

临床荟萃 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 974-979.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.11.002
收稿日期:2023-11-12
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-12-04
通讯作者:
梁祎
E-mail:liangyinfm@sina.com
Received:2023-11-12
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-04
Contact:
Liang Yi
E-mail:liangyinfm@sina.com
摘要:
目的 评价姜黄素对2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者炎症反应及氧化应激的影响。方法 通过检索Pubmed、Embase、Web of science、Cochrane等数据库,收集姜黄素辅助治疗T2DM患者的随机对照临床试验,对符合纳入标准的研究提取数据后,采用RevMan 5.3软件进行系统评价和meta分析。结果 共纳入11项RCT研究,患者645例。与对照组相比, 干预组治疗后超敏C反应蛋白(hs-CRP)水平无明显差异(P=0.07)[SMD=-0.35,95%CI(-0.73,0.03),I2=73%],总抗氧化能力(TAC)水平明显增高(P<0.001)[SMD=0.47,95%CI(0.26,0.68),I2=34%],丙二醛(MDA)水平明显减低(P=0.03)[MD=-0.48,95%CI(-0.91,-0.05),I2=90%]。涉及hs-CRP和MDA的研究异质性较大,进一步根据年龄、治疗时间、姜黄素剂量进行亚组分析未发现异质性来源。结论 补充姜黄素可减轻T2DM患者的氧化应激反应,提高机体抗氧化能力,但对炎症反应无明显改善。
中图分类号:
梁祎. 姜黄素对2型糖尿病患者炎症及氧化应激影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(11): 974-979.
Liang Yi. Meta-analysis of effects of curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(11): 974-979.
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 人数 (干预/对照) | 性别 (女/男) | 年龄 (干预/对照) | 干预措施 | 伴随疾病 | 干预 时间 | 涉及的 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 8周 | TAC,MDA |
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 12周 | CRP |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 25/24 | - | 64.9±7.8/66.5±7.7 | 姜黄素提取物1 000 mg/d | 冠心病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 26/27 | 21/32 | 58.3±9.4/56.2±9.8 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 行血液透析的肾脏病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Adibian [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | 22/22 | 58/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | CRP |
| Hodaei [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | - | 58±8/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | TAC, MDA |
| Adab [ | 伊朗 | 39/26 | 39/36 | 54.76±6/55.66±8.64 | 姜黄粉2 100 mg/d | 高脂血症 | 8周 | TAC, CRP |
| Mokhtari [ | 伊朗 | 25/25 | 11/39 | 57.4±11.7/55.8±9.4 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 糖尿病足溃疡3期 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Dastani [ | 伊朗 | 32/32 | 39/25 | 60.00±7.22/60.53±10.55 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 冠脉疾病 | 12周 | CRP |
| Funamoto [ | 日本 | 15/17 | 10/22 | 70±6/69±7 | 姜黄素180 mg/d | 包括部分糖耐量异常者 | 24周 | CRP |
| Usharani [ | 印度 | 23/21 | 21/23 | 55.52±10.76/49.75±8.18 | NCB-02 (姜黄素提取物300 mg bid) | - | 8周 | MDA |
表1 纳入研究特征
Tab. 1 Characteristics of included studies in the meta-analysis
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 人数 (干预/对照) | 性别 (女/男) | 年龄 (干预/对照) | 干预措施 | 伴随疾病 | 干预 时间 | 涉及的 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 8周 | TAC,MDA |
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 12周 | CRP |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 25/24 | - | 64.9±7.8/66.5±7.7 | 姜黄素提取物1 000 mg/d | 冠心病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 26/27 | 21/32 | 58.3±9.4/56.2±9.8 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 行血液透析的肾脏病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Adibian [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | 22/22 | 58/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | CRP |
| Hodaei [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | - | 58±8/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | TAC, MDA |
| Adab [ | 伊朗 | 39/26 | 39/36 | 54.76±6/55.66±8.64 | 姜黄粉2 100 mg/d | 高脂血症 | 8周 | TAC, CRP |
| Mokhtari [ | 伊朗 | 25/25 | 11/39 | 57.4±11.7/55.8±9.4 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 糖尿病足溃疡3期 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Dastani [ | 伊朗 | 32/32 | 39/25 | 60.00±7.22/60.53±10.55 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 冠脉疾病 | 12周 | CRP |
| Funamoto [ | 日本 | 15/17 | 10/22 | 70±6/69±7 | 姜黄素180 mg/d | 包括部分糖耐量异常者 | 24周 | CRP |
| Usharani [ | 印度 | 23/21 | 21/23 | 55.52±10.76/49.75±8.18 | NCB-02 (姜黄素提取物300 mg bid) | - | 8周 | MDA |
| 纳入研究 | 选择偏倚 | 实施偏倚 | 随访偏倚 | 测量偏倚 | 报告偏倚 | 总体偏倚风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 不明确 | 高风险 |
| Panahi [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 高风险 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adibian [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Hodaei [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adab [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Mokhtari [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Dastani [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Funamoto [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Usharani [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
表2 纳入研究的偏倚风险评估
Tab. 2 Risk of bias of eligible studies in the meta-analysis
| 纳入研究 | 选择偏倚 | 实施偏倚 | 随访偏倚 | 测量偏倚 | 报告偏倚 | 总体偏倚风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 不明确 | 高风险 |
| Panahi [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 高风险 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adibian [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Hodaei [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adab [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Mokhtari [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Dastani [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Funamoto [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Usharani [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >60 | 3 | 68 | 73 | 0.09 | -0.70(-1.52, 0.12) | 81% |
| <60 | 4 | 140 | 138 | 0.49 | -0.13(-0.49, 0.23) | 56% |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 5 | 148 | 152 | 0.07 | -0.50(-1.04, 0.04) | 80% |
| <12 | 2 | 60 | 59 | 0.86 | -0.03(-0.39, 0.33) | 0% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 110 | 109 | 0.50 | 0.09(-0.17, 0.36) | 0% |
| <500 | 4 | 98 | 102 | 0.007 | -0.69(-1.20, -0.19) | 66% |
表3 亚组分析后hs-CRP水平变化的meta分析结果
Tab. 3 Meta-analysis results of hs-CRP levels in subgroup analysis
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >60 | 3 | 68 | 73 | 0.09 | -0.70(-1.52, 0.12) | 81% |
| <60 | 4 | 140 | 138 | 0.49 | -0.13(-0.49, 0.23) | 56% |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 5 | 148 | 152 | 0.07 | -0.50(-1.04, 0.04) | 80% |
| <12 | 2 | 60 | 59 | 0.86 | -0.03(-0.39, 0.33) | 0% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 110 | 109 | 0.50 | 0.09(-0.17, 0.36) | 0% |
| <500 | 4 | 98 | 102 | 0.007 | -0.69(-1.20, -0.19) | 66% |
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >50 | 5 | 120 | 120 | 0.08 | -0.40(-0.86, 0.05) | 89% |
| <50 | 1 | 50 | 50 | <0.001 | -0.83(-1.20, 0.46) | - |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 3 | 76 | 76 | 0.35 | -0.12(-0.37, 0.13) | 68% |
| <12 | 3 | 94 | 94 | 0.01 | -0.90(-1.61, -0.19) | 78% |
| ≥10 | 4 | 97 | 99 | 0.35 | -0.11(-0.33, 0.12) | 52% |
| <10 | 2 | 73 | 71 | 0.001 | -1.17(-1.88, -0.46) | 80% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 96 | 97 | 0.35 | -0.32(-0.97, 0.34) | 85% |
| <500 | 3 | 74 | 73 | 0.11 | -0.65(-1.46, 0.15) | 94% |
表4 亚组分析后MDA水平变化的meta分析结果
Tab. 4 Meta-analysis results of MDA levels in subgroup analysis
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >50 | 5 | 120 | 120 | 0.08 | -0.40(-0.86, 0.05) | 89% |
| <50 | 1 | 50 | 50 | <0.001 | -0.83(-1.20, 0.46) | - |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 3 | 76 | 76 | 0.35 | -0.12(-0.37, 0.13) | 68% |
| <12 | 3 | 94 | 94 | 0.01 | -0.90(-1.61, -0.19) | 78% |
| ≥10 | 4 | 97 | 99 | 0.35 | -0.11(-0.33, 0.12) | 52% |
| <10 | 2 | 73 | 71 | 0.001 | -1.17(-1.88, -0.46) | 80% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 96 | 97 | 0.35 | -0.32(-0.97, 0.34) | 85% |
| <500 | 3 | 74 | 73 | 0.11 | -0.65(-1.46, 0.15) | 94% |
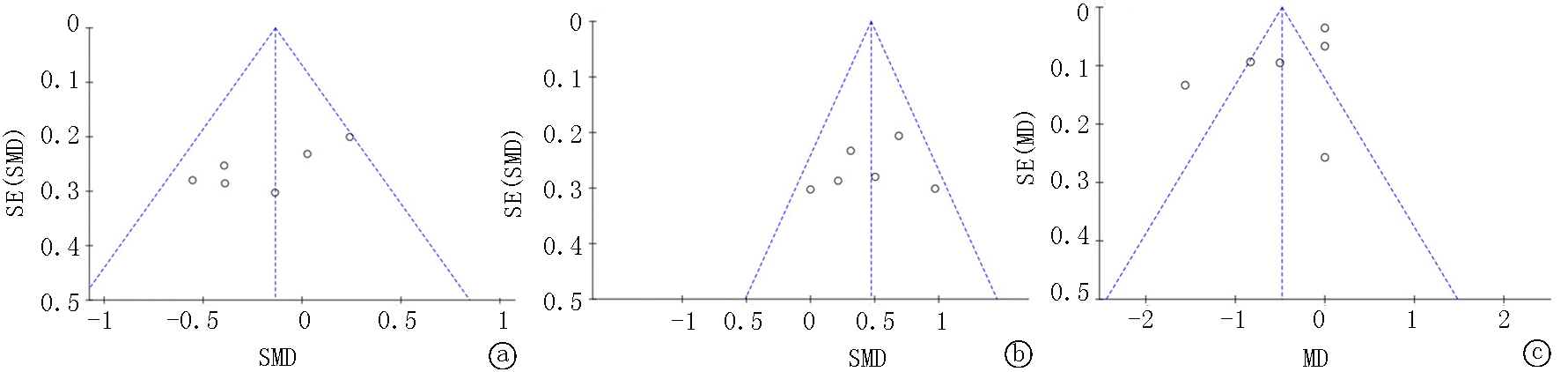
图5 姜黄素对T2DM患者(a)hs-CRP,(b) TAC,(c) MDA水平影响的漏斗图
Fig. 5 Funnel diagram of the effects of curcumin on (a) hs-CRP, (b) TAC, and (c) MDA levels in T2DM patients
| [1] | Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: National cross sectional study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369: m997. |
| [2] |
Derosa G, Maffioli P, Simental-Mendia LE, et al. Effect of curcumin on circulating interleukin-6 concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2016, 111:394-404.
doi: S1043-6618(16)30392-9 pmid: 27392742 |
| [3] |
Mirzaei H, Shakeri A, Rashidi B, et al. Phytosomal curcumin: A review of pharmacokinetic, experimental and clinical studies[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 85: 102-112.
doi: S0753-3322(16)32074-1 pmid: 27930973 |
| [4] | Pivari F, Mingione A, Brasacchio C, et al. Curcumin and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Prevention and treatment[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(8):1837. |
| [5] | Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Kurnianta PDM, et al. Effects of curcumin on glycemic control and lipid profile in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(4):e0215840. |
| [6] |
Panahi Y, Khalili N, Sahebi E, et al. Antioxidant effects of curcuminoids in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2017, 25(1): 25-31.
doi: 10.1007/s10787-016-0301-4 pmid: 27928704 |
| [7] |
Panahi Y, Khalili N, Sahebi E, et al. Effects of curcuminoids plus piperine on glycemic, hepatic and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial[J]. Drug Research, 2018, 68(7): 403-409.
doi: 10.1055/s-0044-101752 pmid: 29458218 |
| [8] |
Shafabakhsh R, Asemi Z, Reiner Z, et al. The effects of nano-curcumin on metabolic status in patients with diabetes on hemodialysis, a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Iran J Kidney Dis, 2020, 14(4): 290-299.
pmid: 32655024 |
| [9] |
Shafabakhsh R, Mobini M, Raygan F, et al. Curcumin administration and the effects on psychological status and markers of inflammation and oxidative damage in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease[J]. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 2020, 40: 77-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.029 pmid: 33183576 |
| [10] |
Adibian M, Hodaei H, Nikpayam O, et al. The effects of curcumin supplementation on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, serum adiponectin, and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(5): 1374-1383.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6328 pmid: 30864188 |
| [11] | Hodaei H, Adibian M, Nikpayam O, et al. The effect of curcumin supplementation on anthropometric indices, insulin resistance and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2019, 11(1):41. |
| [12] |
Adab Z, Eghtesadi S, Vafa MR, et al. Effect of turmeric on glycemic status, lipid profile, hs-CRP, and total antioxidant capacity in hyperlipidemic type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(4): 1173-1181.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6312 pmid: 30859660 |
| [13] |
Mokhtari M, Razzaghi R, Momen-Heravi M. The effects of curcumin intake on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Phytother Res, 2021, 35(4): 2099-2107.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6957 pmid: 33200488 |
| [14] |
Dastani M, Rahimi HR, Askari VR, et al. Three months of combination therapy with nano-curcumin reduces the inflammation and lipoprotein (a) in type 2 diabetic patients with mild to moderate coronary artery disease: Evidence of a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial[J]. Biofactors, 2022, 49(1):108-118.
doi: 10.1002/biof.1874 pmid: 35674733 |
| [15] | Funamoto M, Shimizu K, Sunagawa Y, et al. Effects of highly absorbable curcumin in patients with impaired glucose tolerance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019:8208237. |
| [16] |
Usharani P, Mateen AA, Naidu MU, et al. Effect of NCB-02, atorvastatin and placebo on endothelial function, oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, 8-week study[J]. Drugs R D, 2008, 9(4): 243-250.
doi: 10.2165/00126839-200809040-00004 pmid: 18588355 |
| [17] |
Huang J, Qin S, Huang L, et al. Efficacy and safety of Rhizoma curcumea longae with respect to improving the glucose metabolism of patients at risk for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials[J]. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2019, 32(5): 591-606.
doi: 10.1111/jhn.12648 pmid: 30983042 |
| [18] |
Azhdari M, Karandish M, Mansoori A. Metabolic benefits of curcumin supplementation in patients with metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(5): 1289-1301.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6323 pmid: 30941814 |
| [19] |
Mohammadi S, Kayedpoor P, Karimzadeh-Bardei L, et al. The effect of curcumin on TNF-α, IL-6 and CRP expression in a model of polycystic ovary syndrome as an inflammation state[J]. J Reprod Infertil, 2017, 18(4): 352-360.
pmid: 29201665 |
| [20] | Costantino M, Corno C, Colombo D, et al. Curcumin and related compounds in cancer cells: New avenues for old molecules[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 889816. |
| [21] | Gorabi AM, Abbasifard M, Imani D, et al. Effect of curcumin on C-reactive protein as a biomarker of systemic inflammation: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Phytotherapy research, 2022, 36(1): 85-97. |
| [22] |
Tabrizi R, Vakili S, Akbari M, et al. The effects of curcumin-containing supplements on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(2): 253-262.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6226 pmid: 30402990 |
| [23] | Jiménez-Osorio AS, García-Niño WR, González-Reyes S, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with curcumin on redox status and Nrf2 activation in patients with nondiabetic or diabetic proteinuric chronic kidney disease: A pilot study[J]. J Ren Nutr, 2016, 26(4): 237-244. |
| [24] |
Na LX, Zhang YL, Li Y, et al. Curcumin improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of rats[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2011, 21(7): 526-533.
doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.11.009 pmid: 20227862 |
| [25] | Nie T, Cooper GJS. Mechanisms underlying the antidiabetic activities of polyphenolic compounds: A review[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 798329. |
| [26] | Den Hartogh DJ, Gabriel A, Tsiani E. Antidiabetic properties of curcumin I: Evidence from In Vitro Studies[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(1):118. |
| [1] | 刘翠翠, 朱亚芳, 吕文娟. 不同HRCT表型COPD患者戒烟后肺功能、炎性因子和临床症状变化[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(7): 625-629. |
| [2] | 马千里. 岩藻黄素在认知障碍类疾病中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(6): 572-576. |
| [3] | 王忠奇, 李今朝, 吴南. 急性冠脉综合征患者全身免疫炎症指数与冠状动脉病变严重程度的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(6): 512-517. |
| [4] | 王娇燕, 严超, 应可净. 气道慢性炎症性疾病并发静脉血栓栓塞症的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(5): 470-474. |
| [5] | 王先耀, 施荣杰, 龙均, 字颖. 膳食炎症指数在慢性疾病中的应用现状[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 284-288. |
| [6] | 王欢, 沈婷, 孔颖宏, 居悦俊. 女性糖尿病神经源性膀胱患者抗氧化和炎症因子水平及其临床意义[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(11): 984-988. |
| [7] | 王静, 李彩格, 王婷, 刘子渤, 盖斌, 金杨瑜, 张力辉. 恩格列净与利拉鲁肽联合治疗肥胖/超重2型糖尿病患者的疗效及其对炎症因子的影响:一项前瞻、 随机、开放、平行对照的临床研究[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(10): 909-914. |
| [8] | 吕丽丽, 翟满满, 丁小艳, 陈永清. 线粒体转录因子A介导的线粒体功能障碍在糖尿病心肌病中的作用[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 465-468. |
| [9] | 易静静, 圈启芳, 马婕. 调节小胶质细胞反应性:糖尿病视网膜病变新见解[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 364-368. |
| [10] | 谢少为, 吕小涵, 董艳红, 吕佩源. 抗炎细胞因子在阿尔茨海默病中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 185-188. |
| [11] | 代菁, 陈华茜. 血液透析患者自发性肾破裂1例并文献复习[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1107-1111. |
| [12] | 王思源, 王利, 温新然, 李小青. 新型冠状病毒感染后儿童多系统炎症综合征2例并文献复习[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1112-1116. |
| [13] | 李志勇. 超声诊断短暂颈动脉周围炎症综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(11): 1027-1030. |
| [14] | 张娟, 田茂露, 查艳. 维持性血液透析患者的微炎症状态与促红细胞生成素低反应性贫血[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(10): 949-953. |
| [15] | 轩晓倩, 赵君慧, 杨小茜. 炎性指标在非小细胞肺癌患者预后中的临床意义[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(7): 663-667. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
