

临床荟萃 ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 208-215.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.002
收稿日期:2022-09-06
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-05-11
通讯作者:
杜怡斌
E-mail:dodo1108@163.com
基金资助:Received:2022-09-06
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-05-11
Contact:
Du Yibin
E-mail:dodo1108@163.com
摘要:
目的 比较机器人辅助与徒手置钉两种不同椎弓根螺钉置入方式在脊柱手术中的临床效果,为未来脊柱外科发展方向提供一定理论参考。方法 检索2011年2月至2021年2月发表的相关病例对照研究。检索包括Pubmed、Cochrane Library、CNKI、Embase、WF、VIP在内的6个数据库。依据中英文检索策略,共检索到文献418篇,根据条件进一步筛选后最终纳入13篇文献。提取本文所需数据并使用Review manager 5.3软件进行分析。结果 机器人辅助下置钉较徒手透视引导下置钉准确度较高(95%
中图分类号:
李杨, 杜怡斌. 机器人辅助与徒手椎弓根螺钉置入在脊柱疾病应用效果的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 208-215.
Li Yang, Du Yibin. Meta-analysis of the effect of robot-assisted and free-handed pedicle screw placement in spinal diseases[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 208-215.
| 纳入研究 | 类型 | 国家 | 年份 | 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 性别 (男/女) | 结局指标 | 改良Jadad 质量评价(分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ringel[ | 随机对照 | 德国 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 68 | 14/16 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 67 | 12/18 | ||||||
| Feng[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 40 | 67.6±6.5 | 12/28 | ①③⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 67.9±7.3 | 13/27 | ||||||
| Keric[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 72.3±11.1 | 36/30 | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 68.0±11.2 | 13/11 | ||||||
| Hyun[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 66.5 | 9/21 | ①③④⑤⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 66.8 | 8/22 | ||||||
| Kim[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2015 | 机器人辅助 | 20 | 64.4±11.9 | 11/9 | ①⑥ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 20 | 64.7±8.6 | 8/12 | ||||||
| Lautado[ | 回顾性 | 瑞士 | 2018 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | - | ① | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 48 | 60.7 | |||||||
| Schizas[ | 随机对照 | 瑞士 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | 6/5 | ①③④ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 23 | 66 | 8/15 | ||||||
| Kantelhardt[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2011 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 63.1 | 52/60 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 57 | ||||||||
| Lonjon[ | 随机对照 | 法国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 10 | 63.4±11.0 | 4/6 | ①②③④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | 4/6 | |||||||
| Han[ | 回顾性 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 54.6±11.3 | 55/60 | ①③④⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 56.1±13.4 | 58/61 | ||||||
| Schatlo[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2014 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 52(27-83) | 29/26 | ①②⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 58(23-82) | 28/12 | ||||||
| Roser[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2013 | 机器人辅助 | 18 | - | - | ①③④ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | ||||||||
| 田伟[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 23 | 54.9±11.9 | 17/23 | ①⑥ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 17 |
表1 纳入文献基本特征表
Tab. 1 Basic characteristics of documents included
| 纳入研究 | 类型 | 国家 | 年份 | 组别 | 例数 | 年龄 (岁) | 性别 (男/女) | 结局指标 | 改良Jadad 质量评价(分) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ringel[ | 随机对照 | 德国 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 68 | 14/16 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 67 | 12/18 | ||||||
| Feng[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 40 | 67.6±6.5 | 12/28 | ①③⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 67.9±7.3 | 13/27 | ||||||
| Keric[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 72.3±11.1 | 36/30 | ①②④⑤⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 68.0±11.2 | 13/11 | ||||||
| Hyun[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2017 | 机器人辅助 | 30 | 66.5 | 9/21 | ①③④⑤⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 30 | 66.8 | 8/22 | ||||||
| Kim[ | 随机对照 | 韩国 | 2015 | 机器人辅助 | 20 | 64.4±11.9 | 11/9 | ①⑥ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 20 | 64.7±8.6 | 8/12 | ||||||
| Lautado[ | 回顾性 | 瑞士 | 2018 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | - | ① | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 48 | 60.7 | |||||||
| Schizas[ | 随机对照 | 瑞士 | 2012 | 机器人辅助 | 11 | 65 | 6/5 | ①③④ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 23 | 66 | 8/15 | ||||||
| Kantelhardt[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2011 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 63.1 | 52/60 | ①②④⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 57 | ||||||||
| Lonjon[ | 随机对照 | 法国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 10 | 63.4±11.0 | 4/6 | ①②③④⑥⑦ | 7 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | 4/6 | |||||||
| Han[ | 回顾性 | 中国 | 2019 | 机器人辅助 | 52 | 54.6±11.3 | 55/60 | ①③④⑥⑦ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 70 | 56.1±13.4 | 58/61 | ||||||
| Schatlo[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2014 | 机器人辅助 | 55 | 52(27-83) | 29/26 | ①②⑥⑦ | 6 |
| 透视引导 | 40 | 58(23-82) | 28/12 | ||||||
| Roser[ | 回顾性 | 德国 | 2013 | 机器人辅助 | 18 | - | - | ①③④ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 10 | ||||||||
| 田伟[ | 随机对照 | 中国 | 2016 | 机器人辅助 | 23 | 54.9±11.9 | 17/23 | ①⑥ | 5 |
| 透视引导 | 17 |
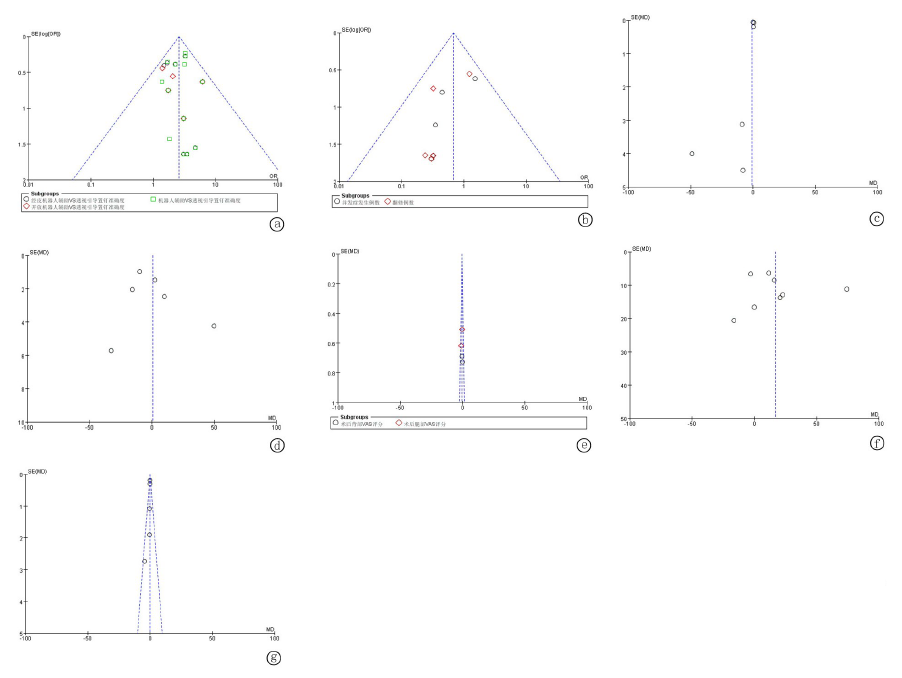
图9 发表偏倚 a.椎弓根置钉准确度发表偏倚漏斗图;b.并发症及翻修例数发表偏倚漏斗图;c.术中辐射强度发表偏倚漏斗图;d.辐射时间发表偏倚漏斗图;e.术后VAS发表偏倚漏斗图;f.术中所需时间发表偏倚漏斗图; g. 住院时长发表偏倚漏斗图
Fig.9 Publication of bias a. Funnel plot of accuracy of pedicle screw placement; b. Funnel plot of complications and revision cases; c. Funnel plot of intraoperative. radiation intensity; d. Funnel plot of intraoperative radiation time; e. Funnel plot of postoperative VAS score; f. Funnel plot of operation time; g. Funnel plot of hospitalization time
| [1] |
Nasser R, Yadla S, Maltenfort MG, et al. Complications in spine surgery[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2010, 13(2):144-157.
doi: 10.3171/2010.3.SPINE09369 URL |
| [2] | Togawa D, Kayanja MM, Reinhardt MK, et al. Bone-mounted miniature robotic guidance for pedicle screw and translaminar facet screw placement: Part 2--Evaluation of system accuracy[J]. Neurosurgery, 2007, 60(2 Suppl 1):S129-S139. |
| [3] | 田伟, 王晋超, 刘亚军, 等. 上颈椎手术方式回顾及应用机器人辅助上颈椎手术的体会[J]. 中国医疗器械信息, 2017, 23(7):9-13. |
| [4] | Joseph JR, Smith BW, Liu X, et al. Current applications of robotics in spine surgery: A systematic review of the literature[J]. Neurosurg Focus, 2017, 42(5):E2. |
| [5] |
Ringel F, Stuer C, Reinke A, et al. Accuracy of robot-assisted placement of lumbar and sacral pedicle screws: A prospective randomized comparison to conventional freehand screw implantation[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012, 37(8):E496-E501.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31824b7767 URL |
| [6] |
Feng S, Tian W, Sun Y, et al. Effect of robot-assisted surgery on lumbar pedicle screw internal fixation in patients with osteoporosis[J]. World Neurosurg, 2019, 125:e1057-e1062.
doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.243 URL |
| [7] |
Keric N, Eum DJ, Afghanyar F, et al. Evaluation of surgical strategy of conventional vs. percutaneous robot-assisted spinal trans-pedicular instrumentation in spondylodiscitis[J]. J Robot Surg, 2017, 11(1):17-25.
doi: 10.1007/s11701-016-0597-5 pmid: 27277255 |
| [8] |
Hyun S, Kim K, Jahng T, et al. Minimally invasive robotic versus open fluoroscopic-guided spinal instrumented fusions: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Spine, 2017, 42(6):353-358.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000001778 URL |
| [9] |
Kim H, Lee SH, Chang B, et al. Monitoring the quality of robot-assisted pedicle screw fixation in the lumbar spine by using a cumulative summation test[J]. Spine, 2015, 40(2):87-94.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000680 URL |
| [10] |
Laudato PA, Pierzchala K, Schizas C. Pedicle screw insertion accuracy using o-arm, robotic guidance, or freehand technique: A comparative study[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2018, 43(6):E373-E378.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002449 URL |
| [11] |
Schizas C, Thein E, Kwiatkowski B, et al. Pedicle screw insertion: robotic assistance versus conventional C-arm fluoroscopy.[J]. Acta orthopaedica Belgica, 2012, 78(2):240-245.
pmid: 22696996 |
| [12] |
Kantelhardt SR, Martinez R, Baerwinkel S, et al. Perioperative course and accuracy of screw positioning in conventional, open robotic-guided and percutaneous robotic-guided, pedicle screw placement[J]. Eur Spine J, 2011, 20(6):860-868.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-011-1729-2 pmid: 21384205 |
| [13] |
Lonjon N, Chan-Seng E, Costalat V, et al. Robot-assisted spine surgery: Feasibility study through a prospective case-matched analysis[J]. Eur Spine J, 2016, 25(3):947-955.
doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3758-8 pmid: 25575857 |
| [14] | Han X, Tian W, Liu Y, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-assisted pedicle screw insertion in thoracolumbar spinal surgery: A prospective randomized controlled trial[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2019:1-8. |
| [15] |
Schatlo B, Molliqaj G, Cuvinciuc V, et al. Safety and accuracy of robot-assisted versus fluoroscopy-guided pedicle screw insertion for degenerative diseases of the lumbar spine: A matched cohort comparison[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2014, 20(6):636-643.
doi: 10.3171/2014.3.SPINE13714 URL |
| [16] | Roser F, Tatagiba M, Maier G. Spinal robotics: Current applications and future perspectives[J]. Neurosurgery, 2013, 72(Suppl 1):12-18. |
| [17] | 田伟, 范明星, 韩晓光, 等. 机器人辅助与传统透视辅助脊柱椎弓根螺钉内固定的临床对比研究[J]. 骨科临床与研究杂志, 2016, 1(1):4-10. |
| [18] |
Bydon M, Alvi M A, Goyal A. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: Definition, natural history, conservative management, and surgical treatment[J]. Neurosurg Clin N Am, 2019, 30(3):299-304.
doi: S1042-3680(19)30016-6 pmid: 31078230 |
| [19] |
Ma XL, Zhao XW, Ma JX, et al. Effectiveness of surgery versus conservative treatment for lumbar spinal stenosis: A system review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Int J Surg, 2017, 44:329-338.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.07.032 URL |
| [20] |
Rustagi T, Drazin D, Oner C, et al. Fractures in spinal ankylosing disorders: A narrative review of disease and injury types, treatment techniques, and Outcomes[J]. J Orthop Trauma, 2017, 31(Suppl 4):S57-S74.
doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000953 URL |
| [21] |
Aizawa T, Kokubun S, Ozawa H, et al. Increasing incidence of degenerative spinal diseases in Japan during 25 years: The registration system of spinal surgery in tohoku university spine society[J]. Tohoku J Exp Med, 2016, 238(2):153-163.
doi: 10.1620/tjem.238.153 pmid: 26876801 |
| [22] |
Jain A, Hassanzadeh H, Puvanesarajah V, et al. Incidence of perioperative medical complications and mortality among elderly patients undergoing surgery for spinal deformity: analysis of 3519 patients[J]. J Neurosurg Spine, 2017, 27(5):534-539.
doi: 10.3171/2017.3.SPINE161011 URL |
| [23] |
Mihailidis HG, Manners S, Churilov L, et al. Is spinal surgery safe in octogenarians?[J]. ANZ Journal of Surgery, 2017, 87(7-8):605-609.
doi: 10.1111/ans.13885 pmid: 28124479 |
| [24] |
Liu JM, Zhang Y, Zhou Y, et al. The effect of screw tunnels on the biomechanical stability of vertebral body after pedicle screws removal: A finite element analysis[J]. Int Orthop, 2017, 41(6):1183-1187.
doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3453-y URL |
| [25] |
Mac-Thiong JM, Parent S, Poitras B, et al. Neurological outcome and management of pedicle screws misplaced totally within the spinal canal[J]. Spine, 2013, 38(3):229-237.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31826980a9 pmid: 22814305 |
| [26] |
Devito DP, Kaplan L, Dietl R, et al. Clinical acceptance and accuracy assessment of spinal implants guided with SpineAssist surgical robot: Retrospective study[J]. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010, 35(24):2109-2115.
doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181d323ab URL |
| [27] |
Li W, Li G, Chen W, et al. The safety and accuracy of robot-assisted pedicle screw internal fixation for spine disease: A meta-analysis[J]. Bone Joint Res, 2020, 9(10):653-666.
doi: 10.1302/2046-3758.910.BJR-2020-0064.R2 pmid: 33101655 |
| [28] |
Wiesner L, Kothe R, Schulitz K P, et al. Clinical evaluation and computed tomography scan analysis of screw tracts after percutaneous insertion of pedicle screws in the lumbar spine[J]. Spine, 2000, 25(5):615-621.
doi: 10.1097/00007632-200003010-00013 pmid: 10749639 |
| [1] | 王娇燕, 章迎春, 任珂明, 马国峰, 应可净. 奥氮平使用合并静脉血栓栓塞症16例临床分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(12): 1108-1113. |
| [2] | 张文超, 李建立. 全身麻醉期间个体化呼气末正压研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(7): 668-672. |
| [3] | 李红蔚, 吴琦. 关注妊娠期静脉血栓栓塞症[J]. 临床荟萃, 2016, 31(4): 359-362. |
| [4] | 姜明明, 袁雅冬. 恶性肿瘤与静脉血栓栓塞症[J]. 临床荟萃, 2016, 31(4): 373-377. |
| [5] | 刘娟;李代红;宋文利. 肾移植术后甲状腺功能监测及其意义[J]. 临床荟萃, 2011, 26(14): 1211-1213. |
| [6] | 韩鸿玲;林珊;李英梅;朱弘政;翟德佩. 接受免疫抑制剂治疗的肾脏病患者急性侵袭性肺部真菌感染的诊治体会[J]. 临床荟萃, 2011, 26(4): 317-319. |
| [7] | 秦金喜. 脑室引流管污染致颅内感染1例[J]. 临床荟萃, 2010, 25(24): 2124-2124. |
| [8] | 李玉凤;张胜利;姚家琳;范彦令. 关于国产吗替麦考酚酯分散片与进口胶囊预防肾移植术后急性排斥反应的比较[J]. 临床荟萃, 2010, 25(13): 1134-1137. |
| [9] | 李亚华;田凤军;王金成;任士卿. 呼吸机使用中脂肪栓塞综合征1例并文献复习[J]. 临床荟萃, 2008, 23(2): 137-138. |
| [10] | 李玉凤;姚家琳;张胜利. 雷帕霉素对肾移植患者术后肾功能的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2005, 20(15): 846-849. |
| [11] | 郭雁宾;吴玉环. 肾移植后环孢菌素A等免疫抑制剂引起肝衰竭3例[J]. 临床荟萃, 2003, 18(7): 404-405. |
| [12] | 沈兆华;赵胜南;陆祖裴. 兄妹4人同患遗传性进行性肾炎及其肾移植成功1例[J]. 临床荟萃, 2002, 17(7): 415-416. |
| [13] | 孙玉秋;俎燕会;汪明明. 电动喷雾麻醉在纤维字器官镜术前的应用[J]. 临床荟萃, 2001, 16(22): 0-0. |
| [14] | 吕聪敏;李莉;冯海新. 经食管程控刺激麻醉剂的选择[J]. 临床荟萃, 2001, 16(7): 336-0. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
