

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 869-877.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.10.001
• 循证研究 • 下一篇
收稿日期:2023-04-20
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2024-01-03
通讯作者:
阮俊文
E-mail:ruanjunwen2020@163.com
基金资助:
Ruan Junwen1( ), Zhou Jianrong2, Liu Weiyou2, Yuan Xiaoliang2, Yan Hao3
), Zhou Jianrong2, Liu Weiyou2, Yuan Xiaoliang2, Yan Hao3
Received:2023-04-20
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2024-01-03
Contact:
Ruan Junwen
E-mail:ruanjunwen2020@163.com
摘要: 目的 系统评价度普利尤单抗治疗支气管哮喘的临床疗效和安全性。 方法 检索中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI)、万方数据库(Wanfang Database)、维普数据库(VIP)、中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM)、Cochrane Library、PubMed、Embase、Web of Science等数据库,检索时间为建库至2023年2月20日,纳入度普利尤单抗治疗支气管哮喘患者的随机对照试验(RCT),使用RevMan5.4软件进行Meta分析。结果 总纳入11项RCTs,共3759例患者,Meta分析结果显示,试验组哮喘急性加重人数[RR=0.48, 95%CI (0.40, 0.57), P<0.01]、哮喘控制问卷评分(Asthma control questionnaire, ACQ)[MD =-0.32, 95%CI (-0.43, -0.21), P<0.01]均少于对照组,试验组第1秒用力呼气容积(Forced expiratory volume in 1s, FEV1)[MD =0.51, 95%CI (0.31, 0.71), P<0.01]、哮喘生活质量问卷评分(Asthma quality of life questionnaire, AQLQ)[MD =0.32, 95%CI (0.20, 0.44), P<0.01]均高于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);在血液嗜酸性粒细胞数<300/μl的哮喘人数[RR=1.10, 95%CI (0.93, 1.31), P=0.26]、不良事件[RR=1.03, 95%CI (0.98, 1.08), P=0.22]、严重不良事件[RR=1.21, 95%CI (0.86, 1.71), P=0.28]等方面,两组基本一致,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 度普利尤单抗可有效减少哮喘急性加重人数、改善肺功能和提高患者的生活质量,且有较好的安全性。
中图分类号:
阮俊文, 周建荣, 刘惟优, 袁小亮, 颜颢. 度普利尤单抗治疗支气管哮喘疗效和安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(10): 869-877.
Ruan Junwen, Zhou Jianrong, Liu Weiyou, Yuan Xiaoliang, Yan Hao. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of dupilumab on the treatment of bronchial asthma[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(10): 869-877.
| 纳入研究 | 病例数 | 平均年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | 疗程 | 结局指标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/C | T | C | T | C | |||||
| Bacharier 2021[ | 273/135 | 8.9±1.6 | 9.0±1.6 | 达必妥100 mg q2w(W≤30kg), 200 mg q2w(W>30kg) | 安慰剂q2w | 52w | ①②③④⑥⑦ | ||
| Busse(a) 2018[ | 634/317 | ≥12 | 达必妥200 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 52w | ② | |||
| Busse(b) 2018[ | 634/317 | ≥12 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 52w | ② | |||
| Domingo 2022[ | 103/107 | 52.9±12.6 | 50.3±12.6 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②④⑥ | ||
| Rabe 2018[ | 103/107 | 51.9±12.5 | 50.7±12.8 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②③⑥⑦ | ||
| Wechsler 2021[ | 75/74 | 51.3±12.7 | 47.0±11.4 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 12w | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ | ||
| Wenzel(a) 2016[ | 150/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥200 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel(b) 2016[ | 154/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥200 mg q4w | 安慰剂q4w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel(c) 2016[ | 157/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel(d) 2016[ | 157/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥300 mg q4w | 安慰剂q4w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel 2013[ | 52/52 | 37.8±13.2 | 41.6±13.1 | 达必妥300 mg qw | 安慰剂qw | 12w | ①④⑥⑦ | ||
表1 纳入研究的基本特征
Tab.1 Basic characteristics of included studies
| 纳入研究 | 病例数 | 平均年龄(岁) | 干预措施 | 疗程 | 结局指标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T/C | T | C | T | C | |||||
| Bacharier 2021[ | 273/135 | 8.9±1.6 | 9.0±1.6 | 达必妥100 mg q2w(W≤30kg), 200 mg q2w(W>30kg) | 安慰剂q2w | 52w | ①②③④⑥⑦ | ||
| Busse(a) 2018[ | 634/317 | ≥12 | 达必妥200 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 52w | ② | |||
| Busse(b) 2018[ | 634/317 | ≥12 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 52w | ② | |||
| Domingo 2022[ | 103/107 | 52.9±12.6 | 50.3±12.6 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②④⑥ | ||
| Rabe 2018[ | 103/107 | 51.9±12.5 | 50.7±12.8 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②③⑥⑦ | ||
| Wechsler 2021[ | 75/74 | 51.3±12.7 | 47.0±11.4 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 12w | ①②③④⑤⑥⑦ | ||
| Wenzel(a) 2016[ | 150/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥200 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel(b) 2016[ | 154/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥200 mg q4w | 安慰剂q4w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel(c) 2016[ | 157/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥300 mg q2w | 安慰剂q2w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel(d) 2016[ | 157/158 | 48.6±13.0 | 达必妥300 mg q4w | 安慰剂q4w | 24w | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | |||
| Wenzel 2013[ | 52/52 | 37.8±13.2 | 41.6±13.1 | 达必妥300 mg qw | 安慰剂qw | 12w | ①④⑥⑦ | ||
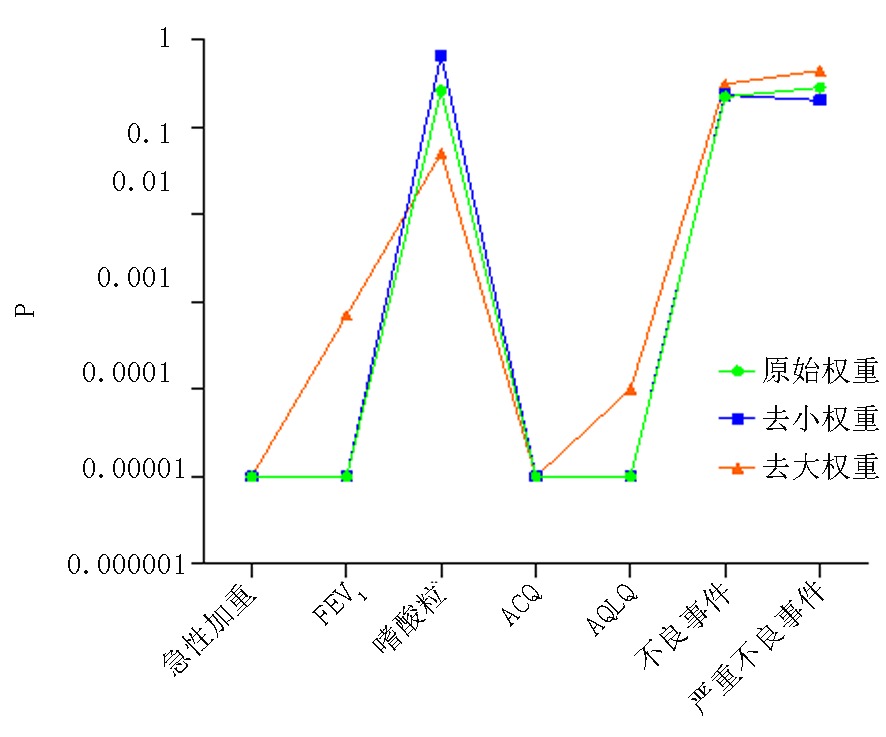
图12 统计学意义分析图 注:“P<0.00001”取值为“P=0.00001”;在“FEV1”、“AQLQ”、“严重不良事件”中,均存在两项相同大权重研究,在去掉两项相同大权重研究后,所得P值为“0.0006/0.0007”、“<0.0001/<0.00001”、“0.44/0.63”,图中P取值为“0.0007”、“<0.0001”、“0.44”
Fig.12 Analytical graph of statistical significance
| [1] | Global Initiative for Asthma. 2021 GINA report, global strategy for asthma management and prevention(2021 update)[EB/OL].https://ginasthma.org/gina-reports. |
| [2] | Allan R, Canham K, Wallace R, et al. Usability and robustness of the wixela inhub dry powder inhaler[J]. Aerosol Med Pμlm Drug Deliv, 2021, 34(2):134-145. |
| [3] |
Huang K, Yang T, Xu J, et al. Prevalence, risk factors and management of asthma in China: A national cross-sectional study[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10196):407-418.
doi: S0140-6736(19)31147-X pmid: 31230828 |
| [4] |
Song WJ, Kang MG, Chang YS, et al. Epidemiology of adμlt asthma in Asia: Toward a better understanding[J]. Asia Pac Allergy, 2014, 4(2):75-85.
doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.2.75 URL |
| [5] |
Chung KF, Wenzel SE, Brozek JL, et al. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma[J]. Eur Respir J, 2014, 43(2):343-373.
doi: 10.1183/09031936.00202013 pmid: 24337046 |
| [6] |
Settipane RA, Kreindler JL, Chung Y, et al. Evaluating direct costs and productivity losses of patients with asthma receiving GINA 4/5 therapy in the United States[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2019, 123(6):564-572.
doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2019.08.462 URL |
| [7] |
Rudolph AK, Walter T, Erkel G. The fungal metabolite cyclonerodiol inhibits IL-4/IL-13 induced Stat6-signaling through blocking the association of Stat6 with p38, ERK1/2 and p300[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2018, 65:392-401.
doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.10.033 URL |
| [8] |
Le Floc'h A, Allinne J, Nagashima K, et al. Dual blockade of IL-4and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Rα antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation[J]. Allergy, 2020, 75(5):1188-1204.
doi: 10.1111/all.v75.5 URL |
| [9] |
Rabe KF, Nair P, Brusselle G, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in glucocorticoid-dependent severe asthma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378(26):2475-2485.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804093 URL |
| [10] | Higgins JPT, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011[EB/OL].http://www.cochrane-handbook.org. |
| [11] |
Bacharier LB, Maspero JF, Katelaris CH, et al. Dupilumab in children with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(24):2230-2240.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2106567 URL |
| [12] |
Busse WW, Maspero JF, Rabe KF, et al. Liberty asthma QUEST: Phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate dupilumab efficacy/safety in patients with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma[J]. Adv Ther, 2018, 35(5):737-748.
doi: 10.1007/s12325-018-0702-4 pmid: 29725983 |
| [13] |
Domingo C, Maspero JF, Castro M, et al. Dupilumab efficacy in steroid-dependent severe asthma by baseline oral corticosteroid dose[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2022, 10(7):1835-1843.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.03.020 pmid: 35398549 |
| [14] |
Wechsler ME, Ruddy MK, Pavord ID, et al. Efficacy and safety of itepekimab in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2021, 385(18):1656-1668.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024257 URL |
| [15] |
Wenzel S, Castro M, Corren J, et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting β2 agonist: A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10039):31-44.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30307-5 pmid: 27130691 |
| [16] |
Wenzel S, Ford L, Pearlman D, et al. Dupilumab in persistent asthma with elevated eosinophil levels[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 368(26):2455-2466.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1304048 URL |
| [17] |
Woodruff PG, Modrek B, Choy DF, et al. T-helper type 2-driven inflammation defines major subphenotypes of asthma[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2009, 180 (5):388-395.
doi: 10.1164/rccm.200903-0392OC URL |
| [18] |
Frøssing L, Silberbrandt A, Von Bülow A, et al. The prevalence of subtypes of type 2 inflammation in an unselected population of patients with severe asthma[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2021, 9 (3):1267-1275.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.09.051 pmid: 33039645 |
| [19] |
Chuang YT, Leung K, Chang YJ, et al. A natural killer T-cell subset that protects against airway hyperreactivity[J]. Allergy Clin Immunol, 2019, 143(2):565-576.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.03.022 URL |
| [20] |
Eger K, Kroes JA, Brinke AT, et al. Long-Term Therapy Response to Anti-IL-5 Biologics in Severe Asthma-A Real-Life Evaluation[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2021, 9(3):1194-1200.
doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.10.010 pmid: 33069885 |
| [21] |
Riccio AM, Dal Negro RW, Micheletto L, et al. Omalizumab modulates bronchial reticular basement membrane thickness and eosinophil infiltration in severe persistent allergic asthma patients[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2012, 25(2):475-484.
doi: 10.1177/039463201202500217 pmid: 22697079 |
| [22] |
Nair P, Pizzichini MMM, Kjarsgaard M, et al. Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum eosinophilia[J]. N Engl J Med, 2009, 360(10):985-993.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805435 URL |
| [23] |
Casale TB, Luskin AT, Busse W, et al. Omalizumab effectiveness by biomarker status in patients with asthma: evidence from PROSPERO, a prospective real-world study[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2019, 7(1):156-164.
doi: S2213-2198(18)30323-4 pmid: 29800752 |
| [24] |
Castro M, Corren J, Pavord ID, et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in moder-ate-to-severe uncontrolled asthma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2018, 378 (26):2486-2496.
doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1804092 URL |
| [25] | Castro M, Rabe KF, Corren J, et al. Dupilumab improves lung function in patients with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma[J]. ERJ Open Res, 2020, 6 (1):00204-2019. |
| [26] |
Dupin C, Belhadi D, Guilleminault L, et al. Effectiveness and safety of dupilumab for the treatment of severe asthma in a real-life French multi-centre adult cohort[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2020, 50 (7):789-798.
doi: 10.1111/cea.13614 pmid: 32469092 |
| [1] | 龚财芳, 赵俊宇, 游川. 接纳与承诺疗法对癌症患者心理健康和生活质量影响的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(2): 101-107. |
| [2] | 肖煌怡, 袁建坤, 严梓予, 曾雯姝, 鲁兰莫, 王峻. 认知干预对遗忘型轻度认知障碍老年患者干预效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 12-19. |
| [3] | 吕畅, 周利明. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌易感相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 779-787. |
| [4] | 李海, 刘文虎, 彭绍鹏, 王飞. 控制性阶梯式减压术对比快速标准大骨瓣减压术治疗重度颅脑损伤疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 788-795. |
| [5] | 侯有玲, 李奕, 关红玉, 罗红霞. 目标导向液体治疗在脑肿瘤切除术中应用效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(8): 686-693. |
| [6] | 金家辉, 杨阳, 秦铜, 何雨欣, 苏美华. 补充益生菌对2型糖尿病患者糖代谢改善的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 581-587. |
| [7] | 肖王静, 李欣梦, 卢松玲, 孙雪华. 重复经颅磁刺激治疗中枢神经源性吞咽障碍疗效及安全性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 588-599. |
| [8] | 倪艺芸, 刘彬, 梁琪, 李晓凤. 白细胞介素6和C反应蛋白预测新型冠状病毒肺炎严重程度的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 493-499. |
| [9] | 尤奕, 高淑清, 徐浩. 肠内营养对食管癌患者术后临床结局影响的系统综述[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 485-492. |
| [10] | 赵哲, 穆培娟, 张冬. 恩度联合顺铂胸腔灌注治疗肺癌合并恶性胸腔积液疗效的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 399-404. |
| [11] | 沃拉孜汗·玛德尼亚提, 迪力夏提·图尔迪麦麦提, 李梦晨, 拜合提尼沙·吐尔地. 宏基因组二代测序技术在肺结核诊断中应用价值的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 389-398. |
| [12] | 马明福, 魏志国, 何铁英. 急性胰腺炎并发胰腺假性囊肿危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 293-301. |
| [13] | 曹宇萌, 张海燕, 刘立新. 非酒精性脂肪性肝病的病理改变与血清铁蛋白和血清铁含量变化关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 197-207. |
| [14] | 马宏莉, 陆皓, 王丹, 焦海星, 李一珂, 李思雨, 吕静. 脑卒中患者残疾危险因素的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(2): 111-116. |
| [15] | 陶嘉楠, 李文茜, 马秀雯, 安琪, 王学红. HER-2在肝细胞癌中表达及临床意义的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1067-1072. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 44
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 155
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||