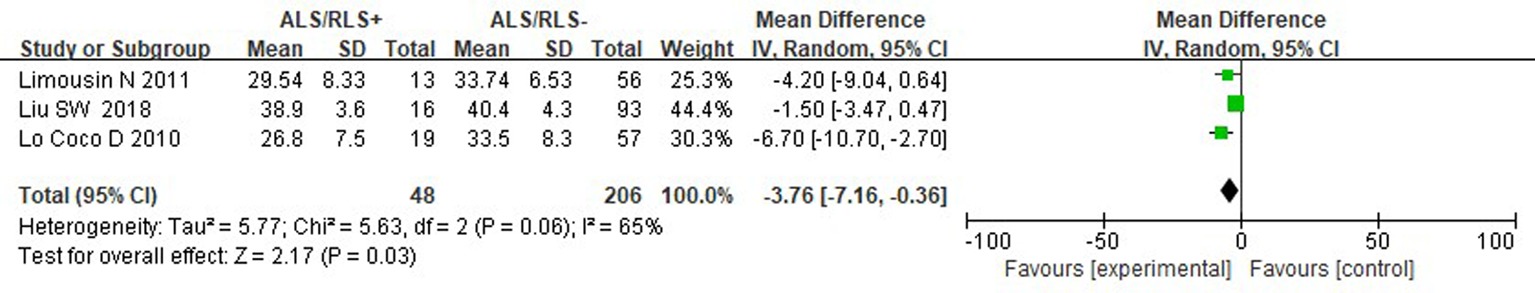
Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 878-882.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.10.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its correlation with disease severity: A meta-analysis
Sun Yanan1, Hao Yifeng2, Li Xiaohong1( )
)
- 1. Department of Neurology,Dalian Municipal Friendship Hospital, Dalian 116001,China
2. Department of Keyuan Community Health Service Center,Shenzhen Longgang District Second People's Hospital,Shenzhen 518116,China
-
Received:2023-05-15Online:2023-10-20Published:2024-01-03 -
Contact:Li Xiaohong E-mail:xhlihh@126.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Yanan, Hao Yifeng, Li Xiaohong. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and its correlation with disease severity: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(10): 878-882.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.10.002
| 纳入文献 | 国家 | 研究类型 | 对照组 例数 | ALS患者一般资料 | NOS 评分 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALS 例数 | 男 (%) | 平均年龄 (岁) | 病程 (月) | 延髓起病 (%) | RLS (%) | |||||
| Limousin[ | 法国 | 队列研究 | 未提供 | 69 | 46.38 | 67.1±10.0 | 29.9±24.6 | 34.78 | 18.84 | 7 |
| Liu[ | 中国 | 病例对照研究 | 109 | 109 | 60.60 | 52.9±10.1 | 15.6±9.7 | 33.00 | 14.68 | 8 |
| Lo Coco[ | 意大利 | 病例对照研究 | 100 | 76 | 57.89 | 58.7±12.8 | 26.5±13.3 | 22.37 | 25 | 7 |
| Reyhani[ | 土耳其 | 队列研究 | 20 | 73 | 49.30 | 58.0±9.9 | 58.5±30 | 45.20 | 26 | 8 |
| Sun[ | 中国 | 病例对照研究 | 206 | 204 | 55.88 | 53.5±9.9 | 14.6±8.9 | 30.00 | 11.30 | 8 |
| Panda[ | 印度 | 病例对照研究 | 190 | 40 | 57.50 | 58.5±12.4 | 28.4±22.3 | 30 | 5 | 6 |
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of ALS patients in the eligible study
| 纳入文献 | 国家 | 研究类型 | 对照组 例数 | ALS患者一般资料 | NOS 评分 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALS 例数 | 男 (%) | 平均年龄 (岁) | 病程 (月) | 延髓起病 (%) | RLS (%) | |||||
| Limousin[ | 法国 | 队列研究 | 未提供 | 69 | 46.38 | 67.1±10.0 | 29.9±24.6 | 34.78 | 18.84 | 7 |
| Liu[ | 中国 | 病例对照研究 | 109 | 109 | 60.60 | 52.9±10.1 | 15.6±9.7 | 33.00 | 14.68 | 8 |
| Lo Coco[ | 意大利 | 病例对照研究 | 100 | 76 | 57.89 | 58.7±12.8 | 26.5±13.3 | 22.37 | 25 | 7 |
| Reyhani[ | 土耳其 | 队列研究 | 20 | 73 | 49.30 | 58.0±9.9 | 58.5±30 | 45.20 | 26 | 8 |
| Sun[ | 中国 | 病例对照研究 | 206 | 204 | 55.88 | 53.5±9.9 | 14.6±8.9 | 30.00 | 11.30 | 8 |
| Panda[ | 印度 | 病例对照研究 | 190 | 40 | 57.50 | 58.5±12.4 | 28.4±22.3 | 30 | 5 | 6 |
| 纳入文献 | 组别 | 例数 | 平均年龄(岁) | 病程(月) | 延髓起病(%) | ALSFRS-R评分 | EDS(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limousin[ | ALS/RLS+ | 13 | 72.62±6.29 | 44.96±36.32 | 30.77% | 29.54±8.33 | 15.38% |
| ALS/RLS- | 56 | 68.59±10.27 | 26.37±19.82 | 35.71% | 33.74±6.53 | 3.57% | |
| Liu[ | ALS/RLS+ | 16 | 54.81±7.32 | 13.2±5.9 | 37.50% | 38.9±3.6 | 43.75% |
| ALS/RLS- | 93 | 52.58±10.53 | 16.0±10.1 | 32.30% | 40.4±4.3 | 10.75% | |
| Lo Coco[ | ALS/RLS+ | 19 | 59.3±11.6 | 25.3±13.4 | 15.80% | 26.8±7.5 | 36.80% |
| ALS/RLS- | 57 | 58.5±13.2 | 27.9±13.2 | 25% | 33.5±8.3 | 22.80% |
Tab. 2 Clinical and epidemiological characteristics of ALS/RLS+ group and ALS/RLS- group
| 纳入文献 | 组别 | 例数 | 平均年龄(岁) | 病程(月) | 延髓起病(%) | ALSFRS-R评分 | EDS(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limousin[ | ALS/RLS+ | 13 | 72.62±6.29 | 44.96±36.32 | 30.77% | 29.54±8.33 | 15.38% |
| ALS/RLS- | 56 | 68.59±10.27 | 26.37±19.82 | 35.71% | 33.74±6.53 | 3.57% | |
| Liu[ | ALS/RLS+ | 16 | 54.81±7.32 | 13.2±5.9 | 37.50% | 38.9±3.6 | 43.75% |
| ALS/RLS- | 93 | 52.58±10.53 | 16.0±10.1 | 32.30% | 40.4±4.3 | 10.75% | |
| Lo Coco[ | ALS/RLS+ | 19 | 59.3±11.6 | 25.3±13.4 | 15.80% | 26.8±7.5 | 36.80% |
| ALS/RLS- | 57 | 58.5±13.2 | 27.9±13.2 | 25% | 33.5±8.3 | 22.80% |
| [1] |
Al-Chalabi A, Hardiman O. The epidemiology of ALS: A conspiracy of genes, environment and time, Nature reviews[J]. Nat Rev Neuro, 2013, 9(11):617-628.
doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2013.203 |
| [2] |
Al-Chalabi A, Calvo A, Chio A, et al. Analysis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis as a multistep process: A population-based modelling study[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2014, 13(11):1108-1113.
doi: S1474-4422(14)70219-4 pmid: 25300936 |
| [3] |
Ravits JM, La Spada AR. ALS motor phenotype heterogeneity, focality, and spread: Deconstructing motor neuron degeneration[J]. Neurology, 2009, 73(10):805-811.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181b6bbbd pmid: 19738176 |
| [4] |
Fang T, Jozsa F, Al-Chalabi A. Nonmotor Symptoms in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A Systematic Review[J]. Int Rev Neurobiol, 2017, 134:1409-1441.
doi: S0074-7742(17)30039-9 pmid: 28805578 |
| [5] |
Talarico G, Canevelli M, Tosto G, et al. Restless legs syndrome in a group of patients with Alzheimer's disease[J]. Am J Alzheimers Dis Other Demen, 2013, 28(2):165-170.
doi: 10.1177/1533317512470208 URL |
| [6] |
Trenkwalder C, Winkelmann J, Inoue Y, et al. Restless legs syndrome-current therapies and management of augmentation[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2015, 11(8):434-445.
doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.122 pmid: 26215616 |
| [7] |
Shi Y, Yu H, Ding D, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of restless legs syndrome among Chinese adults in a rural community of Shanghai in China[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3):e0121215.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121215 URL |
| [8] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9):603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z pmid: 20652370 |
| [9] |
Limousin N, Blasco H, Corcia P, et al. The high frequency of restless legs syndrome in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Amyotroph Lateral Scler, 2011, 12(4):303-306.
doi: 10.3109/17482968.2011.557736 URL |
| [10] |
Liu S, Shen D, Tai H, et al. Restless legs syndrome in Chinese patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Front Neurol, 2018, 9:735.
doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00735 pmid: 30214425 |
| [11] |
Lo Coco D, Piccoli F, La Bella V. Restless legs syndrome in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. Mov Disord, 2010, 25(15):2658-2661.
doi: 10.1002/mds.v25:15 URL |
| [12] |
Reyhani A, Benbir Senel G, Karadeniz D. Effects of Sleep-Related Disorders on the Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis[J]. Neurodegener Dis, 2019, 19(3-4):148-154.
doi: 10.1159/000505575 pmid: 32114585 |
| [13] | Sun X, Zhao X, Liu Q, et al. Study on sleep-wake disorders in patients with genetic and non-genetic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 2020:jnnp-2020-324544. |
| [14] |
Panda S, Gourie-Devi M, Sharma A. Sleep disorders in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A questionnaire-based study from India[J]. Neurol India, 2018, 66(3):700-708.
doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.232327 pmid: 29766929 |
| [15] |
Aylor JP, Brown RH Jr, Cleveland DW. Decoding ALS: From genes to mechanism[J]. Nature, 2016, 539(7628):197-206.
doi: 10.1038/nature20413 |
| [16] |
Dauvilliers Y, Winkelmann J. Restless legs syndrome: Update on pathogenesis[J]. Curr Opin Pulm Med, 2013, 19(6):594-600.
doi: 10.1097/MCP.0b013e328365ab07 pmid: 24048084 |
| [17] |
Tholfsen LK, Larsen JP, Schulz J, et al. Development of excessive daytime sleepiness in early Parkinson disease[J]. Neurology, 2015, 85(2):162-168.
doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001737 pmid: 26085603 |
| [18] |
Baumann CR. Traumatic brain injury and disturbed sleep and wakefulness[J]. Neuromolecular Med, 2012, 14(3): 205-212.
doi: 10.1007/s12017-012-8178-x URL |
| [19] |
Sharma KR, Sheriff S, Maudsley A, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of basal ganglia and thalamus in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis[J]. J Neuroimaging, 2013, 23(3):368-374.
doi: 10.1111/j.1552-6569.2011.00679.x pmid: 22273090 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||