

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 389-398.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.05.001
• 循证研究 • 下一篇
沃拉孜汗·玛德尼亚提, 迪力夏提·图尔迪麦麦提, 李梦晨, 拜合提尼沙·吐尔地( )
)
收稿日期:2023-01-04
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-07-20
通讯作者:
拜合提尼沙·吐尔地, Email:1627971002@qq.com
基金资助:
Wolazihan Madeniyati, Dilixiati Tuerdimaimaiti, Li Mengchen, Baihetinisha Tuerdi( )
)
Received:2023-01-04
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-07-20
Contact:
Baihetinisha Tuerdi, Email:1627971002@qq.com
摘要:
目的 评价宏基因组二代测序(metagenomic next-generation sequencing,mNGS)应用于不同的临床标本对于肺结核(pulmonary tuberculosis,PTB)的诊断价值。方法 计算机检索PubMed、Embase、The Cochrane Library、知网(CNKI)、万方和维普等数据库中于建库至2022年11月公开发表的宏基因组二代测序技术诊断PTB的相关研究,获得的文献经过严格筛选和质量评估,由2名研究人员独立筛选文献, 提取数据,并评估纳入研究偏倚风险之后,采用StataSE16软件和Revman5.3软件进行meta分析。结果 纳入符合标准的文献11篇,共计1995例,meta分析结果显示,mNGS检测肺标本诊断PTB的敏感度为70%(95% CI:58%~79%),特异度为99%(95%CI:98%~100%)、阳性似然比(PLR)为106.9(95%CI:31.1~366.6)、阴性似然比(NLR)为0.31(95%CI:0.21~0.43)、诊断比值比(DOR)为350(95%CI:81~1512)、曲线下面积(AUC)为0.97;mNGS检测支气管肺泡灌洗液(broncho alveolar lavage fluid,BALF)诊断PTB敏感度为71%(95%CI:55%~83%),特异度为99%(95%CI:97%~100%), PLR为76.4(95% CI:26.6~218.9),NLR为0.30(95% CI:0.18~0.48),DOR为258(95%CI:75~895)、AUC为0.99;mNGS检测肺组织诊断PTB敏感度为81%(95%CI:69%~89%),特异度为97%(95% CI:88%~99%),PLR为26.0(95%CI:6.6~102.4),NLR为0.19(95%CI:0.11~0.33),DOR为135(95% CI:29~639)、AUC为0.97。结论 mNGS诊断PTB具有较高的应用价值,尤其在痰菌阴性PTB的诊断价值更突出,可作为一种快速诊断PTB的辅助工具。
中图分类号:
沃拉孜汗·玛德尼亚提, 迪力夏提·图尔迪麦麦提, 李梦晨, 拜合提尼沙·吐尔地. 宏基因组二代测序技术在肺结核诊断中应用价值的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 389-398.
Wolazihan Madeniyati, Dilixiati Tuerdimaimaiti, Li Mengchen, Baihetinisha Tuerdi. Meta-analysis of the application value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(5): 389-398.
| 第一作者 | 年份 | PTB组(例) | 非PTB组(例) | 诊断标准 | 研究方法 | mNGS测序平台 | 标本类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou等[ | 2019 | 13 | 14 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| Shi等[ | 2020 | 48 | 62 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Chen等[ | 2020 | 17 | 20 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺标本 |
| Jin等[ | 2020 | 53 | 424 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| Liu等[ | 2021 | 142 | 111 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF |
| Zhu等[ | 2021 | 46 | 61 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 王春等[ | 2021 | 103 | 24 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 2021 | 100 | 105 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| 赵素娥等[ | 2022 | 95 | 60 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 未知 | BALF |
| Xu等[ | 2022 | 71 | 23 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Fu等[ | 2022 | 46 | 357 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | 肺标本 |
表1 纳入研究文献特征
Tab.1 Characteristics of included studies
| 第一作者 | 年份 | PTB组(例) | 非PTB组(例) | 诊断标准 | 研究方法 | mNGS测序平台 | 标本类型 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhou等[ | 2019 | 13 | 14 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| Shi等[ | 2020 | 48 | 62 | 临床/病原 | 前瞻性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Chen等[ | 2020 | 17 | 20 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺标本 |
| Jin等[ | 2020 | 53 | 424 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| Liu等[ | 2021 | 142 | 111 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF |
| Zhu等[ | 2021 | 46 | 61 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 王春等[ | 2021 | 103 | 24 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | BALF/肺组织/肺标本 |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 2021 | 100 | 105 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | BGISEQ | 肺标本 |
| 赵素娥等[ | 2022 | 95 | 60 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 未知 | BALF |
| Xu等[ | 2022 | 71 | 23 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | BALF |
| Fu等[ | 2022 | 46 | 357 | 临床/病原 | 回顾性研究 | 其他 | 肺标本 |
| 标本类型 | 作者 | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | Zhou等[ | 8 | 0 | 5 | 14 |
| Chen等[ | 14 | 0 | 3 | 20 | |
| Jin等[ | 31 | 7 | 22 | 417 | |
| Zhu等[ | 41 | 1 | 5 | 60 | |
| 王春等[ | 57 | 1 | 46 | 23 | |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 59 | 0 | 41 | 105 | |
| Fu等[ | 36 | 0 | 10 | 357 | |
| BALF | Shi等[ | 23 | 1 | 25 | 61 |
| Chen等[ | 11 | 0 | 3 | 14 | |
| Jin等[ | 11 | 2 | 10 | 108 | |
| Liu等[ | 85 | 0 | 57 | 111 | |
| Zhu等[ | 29 | 1 | 3 | 45 | |
| 王春等[ | 24 | 0 | 17 | 8 | |
| 赵素娥等[ | 55 | 0 | 40 | 60 | |
| Xu等[ | 67 | 0 | 4 | 23 | |
| 肺组织 | Jin等[ | 8 | 1 | 1 | 44 |
| Zhu等[ | 12 | 1 | 2 | 14 | |
| 王春等[ | 28 | 0 | 8 | 4 |
表2 mNGS检测不同临床标本诊断PTB的四格表数据
Tab.2 Data in four tables for the diagnosis of PTB in different clinical specimens detected by mNGS
| 标本类型 | 作者 | TP | FP | FN | TN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | Zhou等[ | 8 | 0 | 5 | 14 |
| Chen等[ | 14 | 0 | 3 | 20 | |
| Jin等[ | 31 | 7 | 22 | 417 | |
| Zhu等[ | 41 | 1 | 5 | 60 | |
| 王春等[ | 57 | 1 | 46 | 23 | |
| 孙雯雯等[ | 59 | 0 | 41 | 105 | |
| Fu等[ | 36 | 0 | 10 | 357 | |
| BALF | Shi等[ | 23 | 1 | 25 | 61 |
| Chen等[ | 11 | 0 | 3 | 14 | |
| Jin等[ | 11 | 2 | 10 | 108 | |
| Liu等[ | 85 | 0 | 57 | 111 | |
| Zhu等[ | 29 | 1 | 3 | 45 | |
| 王春等[ | 24 | 0 | 17 | 8 | |
| 赵素娥等[ | 55 | 0 | 40 | 60 | |
| Xu等[ | 67 | 0 | 4 | 23 | |
| 肺组织 | Jin等[ | 8 | 1 | 1 | 44 |
| Zhu等[ | 12 | 1 | 2 | 14 | |
| 王春等[ | 28 | 0 | 8 | 4 |
| 标本类型 | 敏感度(95% CI) | 特异度(95% CI) | PLR(95% CI) | NLR(95% CI) | DOR(95% CI) | AUC(95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | 70%(58%~79%) | 99%(98%~100%) | 106.9(31.1~366.6) | 0.31(0.21~0.43) | 350(81~1512) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
| BALF | 71%(55%~83%) | 99%(97%~100%) | 76.4(26.6~218.9) | 0.30(0.18~0.48) | 258(75~895) | 0.99(0.98~1.00) |
| 肺组织 | 81%(69%~89%) | 97%(88%~99%) | 26.0(6.6~102.4) | 0.19(0.11~0.33) | 135(29~639) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
表3 mNGS在不同标本类型中诊断PTB的参数汇总
Tab.3 Summary of parameters for mNGS diagnostic of PTB in different specimen types
| 标本类型 | 敏感度(95% CI) | 特异度(95% CI) | PLR(95% CI) | NLR(95% CI) | DOR(95% CI) | AUC(95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肺标本 | 70%(58%~79%) | 99%(98%~100%) | 106.9(31.1~366.6) | 0.31(0.21~0.43) | 350(81~1512) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
| BALF | 71%(55%~83%) | 99%(97%~100%) | 76.4(26.6~218.9) | 0.30(0.18~0.48) | 258(75~895) | 0.99(0.98~1.00) |
| 肺组织 | 81%(69%~89%) | 97%(88%~99%) | 26.0(6.6~102.4) | 0.19(0.11~0.33) | 135(29~639) | 0.97(0.95~0.98) |
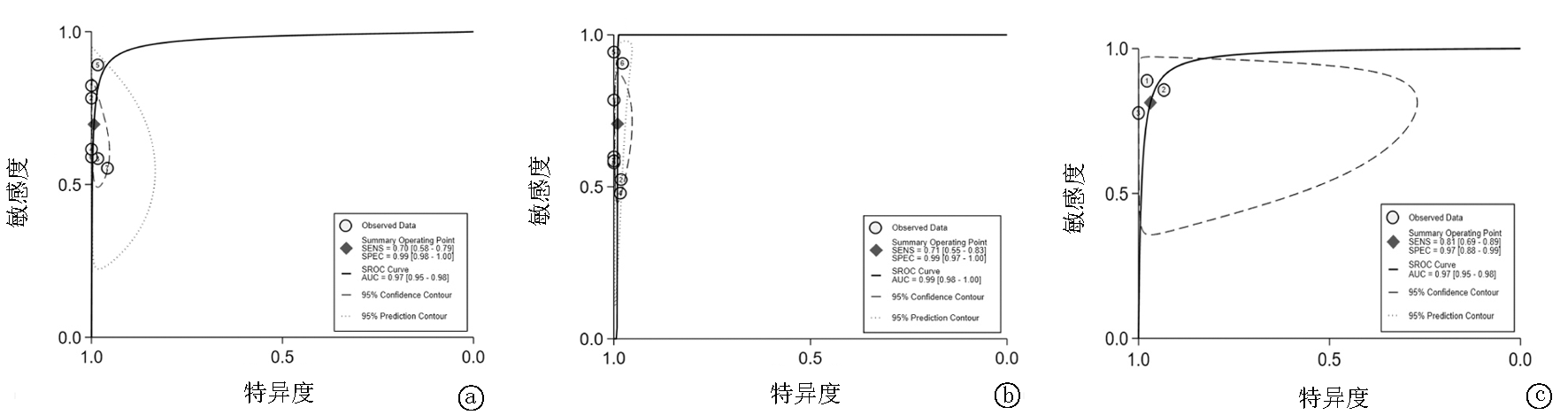
图7 不同标本诊断PTB的SROC曲线 a.mNGS检测肺标本诊断PTB的SROC曲线(图中对应研究编号依次为:①Chen等[13],②Fu等[21],③Jin等[14],④Zhou等[11],⑤Zhu等[16],⑥孙雯雯等[18],⑦王春等[17]);b.mNGS检测BALF诊断PTB的SROC曲线(图中对应研究编号依次为:①Chen 等[13],②jin等[14],③Liu等[15],④Shi等[12],⑤Xu等[20],⑥Zhu等[16],⑦王春等[17],⑧赵素娥等[19]);c.mNGS检测肺组织诊断PTB的SROC曲线(图中对应研究标号依次为:①Jin等[14],②Zhu等[16],③王春等[17])
Fig.7 SROC plot of different specimens for diagnosing PTB a.SROC plot for diagnosing PTB by detecting lung samples with mNGS. b.SROC plot for diagnosing PTB by detecting BALF with mNGS. c.SROC plot for diagnosing PTB by detecting lung tissue with mNGS
| 分组 | 研究数量 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究类型 | 回顾性分析 前瞻性研究 | 7 1 | 71%(58%~83%) 67%(54%~79%) | 0.674 |
| 测序平台 | BGISEQ 其他 | 5 3 | 70%(52%~88%) 72%(47%~97%) | 0.882 |
| 痰涂片情况 | 阴性 阳性 | 2 6 | 89%(81%~97%) 64%(54%~73%) | <0.05 |
表4 mNGS检测 BALF的亚组分析
Tab.4 Subgroup analysis of mNGS detection of BALF
| 分组 | 研究数量 | 敏感度(95%CI) | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究类型 | 回顾性分析 前瞻性研究 | 7 1 | 71%(58%~83%) 67%(54%~79%) | 0.674 |
| 测序平台 | BGISEQ 其他 | 5 3 | 70%(52%~88%) 72%(47%~97%) | 0.882 |
| 痰涂片情况 | 阴性 阳性 | 2 6 | 89%(81%~97%) 64%(54%~73%) | <0.05 |
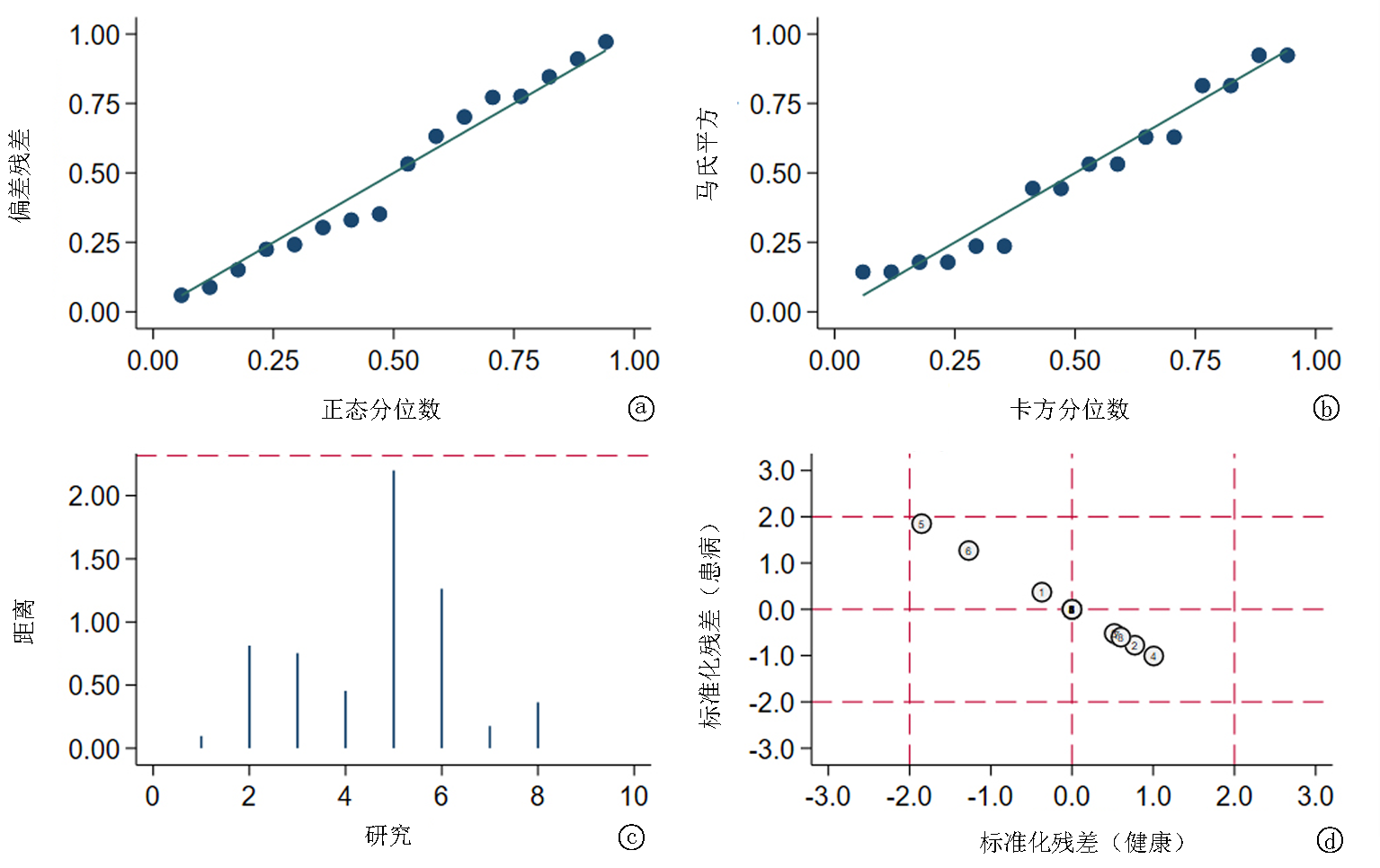
图8 mNGS检测BALF的敏感性分析 a.拟合优度分析;b.双变量正态性分析;c.影响分析;d.异常值检测,图中对应研究编号依次为:①Chen等[13],②jin等[14],③Liu等[15],④Shi等[12],⑤Xu等[20],⑥Zhu等[16],⑦王春等[17],⑧赵素娥等[19]
Fig.8 Sensitivity analysis of mNGS detection of BALF a.Goodness-of-fit; b.Bivariate normality; c.Influence Analysis; d.Outlier Detection
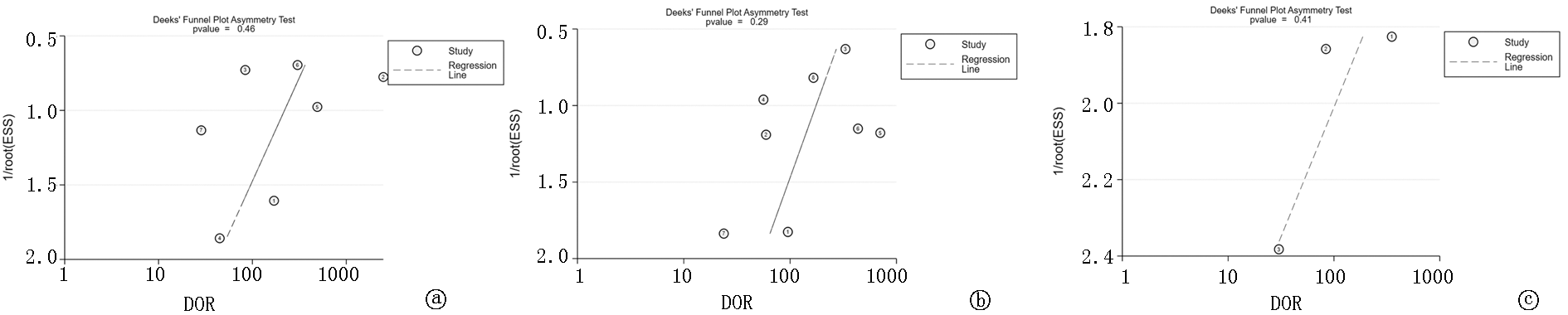
图9 mNGS检测3种标本的Deeks'漏斗图 a.mNGS检测肺标本诊断PTB的Deeks'漏斗图; b.mNGS检测BALF诊断PTB的Deeks'漏斗图; c.mNGS检测肺组织诊断PTB的Deeks'漏斗图
Fig.9 mNGS detects Deeks' funnel plots of 3 specimens a. Deeks' funnel diagram of mNGS detection of lung specimen for diagnosis of PTB; b. Deeks' funnel diagram of mNGS detection of BALF for diagnosis of PTB; c. Deeks' funnel diagram of mNGS detection of lung tissue for diagnosis of PTB
| [1] |
Pezzella AT. History of pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Thorac Surg Clin, 2019, 29(1): 1-17.
doi: S1547-4127(18)30128-2 pmid: 30454916 |
| [2] | 高静韬, 刘宇红. 2021年世界卫生组织全球结核病报告要点解读[J]. 河北医科大学学报, 2022, 43(7): 745-749. |
| [3] |
Muttamba W, Kirenga B, Ssengooba W, et al. Prevalence of tuberculosis risk factors among bacteriologically negative and bacteriologically confirmed tuberculosis patients from five regional referral hospitals in Uganda[J]. Am J Trop Med Hyg, 2019, 100(2): 386-391.
doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.18-0281 URL |
| [4] |
Suárez I, Fünger SM, Kröger S, et al. The diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis[J]. Dtsch Arztebl Int, 2019, 116(43): 729-735.
doi: 10.3238/arztebl.2019.0729 pmid: 31755407 |
| [5] |
Yang C, Zhang S, Yao L, et al. Evaluation of risk factors for false-negative results with an antigen-specific peripheral blood-based quantitative T cell assay (T-SPOT®. TB) in the diagnosis of active tuberculosis: A large-scale retrospective study in China[J]. J Int Med Res, 2018, 46(5): 1815-1825.
doi: 10.1177/0300060518757381 pmid: 29529901 |
| [6] | 卢春容, 房宏霞, 陆普选, 等. WHO 2021年全球结核病报告:全球与中国关键数据分析[J]. 新发传染病电子杂志, 2021, 6(4): 368-372. |
| [7] | 《中华传染病杂志》编辑委员会. 中国宏基因组学第二代测序技术检测感染病原体的临床应用专家共识[J]. 中华传染病杂志, 2020, 38(11): 681-689. |
| [8] | 夏静, 陈磊, 施雨鑫, 等. 宏基因组二代测序技术在结核病诊断中的应用[J]. 中国国境卫生检疫杂志, 2020, 43(1): 74-76. |
| [9] |
Miao Q, Ma Y, Wang Q, et al. Microbiological diagnostic performance of metagenomic next-generation sequencing when applied to clinical practice[J]. Clin Infect Dis, 2018, 67(suppl_2): S231-s240.
doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy693 URL |
| [10] | 张奕杰. 应用宏基因组二代测序技术诊断结核病4例并文献复习[J]. 河北医学, 2021, 27(8): 1377-1382. |
| [11] |
Zhou X, Wu H, Ruan Q, et al. Clinical evaluation of diagnosis efficacy of active mycobacterium tuberculosis complex infection via metagenomic next-generation sequencing of direct clinical samples[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2019, 9: 351.
doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00351 URL |
| [12] |
Shi CL, Han P, Tang PJ, et al. Clinical metagenomic sequencing for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. J Infect, 2020, 81(4): 567-574.
doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.004 URL |
| [13] |
Chen P, Sun W, He Y. Comparison of metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology, culture and GeneXpert MTB/RIF assay in the diagnosis of tuberculosis[J]. J Thorac Dis, 2020, 12(8): 4014-4024.
doi: 10.21037/jtd-20-1232 pmid: 32944313 |
| [14] |
Jin W, Pan J, Miao Q, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of metagenomic next-generation sequencing for active tuberculosis in clinical practice at a tertiary general hospital[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2020, 8(17): 1065.
doi: 10.21037/atm-20-2274 pmid: 33145284 |
| [15] |
Liu X, Chen Y, Ouyang H, et al. Tuberculosis diagnosis by metagenomic next-generation sequencing on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: A cross-sectional analysis[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2021, 104: 50-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.12.063 URL |
| [16] | Zhu N, Zhou D, Li S. Diagnostic accuracy of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in sputum-scarce or smear-negative cases with suspected pulmonary tuberculosis[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2021, 2021: 9970817. |
| [17] | 王春, 王彩英, 刘丹. 宏基因组二代测序对肺结核的诊断价值[J]. 中华生物医学工程杂志, 2021, 27(5): 489-493. |
| [18] | 孙雯雯, 顾瑾, 范琳. 宏基因组二代测序对不同类型结核病的诊断价值[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2021, 44(2): 96-100. |
| [19] | 赵素娥, 高欣, 刘胜岗, 等. 肺泡灌洗液宏基因组二代测序对疑似肺结核的诊断价值[J]. 临床肺科杂志, 2022, 27(5): 722-725, 743. |
| [20] | Xu P, Yang K, Yang L, et al. Next-generation metagenome sequencing shows superior diagnostic performance in acid-fast staining sputum smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis and non-tuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease[J]. Front Microbiol, 2022, 13: 898195. |
| [21] |
Fu M, Cao LJ, Xia HL, et al. The performance of detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in lung biopsy tissue by metagenomic next-generation sequencing[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2022, 22(1): 288.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02079-8 pmid: 35902819 |
| [22] | Mashabela GT, de Wet TJ, Warner DF. Mycobacterium tuberculosis Metabolism[J]. Microbiol Spectr, 2019, 7(4). |
| [23] | Zheng Y, Qiu X, Wang T, et al. The diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in lower respiratory tract infection[J]. Front Cell Infect Microbiol, 2021, 11: 694756. |
| [24] | 刘晓梦, 赵彩彦. 2017年感染性疾病临床进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2018, 33(1): 60-65. |
| [25] | Liu HC, Gao YL, Li DF, et al. Value of xpert MTB/RIF using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Clin Microbiol, 2021, 59(4) :e02170-20. |
| [26] |
Wang J, Han Y, Feng J. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for mixed pulmonary infection diagnosis[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2019, 19(1): 252.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-019-1022-4 pmid: 31856779 |
| [27] |
Xu H, Hu X, Wang W, et al. Clinical application and evaluation of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pulmonary infection with pleural effusion[J]. Infect Drug Resist, 2022, 15: 2813-2824.
doi: 10.2147/IDR.S365757 pmid: 35677528 |
| [28] |
Han D, Li Z, Li R, et al. mNGS in clinical microbiology laboratories: On the road to maturity[J]. Crit Rev Microbiol, 2019, 45(5-6): 668-685.
doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2019.1681933 pmid: 31691607 |
| [29] |
Wang CX, Huang Z, Fang W, et al. Preliminary assessment of nanopore-based metagenomic sequencing for the diagnosis of prosthetic joint infection[J]. Int J Infect Dis, 2020, 97: 54-59.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.044 URL |
| [1] | 龚财芳, 赵俊宇, 游川. 接纳与承诺疗法对癌症患者心理健康和生活质量影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 101-107. |
| [2] | 刘婉琦, 樊树芹, 庄瑞雪, 贺峰, 刘振川, 解忠祥. 成人水痘-带状疱疹病毒相关颅内感染5例临床分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 149-154. |
| [3] | 肖煌怡, 袁建坤, 严梓予, 曾雯姝, 鲁兰莫, 王峻. 认知干预对遗忘型轻度认知障碍老年患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 12-19. |
| [4] | 吕畅, 周利明. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌易感相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 779-787. |
| [5] | 李海, 刘文虎, 彭绍鹏, 王飞. 控制性阶梯式减压术对比快速标准大骨瓣减压术治疗重度颅脑损伤疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 788-795. |
| [6] | 侯有玲, 李奕, 关红玉, 罗红霞. 目标导向液体治疗在脑肿瘤切除术中应用效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(8): 686-693. |
| [7] | 金家辉, 杨阳, 秦铜, 何雨欣, 苏美华. 补充益生菌对2型糖尿病患者糖代谢改善的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 581-587. |
| [8] | 肖王静, 李欣梦, 卢松玲, 孙雪华. 重复经颅磁刺激治疗中枢神经源性吞咽障碍疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 588-599. |
| [9] | 尤奕, 高淑清, 徐浩. 肠内营养对食管癌患者术后临床结局影响的系统综述[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 485-492. |
| [10] | 倪艺芸, 刘彬, 梁琪, 李晓凤. 白细胞介素6和C反应蛋白预测新型冠状病毒肺炎严重程度的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 493-499. |
| [11] | 赵哲, 穆培娟, 张冬. 恩度联合顺铂胸腔灌注治疗肺癌合并恶性胸腔积液疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 399-404. |
| [12] | 黎恒楠, 黄艳, 赵亚娟, 胡桂才. 血清CTRP5与持续非卧床腹膜透析患者左室舒张功能异常的相关性及其诊断价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 324-329. |
| [13] | 马明福, 魏志国, 何铁英. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [14] | 曹宇萌, 张海燕, 刘立新. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的病理改变与血清铁蛋白和血清铁含量变化关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 197-207. |
| [15] | 马宏莉, 陆皓, 王丹, 焦海星, 李一珂, 李思雨, 吕静. 脑卒中患者残疾危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||