

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (1): 20-36.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.01.002
收稿日期:2022-08-02
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2023-03-03
通讯作者:
张维健
E-mail:cheungweijian@163.com
Received:2022-08-02
Online:2023-01-20
Published:2023-03-03
Contact:
Zhang Weijian
E-mail:cheungweijian@163.com
摘要:
目的 系统评价特泽帕肽治疗2型糖尿病(T2DM)患者的疗效及安全性。方法 通过检索CNKI、万方、VIP、Pubmed、Embase及Cochrane library数据库获得符合纳入标准的随机对照研究(RCTs)。结果 共纳入7篇RCTs,共7163名T2DM患者。Meta分析结果显示,5 mg、10 mg、15 mg 3种剂量的特泽帕肽降低糖化血红蛋白(HbA1c)、减轻体重的疗效均明显优于所有对照组[胰高血糖素样肽1受体激动剂(GLP-1RA)、胰岛素、安慰剂],疗效呈剂量依赖性,随剂量增高,显示出更大的疗效,3种剂量下HbA1c降低的幅度分别为[
中图分类号:
谢飞飞, 张维健. 特泽帕肽治疗2型糖尿病患者疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(1): 20-36.
Xie Feifei, Zhang Weijian. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(1): 20-36.
| 纳入研究 | 干预措施 | 样本量(例) | 年龄(岁) | HbA1c(%) | 疗程(周) | 质量等级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frias 2018[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 55 | 57.9±8.2 | 8.2±1.0 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 51 | 56.5±9.9 | 8.2±1.1 | |||
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 53 | 56.0±7.6 | 8.1±1.1 | 26 | B | |
| Dulaglutide 1.5 mg | 54 | 58.7±7.8 | 8.1±1.0 | |||
| Placebo | 51 | 56.6±8.9 | 8.0±0.9 | |||
| Rosenstock 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 121 | 54.1±11.9 | 8.0±0.8 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 121 | 55.8±10.4 | 7.9±0.8 | 40 | A | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 121 | 52.9±12.3 | 7.9±1.0 | |||
| Placebo | 115 | 53.6±12.8 | 8.1±0.8 | |||
| Frías 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 470 | 56.3±10.0 | 8.3±1.1 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 469 | 57.2±10.5 | 8.3±1.0 | 40 | B | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 470 | 55.9±10.4 | 8.3±1.0 | |||
| Semaglutide 1 mg | 469 | 56.9±10.8 | 8.3±1.0 | |||
| Ludvik 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 358 | 57.2±10.1 | 8.2±0.9 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 360 | 57.4±9.7 | 8.2±0.9 | 52 | B | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 359 | 57.5±10.2 | 8.2±0.9 | |||
| Insulin degludec | 360 | 57.5±10.1 | 8.1±0.9 | |||
| Del Prato 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 329 | 62.9±8.6 | 8.5±0.8 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 328 | 63.7±8.7 | 8.6±0.9 | 52 | B | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 338 | 63.7±8.6 | 8.5±1.0 | |||
| Insulin glargine | 1 000 | 63.8±8.5 | 8.5±0.9 | |||
| Dahl 2022[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 116 | 62±10 | 8.3±0.9 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 119 | 60±10 | 8.4±0.8 | 40 | A | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 120 | 61±10 | 8.2±0.9 | |||
| Placebo | 120 | 60±10 | 8.4±0.8 | |||
| Inagaki 2022[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 159 | 56.8±10.1 | 8.2±0.9 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 158 | 56.2±10.3 | 8.2±0.9 | 52 | A | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 160 | 56.0±10.7 | 8.2±0.9 | |||
| Dulaglutide 0.75 mg | 159 | 57.5±10.2 | 8.2±0.9 |
表1 纳入研究基本信息
Tab. 1 Basic information of included studies
| 纳入研究 | 干预措施 | 样本量(例) | 年龄(岁) | HbA1c(%) | 疗程(周) | 质量等级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frias 2018[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 55 | 57.9±8.2 | 8.2±1.0 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 51 | 56.5±9.9 | 8.2±1.1 | |||
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 53 | 56.0±7.6 | 8.1±1.1 | 26 | B | |
| Dulaglutide 1.5 mg | 54 | 58.7±7.8 | 8.1±1.0 | |||
| Placebo | 51 | 56.6±8.9 | 8.0±0.9 | |||
| Rosenstock 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 121 | 54.1±11.9 | 8.0±0.8 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 121 | 55.8±10.4 | 7.9±0.8 | 40 | A | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 121 | 52.9±12.3 | 7.9±1.0 | |||
| Placebo | 115 | 53.6±12.8 | 8.1±0.8 | |||
| Frías 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 470 | 56.3±10.0 | 8.3±1.1 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 469 | 57.2±10.5 | 8.3±1.0 | 40 | B | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 470 | 55.9±10.4 | 8.3±1.0 | |||
| Semaglutide 1 mg | 469 | 56.9±10.8 | 8.3±1.0 | |||
| Ludvik 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 358 | 57.2±10.1 | 8.2±0.9 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 360 | 57.4±9.7 | 8.2±0.9 | 52 | B | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 359 | 57.5±10.2 | 8.2±0.9 | |||
| Insulin degludec | 360 | 57.5±10.1 | 8.1±0.9 | |||
| Del Prato 2021[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 329 | 62.9±8.6 | 8.5±0.8 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 328 | 63.7±8.7 | 8.6±0.9 | 52 | B | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 338 | 63.7±8.6 | 8.5±1.0 | |||
| Insulin glargine | 1 000 | 63.8±8.5 | 8.5±0.9 | |||
| Dahl 2022[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 116 | 62±10 | 8.3±0.9 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 119 | 60±10 | 8.4±0.8 | 40 | A | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 120 | 61±10 | 8.2±0.9 | |||
| Placebo | 120 | 60±10 | 8.4±0.8 | |||
| Inagaki 2022[ | Tirzepatide 5 mg | 159 | 56.8±10.1 | 8.2±0.9 | ||
| Tirzepatide 10 mg | 158 | 56.2±10.3 | 8.2±0.9 | 52 | A | |
| Tirzepatide 15 mg | 160 | 56.0±10.7 | 8.2±0.9 | |||
| Dulaglutide 0.75 mg | 159 | 57.5±10.2 | 8.2±0.9 |
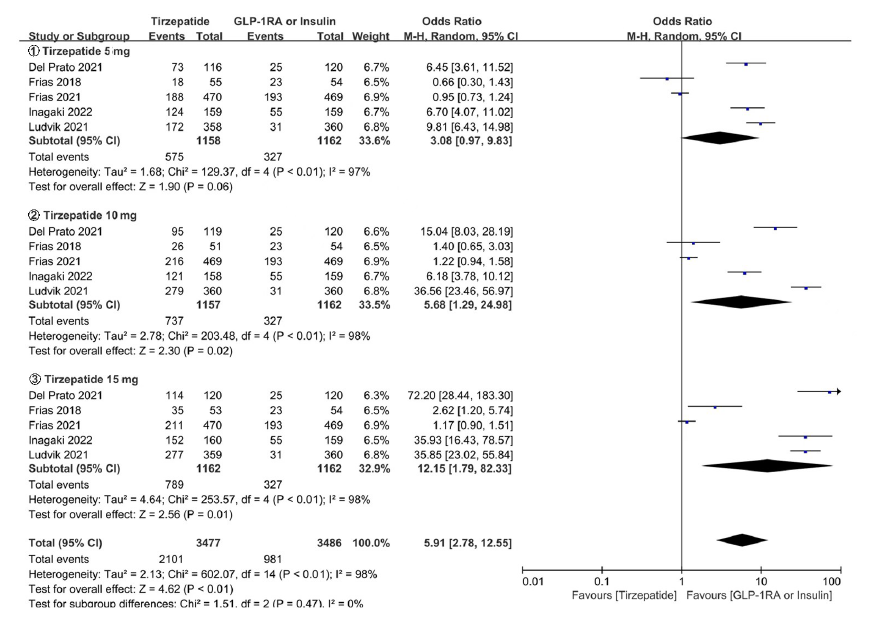
图18b Tirzepatide vs (GLP-1RA 或 Insulin) 胃肠道不良反应亚组meta分析结果
Fig. 18b Meta-analysis results of gastrointestinal adverse reactions in Tirzepatide vs GLP-1RA or Insulin in subgroup
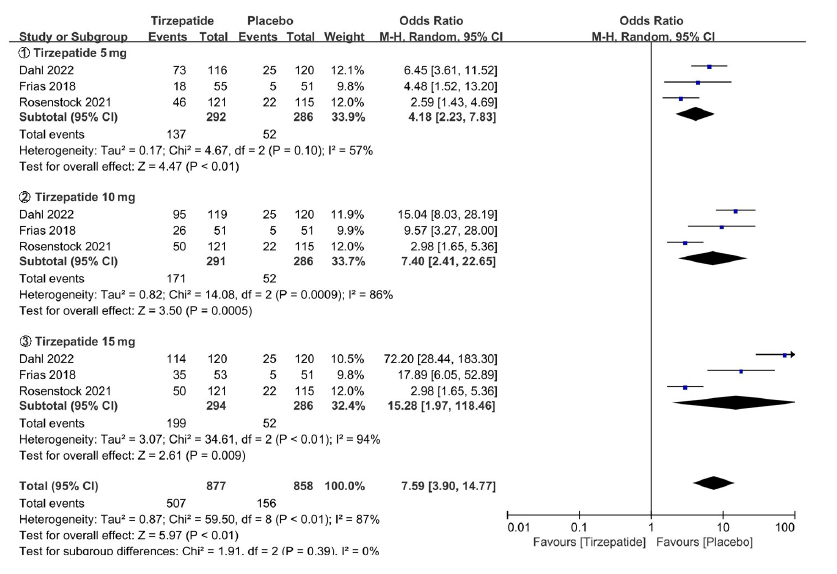
图18c Tirzepatide vs Placebo胃肠道不良反应亚组meta分析结果
Fig. 18c Meta-analysis results of gastrointestinal adverse reactions in Tirzepatide vs Placebo in subgroup
| [1] |
Aroda VR, Bain SC, Cariou B, et al. Efficacy and safety of once-weekly semaglutide versus once-daily insulin glargine as add-on to metformin (with or without sulfonylureas) in insulin-naive patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 4): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational, phase 3a trial[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2017, 5(5):355-366.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(17)30085-2 URL |
| [2] | Frias JP, Nauck MA, Van J, et al. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial[J]. Lancet, 2018, 392(10160):2180-2193. |
| [3] | Higgins JP, Thomas J, Chandler J, et al. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2019. |
| [4] | Rosenstock J, Wysham C, Frías JP, et al. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10295):143-155. |
| [5] |
Frías JP, Davies MJ, Rosenstock J, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(6):503-515.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2107519 URL |
| [6] |
Ludvik B, Giorgino F, Jódar E, et al. Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial [J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10300):583-598.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01443-4 pmid: 34370970 |
| [7] |
Del Prato S, Kahn SE, Pavo I, et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10313):1811-1824.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)02188-7 pmid: 34672967 |
| [8] |
Dahl D, Onishi Y, Norwood P, et al. Effect of subcutaneous tirzepatide vs placebo added to titrated insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: The SURPASS-5 randomized clinical trial[J]. JAMA, 2022, 327(6):534-545.
doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0078 pmid: 35133415 |
| [9] |
Inagaki N, Takeuchi M, Oura T, et al. Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide monotherapy compared with dulaglutide in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS J-mono): A double-blind, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2022, 10(9):623-633.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00188-7 URL |
| [10] |
Zhao FH, Zhou QT, Cong ZT, et al. Structural insights into multiplexed pharmacological actions of tirzepatide and peptide 20 at the GIP, GLP-1 or glucagon receptors[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 1057.
doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28683-0 pmid: 35217653 |
| [11] |
Gribble FM, Reimann F. metabolic Messengers: Glucagon-like peptide 1[J]. Nat metab, 2021, 3(2): 142-148.
doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-00327-x pmid: 33432200 |
| [12] |
Coskun T, Sloop KW, Loghin C, et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept[J]. Mol metab, 2018, 18:3-14.
doi: S2212-8778(18)30900-1 pmid: 30473097 |
| [13] |
Samms RJ, Coghlan MP, Sloop KW. How may GIP enhance the therapeutic efficacy of GLP-1?[J]. Trends Endocrinol metab, 2020, 31(6): 410-421.
doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2020.02.006 URL |
| [14] |
Samms RJ, Christe ME, Collins KA, et al. GIPR agonism mediates weight-independent insulin sensitization by tirzepatide in obese mice[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(12):e146353.
doi: 10.1172/JCI146353 URL |
| [15] |
Thomas MK, Nikooienejad A, Bray R, et al. Dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide improves beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes[J]. J Clin Endocrinol Metab, 2021, 106(2):388-396.
doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa863 pmid: 33236115 |
| [16] |
Heise T, Mari A, DeVries JH, et al. Effects of subcutaneous tirzepatide versus placebo or semaglutide on pancreatic islet function and insulin sensitivity in adults with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-arm, phase 1 clinical trial[J]. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, 2022, 10(6):418-429.
doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00085-7 URL |
| [17] | Finan B, Ma T, Ottaway N, et al. Unimolecular dual incretins maximize metabolic benefits in rodents, monkeys, and humans[J]. Sci Transl Med, 2013, 5(209):209ra151. |
| [18] |
Jastreboff AM, Aronne LJ, Ahmad NN, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity[J]. N Engl J Med, 2022, 387(3):205-216.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2206038 URL |
| [19] |
Tanday N, Flatt PR, Irwin N. metabolic responses and benefits of glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1) receptor ligands[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2022, 179(4):526-541.
doi: 10.1111/bph.15485 URL |
| [20] |
Tan TM, Khoo B. Tirzepatide and the new era of twincretins for diabetes[J]. Lancet, 2021, 398(10295): 95-97.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01390-8 URL |
| [1] | 龚财芳, 赵俊宇, 游川. 接纳与承诺疗法对癌症患者心理健康和生活质量影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 101-107. |
| [2] | 肖煌怡, 袁建坤, 严梓予, 曾雯姝, 鲁兰莫, 王峻. 认知干预对遗忘型轻度认知障碍老年患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 12-19. |
| [3] | 吕畅, 周利明. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌易感相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 779-787. |
| [4] | 李海, 刘文虎, 彭绍鹏, 王飞. 控制性阶梯式减压术对比快速标准大骨瓣减压术治疗重度颅脑损伤疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 788-795. |
| [5] | 侯有玲, 李奕, 关红玉, 罗红霞. 目标导向液体治疗在脑肿瘤切除术中应用效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(8): 686-693. |
| [6] | 金家辉, 杨阳, 秦铜, 何雨欣, 苏美华. 补充益生菌对2型糖尿病患者糖代谢改善的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 581-587. |
| [7] | 肖王静, 李欣梦, 卢松玲, 孙雪华. 重复经颅磁刺激治疗中枢神经源性吞咽障碍疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 588-599. |
| [8] | 尤奕, 高淑清, 徐浩. 肠内营养对食管癌患者术后临床结局影响的系统综述[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 485-492. |
| [9] | 倪艺芸, 刘彬, 梁琪, 李晓凤. 白细胞介素6和C反应蛋白预测新型冠状病毒肺炎严重程度的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 493-499. |
| [10] | 沃拉孜汗·玛德尼亚提, 迪力夏提·图尔迪麦麦提, 李梦晨, 拜合提尼沙·吐尔地. 宏基因组二代测序技术在肺结核诊断中应用价值的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 389-398. |
| [11] | 赵哲, 穆培娟, 张冬. 恩度联合顺铂胸腔灌注治疗肺癌合并恶性胸腔积液疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 399-404. |
| [12] | 马明福, 魏志国, 何铁英. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [13] | 曹宇萌, 张海燕, 刘立新. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的病理改变与血清铁蛋白和血清铁含量变化关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 197-207. |
| [14] | 马宏莉, 陆皓, 王丹, 焦海星, 李一珂, 李思雨, 吕静. 脑卒中患者残疾危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| [15] | 陶嘉楠, 李文茜, 马秀雯, 安琪, 王学红. HER-2在肝细胞癌中表达及临床意义的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1067-1072. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
