

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (8): 686-693.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.08.002
收稿日期:2022-08-25
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
罗红霞
E-mail:luohongxia1232021@163.com
Hou Youling, Li Yi, Guan Hongyu, Luo Hongxia( )
)
Received:2022-08-25
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
Luo Hongxia
E-mail:luohongxia1232021@163.com
摘要:
目的 系统评价目标导向液体治疗在脑肿瘤切除术中的应用效果。方法 计算机检索Pubmed 、Embase、Cochrane Library、Web of Sicense、VIP、CNKI、WanFang Database、CBM数据库(建库至2022年4月),按照纳入排除标准筛选文献,质量评价并提取相关数据后,采用RevMan5.3软件和Stata SE16.0软件进行Meta分析。结果 共纳入17个符合标准的随机对照试验,共计962例患者。 Meta分析结果显示:相比于常规液体组,目标导向组术毕心脏指数(CI)增加[MD=0.45,95%CI(0.36, 0.55),P<0.01],术毕平均动脉压(MBP)升高[MD=6.14,95%CI(4.85,7.44),P<0.01],术中颈静脉球混合血氧饱和度(SjvO2)增加[切开硬脑膜后1 h:MD=4.77,95%CI(2.58,6.96),P<0.01;术毕:MD=4.42,95%CI(1.21,7.62),P=0.007],术毕血乳酸(Lac)水平降低[MD=-0.57,95%CI(-0.77,-0.37),P<0.01],术后神经功能缺损评分(NIHSS)降低[术后24 h:MD=-2.95,95%CI(-3.85,-2.05),P<0.01],术后简易智能量表(MMES)评分升高[术后1 d:MD=1.12,95%CI(0.26,1.99),P=0.01;术后3 d:MD=1.40,95%CI(0.75,2.05),P<0.01]。结论 目标导向液体治疗有助于维持脑肿瘤切除术患者循环稳定,提高组织灌注,改善氧供平衡,减少术后并发症,有利于术后恢复。
中图分类号:
侯有玲, 李奕, 关红玉, 罗红霞. 目标导向液体治疗在脑肿瘤切除术中应用效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(8): 686-693.
Hou Youling, Li Yi, Guan Hongyu, Luo Hongxia. Effect of goal-directed fluid therapy on brain tumor resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(8): 686-693.
| 纳入研究 | 年龄(岁) | 样本量(例) | 监测指标 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标导向液体组 | 常规液体组 | 目标导向液体组 | 常规液体组 | ||||
| Hasanin 2019[ | 41±12 | 39±13 | 31 | 30 | PPV>13 | ⑤ | |
| Mishra 2022[ | 44±12.6 | 39±11 | 20 | 20 | SVV>12 | ①②⑤ | |
| 伍淑韫 2020[ | 18~65 | 30 | 30 | PPV>13 | ②⑤ | ||
| 吴洁 2017[ | 50±9 | 50±9 | 33 | 30 | SVV>12 | ⑤ | |
| 张杰 2012[ | 42±12 | 42±10 | 20 | 20 | SVV>13 | ①②⑤ | |
| 易勇 2016[ | 53±4.8 | 52.5±4.9 | 53 | 53 | SVV>13 | ②④⑤⑥ | |
| 潘晓燕 2017[ | 58 | 57 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ③④⑦⑧ | |||
| 王学飞 2016[ | 39.6±3.6 | 40.1±4.2 | 27 | 25 | SVV>12 | ①②③④ | |
| 王德勇 2019[ | 60.13±12.31 | 60.21±12.24 | 25 | 25 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ⑤⑥ | |
| 王慧霞 2021[ | 40.96±2.29 | 41.87±2.42 | 48 | 47 | SVV>13 | ②⑧ | |
| 田胜兰 2015[ | 54.7±4.2 | 52.5±6.3 | 12 | 12 | SVV>12 | ①②③④ | |
| 莫朴 2015[ | 43.2±9.7 | 40 | 40 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ②⑥ | ||
| 袁柳青 2013(心指数)[ | 18~60 | 14 | 12 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ①⑥ | ||
| 袁柳青 2013(脑氧代谢)[ | 47.3±11.1 | 49.8±10.3 | 14 | 12 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ③④⑤ | |
| 袁柳青 2020(vigileo 监测)[ | 47.1±11.2 | 45.3±12.4 | 20 | 20 | SVV>13 | ⑦⑧ | |
| 袁柳青 2020(基于每博变异)[ | 46.4±8.2 | 45.7±8.1 | 23 | 23 | SVV>13 | ①②⑦⑧ | |
| 赵晓生 2019[ | 19 | 19 | SVV>13 | ⑦⑧ | |||
表1 纳入研究基本特征
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of the eligible studies
| 纳入研究 | 年龄(岁) | 样本量(例) | 监测指标 | 结局指标 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 目标导向液体组 | 常规液体组 | 目标导向液体组 | 常规液体组 | ||||
| Hasanin 2019[ | 41±12 | 39±13 | 31 | 30 | PPV>13 | ⑤ | |
| Mishra 2022[ | 44±12.6 | 39±11 | 20 | 20 | SVV>12 | ①②⑤ | |
| 伍淑韫 2020[ | 18~65 | 30 | 30 | PPV>13 | ②⑤ | ||
| 吴洁 2017[ | 50±9 | 50±9 | 33 | 30 | SVV>12 | ⑤ | |
| 张杰 2012[ | 42±12 | 42±10 | 20 | 20 | SVV>13 | ①②⑤ | |
| 易勇 2016[ | 53±4.8 | 52.5±4.9 | 53 | 53 | SVV>13 | ②④⑤⑥ | |
| 潘晓燕 2017[ | 58 | 57 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ③④⑦⑧ | |||
| 王学飞 2016[ | 39.6±3.6 | 40.1±4.2 | 27 | 25 | SVV>12 | ①②③④ | |
| 王德勇 2019[ | 60.13±12.31 | 60.21±12.24 | 25 | 25 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ⑤⑥ | |
| 王慧霞 2021[ | 40.96±2.29 | 41.87±2.42 | 48 | 47 | SVV>13 | ②⑧ | |
| 田胜兰 2015[ | 54.7±4.2 | 52.5±6.3 | 12 | 12 | SVV>12 | ①②③④ | |
| 莫朴 2015[ | 43.2±9.7 | 40 | 40 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ②⑥ | ||
| 袁柳青 2013(心指数)[ | 18~60 | 14 | 12 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ①⑥ | ||
| 袁柳青 2013(脑氧代谢)[ | 47.3±11.1 | 49.8±10.3 | 14 | 12 | ITBVI:800~1000 ml/m2 | ③④⑤ | |
| 袁柳青 2020(vigileo 监测)[ | 47.1±11.2 | 45.3±12.4 | 20 | 20 | SVV>13 | ⑦⑧ | |
| 袁柳青 2020(基于每博变异)[ | 46.4±8.2 | 45.7±8.1 | 23 | 23 | SVV>13 | ①②⑦⑧ | |
| 赵晓生 2019[ | 19 | 19 | SVV>13 | ⑦⑧ | |||
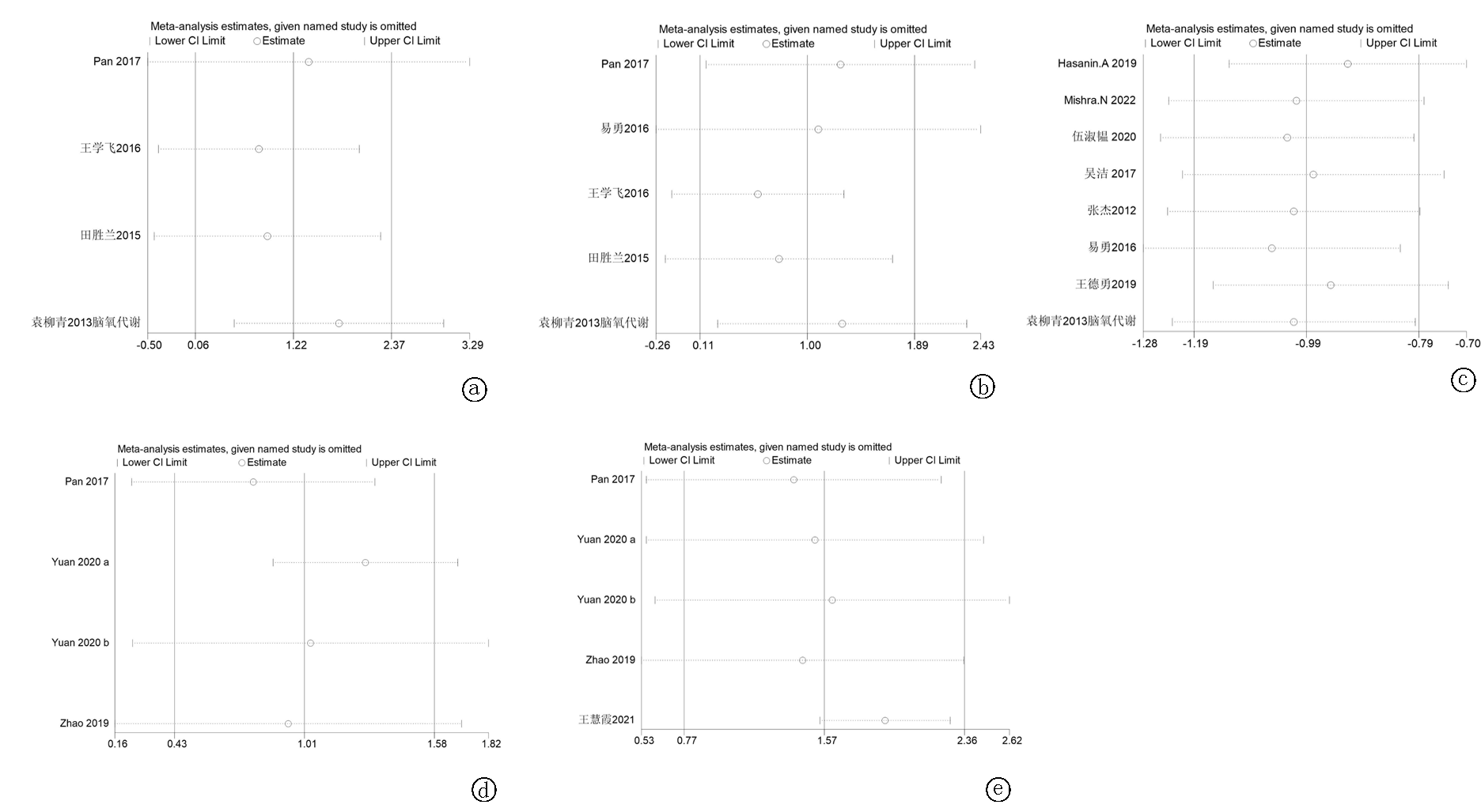
图12 敏感性分析 a.切开1 h SjvO2;b.术毕SjvO2; c.术毕Lac;d.术后1 d MMES评分;e.术后3 d MMES评分
Fig. 12 Sensitivity analysis a.SjvO2 1 hour after incision of the dura;b. SjvO2 at the end of operation; c.Lac at the end of operation; d.MMES score at 1 day postoperatively;e. MMES score at 3 days postoperatively
| [1] | 韩仁强, 周金意, 张思维, 等. 2015年中国脑瘤发病与死亡分析[J]. 中国肿瘤, 2021, 30(1):29-34. |
| [2] |
Gruenbaum SE, Meng L, Bilotta F. Recent trends in the anesthetic management of craniotomy for supratentorial tumor resection[J]. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol, 2016, 29(5): 552-557.
doi: 10.1097/ACO.0000000000000365 pmid: 27285727 |
| [3] |
Brandstrup B, Tønnesen H, Beier-Holgersen R, et al. Effects of intravenous fluid restriction on postoperative complications: Comparison of two perioperative fluid regimens: A randomized assessor-blinded multicenter trial[J]. Ann Surg, 2003, 238(5): 641-648.
doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000094387.50865.23 pmid: 14578723 |
| [4] | Wrzosek A, Jakowicka-Wordliczek J, Zajaczkowska R, et al. Perioperative restrictive versus goal‐directed fluid therapy for adults undergoing major non‐cardiac surgery[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2019, 12(12):CD012767. |
| [5] | Ryu T. Fluid management in patients undergoing neurosurgery[J]. Anesth Pain Med (Seoul), 2021, 16(3): 215-224. |
| [6] | 何小义, 邹学军, 刑浩然. 目标导向液体治疗用于加速康复外科的新进展[J]. 基础医学与临床, 2020, 40(7):995-998. |
| [7] | 王骜, 章放香, 彭晶, 等. 围手术期目标导向液体治疗的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2021, 27(20):4058-4062. |
| [8] | Mayer J, Boldt J, Mengistu A M, et al. Goal-directed intraoperative therapy based on autocalibrated arterial pressure waveform analysis reduces hospital stay in high-risk surgical patients: A randomized, controlled trial[J]. Critical Care, 2010, 14(1): 1-9. |
| [9] | Benes J, Chytra I, Altmann P, et al. Intraoperative fluid optimization using stroke volume variation in high risk surgical patients: Results of prospective randomized study[J]. Critical Care, 2010, 14(3): 1-15. |
| [10] |
Rhodes A, Cecconi M, Hamilton M, et al. Goal-directed therapy in high-risk surgical patients: A 15-year follow-up study[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2010, 36(8): 1327-1332.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-010-1869-6 pmid: 20376431 |
| [11] | Dalfino L, Giglio MT, Puntillo F, et al. Haemodynamic goal-directed therapy and postoperative infections: Earlier is better. A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Critical Care, 2011, 15(3): 1-14. |
| [12] |
Hasanin A, Zanata T, Osman S, et al. Pulse pressure variation-guided fluid therapy during supratentorial brain tumour excision: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Open Access Maced J Med Sci, 2019, 7(15): 2474-2479.
doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2019.682 pmid: 31666850 |
| [13] |
Mishra N, Rath G P, Bithal P K, et al. Effect of goal-directed intraoperative fluid therapy on duration of hospital stay and postoperative complications in patients undergoing excision of large supratentorial tumors[J]. Neurol India, 2022, 70(1): 108-114.
doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.336329 pmid: 35263862 |
| [14] | 伍淑韫, 刘湘杰, 王涛. 脉压变异度指导的目标导向液体治疗在幕上肿瘤切除术中的应用[J]. 云南医药, 2020, 41(2):162-164. |
| [15] | 吴洁, 马艳辉, 张瑛, 等. 每搏变异度指导目标导向液体管理在幕上肿瘤切除术中的应用[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2017, 33(5):425-429. |
| [16] | 张杰, 施庆余, 罗爱林. 麻醉期间目标导向液体治疗对胶质瘤开颅切除术患者预后的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2012, 41(1):99-102. |
| [17] | 易勇, 周章明, 梁张. 目标导向液体治疗对脑膜瘤切除术患者脑代谢和手术后康复的影响[J]. 中国肿瘤临床与康复, 2016, 23(8):925-928. |
| [18] | 潘晓燕. 胸腔内血容量指数指导的GDFT对脑肿瘤切除术患者术后认知影响[J]. 现代仪器与医疗, 2017, 23(5):123-124. |
| [19] | 王学飞. 目标导向液体对择期神经外科手术患者术中颅内压及脑氧供需平衡的影响[J]. 河南医学研究, 2016, 25(11):1988-1989. |
| [20] | 王德勇, 石祥飞. 目标导向液体治疗对脑肿瘤切除术后氧代谢的影响[J]. 中国继续医学教育, 2019, 11(28):112-114. |
| [21] |
王慧霞, 廉欢. 术中目标导向液体对脑肿瘤切除术后患者血液动力学指标及血清中S-100β浓度的影响[J]. 中国疗养医学, 2021, 30(4):406-408.
doi: 10.13517/j.cnki.ccm.2021.04.026 |
| [22] | 田胜兰, 周游, 冯丹. 目标导向液体治疗在择期神经外科手术中对颅内压和脑氧供需平衡的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(医学版), 2015, 44(1):106-109. |
| [23] | 莫朴, 陈海林, 利鸿胜. 麻醉期间目标导向液体治疗对胶质瘤开颅切除术患者预后的影响[J]. 中国当代医药, 2015, 22(35):112-114+117. |
| [24] | 袁柳青, 李凤仙, 徐世元, 等. 目标导向液体治疗对脑膜瘤切除术患者心指数及术后康复的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2013, 29(9):1458-1460. |
| [25] | 袁柳青, 李凤仙, 刘世乐, 等. 目标导向液体治疗对脑膜瘤切除术患者脑氧代谢的影响[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2013, 29(4):317-321. |
| [26] | 袁柳青, 梁伟东, 李晓玲, 等. Vigileo监测SVV指导目标导向液体治疗在脑膜瘤切除术中的应用[J]. 赣南医学院学报, 2020, 40(4):392-395. |
| [27] | 袁柳青, 梁伟东, 李晓玲, 等. 基于每博量变异的目标导向液体治疗对脑膜瘤切除术血流动力学和S100β蛋白的影响[J]. 实用医学杂志, 2020, 36(22):3126-3129. |
| [28] | 赵晓生, 王群涛, 赵芳芳, 等. 目标导向液体治疗脑肿瘤及对患者围术期认知功能的影响研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2019, 22(S1):48-50. |
| [29] | 伊敏敏, 郭永清. 神经外科颅脑肿瘤手术围手术期脑保护的研究进展[J]. 医学综述, 2020, 26(17):3491-3495. |
| [30] | 梁禹. 神经外科麻醉进展[J]. 医学综述, 2008, 14(24):3805-3808. |
| [31] |
Berger K, Francony G, Bouzat P, et al. Prone position affects stroke volume variation performance in predicting fluid responsiveness in neurosurgical patients[J]. Minerva Anestesiol, 2015, 81(6): 628-635.
pmid: 25263024 |
| [32] |
van der Jagt M. Fluid management of the neurological patient: A concise review[J]. Critical Care, 2016, 20(1): 1-11.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-1178-0 URL |
| [33] |
Orfanakis A, Brambrink AM. Long-term outcome call into question the benefit of positive fluid balance and colloid treatment after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage[J]. Neurocrit Care, 2013, 19(2):137-139.
pmid: 24022830 |
| [34] |
Acheampong A, Vincent JL. A positive fluid balance is an independent prognostic factor in patients with sepsis[J]. Crit Care, 2015, 19(1):251.
doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0970-1 URL |
| [35] |
Mascia L, Sakr Y, Pasero D, et al. Extracranial complications in patients with acute brain injury: A post-hoc analysis of the SOAP study[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2008, 34(4):720-727.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-007-0974-7 URL |
| [36] |
Kirov MY, Kuzkov VV, Molnar Z. Perioperative haemodynamic therapy[J]. Curr Opin Crit Care, 2010, 16(4): 384-392.
doi: 10.1097/MCC.0b013e32833ab81e pmid: 20508520 |
| [37] |
Luo J, Xue J, Liu J, et al. Goal-directed fluid restriction during brain surgery: A prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2017, 7(1): 16.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-017-0239-8 pmid: 28211020 |
| [38] |
Zhang N, Liang M, Zhang DD, et al. Effect of goal-directed fluid therapy on early cognitive function in elderly patients with spinal stenosis: A Case-Control Study[J]. Int J Surg, 2018, 54(Pt A): 201-205.
doi: S1743-9191(18)30687-3 pmid: 29678619 |
| [39] |
Tang A, Zhou S. Analysis on the application value of goal-directed fluid therapy in patients undergoing laparoscopy-assisted radical gastrectomy with fast-track anesthesia[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2021, 13(5):5174-5182.
pmid: 34150106 |
| [40] |
Crum RM, Anthony JC, Bassett SS, et al. Population-based norms for the Mini-Mental State Examination by age and educational level[J]. JAMA, 1993, 269(18): 2386-2391.
doi: 10.1001/jama.1993.03500180078038 URL |
| [1] | 龚财芳, 赵俊宇, 游川. 接纳与承诺疗法对癌症患者心理健康和生活质量影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 101-107. |
| [2] | 肖煌怡, 袁建坤, 严梓予, 曾雯姝, 鲁兰莫, 王峻. 认知干预对遗忘型轻度认知障碍老年患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 12-19. |
| [3] | 李海, 刘文虎, 彭绍鹏, 王飞. 控制性阶梯式减压术对比快速标准大骨瓣减压术治疗重度颅脑损伤疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 788-795. |
| [4] | 吕畅, 周利明. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌易感相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 779-787. |
| [5] | 金家辉, 杨阳, 秦铜, 何雨欣, 苏美华. 补充益生菌对2型糖尿病患者糖代谢改善的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 581-587. |
| [6] | 肖王静, 李欣梦, 卢松玲, 孙雪华. 重复经颅磁刺激治疗中枢神经源性吞咽障碍疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 588-599. |
| [7] | 尤奕, 高淑清, 徐浩. 肠内营养对食管癌患者术后临床结局影响的系统综述[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 485-492. |
| [8] | 倪艺芸, 刘彬, 梁琪, 李晓凤. 白细胞介素6和C反应蛋白预测新型冠状病毒肺炎严重程度的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 493-499. |
| [9] | 沃拉孜汗·玛德尼亚提, 迪力夏提·图尔迪麦麦提, 李梦晨, 拜合提尼沙·吐尔地. 宏基因组二代测序技术在肺结核诊断中应用价值的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 389-398. |
| [10] | 赵哲, 穆培娟, 张冬. 恩度联合顺铂胸腔灌注治疗肺癌合并恶性胸腔积液疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 399-404. |
| [11] | 马明福, 魏志国, 何铁英. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [12] | 曹宇萌, 张海燕, 刘立新. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的病理改变与血清铁蛋白和血清铁含量变化关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 197-207. |
| [13] | 马宏莉, 陆皓, 王丹, 焦海星, 李一珂, 李思雨, 吕静. 脑卒中患者残疾危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| [14] | 陶嘉楠, 李文茜, 马秀雯, 安琪, 王学红. HER-2在肝细胞癌中表达及临床意义的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1067-1072. |
| [15] | 柯孟婷, 陈慰. 瑞舒伐他汀降压作用的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(11): 965-971. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 35
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 176
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||