Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 293-298.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.04.001
Correlation between cardiac troponin and D-dimer levels and mortality in COVID-19 critical illness patients: A meta analysis
Guo Ru1, Liu Ruihong1, Lin Xuefeng2( ), Han Xuanmao2, Zhang Zhu2, Chen Ruiying2
), Han Xuanmao2, Zhang Zhu2, Chen Ruiying2
- 1. Graduate School,Baotou Medical College,Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology, Baotou 014040,China
2. Department of Cardiology,the First Affiliated Hospital of Baotou Medical College, Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology,Baotou 014010,China
-
Received:2021-12-01Online:2022-04-20Published:2022-05-13 -
Contact:Lin Xuefeng E-mail:1156961689@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Ru, Liu Ruihong, Lin Xuefeng, Han Xuanmao, Zhang Zhu, Chen Ruiying. Correlation between cardiac troponin and D-dimer levels and mortality in COVID-19 critical illness patients: A meta analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(4): 293-298.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.04.001
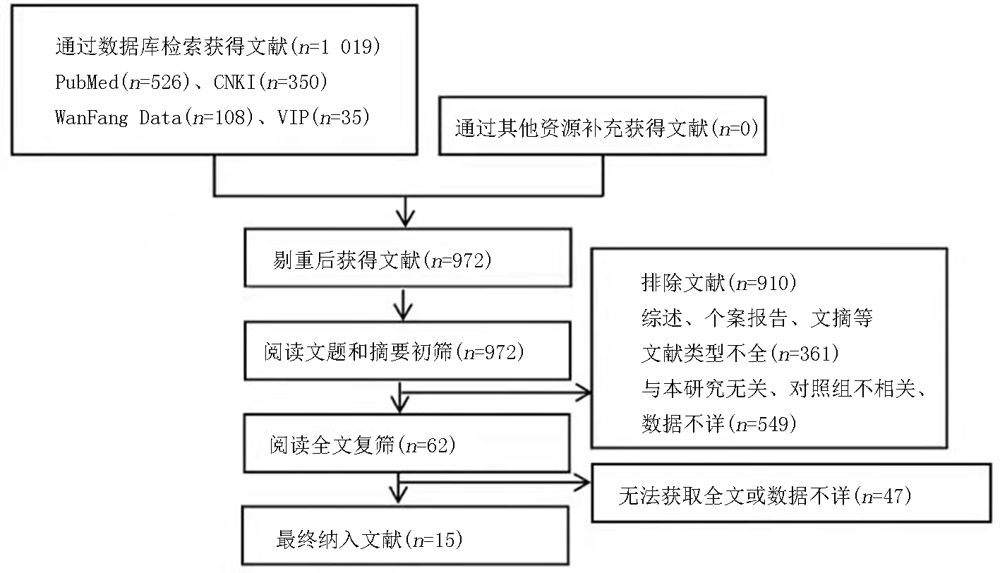
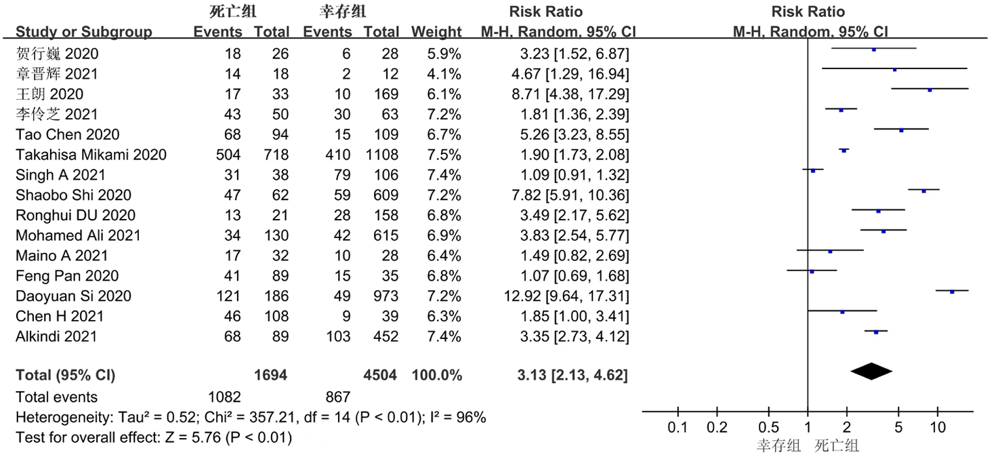
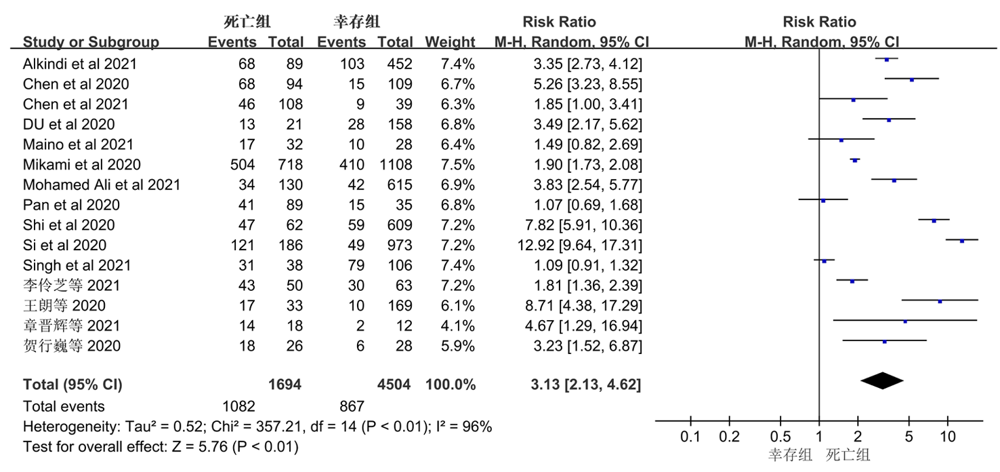
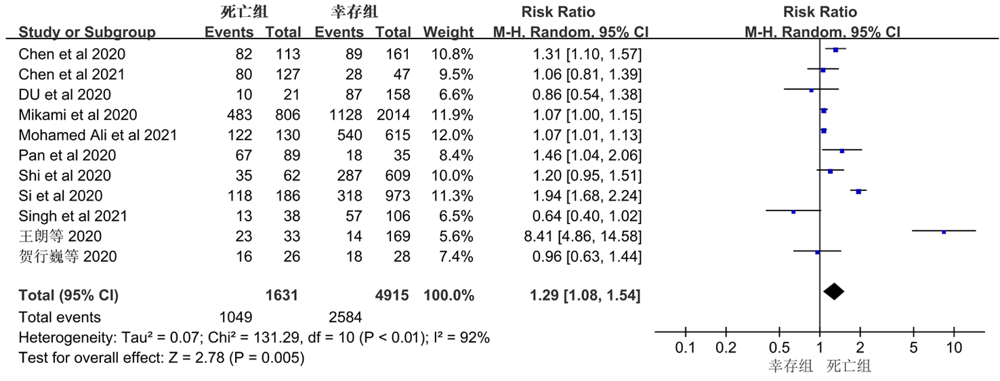
| 纳入研究 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 研究总人数 | cTn截止值 | 样本量(例) | cTn升高人数(例) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 死亡组 | 幸存组 | 死亡组 | 幸存组 | ||||||
| Si et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 1 159 | >26.2 pg/ml | 186 | 973 | 121/186 | 49/973 | |
| Pan et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 124 | >19.3 μg/ml | 89 | 35 | 41/89 | 15/35 | |
| Shi et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 671 | >0.04 ng/ml | 62 | 609 | 47/62 | 59/609 | |
| Mikami et al[ | 2020 | 纽约 | 2 820 | >0.03 ng/ml | 806 | 2 014 | 504/718 | 410/1 108 | |
| Du et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 179 | ≥0.05 ng/ml | 21 | 158 | 13/21 | 28/158 | |
| Chen et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 274 | 15.6 pg/ml | 113 | 161 | 68/94 | 15/109 | |
| 王朗等[ | 2020 | 中国 | 202 | >0.04 μg/L | 33 | 169 | 17/33 | 10/169 | |
| 贺行巍等[ | 2020 | 中国 | 54 | >34.3 ng/L | 26 | 28 | 18/26 | 6/28 | |
| 章晋辉等[ | 2021 | 中国 | 30 | >0.014 ng/ml | 18 | 12 | 14/18 | 2/12 | |
| 李伶芝等[ | 2021 | 中国 | 113 | >0.04 μg/L | 50 | 63 | 43/50 | 30/63 | |
| Maino et al[ | 2021 | 意大利 | 60 | / | 32 | 28 | 17/32 | 10/28 | |
| Mohamed Ali et al[ | 2021 | 迪拜 | 745 | ≥52 ng/L | 130 | 615 | 34/130 | 42/615 | |
| Singh et al[ | 2021 | 美国 | 144 | / | 38 | 106 | 31/38 | 79/106 | |
| Chen et al[ | 2021 | 中国 | 174 | >28 pg/ml | 127 | 47 | 46/108 | 9/39 | |
| Alkindi et al[ | 2021 | 阿曼 | 541 | >14 ng/L | 89 | 452 | 68/89 | 103/452 | |
| 纳入研究 | 发表年份 | 国家 | 研究总人数 | cTn截止值 | 样本量(例) | cTn升高人数(例) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 死亡组 | 幸存组 | 死亡组 | 幸存组 | ||||||
| Si et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 1 159 | >26.2 pg/ml | 186 | 973 | 121/186 | 49/973 | |
| Pan et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 124 | >19.3 μg/ml | 89 | 35 | 41/89 | 15/35 | |
| Shi et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 671 | >0.04 ng/ml | 62 | 609 | 47/62 | 59/609 | |
| Mikami et al[ | 2020 | 纽约 | 2 820 | >0.03 ng/ml | 806 | 2 014 | 504/718 | 410/1 108 | |
| Du et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 179 | ≥0.05 ng/ml | 21 | 158 | 13/21 | 28/158 | |
| Chen et al[ | 2020 | 中国 | 274 | 15.6 pg/ml | 113 | 161 | 68/94 | 15/109 | |
| 王朗等[ | 2020 | 中国 | 202 | >0.04 μg/L | 33 | 169 | 17/33 | 10/169 | |
| 贺行巍等[ | 2020 | 中国 | 54 | >34.3 ng/L | 26 | 28 | 18/26 | 6/28 | |
| 章晋辉等[ | 2021 | 中国 | 30 | >0.014 ng/ml | 18 | 12 | 14/18 | 2/12 | |
| 李伶芝等[ | 2021 | 中国 | 113 | >0.04 μg/L | 50 | 63 | 43/50 | 30/63 | |
| Maino et al[ | 2021 | 意大利 | 60 | / | 32 | 28 | 17/32 | 10/28 | |
| Mohamed Ali et al[ | 2021 | 迪拜 | 745 | ≥52 ng/L | 130 | 615 | 34/130 | 42/615 | |
| Singh et al[ | 2021 | 美国 | 144 | / | 38 | 106 | 31/38 | 79/106 | |
| Chen et al[ | 2021 | 中国 | 174 | >28 pg/ml | 127 | 47 | 46/108 | 9/39 | |
| Alkindi et al[ | 2021 | 阿曼 | 541 | >14 ng/L | 89 | 452 | 68/89 | 103/452 | |
| 纳入研究 | 发表年份 | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Pan et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Shi et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Mikami et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Du et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Chen et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 王朗等[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 贺行巍等[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 章晋辉等[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 李伶芝等[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Maino et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Mohamed Ali et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Singh et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Chen et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Alkindi et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 纳入研究 | 发表年份 | ① | ② | ③ | ④ | ⑤ | ⑥ | ⑦ | ⑧ | 总分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Pan et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Shi et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Mikami et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Du et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Chen et al[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 王朗等[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 贺行巍等[ | 2020 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 章晋辉等[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| 李伶芝等[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Maino et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Mohamed Ali et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Singh et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Chen et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Alkindi et al[ | 2021 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| [1] |
Driggin E, Madhavan MV, Bikdeli B. et al. Cardiovascular considerations for patients, health care workers, and health systems during the COVID-19 pandemic[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2020, 75(18):2352-2371.
doi: S0735-1097(20)34637-4 pmid: 32201335 |
| [2] |
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X. et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10223):497-506.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 URL |
| [3] | American College of Cardiology: Troponin and BNP Use in COVID-19[EB/OL]. Available online at https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/articles/2020/03/18/15/25/troponin-and-bnp-use-in-covid19. Last accessed April 6th 2020. |
| [4] |
Mahajan K, Chandra KS. Cardiovascular comorbidities and complications associated with coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Med J Armed Forces India, 2020, 76(3):253-260.
doi: 10.1016/j.mjafi.2020.05.004 URL |
| [5] |
Shi S, Qin M, Shen B. et al. Association of cardiac injury with mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2020, 5(7):802-810.
doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.0950 URL |
| [6] |
Guo T, Fan Y, Chen M. et al. Cardiovascular implications of fatal outcomes of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)[J]. JAMA Cardiol, 2020, 5(7):811-818.
doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1017 URL |
| [7] | Zheng Z, Peng F, Xu B. et al. Risk factors of critical & mortal COVID-19 cases: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. J Infect, 2020, 81(2):e16-e25. |
| [8] |
Santoso A, Pranata R, Wibowo A. et al. Cardiac injury is associated with mortality and critically ill pneumonia in COVID-19: A meta-analysis[J]. Am J Emerg Med, 2021, 44:352-357.
doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.04.052 URL |
| [9] |
Li JW, Han TW, Woodward M. et al. The impact of 2019 novel coronavirus on heart injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2020, 63(4):518-524.
doi: 10.1016/j.pcad.2020.04.008 URL |
| [10] | 王建中, 袁家颖, 普程伟, 等. 传染性非典型肺炎患者凝血功能的变化[J]. 中华检验医学杂志, 2004, 27(8):23-25. |
| [11] |
Querol-Ribelles JM, Tenias JM, Grau E. et al. Plasma d-dimer levels correlate with outcomes in patients with community-acquired pneumonia[J]. Chest, 2004, 126(4):1087-1092.
pmid: 15486368 |
| [12] | 韩利, 张筠, 张铁栓. 重症肺炎患者D-二聚体、纤维蛋白原、IL-6水平变化及其临床意义[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2017, 16(1):71-73. |
| [13] |
Kollef MH, Eisenberg PR, Shannon W. A rapid assay for the detection of circulating D-dimer is associated with clinical outcomes among critically ill patients[J]. Crit Care Med, 1998, 26(6):1054-1060.
pmid: 9635655 |
| [14] |
Stang A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses[J]. Eur J Epidemiol, 2010, 25(9):603-605.
doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z URL |
| [15] |
Si D, Du B, Ni L. et al. Death, discharge and arrhythmias among patients with COVID-19 and cardiac injury[J]. CMAJ, 2020, 192(28):E791-E798.
doi: 10.1503/cmaj.200879 URL |
| [16] |
Pan F, Yang L, Li Y. et al. Factors associated with death outcome in patients with severe coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19): A case-control study[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2020, 17(9):1281-1292.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.46614 URL |
| [17] |
Shi S, Qin M, Cai Y, et al. Characteristics and clinical significance of myocardial injury in patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019[J]. Eur Heart J, 2020, 41(22):2070-2079.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa408 URL |
| [18] |
Mikami T, Miyashita H, Yamada T. et al. Risk factors for mortality in patients with COVID-19 in New York city[J]. J Gen Intern Med, 2021, 36(1):17-26.
doi: 10.1007/s11606-020-05983-z URL |
| [19] | Du RH, Liang LR, Yang CQ. et al. Predictors of mortality for patients with COVID-19 pneumonia caused by SARS-CoV-2: A prospective cohort study[J]. Eur Respir J, 2020, 55(5):2000524. |
| [20] | Chen T, Wu D, Chen H. et al. Clinical characteristics of 113 deceased patients with coronavirus disease 2019: Retrospective study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 368:m1091. |
| [21] | 王朗, 何文博, 余小梅, 等. 心肌损伤对新型冠状病毒肺炎患者临床预后的影响[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2020, 48(6):461-466. |
| [22] | 贺行巍, 赖金胜, 程佳, 等. 重型/危重型新型冠状病毒肺炎患者合并心肌损伤对预后的影响[J]. 中华心血管病杂志, 2020, 48(6):456-460. |
| [23] | 章晋辉, 徐留胜, 郭雨萌, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎患者临床特征与心肌损伤标志物的变化[J]. 医学新知, 2021, 31(5):342-349. |
| [24] | 李伶芝, 何兵, 张淑娣, 等. 危重型新型冠状病毒肺炎心肌损伤与死亡的关系[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2021, 37(1):6-10. |
| [25] |
Maino A, Di Stasio E, Grimaldi MC. et al. Prevalence and characteristics of myocardial injury during COVID-19 pandemic:A new role for high-sensitive troponin[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2021, 338:278-285.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.06.028 URL |
| [26] | Mohamed Ali S, Musa A, Omar Muhammed K. et al. Prolonged corrected QT interval in hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Dubai, United Arab Emirates: A single-center, retrospective study[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(11):3000605211056834. |
| [27] |
Singh A, Akbar MS, McElroy D. et al. The electrocardiographic manifestations and derangements of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19)[J]. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J, 2021, 21(3):156-161.
doi: 10.1016/j.ipej.2021.02.005 URL |
| [28] |
Chen H, Li X, Marmar T. et al. Cardiac troponin I association with critical illness and death risk in 726 seriously ill COVID-19 patients: A retrospective cohort study[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18(6):1474-1483.
doi: 10.7150/ijms.53641 URL |
| [29] |
Alkindi F, Alhashmi K, Nadar S. et al. Cardiovascular manifestations and outcomes in patients admitted with severe COVID-19: Middle eastern country multicenter data[J]. Heart Views, 2021, 22(1):20-26.
doi: 10.4103/HEARTVIEWS.HEARTVIEWS_224_20 pmid: 34276884 |
| [30] | 郭颖, 裴作为, 朱火兰, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎相关心肌损伤的临床管理专家建议(第一版)[J]. 中国循环杂志, 2020, 35(4):326-330. |
| [31] | Lippi G, Cervellin G, Sanchis-Gomar F. Predicting mortality with cardiac troponins: Recent insights from meta-analyses[J]. Diagnosis (Berl), 2019, 8(1):37-49. |
| [32] |
Vrsalovic M. Prognostic effect of cardiac troponin elevation in acute aortic dissection: A meta-analysis[J]. Int J Cardiol, 2016, 214:277-278.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.03.230 pmid: 27082771 |
| [33] | 中国疾病预防控制中心新型冠状病毒肺炎应急响应机制流行病学组. 新型冠状病毒肺炎流行病学特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(2):145-151. |
| [34] |
Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X. et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study[J]. Lancet, 2020, 395(10223): 507-513.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7 URL |
| [35] |
Badawi A, Ryoo SG. Prevalence of comorbidities in the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2016, 49:129-133.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2016.06.015 pmid: 27352628 |
| [36] |
Channappanavar R, Fett C, Mack M. et al. Sexbased differences in susceptibility to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection[J]. J Immunol, 2017, 198(10): 4046-4053.
doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1601896 pmid: 28373583 |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 145
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 667
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||