Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 811-819.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.09.010
Previous Articles Next Articles
Analysis of bioinformatics in pediatric influenza based on chip with high-throughput
- Department of Pediatrics, Taikang Tongji (Wuhan) Hospital, Wuhan 430050, China
-
Received:2021-05-21Online:2021-09-20Published:2021-10-05 -
Contact:Li Xiaolan E-mail:1138914165@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Jin Hong, Li Xiaolan. Analysis of bioinformatics in pediatric influenza based on chip with high-throughput[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(9): 811-819.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.09.010
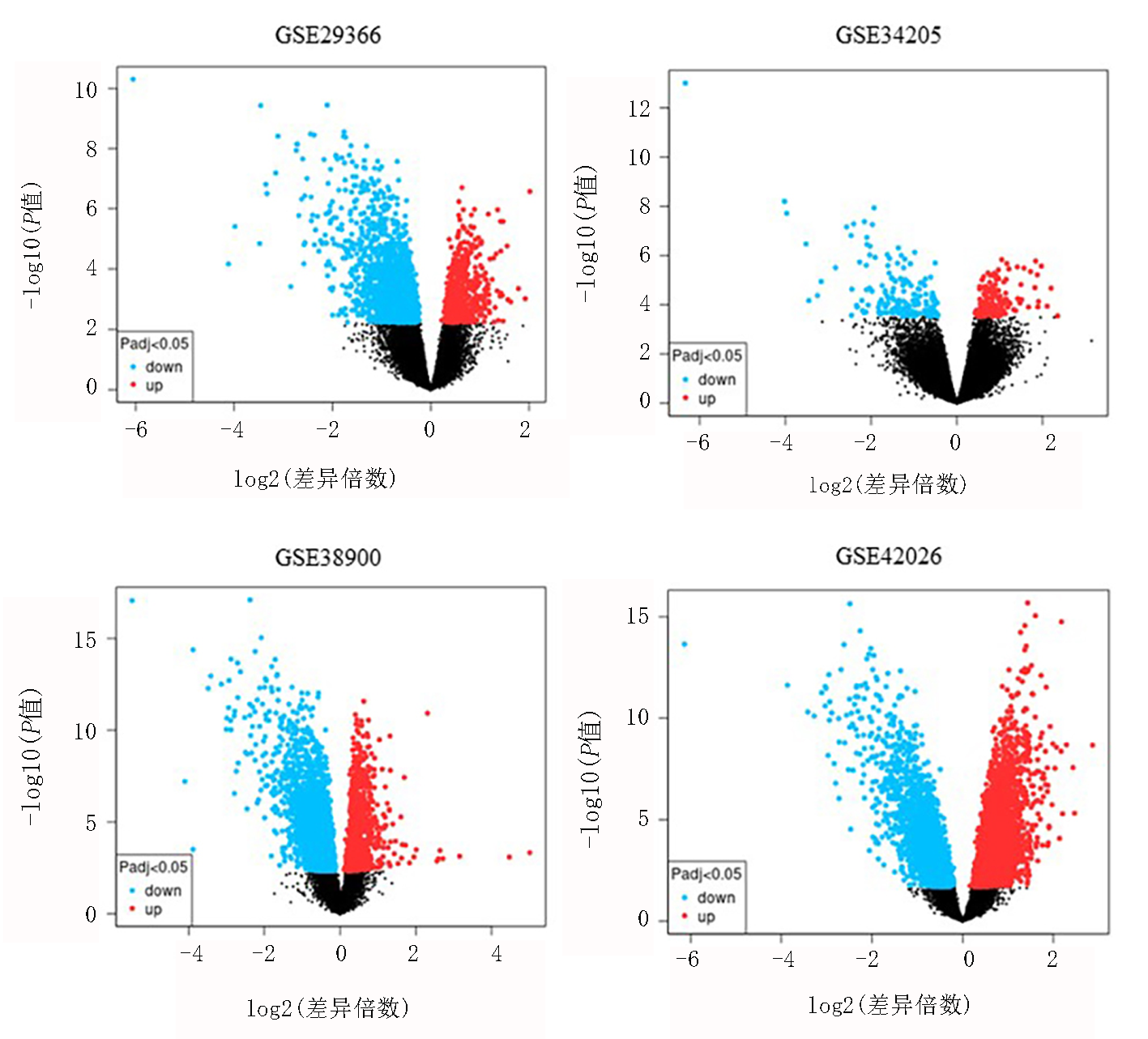
| GEO | 年份 | 流感患者 (例) | 对照组 (例) | 上调基因 (个) | 下调基因 (个) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE42026 | 2013 | 19 | 33 | 344 | 418 |
| GSE29366 | 2015 | 19 | 12 | 59 | 312 |
| GSE34205 | 2012 | 28 | 12 | 37 | 93 |
| GSE38900 | 2013 | 16 | 27 | 47 | 276 |
| GEO | 年份 | 流感患者 (例) | 对照组 (例) | 上调基因 (个) | 下调基因 (个) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE42026 | 2013 | 19 | 33 | 344 | 418 |
| GSE29366 | 2015 | 19 | 12 | 59 | 312 |
| GSE34205 | 2012 | 28 | 12 | 37 | 93 |
| GSE38900 | 2013 | 16 | 27 | 47 | 276 |
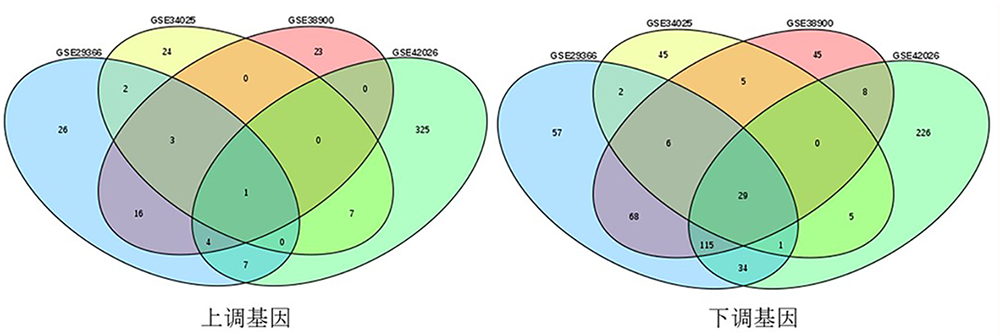
| 组别 | 基因 |
|---|---|
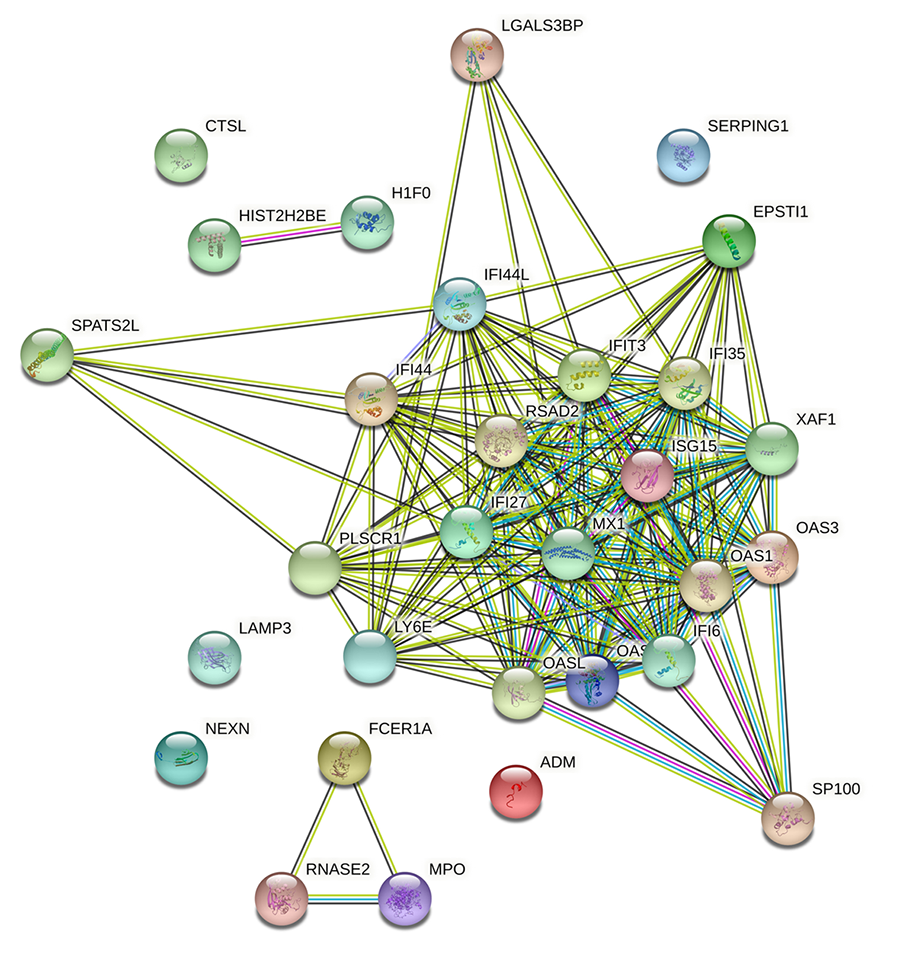
| 下调 | SP100 IFI6 IFI44L LAMP3 SERPING1 OAS2 PLSCR1 RNASE2 NEXN CTSL IFI27 IFI35 OAS3 RSAD2 OAS1 MX1 MPO LY6E LGALS3BP ADM XAF1 SPATS2L EPSTI1 OASL HIST2H2BE IFI44 H1F0 ISG15 IFIT3 |
| 上调 | FCER1A |
| 组别 | 基因 |
|---|---|
| 下调 | SP100 IFI6 IFI44L LAMP3 SERPING1 OAS2 PLSCR1 RNASE2 NEXN CTSL IFI27 IFI35 OAS3 RSAD2 OAS1 MX1 MPO LY6E LGALS3BP ADM XAF1 SPATS2L EPSTI1 OASL HIST2H2BE IFI44 H1F0 ISG15 IFIT3 |
| 上调 | FCER1A |
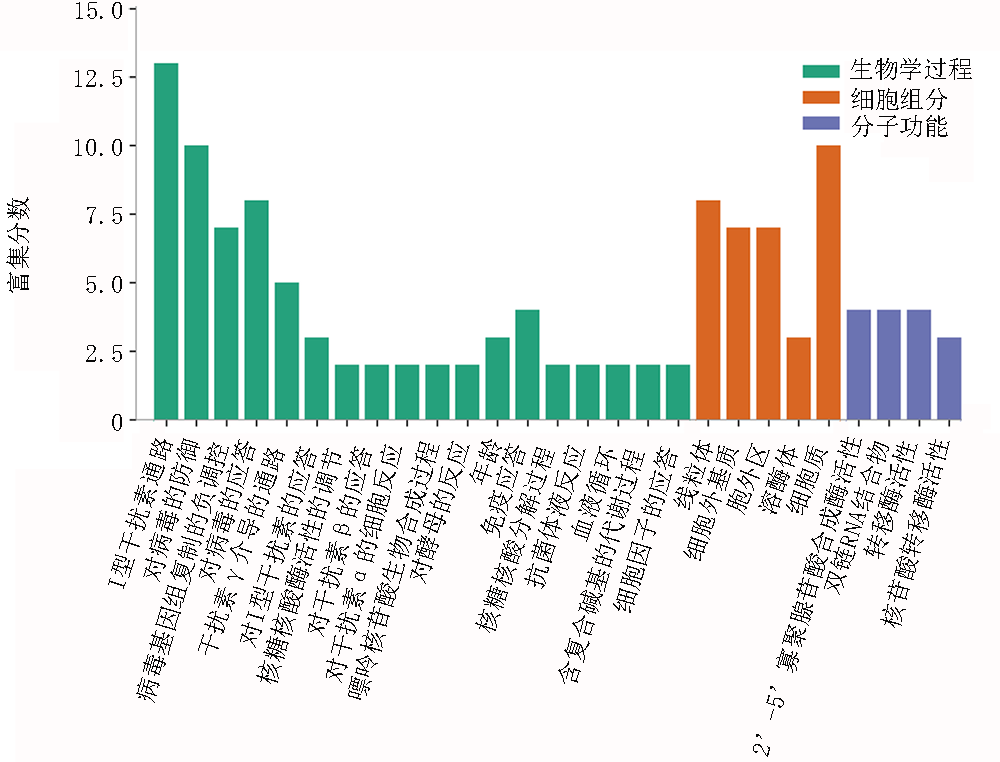
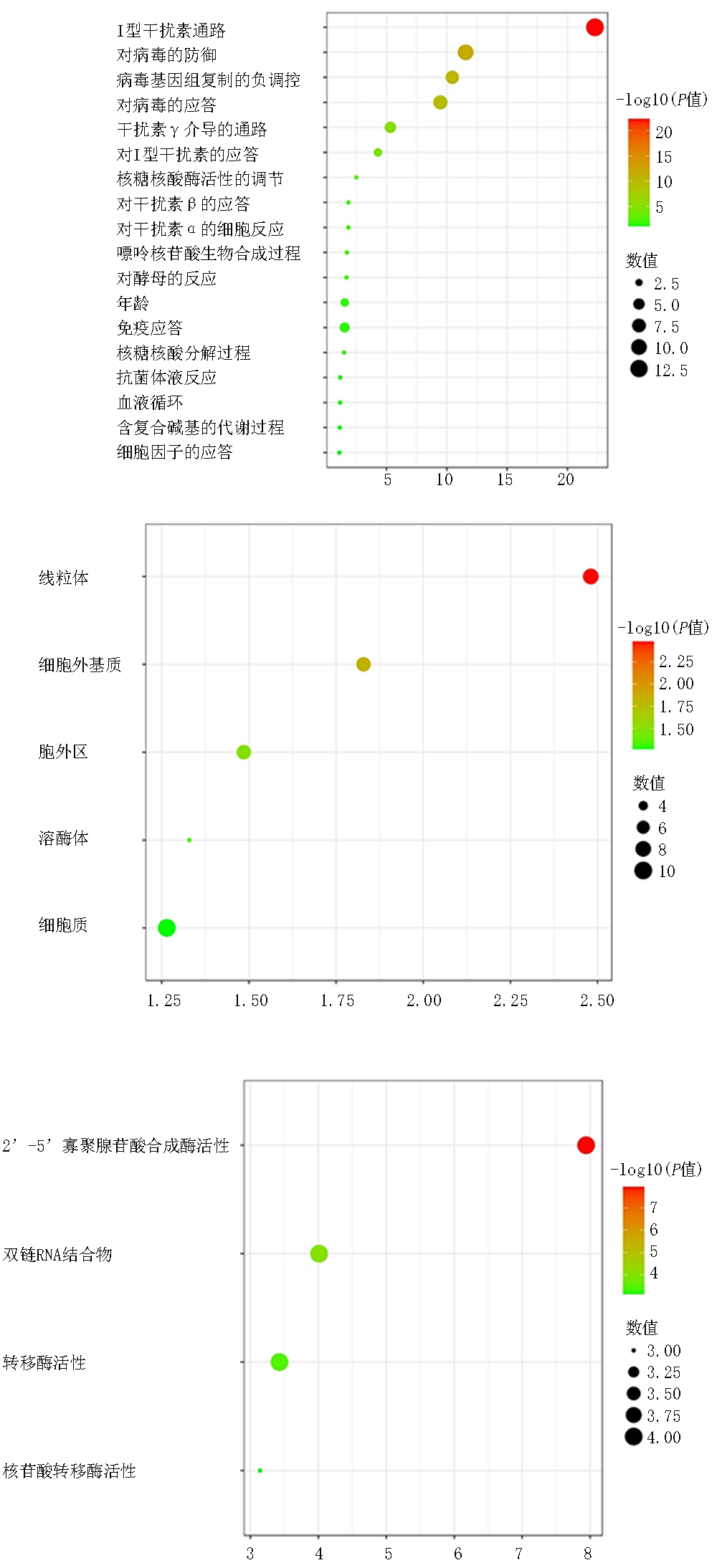
| 类别 | 项目 | GO名称 | 基因数量 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | GO:0060337 | Ⅰ型干扰素通路 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0071357 | Ⅰ型干扰素的细胞反应 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0034340 | Ⅰ型干扰素的应答 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0051607 | 对病毒的防御 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0009615 | 对病毒的应答 | 15 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0006952 | 防御反应 | 22 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0051707 | 对其他生物的反应 | 18 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0043207 | 对外界生物刺激的反应 | 18 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0009607 | 生物刺激反应 | 18 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0098542 | 对其他生物的防御反应 | 15 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0006955 | 免疫反应 | 23 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0045069 | 病毒基因组复制的调控 | 9 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:1903900 | 病毒生命周期的调控 | 10 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0043903 | 共生的调节,包括通过寄生的互惠共生 | 11 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0019079 | 病毒基因组复制 | 9 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0045087 | 先天性免疫应答 | 17 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0050792 | 病毒变化的过程调节 | 10 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005737 | 细胞质 | 26 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0034774 | 分泌颗粒内腔 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005739 | 线粒体 | 8 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0060205 | 胞质囊腔 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0031983 | 囊腔 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005741 | 线粒体外膜 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0062023 | 含胶原的细胞外基质 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005775 | 空泡内腔 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0097232 | 层状体膜 | 1 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0097233 | 肺泡板层体膜 | 1 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0031968 | 细胞器外膜 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0019867 | 外膜 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005637 | 核内膜 | 2 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0031966 | 线粒体膜 | 5 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0044444 | 胞质部分 | 22 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005740 | 线粒体被膜 | 5 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0097013 | 吞噬泡腔 | 1 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0001730 | 2'-5'-寡聚腺苷酸合成酶活性 | 3 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0003725 | 双链RNA结合物 | 4 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0070566 | 腺苷转移酶活性 | 3 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0030550 | 乙酰胆碱受体抑制剂活性 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0005521 | 核纤层蛋白结合 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0030548 | 乙酰胆碱受体调节活性 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0099602 | 神经递质受体调节活性 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0016779 | 核苷酸转移酶活性 | 3 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0031700 | 肾上腺髓质受体结合 | 1 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0097655 | 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族蛋白结合 | 1 | <0.01 |
| 类别 | 项目 | GO名称 | 基因数量 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | GO:0060337 | Ⅰ型干扰素通路 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0071357 | Ⅰ型干扰素的细胞反应 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0034340 | Ⅰ型干扰素的应答 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0051607 | 对病毒的防御 | 14 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0009615 | 对病毒的应答 | 15 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0006952 | 防御反应 | 22 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0051707 | 对其他生物的反应 | 18 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0043207 | 对外界生物刺激的反应 | 18 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0009607 | 生物刺激反应 | 18 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0098542 | 对其他生物的防御反应 | 15 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0006955 | 免疫反应 | 23 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0045069 | 病毒基因组复制的调控 | 9 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:1903900 | 病毒生命周期的调控 | 10 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0043903 | 共生的调节,包括通过寄生的互惠共生 | 11 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0019079 | 病毒基因组复制 | 9 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0045087 | 先天性免疫应答 | 17 | <0.01 |
| BP | GO:0050792 | 病毒变化的过程调节 | 10 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005737 | 细胞质 | 26 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0034774 | 分泌颗粒内腔 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005739 | 线粒体 | 8 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0060205 | 胞质囊腔 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0031983 | 囊腔 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005741 | 线粒体外膜 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0062023 | 含胶原的细胞外基质 | 4 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005775 | 空泡内腔 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0097232 | 层状体膜 | 1 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0097233 | 肺泡板层体膜 | 1 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0031968 | 细胞器外膜 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0019867 | 外膜 | 3 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005637 | 核内膜 | 2 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0031966 | 线粒体膜 | 5 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0044444 | 胞质部分 | 22 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0005740 | 线粒体被膜 | 5 | <0.01 |
| CC | GO:0097013 | 吞噬泡腔 | 1 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0001730 | 2'-5'-寡聚腺苷酸合成酶活性 | 3 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0003725 | 双链RNA结合物 | 4 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0070566 | 腺苷转移酶活性 | 3 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0030550 | 乙酰胆碱受体抑制剂活性 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0005521 | 核纤层蛋白结合 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0030548 | 乙酰胆碱受体调节活性 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0099602 | 神经递质受体调节活性 | 2 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0016779 | 核苷酸转移酶活性 | 3 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0031700 | 肾上腺髓质受体结合 | 1 | <0.01 |
| MF | GO:0097655 | 丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂家族蛋白结合 | 1 | <0.01 |
| 类型 | 名称 | 数量 | 描述 | 基因名称 | FDR | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
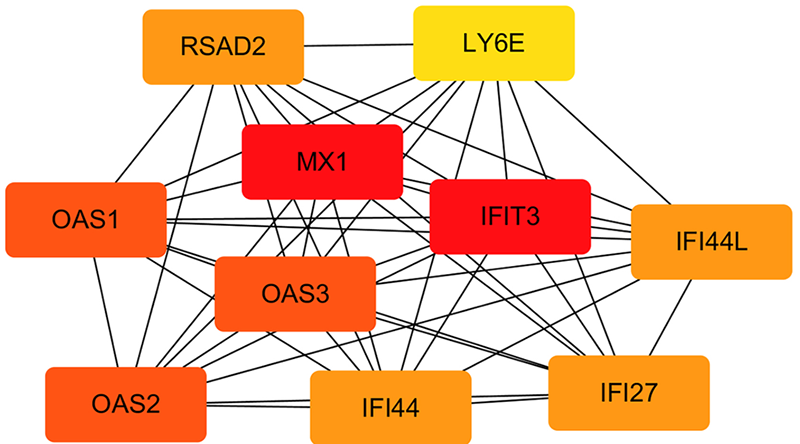
| KEGG | hsa05164 | 5 | 甲型流感 | RSAD2, OAS1, OAS2, OAS3, MX1 | 0.003173 | <0.01 |
| KEGG | hsa05162 | 4 | 麻疹 | OAS1, OAS2, OAS3, MX1 | 0.012997 | <0.01 |
| KEGG | hsa05168 | 4 | 单纯疱疹病毒感染 | SP100, OAS1, OAS2, OAS3 | 0.021615 | <0.01 |
| KEGG | hsa05160 | 3 | 丙型肝炎 | OAS1, OAS2, OAS3 | 0.102459 | 0.02 |
| 类型 | 名称 | 数量 | 描述 | 基因名称 | FDR | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG | hsa05164 | 5 | 甲型流感 | RSAD2, OAS1, OAS2, OAS3, MX1 | 0.003173 | <0.01 |
| KEGG | hsa05162 | 4 | 麻疹 | OAS1, OAS2, OAS3, MX1 | 0.012997 | <0.01 |
| KEGG | hsa05168 | 4 | 单纯疱疹病毒感染 | SP100, OAS1, OAS2, OAS3 | 0.021615 | <0.01 |
| KEGG | hsa05160 | 3 | 丙型肝炎 | OAS1, OAS2, OAS3 | 0.102459 | 0.02 |
| [1] |
Itolikar S, Nadkar MY. H1N1 revisited after six years: Then and now[J]. J Assoc Physicians India, 2015, 63:41-43.
pmid: 26591169 |
| [2] |
Webster RG, Govorkova EA. Continuing challenges in influenza[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2014, 1323(1):115-39.
doi: 10.1111/nyas.12462 URL |
| [3] |
Kondrich J, Rosenthal M. Influenza in children[J]. Curr Opin Pediatr, 2017, 29(3):297-302.
doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000495 URL |
| [4] |
Committee On Infectious Diseases. Recommendations for prevention and control of influenza in children, 2019-2020[J]. Pediatrics, 2019, 144(4):e20192478.
doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2478 URL |
| [5] |
Shim JM, Kim J, Tenson T, et al. Influenza virus infection, interferon response, viral counter-response, and apoptosis[J]. Viruses, 2017, 9(8):223.
doi: 10.3390/v9080223 URL |
| [6] |
Hou F, Sun L, Zheng H, et al. MAVS forms functional prion-like aggregates to activate and propagate antiviral innate immune response[J]. Cell, 2011, 146(3):448-461.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.041 URL |
| [7] |
Yoshizumi T, Ichinohe T, Sasaki O, et al. Influenza A virus protein PB1-F2 translocates into mitochondria via Tom40 channels and impairs innate immunity[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5:4713.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms5713 pmid: 25140902 |
| [8] |
Wang R, Zhu Y, Lin X, et al. Influenza M2 protein regulates MAVS-mediated signaling pathway through interacting with MAVS and increasing ROS production[J]. Autophagy, 2019, 15(7):1163-1181.
doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1580089 URL |
| [9] |
Xu F, Song H, An B, et al. NF-κB-dependent IFIT3 induction by HBx promotes Hepatitis B virus replication[J]. Front Microbiol, 2019, 10:2382.
doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02382 URL |
| [10] |
Yang Y, Zhou Y, Hou J, et al. Hepatic IFIT3 predicts interferon-α therapeutic response in patients of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Hepatology, 2017, 66(1):152-166.
doi: 10.1002/hep.v66.1 URL |
| [11] |
Li Y, Wen Z, Zhou H, et al. Porcine interferon-induced protein with tetratricopeptide repeats 3, poIFIT3, inhibits swine influenza virus replication and potentiates IFN-β production[J]. Dev Comp Immunol, 2015, 50(1):49-57.
doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.10.008 URL |
| [12] |
Lindenmann J. Resistance of mice to mouse-adapted influenza A virus[J]. Virology, 1962, 16:203-204.
doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90297-0 URL |
| [13] |
Jung HE, Oh JE, Lee HK. Cell-penetrating Mx1 enhances anti-viral resistance against mucosal influenza viral infection[J]. Viruses, 2019, 11(2):109.
doi: 10.3390/v11020109 URL |
| [14] |
Lohöfener J, Steinke N, Kay-Fedorov P, et al. The activation mechanism of 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase gives new insights into OAS/cGAS triggers of innate immunity[J]. Structure, 2015, 23(5):851-862.
doi: S0969-2126(15)00090-8 pmid: 25892109 |
| [15] |
Li Y, Banerjee S, Wang Y, et al. Activation of RNase L is dependent on OAS3 expression during infection with diverse human viruses[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2016, 113(8):2241-2246.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519657113 URL |
| [16] |
Sadler AJ, Williams BR. Interferon-inducible antiviral effectors[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2008, 8:559-568.
doi: 10.1038/nri2314 URL |
| [17] |
Mihm U, Ackermann O, Welsch C, et al. Clinical relevance of the 2'-5'-oligoadenylate synthetase/RNase L system for treatment response in chronic hepatitis C[J]. J Hepatol, 2009, 50:49-58.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.08.024 URL |
| [18] |
Liao X, Xie H, Li S, et al. 2', 5'-oligoadenylate synthetase 2 (OAS2) inhibits Zika virus replication through activation of type Ⅰ IFN signaling pathway[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(4):418.
doi: 10.3390/v12040418 URL |
| [19] |
Tang BM, Shojaei M, Parnell GP, et al. A novel immune biomarker IFI27 discriminates between influenza and bacteria in patients with suspected respiratory infection[J]. Eur Respir J, 2017, 49(6):1602098.
doi: 10.1183/13993003.02098-2016 URL |
| [1] | Zhao Xin, Liu Yun. Generative artificial intelligence: Ethical review on the empowerment in medical humanities education [J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 65-69. |
| [2] | Nie Fang, Luo Jun. Analysis of early risk factors for infectious mononucleosis in children from Chengdu city [J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(11): 1008-1011. |
| [3] | Mao Rong, Tao Qianshan, Shen Yuanyuan, Dong Yi. A case with extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma-related hemophagocyte syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(7): 635-639. |
| [4] | Wang Jingwei, Ji Yunfei, Zhou Di. Exploration path on integrating red doctor’s spirit into curricular ideology of medical humanities course [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(10): 938-941. |
| [5] | Hou Wei, Zhang Lijun, Zhang Man, Wang Yakun, Tian Liyuan. Epidemiological investigation of adenovirus respiratory tract infection in hospitalized children [J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(10): 916-920. |
| [6] | Cui Tingting, Zhang Jia, Wang Jingshi, Wang Zhao. Epstein-Barr virus-driven hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(10): 910-915. |
| [7] | Xu Huaa, Chen Jiab. Bioinformatics analysis of differential genes and potential therapeutic drugs in primary Sjgren's syndrome [J]. Clinical Focus, 2020, 35(6): 533-540. |
| [8] | Wang Yankun1, Ma Junji2, Zhang Ming2. Role of cytokeratin 7 in pathological diagnosis of liver cirrhosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2019, 34(2): 124-127. |
| [9] | Liu Xiaomeng, Zhao Caiyan. Clinical advances in infectious diseases in 2017 [J]. Clinical Focus, 2018, 33(1): 60-65. |
| [10] | Wu Shucai1a, Yang Yonghui1b, Guo Sumin1c, Du Jiejie2, Song Lichao2, Gao Li2. Relationship between human angiopoietin1 and pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(9): 1019-1022. |
| [11] | Zhao Xia, Guo Xin, Wang Rong, Zhang Dongcheng. Clinical observation on Shengxuening treating anemia in peritoneal dialysis patients [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(9): 1015-1018. |
| [12] | Qian Zhengyao, Li Guangping, Li Jiao, Liang Xue, Xu Zhao, Chen Yan, Zhao Hui. Relationship between PCSK9 and inflammation factor expression in ox-LDL-induced endothelial cells apoptosis [J]. Clinical Focus, 2016, 31(4): 396-402. |
| [13] | Li Xiaolan;Li Xiaojun;Liu Xiao;Xie Fan. Combined vaccination in treatment of children with recurrent respiratory tract infection and influence on cellular immunologic function [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(4): 387-389. |
| [14] | Huang Jinhong;Yang Jicheng;Zhao Daguo;Xie Yufeng;Ling Chunhua;Sheng Jianhua;Zhao Yungen. Inhibitory and radiosensitizing effects of adenovirus-mediated IL-24 gene on human lung adenocarcinoma [J]. Clinical Focus, 2015, 30(1): 89-94. |
| [15] | ZHU Ji-jun;SHI Hai-cun;ZHOU Gui-long. Comparison of low dose and high dose human gamma globulin in therapy for acute Guillian-Barre syndrome [J]. CLINICAL FOCUS, 2009, 24(16): 1409-1411. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||