

临床荟萃 ›› 2024, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 20-29.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2024.01.003
赵旭辉1, 黄小敏1, 达德转2, 许焱1, 崔晓东1, 李红玲2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-06-17
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2024-03-22
通讯作者:
李红玲,Email: lihongling1969@126.com
基金资助:
Zhao Xuhui1, Huang Xiaomin1, Da Dezhuan2, Xu Yan1, Cui Xiaodong1, Li Hongling2( )
)
Received:2023-06-17
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2024-03-22
摘要:
目的 通过利用生物信息学开发糖酵解相关基因以预测胃癌(gastric cancer, GC)患者预后。方法 使用癌症基因组图谱数据库中GC患者信使核糖核酸表达谱数据, 通过进行基因集富集分析以鉴定GC组织和正常组织间显著差异的基因集。通过最小绝对收缩和选择算子回归分析构建糖酵解相关基因预测GC患者预后的模型,并使用 Kaplan-Meier 分析、受试者工作特征曲线、单因素及多因素 Cox 回归分析验证模型预测性能。采用基因集变异分析分析高低风险组间生物途径状态的差异。结果 获得15个糖酵解相关基因(PFKFB2、UHRF1、ACYP1、CLDN9、STC1、EFNA3、NUP50、ADH4、ANGPTL4、PKP2、VCAN、HIF 1A、LHX9、ANKZF1、ALDH3A2)与GC患者预后相关。根据15个基因特征风险评分,通过Cox回归分析将患者分为高风险组和低风险组。这15个基因标记是GC患者预后的独立生物标志物,低风险评分的GC患者预后更好。结合基因标记和临床预后因素的列线图可有效预测总生存期及无疾病生存期。结论 建立的15个糖酵解相关基因标记可作为预测GC患者预后的可靠工具,可能为GC提供潜在的糖酵解治疗靶点。
中图分类号:
赵旭辉, 黄小敏, 达德转, 许焱, 崔晓东, 李红玲. 基于生物信息学筛选影响胃癌患者预后的糖酵解相关基因[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 20-29.
Zhao Xuhui, Huang Xiaomin, Da Dezhuan, Xu Yan, Cui Xiaodong, Li Hongling. Screening of glycolysis-related genes for predicting the prognosis of patients with gastric cancer: Based on bioinformatics[J]. Clinical Focus, 2024, 39(1): 20-29.
| 序号 | 基因 | 离散系数 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.0962952004774155 | |
| 2 | -0.129632577184322 | |
| 3 | -0.0519404248232357 | |
| 4 | 0.239072070967019 | |
| 5 | 0.147337518442243 | |
| 6 | -0.0836373085400017 | |
| 7 | -0.0370752619271387 | |
| 8 | 0.121593689211912 | |
| 9 | 0.0135857127689336 | |
| 10 | -0.0113107594377815 | |
| 11 | 0.0872242032080347 | |
| 12 | 0.114552783094288 | |
| 13 | 0.891795946885758 | |
| 14 | -0.0217432055166958 | |
| 15 | -0.093175891304856 |
表1 通过LASSO回归分析得到与GC患者预后相关的15个糖酵解相关基因
Tab.1 Screened 15 glycolysis-related genes for predicting the prognosis of GC patients using LASSO regression analysis
| 序号 | 基因 | 离散系数 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -0.0962952004774155 | |
| 2 | -0.129632577184322 | |
| 3 | -0.0519404248232357 | |
| 4 | 0.239072070967019 | |
| 5 | 0.147337518442243 | |
| 6 | -0.0836373085400017 | |
| 7 | -0.0370752619271387 | |
| 8 | 0.121593689211912 | |
| 9 | 0.0135857127689336 | |
| 10 | -0.0113107594377815 | |
| 11 | 0.0872242032080347 | |
| 12 | 0.114552783094288 | |
| 13 | 0.891795946885758 | |
| 14 | -0.0217432055166958 | |
| 15 | -0.093175891304856 |
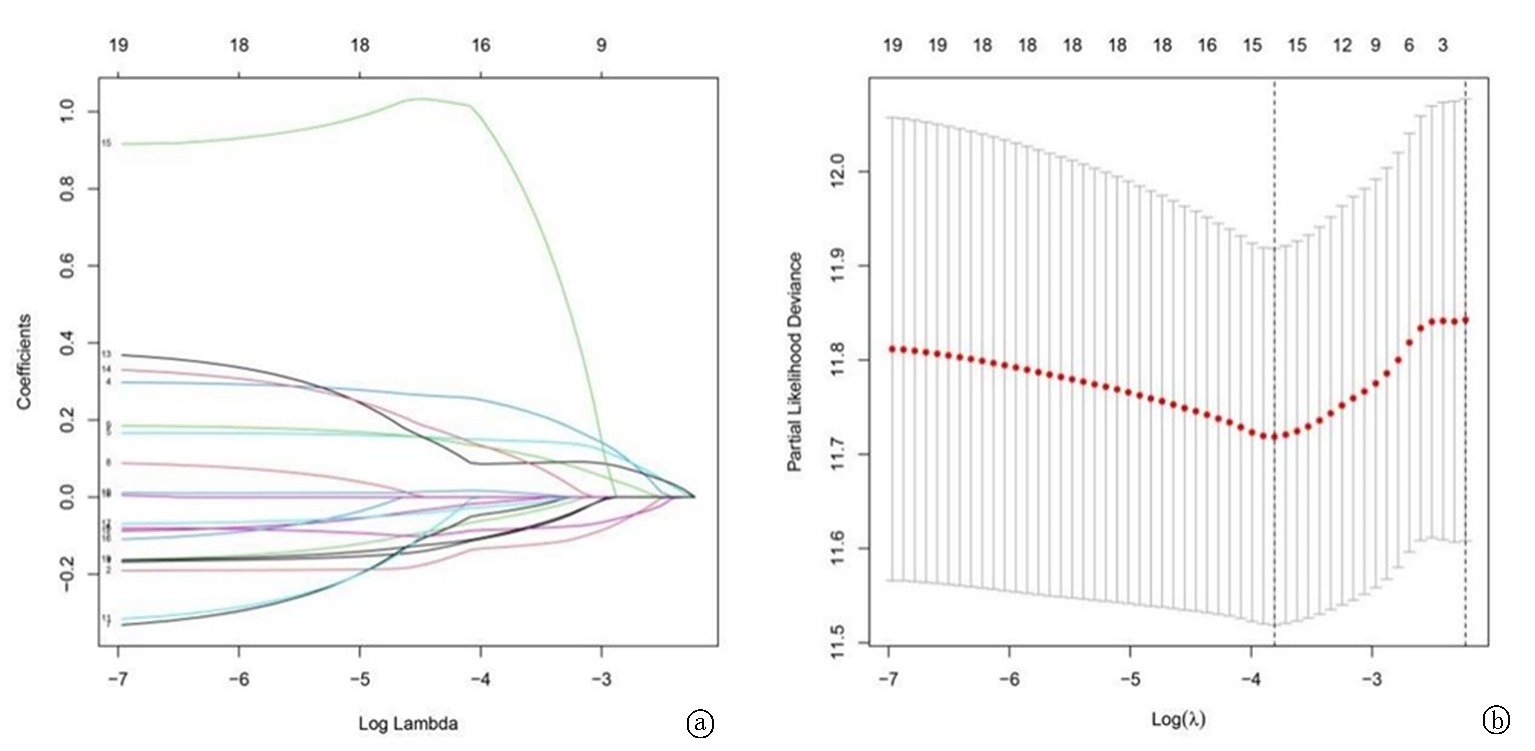
图2 用于构建最终预测模型的 LASSO 回归分析 a.选择LASSO模型中的最优参数(λ);使用最小标准在最佳值绘制垂直虚线; b. LASSO 分布的部分似然偏差
Fig. 2 LASSO regression analysis for construction of the final prediction model a.Determine the optimal parameter(λ) for the LASSO model; plot a vertical dashed line at the optimal value using the minimum criterion; b.Partial likelihood deviance of the LASSO distribution

图5 基于糖酵解和临床因素的列线图 a.包含年龄和风险评分的列线图,以预测1年、3年和5年的OS; b.列线图的校准图; c.风险、列线图和其他临床特征的ROC曲线
Fig.5 Nomogram considering glycolysis and clinical factors a.Nomogram illustrating age and risk score for predicting 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year OS; b.Colibration plot of nomogram; c.ROC curves of risk, nomogram and other clinical features

图6 临床特征的单因素、多因素分析及ROC曲线 a.单变量分析; b.多变量分析; c.ROC曲线
Fig.6 Univariate and multivariate analysis and ROC cure for clinical characteristics a.Univariate analysis; b.Multivariate analysis; c.ROC curve
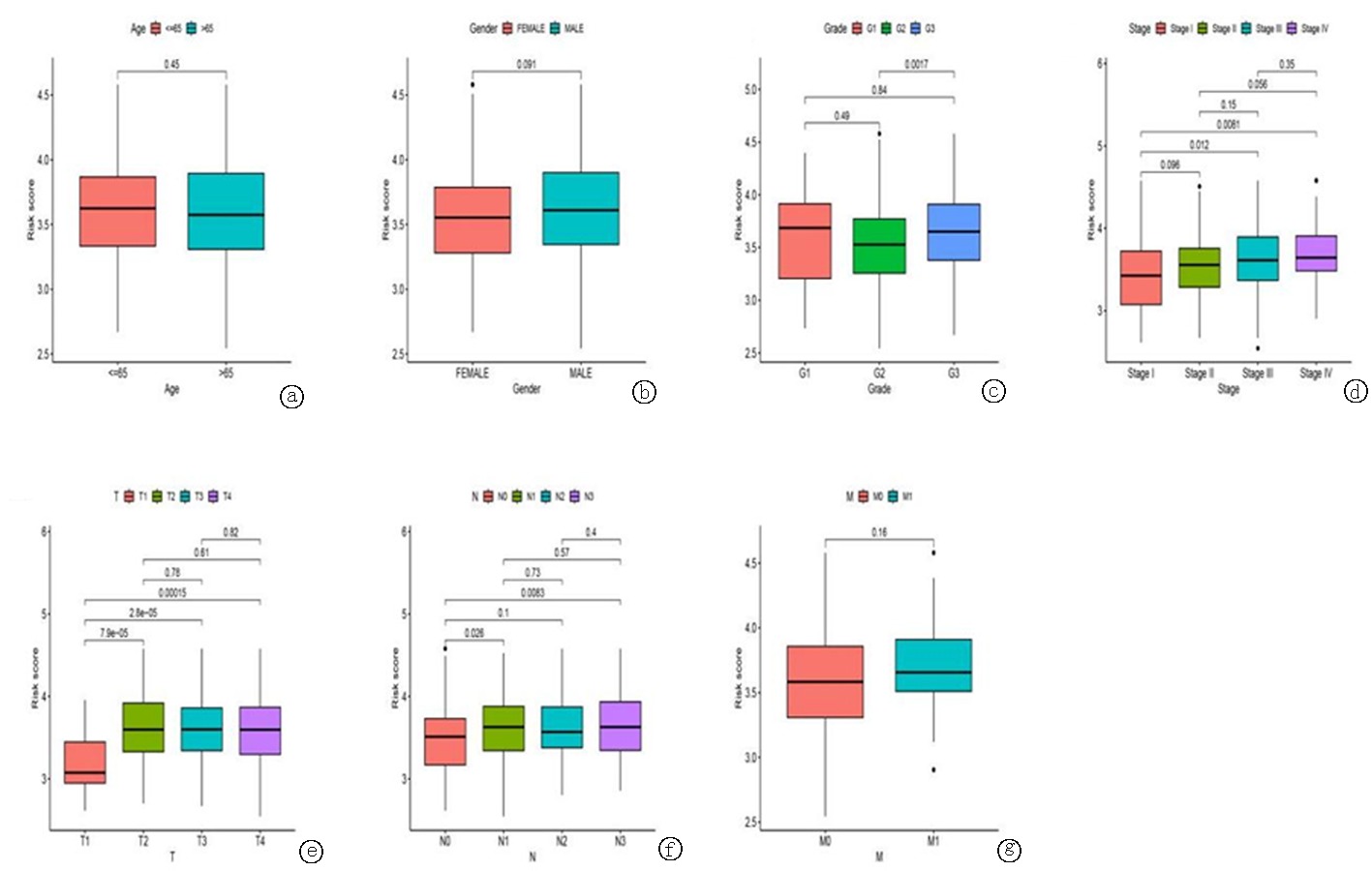
图7 基于糖酵解相关基因的临床相关性分析 a.年龄; b.性别; c.分级; d.分期; e-g.TNM分期
Fig.7 Correlation analysis based on glycolysis-related genes a.Age; b.Gender; c.Grade; d.staging; e-g.TNM staging
| [1] |
Thrift AP, El-Serag HB. Burden of gastric cancer[J]. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2020, 18(3):534-542.
doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.07.045 URL |
| [2] |
Sexton RE, Al Hallak MN, Diab M, et al. Gastric cancer: A comprehensive review of current and future treatment strategies[J]. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 2020, 39(4):1179-1203.
doi: 10.1007/s10555-020-09925-3 |
| [3] |
Kang YK, Boku N, Satoh T, et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial[J]. Lancet, 2017, 390(10111):2461-2471.
doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31827-5 URL |
| [4] | Kang JH, Lee SI, Lim DH, et al. Salvage chemotherapy for pretreated gastric cancer: A randomized phase III trial comparing chemotherapy plus best supportive care with best supportive care alone[J]. Clin Oncol, 2012, 30(13):1513-1518. |
| [5] |
Chen LT, Satoh T, Ryu MH, et al. A phase 3 study of nivolumab in previously treated advanced gastric or gastroesophageal junction cancer (ATTRACTION-2): 2-year update data[J]. Gastric Cancer, 2020, 23(3):510-519.
doi: 10.1007/s10120-019-01034-7 |
| [6] |
Muro K, Chung HC, Shankaran V, et al. Pembrolizumab for patients with PD-L1-positive advanced gastric cancer (KEYNOTE-012): A multicentre, open-label, phase 1b trial[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2016, 17(6):717-726.
doi: S1470-2045(16)00175-3 pmid: 27157491 |
| [7] |
Vaupel P, Schmidberger H, Mayer A. The Warburg effect: Essential part of metabolic reprogramming and central contributor to cancer progression[J]. Int J Radiat Biol, 2019, 95(7):912-919.
doi: 10.1080/09553002.2019.1589653 pmid: 30822194 |
| [8] |
Dhup S, Dadhich RK, Porporato PE, et al. Multiple biological activities of lactic acid in cancer: Influences on tumor growth, angiogenesis and metastasis[J]. Curr Pharm Des, 2012, 18(10):1319-1330.
doi: 10.2174/138161212799504902 URL |
| [9] |
Hu H, Juvekar A, Lyssiotis CA, et al. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates glycolysis through mobilization of aldolase from the actin cytoskeleton[J]. Cell, 2016, 164(3):433-446.
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.12.042 pmid: 26824656 |
| [10] | Massari F, Ciccarese C, Santoni M, et al. Metabolic phenotype of bladder cancer[J]. Cancer Treat Rev, 2016,45:46-57. |
| [11] | Lv Z, Qi L, Hu X, et al. Identification of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature correlates with the prognosis and therapeutic responses in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma[J]. Front Oncol, 2021,11:633950. |
| [12] |
Liu C, Li Y, Wei M, et al. Identification of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature that can predict the survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Cell Cycle, 2019, 18(5):568-579.
doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1578146 pmid: 30727821 |
| [13] | Jiang L, Zhao L, Bi J, et al. Glycolysis gene expression profilings screen for prognostic risk signature of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(23):10861-10882. |
| [14] |
Ruan Y, Tang Q, Qiao J, et al. Identification of a novel glycolysis-related prognosis risk signature in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2023, 13:1171496.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1171496 URL |
| [15] |
He M, Hu C, Deng J, et al. Identification and validation of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis and therapeutic response in triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Adv Ther, 2023, 40: 310-330.
doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02330-y |
| [16] |
Yu J, Liu TT, Liang LL, et al. Identification and validation of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis in ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2021, 21: 353.
doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02045-0 pmid: 34229669 |
| [17] |
Zhu J, Wang S, Bai H, et al. Identification of a novel glycolysis-related gene signature for predicting the survival of patients with colon adenocarcinoma[J]. Scand J Gastroenterol, 2022, 57(2):214-221.
doi: 10.1080/00365521.2021.1989026 URL |
| [18] |
Yu S, Hu C, Cai L, et al. Seven-gene signature based on glycolysis is closely related to the prognosis and tumor immune infiltration of patients with gastric cancer[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10:1778.
doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01778 pmid: 33072557 |
| [19] |
Liu Y, Wu M, Cao J, et al. Identification and verification of a glycolysis-related gene signature for gastric cancer[J]. Ann Transl Med, 2022, 10: 1010.
doi: 10.21037/atm-22-3980 pmid: 36267782 |
| [20] | 陈艳昕, 刘庆滨, 黄江梅, 等. 葡萄糖转运蛋白1在胃癌的表达及临床病理意义[J]. 临床荟萃, 2012, 27(8):694-695. |
| [21] |
Nehring H, Meierjohann S, Friedmann Angeli JP. Emerging aspects in the regulation of ferroptosis[J]. Biochem Soc Trans, 2020, 48(5):2253-2259.
doi: 10.1042/BST20200523 URL |
| [22] |
Vaupel P, Multhoff G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: Historical dogma versus current understanding[J]. J Physiol, 2021, 599(6):1745-1757.
doi: 10.1113/tjp.v599.6 URL |
| [23] | Hu Q, Qin Y, Ji S, et al. UHRF1 promotes aerobic glycolysis and proliferation via suppression of SIRT4 in pancreatic cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2019,452:226-236. |
| [24] |
Zhao S, Guan B, Mi Y, et al. LncRNA MIR17HG promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by mediating a glycolysis-associated positive feedback circuit[J]. Oncogene, 2021, 40(28):4709-4724.
doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01859-6 pmid: 34145399 |
| [25] |
Cai L, Ye Y, Jiang Q, et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART1 induces tumour metastasis by regulating PTEN-dependent pathways in nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6: 7353.
doi: 10.1038/ncomms8353 pmid: 26135619 |
| [26] |
Iizasa H, Kim H, Kartika AV, et al. Corrigendum: Role of viral and host microRNAs in immune regulation of Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 498.
doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00498 pmid: 32318060 |
| [27] | 程燕妮, 刘佳, 袁野, 等. 丙酮酸激酶M2型在恶性肿瘤中的表达及其临床检测研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(3):279-284. |
| [1] | 刘丽丽, 袁宇婷, 赖耿良, 田川, 蓝翔, 叶中绿. 儿童急性淋巴细胞白血病第15天微小残留与预后的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 47-52. |
| [2] | 崔兰丹, 杨春燕. 脓毒症患者甲状腺激素的变化特点及研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2024, 39(1): 70-74. |
| [3] | 吕畅, 周利明. TNF-α-308基因多态性与胃癌易感相关性的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(9): 779-787. |
| [4] | 王涛, 高玉伟, 王兴华, 胡秀红, 崔红蕊, 徐保振, 杨洪娟. 抗磷脂酶A2受体抗体与特发性膜性肾病的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(7): 606-612. |
| [5] | 高秦宇, 包蓓艳, 金燕, 赵宇. IgA肾病合并抑郁状态患者的临床特征和预后影响因素分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 510-515. |
| [6] | 孙星星, 林海. 儿童重症肺炎的免疫功能变化及预后危险因素[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(6): 521-525. |
| [7] | 王英南, 赵琦, 白海威, 武丹娜, 魏金梅, 李省江, 李锐凌, 张瑞星. 胃癌合并脑梗死的临床特点及危险因素分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(5): 417-422. |
| [8] | 贺翔渝, 潘燕, 张小林. 血清脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平与急性缺血性脑卒中病情及预后的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 315-318. |
| [9] | 杨金强, 张仁敏. 降钙素原与血小板比值评估发热伴血小板减少综合征预后的价值[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4): 346-351. |
| [10] | 王军宏, 高振华, 章荣龙, 姬浩民, 赵信科, 达明绪. 1980-2021年胃癌诊断文献相关质量分析——基于Web of Science 数据库的文献计量学分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(12): 1117-1124. |
| [11] | 黄小敏, 赵旭辉, 达德转, 马桃梅, 李红玲. EB病毒感染和程序性死亡受体配体1表达在晚期胃癌免疫靶向治疗中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(11): 1048-1052. |
| [12] | 张娜, 孙越, 董晗, 赵鹏, 杨昕, 祁源, 王玲玲. SPARC表达水平与非小细胞肺癌患者预后关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(11): 972-978. |
| [13] | 王会新, 赵芳晴, 张馨妍, 侯晓雯. 中国人尿酸水平与急性缺血性脑卒中患者预后关系的meta分析[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(9): 785-790. |
| [14] | 邢婷婷, 高俊茶. Presepsin在急性胰腺炎中的研究进展[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(8): 764-768. |
| [15] | 轩晓倩, 赵君慧, 杨小茜. 炎性指标在非小细胞肺癌患者预后中的临床意义[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(7): 663-667. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||