Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 325-331.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.04.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
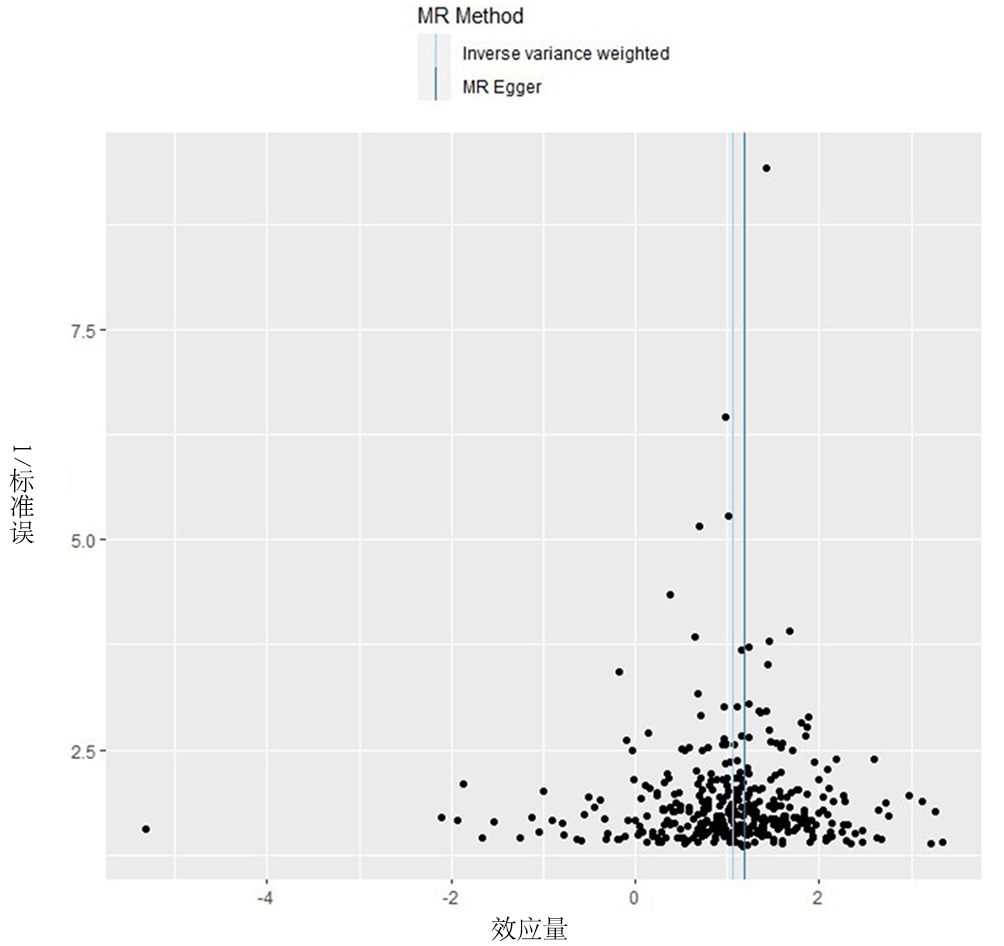
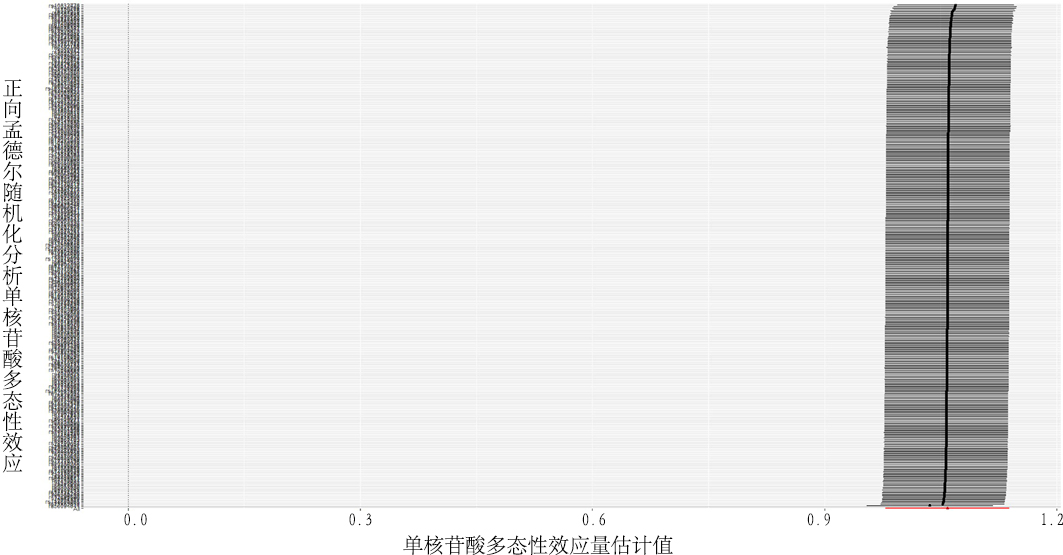
Bidirectional Mendelian randomization study of causality between body mass index and type 2 diabetes in a European population
Sun Hui1, Liu Haiying2, Ren Junhao1, Li Jinxia1( )
)
- 1. Clinical Laboratory Center, Xi'an International Medical Center Hospital, Xi'an 710000, China
2. Xi'an Changan District Health and Family Planning Comprehensive Supervision, Xi'an 710000, China
-
Received:2023-10-09Online:2024-04-20Published:2024-06-27 -
Contact:Li Jinxia, Email:94396012@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Hui, Liu Haiying, Ren Junhao, Li Jinxia. Bidirectional Mendelian randomization study of causality between body mass index and type 2 diabetes in a European population[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(4): 325-331.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.04.005
| Trait | GWAS ID | Sample size | N (case) | N (control) | Number of SNPs | Population | Sex | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | ukb-b-19953 | 461, 460 | N/A | N/A | 9, 851, 867 | European | Males and Females | 2018 |
| T2DM | ebi-a-GCST006867 | 655, 666 | 61714 | 1178 | 5, 030, 727 | European | Males and Females | 2018 |
Tab.1 GWAS data sources and types
| Trait | GWAS ID | Sample size | N (case) | N (control) | Number of SNPs | Population | Sex | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | ukb-b-19953 | 461, 460 | N/A | N/A | 9, 851, 867 | European | Males and Females | 2018 |
| T2DM | ebi-a-GCST006867 | 655, 666 | 61714 | 1178 | 5, 030, 727 | European | Males and Females | 2018 |
| Number | SNPs | Pos | CHR | EAF | EA | OA | Beta | SE | P | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rs1000096 | 38692835 | 4 | 0.39594 | T | C | -0.0133384 | 0.002031 | 5.10E-11 | 43.13038659 |
| 2 | rs10063055 | 140990108 | 5 | 0.251841 | T | C | 0.0136775 | 0.00227 | 1.70E-09 | 36.30748534 |
| 3 | rs10099330 | 143383694 | 8 | 0.449841 | G | A | 0.0124247 | 0.001989 | 4.20E-10 | 39.01860049 |
| 4 | rs10160769 | 76474827 | 11 | 0.214929 | C | G | -0.0155862 | 0.002422 | 1.20E-10 | 41.41291473 |
| 5 | rs10169594 | 41637688 | 2 | 0.360259 | C | T | 0.0121875 | 0.002055 | 3.00E-09 | 35.17063788 |
| 6 | rs10172070 | 208307761 | 2 | 0.144835 | T | C | 0.0161392 | 0.002784 | 6.70E-09 | 33.61826643 |
| 7 | rs10182416 | 104242992 | 2 | 0.511854 | G | A | 0.0130378 | 0.001971 | 3.70E-11 | 43.74068309 |
| 8 | rs10505836 | 19288508 | 12 | 0.860918 | C | A | 0.0184851 | 0.002871 | 1.20E-10 | 41.45907232 |
| 9 | rs1064213 | 118650996 | 10 | 0.246269 | T | C | 0.0175643 | 0.002298 | 2.20E-14 | 58.37631077 |
| 10 | rs10742752 | 198950240 | 2 | 0.480617 | A | G | 0.0149301 | 0.001971 | 3.70E-14 | 57.32304216 |
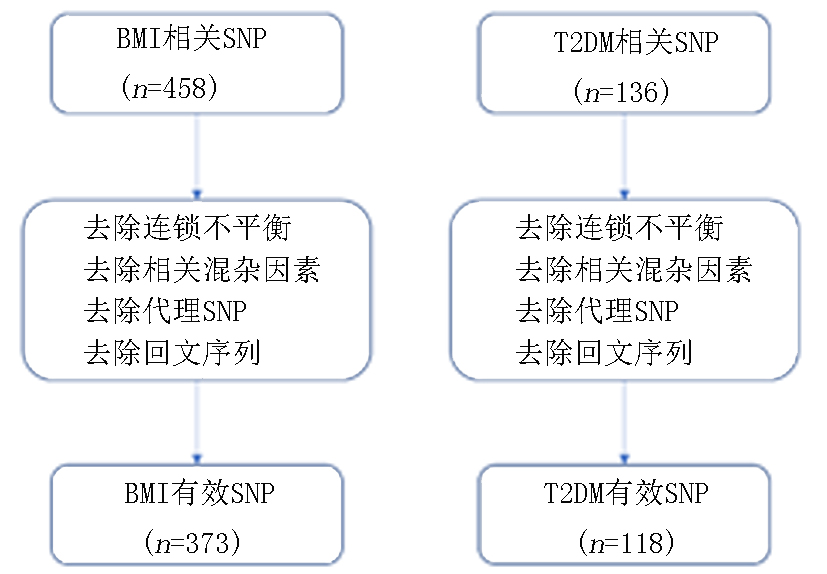
Tab.2 Forward MR analysis of some basic information of instrumental variables
| Number | SNPs | Pos | CHR | EAF | EA | OA | Beta | SE | P | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rs1000096 | 38692835 | 4 | 0.39594 | T | C | -0.0133384 | 0.002031 | 5.10E-11 | 43.13038659 |
| 2 | rs10063055 | 140990108 | 5 | 0.251841 | T | C | 0.0136775 | 0.00227 | 1.70E-09 | 36.30748534 |
| 3 | rs10099330 | 143383694 | 8 | 0.449841 | G | A | 0.0124247 | 0.001989 | 4.20E-10 | 39.01860049 |
| 4 | rs10160769 | 76474827 | 11 | 0.214929 | C | G | -0.0155862 | 0.002422 | 1.20E-10 | 41.41291473 |
| 5 | rs10169594 | 41637688 | 2 | 0.360259 | C | T | 0.0121875 | 0.002055 | 3.00E-09 | 35.17063788 |
| 6 | rs10172070 | 208307761 | 2 | 0.144835 | T | C | 0.0161392 | 0.002784 | 6.70E-09 | 33.61826643 |
| 7 | rs10182416 | 104242992 | 2 | 0.511854 | G | A | 0.0130378 | 0.001971 | 3.70E-11 | 43.74068309 |
| 8 | rs10505836 | 19288508 | 12 | 0.860918 | C | A | 0.0184851 | 0.002871 | 1.20E-10 | 41.45907232 |
| 9 | rs1064213 | 118650996 | 10 | 0.246269 | T | C | 0.0175643 | 0.002298 | 2.20E-14 | 58.37631077 |
| 10 | rs10742752 | 198950240 | 2 | 0.480617 | A | G | 0.0149301 | 0.001971 | 3.70E-14 | 57.32304216 |
| Number | SNPs | Position | CHR | EAF | EA | OA | β | SE | P | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rs10077431 | 112927686 | 5 | 0.21786 | A | C | -0.0487 | 0.0089 | 4.75E-08 | 29.94180028 |
| 2 | rs10087241 | 30863722 | 8 | 0.593614 | A | G | -0.0475 | 0.008 | 2.80E-09 | 35.25390625 |
| 3 | rs10100265 | 10633159 | 8 | 0.613716 | C | A | -0.0491 | 0.0079 | 6.29E-10 | 38.62858516 |
| 4 | rs10114341 | 96919182 | 9 | 0.44029 | C | T | -0.0409 | 0.0072 | 1.15E-08 | 32.26871142 |
| 5 | rs10401969 | 19407718 | 19 | 0.076171 | C | T | 0.0921 | 0.0133 | 4.13E-12 | 47.95302165 |
| 6 | rs1050226 | 7281654 | 6 | 0.408461 | G | A | -0.0491 | 0.0074 | 3.34E-11 | 44.02501826 |
| 7 | rs1061813 | 14847331 | 5 | 0.535045 | A | G | -0.0429 | 0.0073 | 3.37E-09 | 34.5357478 |
| 8 | rs1063355 | 32627714 | 6 | 0.609122 | G | T | 0.0709 | 0.0079 | 3.72E-19 | 80.54494472 |
| 9 | rs10740322 | 71485458 | 10 | 0.6872 | A | G | 0.0477 | 0.0085 | 2.11E-08 | 31.49190311 |
| 10 | rs10811661 | 22134094 | 9 | 0.173071 | C | T | -0.1569 | 0.0098 | 4.13E-58 | 256.3266347 |
Tab.3 Reverse MR analysis of some basic information of instrumental variables
| Number | SNPs | Position | CHR | EAF | EA | OA | β | SE | P | F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | rs10077431 | 112927686 | 5 | 0.21786 | A | C | -0.0487 | 0.0089 | 4.75E-08 | 29.94180028 |
| 2 | rs10087241 | 30863722 | 8 | 0.593614 | A | G | -0.0475 | 0.008 | 2.80E-09 | 35.25390625 |
| 3 | rs10100265 | 10633159 | 8 | 0.613716 | C | A | -0.0491 | 0.0079 | 6.29E-10 | 38.62858516 |
| 4 | rs10114341 | 96919182 | 9 | 0.44029 | C | T | -0.0409 | 0.0072 | 1.15E-08 | 32.26871142 |
| 5 | rs10401969 | 19407718 | 19 | 0.076171 | C | T | 0.0921 | 0.0133 | 4.13E-12 | 47.95302165 |
| 6 | rs1050226 | 7281654 | 6 | 0.408461 | G | A | -0.0491 | 0.0074 | 3.34E-11 | 44.02501826 |
| 7 | rs1061813 | 14847331 | 5 | 0.535045 | A | G | -0.0429 | 0.0073 | 3.37E-09 | 34.5357478 |
| 8 | rs1063355 | 32627714 | 6 | 0.609122 | G | T | 0.0709 | 0.0079 | 3.72E-19 | 80.54494472 |
| 9 | rs10740322 | 71485458 | 10 | 0.6872 | A | G | 0.0477 | 0.0085 | 2.11E-08 | 31.49190311 |
| 10 | rs10811661 | 22134094 | 9 | 0.173071 | C | T | -0.1569 | 0.0098 | 4.13E-58 | 256.3266347 |
| [1] | Hassanein M, Afandi B, Yakoob Ahmedani M, et al. Diabetes and ramadan: Practical guidelines 2021[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2022, 185:109185. |
| [2] | Radeepa R, Prabhakaran D, Mohan V. Emerging economies and diabetes and cardiovascular disease[J]. Diabetes Technol Ther, 2012, 14(Suppl 1):S59-67. |
| [3] |
Heng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(2):88-98.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151 pmid: 29219149 |
| [4] |
Simmonds M, Llewellyn A, Owen CG, et al. Predicting adult obesity from childhood obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Obes Rev, 2016, 17(2):95-107.
doi: 10.1111/obr.12334 pmid: 26696565 |
| [5] | Walsh JS, Vilaca T. Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes and Bone in Adults[J]. Calcif Tissue Int, 2017, 100(5):528-535. |
| [6] | Lin X, Li H. Obesity: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics[J]. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), 2021, 12:706978. |
| [7] | Fink J, Seifert G, Blüher M, et al. Obesity surgery[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2022, 119(5):70-80. |
| [8] |
Bowden J, Holmes MV. Meta-analysis and mendelian randomization: A review[J]. Res Synth Methods, 2019, 10(4):486-496.
doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1346 pmid: 30861319 |
| [9] |
Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian Randomization[J]. JAMA, 2017, 318(19):1925-1926.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.17219 pmid: 29164242 |
| [10] | Birney E. Mendelian randomization[J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med, 2022, 12(4):a041302. |
| [11] | Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2014, 23(R1):R89-98. |
| [12] |
Burgess S, Bowden J, Fall T, et al. Sensitivity analyses for robust causal inference from mendelian randomization analyses with multiple genetic variants[J]. Epidemiology, 2017, 28(1):30-42.
pmid: 27749700 |
| [13] |
Slob EAW, Groenen PJF, Thurik AR, et al. A note on the use of egger regression in mendelian randomization studies[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2017, 46(6):2094-2097.
doi: 10.1093/ije/dyx191 pmid: 29025040 |
| [14] |
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Haycock PC, et al. Consistent estimation in mendelian randomization with some invalid instruments using a weighted median estimator[J]. Genet Epidemiol, 2016, 40(4):304-314.
doi: 10.1002/gepi.21965 pmid: 27061298 |
| [15] |
Bowden J, Davey Smith G, Burgess S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(2):512-525.
doi: 10.1093/ije/dyv080 pmid: 26050253 |
| [16] |
Gronau QF, Wagenmakers EJ. Limitations of bayesian leave-one-out cross-validation for model selection[J]. Comput Brain Behav, 2019, 2(1):1-11.
doi: 10.1007/s42113-018-0011-7 pmid: 30906917 |
| [17] |
Gill RS, Sharma AM, Gill SS, et al. The impact of obesity on diabetes mellitus and the role of bariatric surgery[J]. Maturitas, 2011, 69(2):137-40.
doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2011.03.020 pmid: 21493021 |
| [18] |
Lloyd-Jones DM, Liu K, Colangelo LA, et al. Consistently stable or decreased body mass index in young adulthood and longitudinal changes in metabolic syndrome components: The coronary artery risk development in young adults study[J]. Circulation, 2007, 115(8):1004-11.
pmid: 17283263 |
| [19] | Sabin MA, Magnussen CG, Juonala M, et al. Insulin and BMI as predictors of adult type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Pediatrics, 2015, 135(1):e144-e151. |
| [20] | 包绮晗, 李承圣, 王浩桦, 等. 基于孟德尔随机化法的BMI与2型糖尿病因果关系研究[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2022, 57(5):645-649. |
| [21] | 贺媛, 曾强, 赵小兰. 中国成人肥胖、中心性肥胖与高血压和糖尿病的相关性研究[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2015, 40(10):803-808. |
| [22] |
Dale CE, Fatemifar G, Palmer TM, et al. Causal associations of adiposity and body fat distribution with coronary heart disease, stroke subtypes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A mendelian randomization analysis[J]. Circulation, 2017, 135(24):2373-2388.
doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026560 pmid: 28500271 |
| [23] | Pérez-Torres I, Castrejón-Téllez V, Soto ME, et al. Oxidative stress, plant natural antioxidants, and obesity[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(4):1786. |
| [24] |
Santareno S, Cerqueira J, Portugues J, et al. Papel do tecido adiposo e dos macrófagos no estado de inflamação crónica associadaà obesidade: Implicações clínicas [The role of adipose tissue and macrophages in chronic inflammation associated with obesity: Linical implications][J]. Acta Med Port, 2008, 21(5):489-496.
pmid: 19187692 |
| [25] |
Engin A. The pathogenesis of obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2017, 960:221-245.
doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-48382-5_9 pmid: 28585201 |
| [26] | Yaribeygi H, Sathyapalan T, Atkin SL, et al. Molecular mechanisms linking oxidative stress and diabetes mellitus[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2020, 2020:8609213. |
| [1] | Wei Zeng, Cao Ling, She Dunmin, Liu Yan, Wang Yan, Zhang Zhenwen. The causes of death in 54 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with COVID-19 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(9): 806-812. |
| [2] | Liu Jing, Luo Na, Feng Shangyong, Wang Yan, Zhang Zhenwen, She Dunmin. Prevalence and risk factors of hyperuricemia in health examination population in Yangzhou, 2020 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 428-432. |
| [3] | Gao Shixin, Song Bing, Shi Kexin. Diagnosis value of serum lipoprotein α, cystatin-C and uric acid on early diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 248-252. |
| [4] | Gao Pengli, Chen Lili, Tian Fen, Zhang Jiaqian, Chen Yipeng, Qi Xiaojing, Xing Guangqun. Impact of body mass index in the clinicopathology and prognosis of patients with IgA nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(3): 234-242. |
| [5] | Shang Bofei, Sun Yuqian, Wang Xinyu, Chang Yingjun, Liu Yanrong, Wang Yu, Huang Xiaojun, Zhao Xiaosu. Effects of female healthy donor characteristics on CD34+ cells and immune cells in the mixed collection [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(10): 904-908. |
| [6] | Xu Naa, Guo Shuqina, Zhang Yunlianga, Ma Jingxuana,Wang Hea, . Relationship study between serum secreted frizzledrelated protein 5 level and diabetic nephropathy [J]. Clinical Focus, 2017, 32(3): 233-236. |
| [7] | Pan Bin, Ma Xiufen, Mao Hongyan. Weight gain and postmenopausal breast cancer risk: a doseresponse metaanalysis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(10): 1131-1136. |
| [8] | Yang Zhihong;Yang Guifeng;Gao Lin;Li Fang;Zhang Pengyu;Fan Xinna;Wang Qian;Jiao Junfeng. Bone mineral density of the elderly in Qinhuangdao city and its relationship with body mass index [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(1): 78-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||