

临床荟萃 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 314-319.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.04.003
王茜1, 尹万红1( ), 邹同娟1, 铁馨1, 朱俊臣2, 陈侣林2, 曾学英1
), 邹同娟1, 铁馨1, 朱俊臣2, 陈侣林2, 曾学英1
收稿日期:2024-03-12
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-06-27
通讯作者:
尹万红,Email: 作者简介:注:第一作者目前工作单位为成都大学附属医院重症医学科
基金资助:
Wang Qian1, Yin Wanhong1( ), Zou Tongjuan1, Tie Xin1, Zhu Junchen2, Chen Lyulin2, Zeng Xueying1
), Zou Tongjuan1, Tie Xin1, Zhu Junchen2, Chen Lyulin2, Zeng Xueying1
Received:2024-03-12
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-06-27
Contact:
Yin Wanhong, Email: 摘要:
目的 分析脓毒症机械通气患者不同肺部超声表型的临床特征,探讨肺部超声重力依赖肺失充气表型对脓毒症机械通气患者不良预后的相关性。方法 回顾性分析2019年4月至2020年10月四川大学华西医院重症医学科收治的机械通气脓毒症患者155例,按照28 d预后情况分为生存组(n=124)和死亡组(n=31),通过单因素和多因素Cox回顾分析肺部超声重力依赖失充气表型对患者28 d预后结局的影响。绘制Kaplan-Meier 曲线分析重力依赖性和非重力依赖失充气表型与28 d预后生存的关系。结果 单因素Cox回归分析发现,白细胞介素-6、SOFA评分、机械通气时间(h)、间质性失充气、实变性失充气、不张性失充气、存在重力依赖性失充气改变与患者28 d预后结局相关(P<0.05),进一步通过多因素Cox分析校正后发现存在间质性失充气肺部超声模式、机械通气时间和存在重力依赖性失充气改变与患者不良预后结局相关(P<0.05),重力依赖肺失充气表型的死亡风险是非重力依赖肺失充气表型的的2.003倍(HR=2.003, P=0.028, 95%CI=1.112-6.387)。结论 重力依赖肺失充气肺部超声表型可作为脓毒症机械通气患者不良预后的预测指标。
中图分类号:
王茜, 尹万红, 邹同娟, 铁馨, 朱俊臣, 陈侣林, 曾学英. 机械通气脓毒症患者肺部超声重力依赖失充气表型与不良预后的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(4): 314-319.
Wang Qian, Yin Wanhong, Zou Tongjuan, Tie Xin, Zhu Junchen, Chen Lyulin, Zeng Xueying. Correlation between the lung ultrasound phenotype of gravity-dependent deaeration and poor prognosis in sepsis patients requiring mechanical ventilation[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(4): 314-319.
| 定义 | 肺部超声病理生理模式定义 | MLUS (分) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 检查区域胸膜正常+A线 | 0 |
| A1 | 检查区域胸膜滑动征消失+A线,可见“肺点” | NM |
| B1 | 检查区域3根以上少量B线 | 1 |
| B2 | 检查区域多根融合的B线 | 1 |
| C1 | 检查区域胸膜下肺小叶完全失充气,直径0.5 cm~1 cm,即“碎片征” | 3 |
| C2 | 检查区域实质回声混杂不均,大片实变,动态支气管征,胸水较少(液性暗区小于3 cm) | 3 |
| C3 | 检查区域实质回声相对均一,肺组织容积减少,大量胸水压迫,不张肺组织呈“水母征”,外缘胸膜光滑,支气管气相征早期明显,且动态支气管气征较多 | 3 |
| C4 | 检查区域实质回声相对均一,类似肝脏回声(肝样变),肺组织容积明显减少,胸水量少,早期呈静态支气管征,后期减少或无支气管征 | 3 |
表1 各区域肺部超声病理生理模式
Tab.1 Lung ultrasound pathophysiological patterns in each region
| 定义 | 肺部超声病理生理模式定义 | MLUS (分) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 检查区域胸膜正常+A线 | 0 |
| A1 | 检查区域胸膜滑动征消失+A线,可见“肺点” | NM |
| B1 | 检查区域3根以上少量B线 | 1 |
| B2 | 检查区域多根融合的B线 | 1 |
| C1 | 检查区域胸膜下肺小叶完全失充气,直径0.5 cm~1 cm,即“碎片征” | 3 |
| C2 | 检查区域实质回声混杂不均,大片实变,动态支气管征,胸水较少(液性暗区小于3 cm) | 3 |
| C3 | 检查区域实质回声相对均一,肺组织容积减少,大量胸水压迫,不张肺组织呈“水母征”,外缘胸膜光滑,支气管气相征早期明显,且动态支气管气征较多 | 3 |
| C4 | 检查区域实质回声相对均一,类似肝脏回声(肝样变),肺组织容积明显减少,胸水量少,早期呈静态支气管征,后期减少或无支气管征 | 3 |
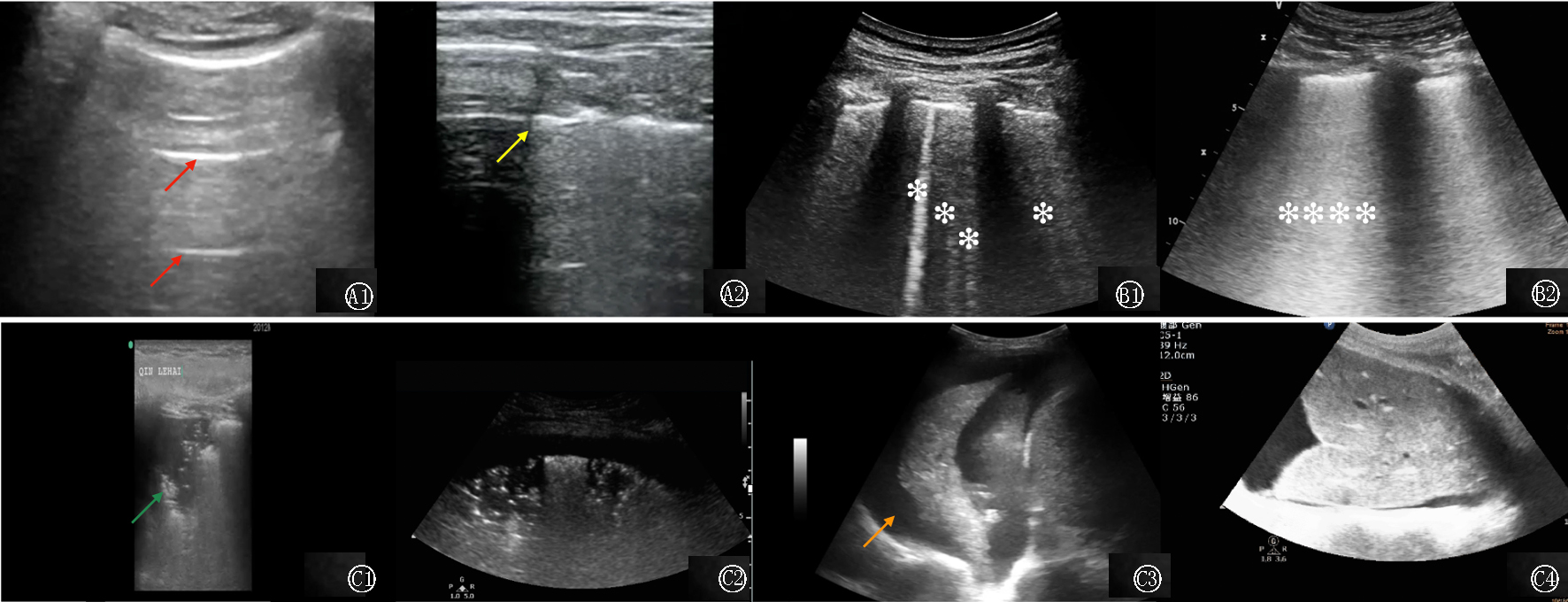
图1 不同肺部超声模式 红色箭头显示高回声的A线,黄色箭头显示“肺点”提示气胸,绿色箭头显示“碎片征”,橙色箭头显示“水母征”提示胸腔积液;单片雪花形成的孤立高回声垂直线B线; 雪花聚集形成的融合的高回声垂直的B线
Fig.1 Different lung ultrasound patterns The red arrows presented A-lines(hyperechoic horizontal line); The yellow arrow presented “lung point” indicating pneumothorax; The green arrow presented “fragment sign”; The orange arrow presented “jellyfish sign” indicating pleural effusion; Presented B1-lines (isolated hyperechoic vertical line, marked by snowflake), Presented B2-lines(coalescent hyperechoic vertical line, marked by snowflakes)
| 指标 | 总体( | 生存组( | 死亡组( | 统计值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 57.5±15.2 | 56.02±14.43 | 62.08±16.75 | 0.032 | |
| 性别[例(%)] | |||||
| 男性 女性 | 103(66.5) 52(33.5) | 79(67.52) 38(32.48) | 24(63.16) 14(36.84) | χ2=0.245 | 0.621 |
| 体温(℃) | 37.6±0.9 | 37.6±0.95 | 37.48±0.82 | 0.465 | |
| 心率(次/min) | 115.00±24.00 | 112.8±24.43 | 119.6±21.85 | 0.130 | |
| MAAP(mmHg) | 70.3±12.0 | 70.81±11.66 | 68.61±11.35 | 0.309 | |
| 血氧饱和度(%) | 96.7±3.5 | 96.82±3.58 | 96.42±3.26 | 0.542 | |
| 呼吸频率 (次/min) | 24.4±4.6 | 24.1±4.33 | 25.42±5.22 | 0.124 | |
| 乳酸(mmol/L) | 2.0(1.5, 2.6) | 1.9(1.4, 2.3) | 2.5(1.8, 3) | 0.006 | |
| 氧合指数 | 221.25(149.8, 288.29) | 224(153.75, 279.75) | 204.665(121, 309) | 0.294 | |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 11.17(7.42, 14.34) | 10.57(7.42, 13.64) | 11.935(8.32, 17.09) | 0.054 | |
| C-反应蛋白(mg/L) | 79.0(16.2, 137) | 72(10.2, 137) | 94.9(39, 140) | 0.079 | |
| 白细胞介素6(ng/L) | 64.0(18.77, 164.0) | 61.08(39.34, 109.4) | 93(48, 306.3) | 0.022 | |
| 降钙素原(μg/L) | 1.16(0.26, 8.4) | 0.81(0.17, 3.9) | 6.59(0.78, 12.1) | 0.008 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ评分(分) | 25.1±6.5 | 23.69±6.04 | 29.26±6.34 | <0.01 | |
| SOFA评分(分) | 10.1±4.0 | 9.48±3.9 | 11.82±3.94 | 0.002 | |
| 合并高血压[例(%)] | |||||
| 是 否 | 58(37.4) 97(62.6) | 43(36.7) 74(63.2) | 15(39.5) 23(60.5) | χ2=0.091 | 0.763 |
| 合并糖尿病[例(%)] | |||||
| 是 否 | 30(19.4) 125(80.6) | 19(16.2) 98(83.8) | 11(28.9) 27(71.1) | χ2=2.968 | 0.085 |
| 主要感染部位[例(%)] | |||||
| 肺部 | 93(60.0) | 76(64.9) | 17(44.7) | ||
| 腹部 | 50(32.3) | 31(26.5) | 19(50.0) | ||
| 颈部脓肿 | 4(2.6) | 4(3.4) | 0 | - | 0.079 |
| 泌尿系 | 4(2.6) | 3(2.6) | 1(2.6) | ||
| 肛周脓肿 | 2(1.3) | 1(0.9) | 1(2.6) | ||
| 血源性 | 2(1.3) | 2(1.7) | 0 | ||
| NE[μg/(kg·min)] | 0.19(0.10, 0.46) | 0.05(0, 0.15714) | 0.344155(0.18182, 0.8) | <0.01 | |
| MLUS(分) | 16.88±8.38 | 16.06±7.81 | 19.39±9.64 | 0.032 | |
| 间质性失充气模式[例(%)] | |||||
| 否 是 | 98(63.2) 57(36.8) | 79(67.5) 38(32.5) | 19(50.0) 19(50.0) | χ2=3.7874 | 0.052 |
| 不张性失充气模式[例(%)] | |||||
| 否 是 | 111(71.6) 44(28.4) | 83(70.9) 34(29.1) | 28(73.7) 10(26.3) | χ2=0.1062 | 0.742 |
| 实变性失充气模式[例(%)] | |||||
| 否 是 | 57(36.8) 98(63.2) | 46(39.3) 71(60.7) | 11(28.9) 27(71.1) | χ2=1.326 | 0.250 |
| 住院时间(d) | 23(14, 38) | 26(16, 44) | 14.5(8, 29) | 0.001 | |
| ICU住院时间(d) | 16(8, 29) | 17(9, 33) | 13(7, 24) | 0.050 | |
| 机械通气时间(h) | 241(114, 472.29) | 227(97, 443.65) | 305(183.53, 572.07) | 0.026 |
表2 两组临床资料比较
Tab.2 Comparison of clinical data between the two groups
| 指标 | 总体( | 生存组( | 死亡组( | 统计值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 57.5±15.2 | 56.02±14.43 | 62.08±16.75 | 0.032 | |
| 性别[例(%)] | |||||
| 男性 女性 | 103(66.5) 52(33.5) | 79(67.52) 38(32.48) | 24(63.16) 14(36.84) | χ2=0.245 | 0.621 |
| 体温(℃) | 37.6±0.9 | 37.6±0.95 | 37.48±0.82 | 0.465 | |
| 心率(次/min) | 115.00±24.00 | 112.8±24.43 | 119.6±21.85 | 0.130 | |
| MAAP(mmHg) | 70.3±12.0 | 70.81±11.66 | 68.61±11.35 | 0.309 | |
| 血氧饱和度(%) | 96.7±3.5 | 96.82±3.58 | 96.42±3.26 | 0.542 | |
| 呼吸频率 (次/min) | 24.4±4.6 | 24.1±4.33 | 25.42±5.22 | 0.124 | |
| 乳酸(mmol/L) | 2.0(1.5, 2.6) | 1.9(1.4, 2.3) | 2.5(1.8, 3) | 0.006 | |
| 氧合指数 | 221.25(149.8, 288.29) | 224(153.75, 279.75) | 204.665(121, 309) | 0.294 | |
| 白细胞计数(×109/L) | 11.17(7.42, 14.34) | 10.57(7.42, 13.64) | 11.935(8.32, 17.09) | 0.054 | |
| C-反应蛋白(mg/L) | 79.0(16.2, 137) | 72(10.2, 137) | 94.9(39, 140) | 0.079 | |
| 白细胞介素6(ng/L) | 64.0(18.77, 164.0) | 61.08(39.34, 109.4) | 93(48, 306.3) | 0.022 | |
| 降钙素原(μg/L) | 1.16(0.26, 8.4) | 0.81(0.17, 3.9) | 6.59(0.78, 12.1) | 0.008 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ评分(分) | 25.1±6.5 | 23.69±6.04 | 29.26±6.34 | <0.01 | |
| SOFA评分(分) | 10.1±4.0 | 9.48±3.9 | 11.82±3.94 | 0.002 | |
| 合并高血压[例(%)] | |||||
| 是 否 | 58(37.4) 97(62.6) | 43(36.7) 74(63.2) | 15(39.5) 23(60.5) | χ2=0.091 | 0.763 |
| 合并糖尿病[例(%)] | |||||
| 是 否 | 30(19.4) 125(80.6) | 19(16.2) 98(83.8) | 11(28.9) 27(71.1) | χ2=2.968 | 0.085 |
| 主要感染部位[例(%)] | |||||
| 肺部 | 93(60.0) | 76(64.9) | 17(44.7) | ||
| 腹部 | 50(32.3) | 31(26.5) | 19(50.0) | ||
| 颈部脓肿 | 4(2.6) | 4(3.4) | 0 | - | 0.079 |
| 泌尿系 | 4(2.6) | 3(2.6) | 1(2.6) | ||
| 肛周脓肿 | 2(1.3) | 1(0.9) | 1(2.6) | ||
| 血源性 | 2(1.3) | 2(1.7) | 0 | ||
| NE[μg/(kg·min)] | 0.19(0.10, 0.46) | 0.05(0, 0.15714) | 0.344155(0.18182, 0.8) | <0.01 | |
| MLUS(分) | 16.88±8.38 | 16.06±7.81 | 19.39±9.64 | 0.032 | |
| 间质性失充气模式[例(%)] | |||||
| 否 是 | 98(63.2) 57(36.8) | 79(67.5) 38(32.5) | 19(50.0) 19(50.0) | χ2=3.7874 | 0.052 |
| 不张性失充气模式[例(%)] | |||||
| 否 是 | 111(71.6) 44(28.4) | 83(70.9) 34(29.1) | 28(73.7) 10(26.3) | χ2=0.1062 | 0.742 |
| 实变性失充气模式[例(%)] | |||||
| 否 是 | 57(36.8) 98(63.2) | 46(39.3) 71(60.7) | 11(28.9) 27(71.1) | χ2=1.326 | 0.250 |
| 住院时间(d) | 23(14, 38) | 26(16, 44) | 14.5(8, 29) | 0.001 | |
| ICU住院时间(d) | 16(8, 29) | 17(9, 33) | 13(7, 24) | 0.050 | |
| 机械通气时间(h) | 241(114, 472.29) | 227(97, 443.65) | 305(183.53, 572.07) | 0.026 |
| 因素 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 1.021 | 0.996, 1.047 | 0.094 | |
| 乳酸 | 0.934 | 0.444, 1.963 | 0.857 | |
| 氧合指数 | 0.801 | 0.531, 1.206 | 0.288 | |
| 白细胞介素6 | 1.374 | 1.17, 1.614 | 0.000 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ评分 | 1.000 | 0.996, 1.004 | 0.960 | |
| SOFA评分 | 1.055 | 1.018, 1.093 | 0.003 | |
| 是否应用血管活性药物 | 是 vs 否 | 1.002 | 0.998, 1.006 | 0.309 |
| MLUS | 1.000 | 0.999, 1.001 | 0.767 | |
| 间质性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.019 | 1.001, 1.038 | 0.042 |
| 不张性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.111 | 1.057, 1.167 | <0.01 |
| 实变性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.148 | 1.06, 1.243 | 0.001 |
| 机械通气时间 | 3.324 | 1.271, 8.694 | 0.014 | |
| 重力依赖失充气 | 是 vs 否 | 2.665 | 1.26, 4.768 | 0.008 |
表3 影响脓毒症机械通气患者28 d预后的单因素COX比例风险分析
Tab.3 Univariate COX proportional risk analysis of 28-day prognosis in sepsis patients requiring mechanical ventilation
| 因素 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 1.021 | 0.996, 1.047 | 0.094 | |
| 乳酸 | 0.934 | 0.444, 1.963 | 0.857 | |
| 氧合指数 | 0.801 | 0.531, 1.206 | 0.288 | |
| 白细胞介素6 | 1.374 | 1.17, 1.614 | 0.000 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ评分 | 1.000 | 0.996, 1.004 | 0.960 | |
| SOFA评分 | 1.055 | 1.018, 1.093 | 0.003 | |
| 是否应用血管活性药物 | 是 vs 否 | 1.002 | 0.998, 1.006 | 0.309 |
| MLUS | 1.000 | 0.999, 1.001 | 0.767 | |
| 间质性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.019 | 1.001, 1.038 | 0.042 |
| 不张性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.111 | 1.057, 1.167 | <0.01 |
| 实变性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.148 | 1.06, 1.243 | 0.001 |
| 机械通气时间 | 3.324 | 1.271, 8.694 | 0.014 | |
| 重力依赖失充气 | 是 vs 否 | 2.665 | 1.26, 4.768 | 0.008 |
| 因素 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.968 | 0.933, 1.005 | 0.086 | |
| 乳酸 | 0.841 | 0.345, 2.05 | 0.703 | |
| 氧合指数 | 0.496 | 0.267, 0.924 | 0.027 | |
| 白细胞介素6 | 1.500 | 1.117, 2.016 | 0.007 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ评分 | 1.007 | 1.001, 1.014 | 0.035 | |
| SOFA评分 | 1.027 | 0.974, 1.083 | 0.320 | |
| 间质性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 0.998 | 0.964, 1.033 | 0.910 |
| 不张性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.147 | 1.053, 1.249 | 0.002 |
| 实变性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.146 | 0.995, 1.321 | 0.059 |
| 机械通气时间 | 1.616 | 0.431, 6.058 | 0.476 | |
| 重力依赖性失充气 | 是 vs 否 | 2.003 | 1.112, 6.387 | 0.028 |
表4 影响脓毒症机械通气患者28 d预后的多因素COX比例风分析
Tab.4 Multivariate COX proportional risk analysis of 28-day prognosis in sepsis patients requiring mechanical ventilation
| 因素 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.968 | 0.933, 1.005 | 0.086 | |
| 乳酸 | 0.841 | 0.345, 2.05 | 0.703 | |
| 氧合指数 | 0.496 | 0.267, 0.924 | 0.027 | |
| 白细胞介素6 | 1.500 | 1.117, 2.016 | 0.007 | |
| APACHE Ⅱ评分 | 1.007 | 1.001, 1.014 | 0.035 | |
| SOFA评分 | 1.027 | 0.974, 1.083 | 0.320 | |
| 间质性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 0.998 | 0.964, 1.033 | 0.910 |
| 不张性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.147 | 1.053, 1.249 | 0.002 |
| 实变性失充气模式 | 是 vs 否 | 1.146 | 0.995, 1.321 | 0.059 |
| 机械通气时间 | 1.616 | 0.431, 6.058 | 0.476 | |
| 重力依赖性失充气 | 是 vs 否 | 2.003 | 1.112, 6.387 | 0.028 |
| [1] |
Gorman EA, O'Kane CM, McAuley DF. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults: Diagnosis, outcomes, long-term sequelae, and management[J]. Lancet, 2022, 400(10358):1157-1170.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01439-8 pmid: 36070788 |
| [2] | Joffre J, Hellman J, Ince C, et al. Endothelial responses in sepsis[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2020, 202(3):361-370. |
| [3] | Bode C, Weis S, Sauer A, et al. Targeting the host response in sepsis: Current approaches and future evidence[J]. Crit Care, 2023, 27(1):478. |
| [4] | Buda N, Mendrala K, Skoczyński S, et al. Basics of Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasonography[J]. N Engl J Med, 2023, 389(21):e44. |
| [5] | Guérin C, Reignier J, Richard JC, et al. Prone positioning in severe acute respiratory distress syndrome[J]. N Engl J Med, 2013, 368(23):2159-2168. |
| [6] |
Papazian L, Schmidt M, Hajage D, et al. Effect of prone positioning on survival in adult patients receiving venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2022, 48(3):270-280.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06604-x pmid: 35037993 |
| [7] | Wang Q, Zhu J, Chen L, et al. Successful treatment of severe ARDS caused by accidental inhalation of nitric acid fumes with veno-venous ECMO: A case report and literature review[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2022, 101(30):e29447. |
| [8] | Haaksma ME, Smit JM, Heldeweg MLA, et al. Extended lung ultrasound to differentiate between pneumonia and atelectasis in critically ill patients: A diagnostic accuracy study[J]. Crit Care Med, 2022, 50(5):750-759. |
| [9] | Smit MR, Hagens LA, Heijnen NFL, et al. Lung ultrasound prediction model for acute respiratory distress syndrome: A multicenter prospective observational study[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2023, 207(12):1591-1601. |
| [10] |
Dargent A, Chatelain E, Si-Mohamed S, et al. Lung ultrasound score as a tool to monitor disease progression and detect ventilator-associated pneumonia during COVID-19-associated ARDS[J]. Heart Lung, 2021, 50(5):700-705.
doi: 10.1016/j.hrtlng.2021.05.003 pmid: 34107394 |
| [11] |
Costamagna A, Pivetta E, Goffi A, et al. Clinical performance of lung ultrasound in predicting ARDS morphology[J]. Ann Intensive Care, 2021, 11(1):51.
doi: 10.1186/s13613-021-00837-1 pmid: 33779834 |
| [12] | Smit JM, Haaksma ME, Winkler MH, et al. Lung ultrasound in a tertiary intensive care unit population: A diagnostic accuracy study[J]. Crit Care, 2021, 25(1):339. |
| [13] |
Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2021, 47(11):1181-1247.
doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y pmid: 34599691 |
| [14] |
Chiumello D, Mongodi S, Algieri I, et al. Assessment of lung aeration and recruitment by CT scan and ultrasound in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients[J]. Crit Care Med, 2018, 46(11):1761-1768.
doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003340 pmid: 30048331 |
| [15] |
Wang Y, Shen Z, Lu X, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of ultrasound for the diagnosis of acute pulmonary edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Med Ultrason, 2018, 1(1):32-36.
doi: 10.11152/mu-1223 pmid: 29400365 |
| [16] |
Yin W, Zou T, Qin Y, et al. Poor lung ultrasound score in shock patients admitted to the ICU is associated with worse outcome[J]. BMC Pulm Med, 2019, 19(1):1.
doi: 10.1186/s12890-018-0755-9 pmid: 30606165 |
| [17] |
Zou T, Yin W, Diddams M, et al. The global and regional lung ultrasound score can accurately evaluate the severity of lung disease in critically ill patients[J]. J Ultrasound Med, 2020, 39(9):1879-1880.
doi: 10.1002/jum.15278 pmid: 32302014 |
| [18] | 曾学英, 尹万红, 邹同娟, 等. 机械通气的休克患者肺部非重力依赖区超声评分与不良预后的相关性研究[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2019, 50(6):798-802. |
| [19] | Zou T, Yin W, Kang Y. Application of critical care ultrasound in patients with COVID-19: Our experience and perspective[J]. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control, 2020, 67(11):2197-2206. |
| [20] | Zochios V, Yusuff H, Schmidt M, et al. Acute right ventricular injury phenotyping in ARDS[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2023, 49(1):99-102. |
| [1] | 庞樱容, 孙欣. sST2在心血管疾病中作用的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(5): 460-465. |
| [2] | 宋梦姣, 王睿琪, 曹灿, 程光森, 刘羽, 李忠亮, 杨建豪. 血尿酸与首次急性缺血性脑卒中患者TOAST分型及预后的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(3): 216-221. |
| [3] | 赵旭辉, 黄小敏, 达德转, 许焱, 崔晓东, 李红玲. 基于生物信息学筛选影响胃癌患者预后的糖酵解相关基因[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 20-29. |
| [4] | 黄赛虎, 龙中洁, 董兴强, 孟祥营, 吴水燕, 柏振江. 血液肿瘤患儿合并脓毒血症的病原学特点及临床特征[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 38-42. |
| [5] | 刘丽丽, 袁宇婷, 赖耿良, 田川, 蓝翔, 叶中绿. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病第15天微小残留与预后的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 47-52. |
| [6] | 崔兰丹, 杨春燕. 脓毒症患者甲状腺激素的变化特点及研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 70-74. |
| [7] | 王涛, 高玉伟, 王兴华, 胡秀红, 崔红蕊, 徐保振, 杨洪娟. 抗磷脂酶A2受体抗体与特发性膜性肾病的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 606-612. |
| [8] | 高秦宇, 包蓓艳, 金燕, 赵宇. IgA肾病合并抑郁状态患者的临床特征和预后影响因素分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 510-515. |
| [9] | 孙星星, 林海. 儿童重症肺炎的免疫功能变化及预后危险因素[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 521-525. |
| [10] | 贺翔渝, 潘燕, 张小林. 血清脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平与急性缺血性脑卒中病情及预后的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 315-318. |
| [11] | 杨金强, 张仁敏. 降钙素原与血小板比值评估发热伴血小板减少综合征预后的价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 346-351. |
| [12] | 唐爱军, 汪丽韡. 脓毒症患者入院时血小板计数及凝血指标对28天生存状况的预测价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(3): 250-254. |
| [13] | 张娜, 孙越, 董晗, 赵鹏, 杨昕, 祁源, 王玲玲. SPARC表达水平与非小细胞肺癌患者预后关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(11): 972-978. |
| [14] | 周利娟, 诸彭伟, 曹梅, 程真梅, 吴峤微, 李勇. 铁蛋白、红细胞参数及血浆D-二聚体与儿童脓毒症的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(1): 60-63. |
| [15] | 王会新, 赵芳晴, 张馨妍, 侯晓雯. 中国人尿酸水平与急性缺血性脑卒中患者预后关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(9): 785-790. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||