Clinical Focus ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 974-979.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.11.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meta-analysis of effects of curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Department of Endocrinology,Affiliated Hospital of Jilin Medical University,Jilin 132000,China
-
Received:2023-11-12Online:2024-11-20Published:2024-12-04 -
Contact:Liang Yi E-mail:liangyinfm@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liang Yi. Meta-analysis of effects of curcumin on inflammation and oxidative stress of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(11): 974-979.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.11.002
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 人数 (干预/对照) | 性别 (女/男) | 年龄 (干预/对照) | 干预措施 | 伴随疾病 | 干预 时间 | 涉及的 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 8周 | TAC,MDA |
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 12周 | CRP |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 25/24 | - | 64.9±7.8/66.5±7.7 | 姜黄素提取物1 000 mg/d | 冠心病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 26/27 | 21/32 | 58.3±9.4/56.2±9.8 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 行血液透析的肾脏病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Adibian [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | 22/22 | 58/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | CRP |
| Hodaei [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | - | 58±8/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | TAC, MDA |
| Adab [ | 伊朗 | 39/26 | 39/36 | 54.76±6/55.66±8.64 | 姜黄粉2 100 mg/d | 高脂血症 | 8周 | TAC, CRP |
| Mokhtari [ | 伊朗 | 25/25 | 11/39 | 57.4±11.7/55.8±9.4 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 糖尿病足溃疡3期 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Dastani [ | 伊朗 | 32/32 | 39/25 | 60.00±7.22/60.53±10.55 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 冠脉疾病 | 12周 | CRP |
| Funamoto [ | 日本 | 15/17 | 10/22 | 70±6/69±7 | 姜黄素180 mg/d | 包括部分糖耐量异常者 | 24周 | CRP |
| Usharani [ | 印度 | 23/21 | 21/23 | 55.52±10.76/49.75±8.18 | NCB-02 (姜黄素提取物300 mg bid) | - | 8周 | MDA |
Tab. 1 Characteristics of included studies in the meta-analysis
| 纳入研究 | 国家 | 人数 (干预/对照) | 性别 (女/男) | 年龄 (干预/对照) | 干预措施 | 伴随疾病 | 干预 时间 | 涉及的 结局指标 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 8周 | TAC,MDA |
| Panahi [ | 伊朗 | 50/50 | 49/51 | 43±8/41±7 | 姜黄素C3复合物1 000 mg/d+胡椒碱10 mg/d | - | 12周 | CRP |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 25/24 | - | 64.9±7.8/66.5±7.7 | 姜黄素提取物1 000 mg/d | 冠心病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 伊朗 | 26/27 | 21/32 | 58.3±9.4/56.2±9.8 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 行血液透析的肾脏病 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Adibian [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | 22/22 | 58/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | CRP |
| Hodaei [ | 伊朗 | 21/23 | - | 58±8/60±7 | 姜黄素提取物1 500 mg/d | - | 10周 | TAC, MDA |
| Adab [ | 伊朗 | 39/26 | 39/36 | 54.76±6/55.66±8.64 | 姜黄粉2 100 mg/d | 高脂血症 | 8周 | TAC, CRP |
| Mokhtari [ | 伊朗 | 25/25 | 11/39 | 57.4±11.7/55.8±9.4 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 糖尿病足溃疡3期 | 12周 | TAC, MDA, CRP |
| Dastani [ | 伊朗 | 32/32 | 39/25 | 60.00±7.22/60.53±10.55 | 纳米姜黄素80 mg/d | 冠脉疾病 | 12周 | CRP |
| Funamoto [ | 日本 | 15/17 | 10/22 | 70±6/69±7 | 姜黄素180 mg/d | 包括部分糖耐量异常者 | 24周 | CRP |
| Usharani [ | 印度 | 23/21 | 21/23 | 55.52±10.76/49.75±8.18 | NCB-02 (姜黄素提取物300 mg bid) | - | 8周 | MDA |
| 纳入研究 | 选择偏倚 | 实施偏倚 | 随访偏倚 | 测量偏倚 | 报告偏倚 | 总体偏倚风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 不明确 | 高风险 |
| Panahi [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 高风险 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adibian [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Hodaei [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adab [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Mokhtari [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Dastani [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Funamoto [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Usharani [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
Tab. 2 Risk of bias of eligible studies in the meta-analysis
| 纳入研究 | 选择偏倚 | 实施偏倚 | 随访偏倚 | 测量偏倚 | 报告偏倚 | 总体偏倚风险 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Panahi [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 不明确 | 高风险 |
| Panahi [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 高风险 | 高风险 |
| Shafabakhsh [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adibian [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Hodaei [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Adab [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Mokhtari [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Dastani [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Funamoto [ | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 |
| Usharani [ | 不明确 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 低风险 | 不明确 |
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >60 | 3 | 68 | 73 | 0.09 | -0.70(-1.52, 0.12) | 81% |
| <60 | 4 | 140 | 138 | 0.49 | -0.13(-0.49, 0.23) | 56% |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 5 | 148 | 152 | 0.07 | -0.50(-1.04, 0.04) | 80% |
| <12 | 2 | 60 | 59 | 0.86 | -0.03(-0.39, 0.33) | 0% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 110 | 109 | 0.50 | 0.09(-0.17, 0.36) | 0% |
| <500 | 4 | 98 | 102 | 0.007 | -0.69(-1.20, -0.19) | 66% |
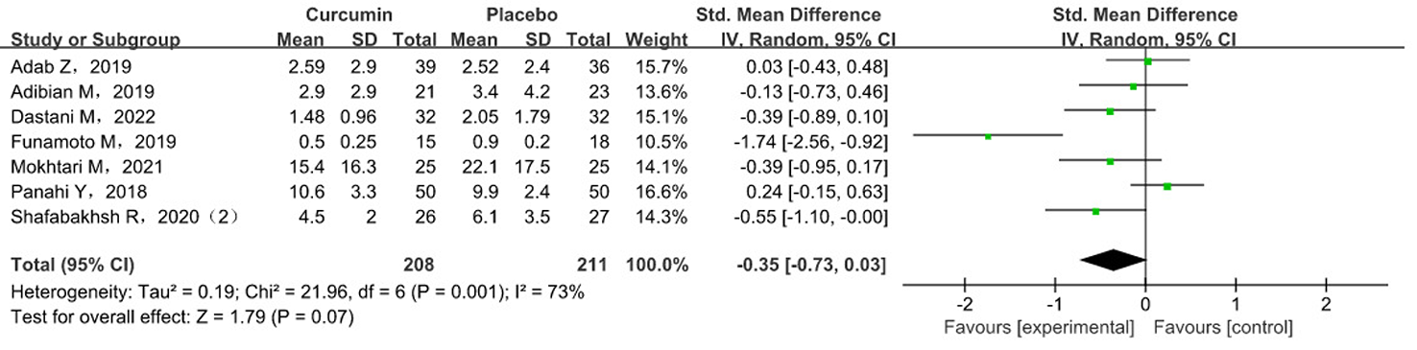
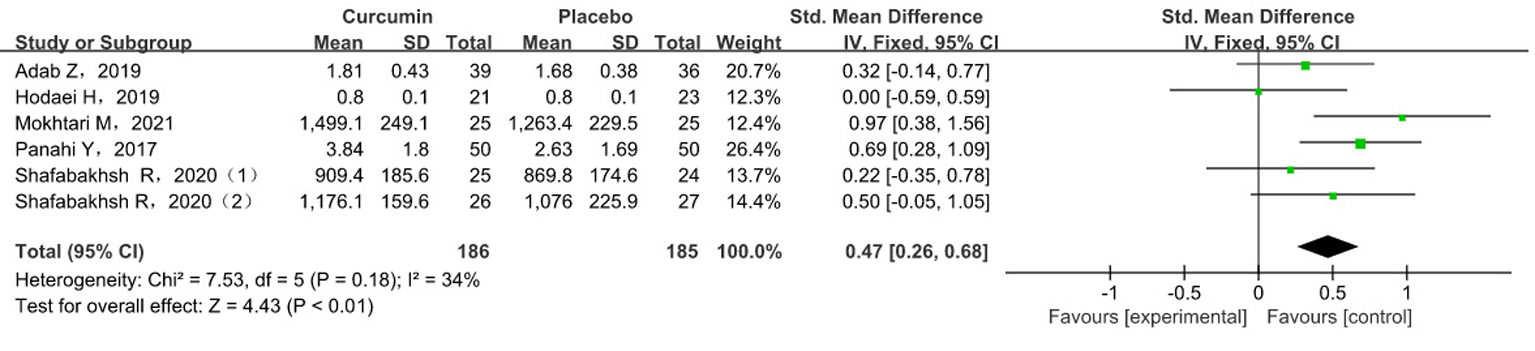
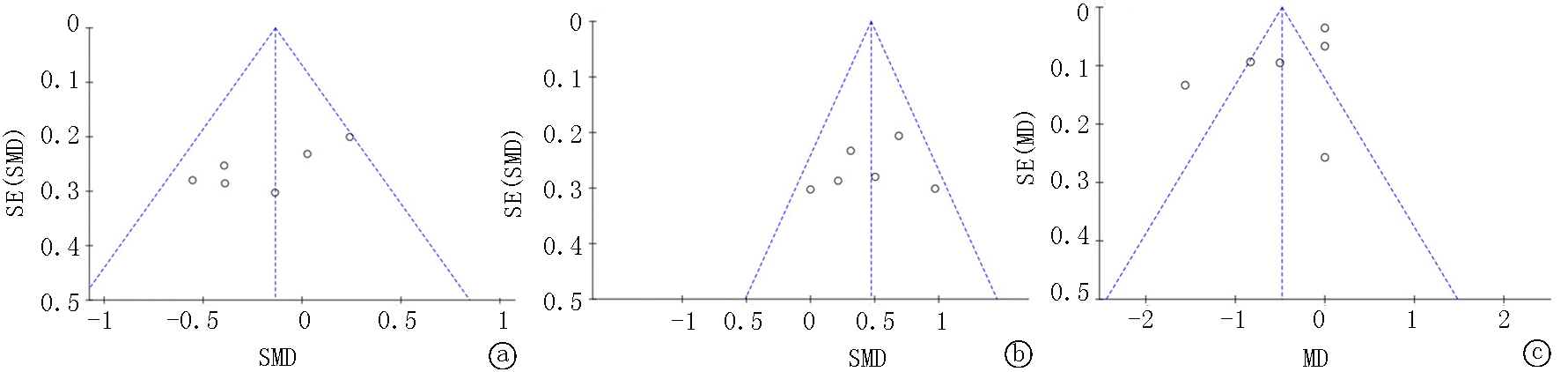
Tab. 3 Meta-analysis results of hs-CRP levels in subgroup analysis
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >60 | 3 | 68 | 73 | 0.09 | -0.70(-1.52, 0.12) | 81% |
| <60 | 4 | 140 | 138 | 0.49 | -0.13(-0.49, 0.23) | 56% |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 5 | 148 | 152 | 0.07 | -0.50(-1.04, 0.04) | 80% |
| <12 | 2 | 60 | 59 | 0.86 | -0.03(-0.39, 0.33) | 0% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 110 | 109 | 0.50 | 0.09(-0.17, 0.36) | 0% |
| <500 | 4 | 98 | 102 | 0.007 | -0.69(-1.20, -0.19) | 66% |
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >50 | 5 | 120 | 120 | 0.08 | -0.40(-0.86, 0.05) | 89% |
| <50 | 1 | 50 | 50 | <0.001 | -0.83(-1.20, 0.46) | - |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 3 | 76 | 76 | 0.35 | -0.12(-0.37, 0.13) | 68% |
| <12 | 3 | 94 | 94 | 0.01 | -0.90(-1.61, -0.19) | 78% |
| ≥10 | 4 | 97 | 99 | 0.35 | -0.11(-0.33, 0.12) | 52% |
| <10 | 2 | 73 | 71 | 0.001 | -1.17(-1.88, -0.46) | 80% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 96 | 97 | 0.35 | -0.32(-0.97, 0.34) | 85% |
| <500 | 3 | 74 | 73 | 0.11 | -0.65(-1.46, 0.15) | 94% |
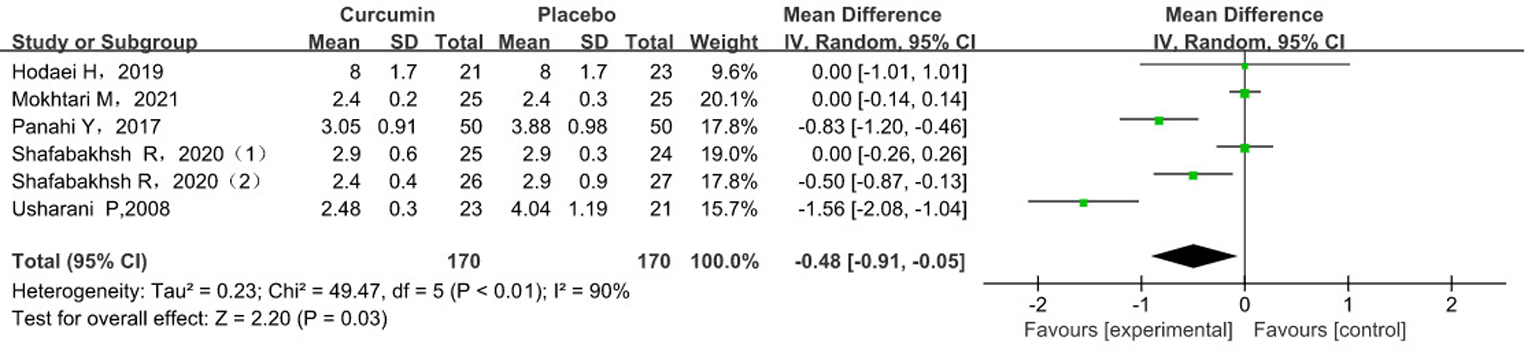
Tab. 4 Meta-analysis results of MDA levels in subgroup analysis
| 亚组 | 研究数 | 干预组数量 | 对照组数量 | P | 效应量(95%CI) | I2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | ||||||
| >50 | 5 | 120 | 120 | 0.08 | -0.40(-0.86, 0.05) | 89% |
| <50 | 1 | 50 | 50 | <0.001 | -0.83(-1.20, 0.46) | - |
| 干预时间(w) | ||||||
| ≥12 | 3 | 76 | 76 | 0.35 | -0.12(-0.37, 0.13) | 68% |
| <12 | 3 | 94 | 94 | 0.01 | -0.90(-1.61, -0.19) | 78% |
| ≥10 | 4 | 97 | 99 | 0.35 | -0.11(-0.33, 0.12) | 52% |
| <10 | 2 | 73 | 71 | 0.001 | -1.17(-1.88, -0.46) | 80% |
| 干预剂量(mg/d) | ||||||
| ≥500 | 3 | 96 | 97 | 0.35 | -0.32(-0.97, 0.34) | 85% |
| <500 | 3 | 74 | 73 | 0.11 | -0.65(-1.46, 0.15) | 94% |
| [1] | Li Y, Teng D, Shi X, et al. Prevalence of diabetes recorded in mainland China using 2018 diagnostic criteria from the American Diabetes Association: National cross sectional study[J]. BMJ, 2020, 369: m997. |
| [2] |
Derosa G, Maffioli P, Simental-Mendia LE, et al. Effect of curcumin on circulating interleukin-6 concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Pharmacol Res, 2016, 111:394-404.
doi: S1043-6618(16)30392-9 pmid: 27392742 |
| [3] |
Mirzaei H, Shakeri A, Rashidi B, et al. Phytosomal curcumin: A review of pharmacokinetic, experimental and clinical studies[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2017, 85: 102-112.
doi: S0753-3322(16)32074-1 pmid: 27930973 |
| [4] | Pivari F, Mingione A, Brasacchio C, et al. Curcumin and type 2 diabetes mellitus: Prevention and treatment[J]. Nutrients, 2019, 11(8):1837. |
| [5] | Poolsup N, Suksomboon N, Kurnianta PDM, et al. Effects of curcumin on glycemic control and lipid profile in prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(4):e0215840. |
| [6] |
Panahi Y, Khalili N, Sahebi E, et al. Antioxidant effects of curcuminoids in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Inflammopharmacology, 2017, 25(1): 25-31.
doi: 10.1007/s10787-016-0301-4 pmid: 27928704 |
| [7] |
Panahi Y, Khalili N, Sahebi E, et al. Effects of curcuminoids plus piperine on glycemic, hepatic and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial[J]. Drug Research, 2018, 68(7): 403-409.
doi: 10.1055/s-0044-101752 pmid: 29458218 |
| [8] |
Shafabakhsh R, Asemi Z, Reiner Z, et al. The effects of nano-curcumin on metabolic status in patients with diabetes on hemodialysis, a randomized, double blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Iran J Kidney Dis, 2020, 14(4): 290-299.
pmid: 32655024 |
| [9] |
Shafabakhsh R, Mobini M, Raygan F, et al. Curcumin administration and the effects on psychological status and markers of inflammation and oxidative damage in patients with type 2 diabetes and coronary heart disease[J]. Clin Nutr ESPEN, 2020, 40: 77-82.
doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2020.09.029 pmid: 33183576 |
| [10] |
Adibian M, Hodaei H, Nikpayam O, et al. The effects of curcumin supplementation on high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, serum adiponectin, and lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(5): 1374-1383.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6328 pmid: 30864188 |
| [11] | Hodaei H, Adibian M, Nikpayam O, et al. The effect of curcumin supplementation on anthropometric indices, insulin resistance and oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind clinical trial[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2019, 11(1):41. |
| [12] |
Adab Z, Eghtesadi S, Vafa MR, et al. Effect of turmeric on glycemic status, lipid profile, hs-CRP, and total antioxidant capacity in hyperlipidemic type 2 diabetes mellitus patients[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(4): 1173-1181.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6312 pmid: 30859660 |
| [13] |
Mokhtari M, Razzaghi R, Momen-Heravi M. The effects of curcumin intake on wound healing and metabolic status in patients with diabetic foot ulcer: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Phytother Res, 2021, 35(4): 2099-2107.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6957 pmid: 33200488 |
| [14] |
Dastani M, Rahimi HR, Askari VR, et al. Three months of combination therapy with nano-curcumin reduces the inflammation and lipoprotein (a) in type 2 diabetic patients with mild to moderate coronary artery disease: Evidence of a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial[J]. Biofactors, 2022, 49(1):108-118.
doi: 10.1002/biof.1874 pmid: 35674733 |
| [15] | Funamoto M, Shimizu K, Sunagawa Y, et al. Effects of highly absorbable curcumin in patients with impaired glucose tolerance and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus[J]. J Diabetes Res, 2019:8208237. |
| [16] |
Usharani P, Mateen AA, Naidu MU, et al. Effect of NCB-02, atorvastatin and placebo on endothelial function, oxidative stress and inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, 8-week study[J]. Drugs R D, 2008, 9(4): 243-250.
doi: 10.2165/00126839-200809040-00004 pmid: 18588355 |
| [17] |
Huang J, Qin S, Huang L, et al. Efficacy and safety of Rhizoma curcumea longae with respect to improving the glucose metabolism of patients at risk for cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials[J]. J Hum Nutr Diet, 2019, 32(5): 591-606.
doi: 10.1111/jhn.12648 pmid: 30983042 |
| [18] |
Azhdari M, Karandish M, Mansoori A. Metabolic benefits of curcumin supplementation in patients with metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(5): 1289-1301.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6323 pmid: 30941814 |
| [19] |
Mohammadi S, Kayedpoor P, Karimzadeh-Bardei L, et al. The effect of curcumin on TNF-α, IL-6 and CRP expression in a model of polycystic ovary syndrome as an inflammation state[J]. J Reprod Infertil, 2017, 18(4): 352-360.
pmid: 29201665 |
| [20] | Costantino M, Corno C, Colombo D, et al. Curcumin and related compounds in cancer cells: New avenues for old molecules[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 889816. |
| [21] | Gorabi AM, Abbasifard M, Imani D, et al. Effect of curcumin on C-reactive protein as a biomarker of systemic inflammation: An updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Phytotherapy research, 2022, 36(1): 85-97. |
| [22] |
Tabrizi R, Vakili S, Akbari M, et al. The effects of curcumin-containing supplements on biomarkers of inflammation and oxidative stress: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Phytother Res, 2019, 33(2): 253-262.
doi: 10.1002/ptr.6226 pmid: 30402990 |
| [23] | Jiménez-Osorio AS, García-Niño WR, González-Reyes S, et al. The effect of dietary supplementation with curcumin on redox status and Nrf2 activation in patients with nondiabetic or diabetic proteinuric chronic kidney disease: A pilot study[J]. J Ren Nutr, 2016, 26(4): 237-244. |
| [24] |
Na LX, Zhang YL, Li Y, et al. Curcumin improves insulin resistance in skeletal muscle of rats[J]. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, 2011, 21(7): 526-533.
doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.11.009 pmid: 20227862 |
| [25] | Nie T, Cooper GJS. Mechanisms underlying the antidiabetic activities of polyphenolic compounds: A review[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2021, 12: 798329. |
| [26] | Den Hartogh DJ, Gabriel A, Tsiani E. Antidiabetic properties of curcumin I: Evidence from In Vitro Studies[J]. Nutrients, 2020, 12(1):118. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||