Clinical Focus ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 303-310.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.04.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Association between rs1799971 polymorphism in mu opioid receptor 1 gene and susceptibility to alcohol dependence: a meta-analysis
Wang Linglia, Zhao Zhiqiangb, Jin Xinronga( )
)
- a. Department of Psychiatry; b. Department of Addiction Medicine, Xinjiang Mental Health Center, Urumqi 4th People's Hospital, Urumqi 830002, China
-
Received:2020-09-23Online:2021-04-20Published:2021-05-13 -
Contact:Jin Xinrong E-mail:3250783547@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Lingli, Zhao Zhiqiang, Jin Xinrong. Association between rs1799971 polymorphism in mu opioid receptor 1 gene and susceptibility to alcohol dependence: a meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2021, 36(4): 303-310.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2021.04.002
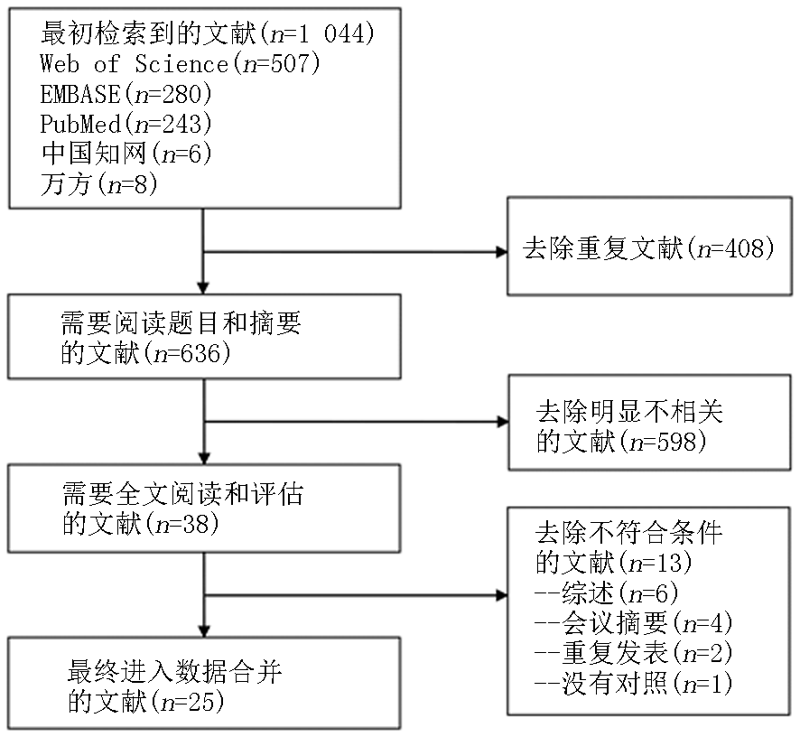
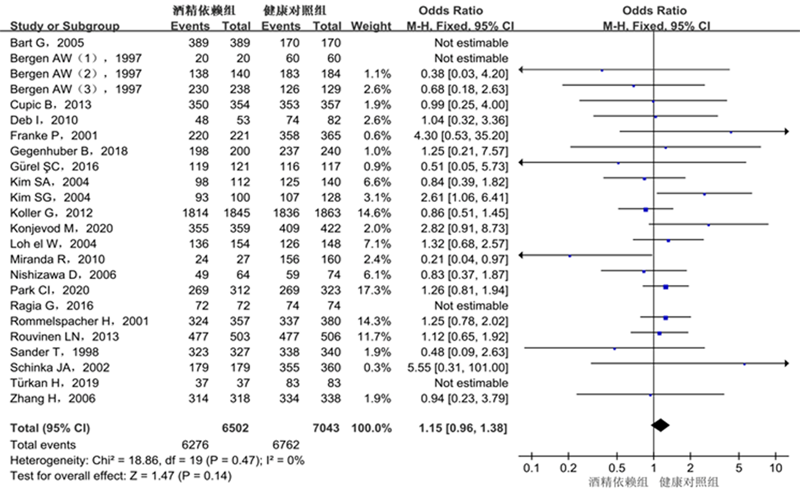
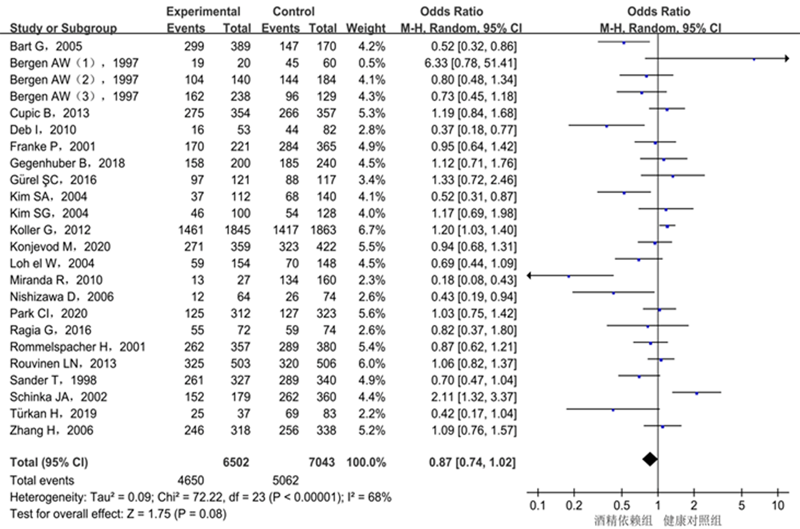
| 作者 | 年份 | 国家 | 种族 | 性别(男:女) 病例组/对照组 | 诊断标准 | 研究类型 | 病例组基因型(例) | 对照组基因型(例) | HWE P值 | NOS评分 (分) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | AG | GG | AA | AG | GG | ||||||||||
| Bergen AW(1)[ | 1997 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 19 | 1 | 0 | 45 | 15 | 0 | 0.269 | 8 | |
| Bergen AW(2)[ | 1997 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 104 | 34 | 2 | 144 | 39 | 1 | 0.340 | 8 | |
| Bergen AW(3)[ | 1997 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 162 | 68 | 8 | 96 | 30 | 3 | 0.290 | 8 | |
| Kim SA[ | 2004 | 韩国 | 亚洲人 | 127:0/185:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 46 | 47 | 7 | 54 | 53 | 21 | 0.202 | 6 | |
| Rommelspacher H[ | 2001 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 282:45/未报道 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 262 | 62 | 33 | 289 | 48 | 43 | 0.001 | 6 | |
| Kim SG[ | 2004 | 韩国 | 亚洲人 | 106:6/80:60 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 37 | 61 | 14 | 68 | 57 | 15 | 0.559 | 5 | |
| Koller G[ | 2012 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 1403:442/ 935:928 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 1461 | 353 | 31 | 1417 | 419 | 27 | 0.528 | 7 | |
| Loh el W[ | 2004 | 中国 | 亚洲人 | 149:9/ 147:2 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 59 | 77 | 18 | 70 | 56 | 22 | 0.061 | 6 | |
| Miranda R[ | 2010 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 9:18/ 89:71 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 134 | 22 | 4 | 0.016 | 8 | |
| Sander T[ | 1998 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 261 | 62 | 4 | 289 | 49 | 2 | 0.961 | 8 | |
| Franke P[ | 2001 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 170 | 50 | 1 | 284 | 74 | 7 | 0.403 | 8 | |
| Türkan H[ | 2019 | 土耳其 | 高加索人 | 87: 16/ 58:25 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 25 | 12 | 0 | 69 | 14 | 0 | 0.402 | 6 | |
| Park CI[ | 2020 | 韩国 | 亚洲人 | 314: 0/ 324:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 125 | 144 | 43 | 127 | 142 | 54 | 0.188 | 7 | |
| Ragia G[ | 2016 | 希腊 | 高加索人 | 72: 0/ 74:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 55 | 17 | 0 | 59 | 15 | 0 | 0.332 | 6 | |
| Gegenhuber B[ | 2018 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 113:87/133:107 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 158 | 40 | 2 | 185 | 52 | 3 | 0.760 | 8 | |
| Zhang H[ | 2006 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 246 | 68 | 4 | 256 | 78 | 4 | 0.014 | 7 | |
| Deb I[ | 2010 | 印度 | 亚洲人 | 53:0/82:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 16 | 32 | 5 | 44 | 30 | 8 | 0.397 | 6 | |
| Schinka JA[ | 2002 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 152 | 27 | 0 | 262 | 93 | 5 | 0.309 | 7 | |
| Cupic B[ | 2013 | 克罗地亚 | 高加索人 | 354:0/234:0 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 275 | 75 | 4 | 266 | 87 | 4 | 0.288 | 7 | |
| Nishizawa D[ | 2006 | 日本 | 亚洲人 | 50: 8/ 23:51 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 12 | 37 | 15 | 26 | 33 | 15 | 0.450 | 6 | |
| Bart G[ | 2005 | 瑞士 | 高加索人 | 281:108/82:88 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 299 | 90 | 0 | 147 | 23 | 0 | 0.344 | 7 | |
| Konjevod M[ | 2020 | 克罗地亚 | 高加索人 | 303:56/ 373:49 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 271 | 84 | 4 | 323 | 86 | 13 | 0.019 | 6 | |
| Gürel? C[ | 2016 | 土耳其 | 高加索人 | 124:0/118:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 97 | 22 | 2 | 88 | 28 | 1 | 0.446 | 7 | |
| Rouvinen-Lagerstr?m N[ | 2013 | 芬兰 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅳ | 队列研究 | 325 | 152 | 26 | 320 | 157 | 29 | 0.102 | 8 | |
| 作者 | 年份 | 国家 | 种族 | 性别(男:女) 病例组/对照组 | 诊断标准 | 研究类型 | 病例组基因型(例) | 对照组基因型(例) | HWE P值 | NOS评分 (分) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AA | AG | GG | AA | AG | GG | ||||||||||
| Bergen AW(1)[ | 1997 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 19 | 1 | 0 | 45 | 15 | 0 | 0.269 | 8 | |
| Bergen AW(2)[ | 1997 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 104 | 34 | 2 | 144 | 39 | 1 | 0.340 | 8 | |
| Bergen AW(3)[ | 1997 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 162 | 68 | 8 | 96 | 30 | 3 | 0.290 | 8 | |
| Kim SA[ | 2004 | 韩国 | 亚洲人 | 127:0/185:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 46 | 47 | 7 | 54 | 53 | 21 | 0.202 | 6 | |
| Rommelspacher H[ | 2001 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 282:45/未报道 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 262 | 62 | 33 | 289 | 48 | 43 | 0.001 | 6 | |
| Kim SG[ | 2004 | 韩国 | 亚洲人 | 106:6/80:60 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 37 | 61 | 14 | 68 | 57 | 15 | 0.559 | 5 | |
| Koller G[ | 2012 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 1403:442/ 935:928 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 1461 | 353 | 31 | 1417 | 419 | 27 | 0.528 | 7 | |
| Loh el W[ | 2004 | 中国 | 亚洲人 | 149:9/ 147:2 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 59 | 77 | 18 | 70 | 56 | 22 | 0.061 | 6 | |
| Miranda R[ | 2010 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 9:18/ 89:71 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 13 | 11 | 3 | 134 | 22 | 4 | 0.016 | 8 | |
| Sander T[ | 1998 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 261 | 62 | 4 | 289 | 49 | 2 | 0.961 | 8 | |
| Franke P[ | 2001 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 170 | 50 | 1 | 284 | 74 | 7 | 0.403 | 8 | |
| Türkan H[ | 2019 | 土耳其 | 高加索人 | 87: 16/ 58:25 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 25 | 12 | 0 | 69 | 14 | 0 | 0.402 | 6 | |
| Park CI[ | 2020 | 韩国 | 亚洲人 | 314: 0/ 324:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 125 | 144 | 43 | 127 | 142 | 54 | 0.188 | 7 | |
| Ragia G[ | 2016 | 希腊 | 高加索人 | 72: 0/ 74:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 55 | 17 | 0 | 59 | 15 | 0 | 0.332 | 6 | |
| Gegenhuber B[ | 2018 | 德国 | 高加索人 | 113:87/133:107 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 158 | 40 | 2 | 185 | 52 | 3 | 0.760 | 8 | |
| Zhang H[ | 2006 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 246 | 68 | 4 | 256 | 78 | 4 | 0.014 | 7 | |
| Deb I[ | 2010 | 印度 | 亚洲人 | 53:0/82:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 16 | 32 | 5 | 44 | 30 | 8 | 0.397 | 6 | |
| Schinka JA[ | 2002 | 美国 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 152 | 27 | 0 | 262 | 93 | 5 | 0.309 | 7 | |
| Cupic B[ | 2013 | 克罗地亚 | 高加索人 | 354:0/234:0 | ICD-10 | 病例-对照 | 275 | 75 | 4 | 266 | 87 | 4 | 0.288 | 7 | |
| Nishizawa D[ | 2006 | 日本 | 亚洲人 | 50: 8/ 23:51 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 12 | 37 | 15 | 26 | 33 | 15 | 0.450 | 6 | |
| Bart G[ | 2005 | 瑞士 | 高加索人 | 281:108/82:88 | DSM-Ⅲ-R | 病例-对照 | 299 | 90 | 0 | 147 | 23 | 0 | 0.344 | 7 | |
| Konjevod M[ | 2020 | 克罗地亚 | 高加索人 | 303:56/ 373:49 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 271 | 84 | 4 | 323 | 86 | 13 | 0.019 | 6 | |
| Gürel? C[ | 2016 | 土耳其 | 高加索人 | 124:0/118:0 | DSM-Ⅳ | 病例-对照 | 97 | 22 | 2 | 88 | 28 | 1 | 0.446 | 7 | |
| Rouvinen-Lagerstr?m N[ | 2013 | 芬兰 | 高加索人 | 未报道/未报道 | DSM-Ⅳ | 队列研究 | 325 | 152 | 26 | 320 | 157 | 29 | 0.102 | 8 | |
| 遗传模型 | 遗传关联 | 研究 数量 | 异质性检验 | 统计 模型 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR值 | 95%CI | P值 | I2(%) | P值 | |||
| 总人群 | |||||||
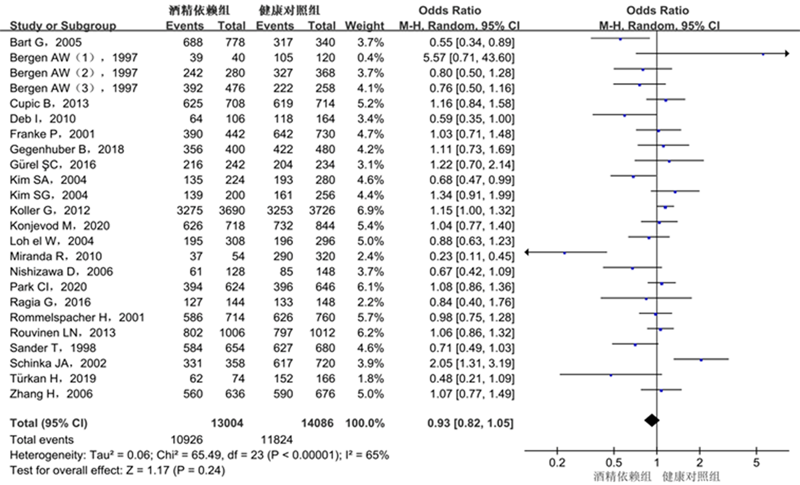
| A vs. G | 0.93 | 0.82 ~ 1.05 | 0.24 | 24 | 65 | <0.01 | R |
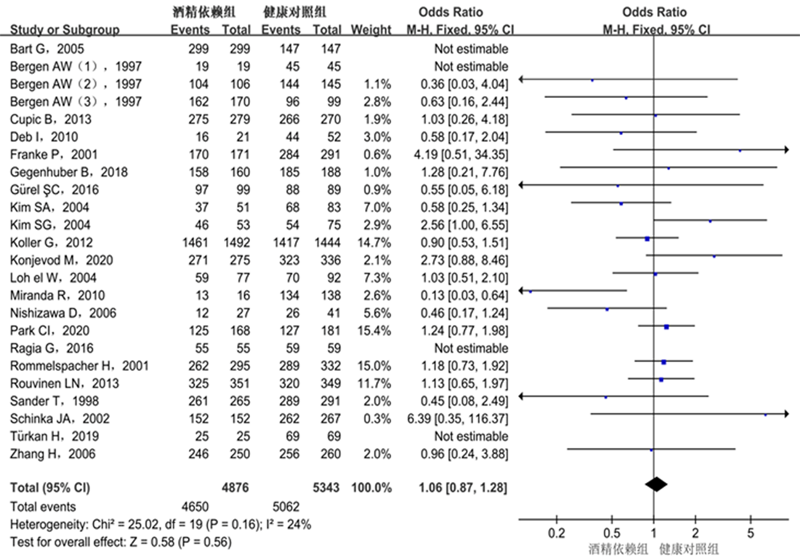
| AA vs. GG | 1.06 | 0.87 ~ 1.28 | 0.56 | 20 | 24 | 0.16 | F |
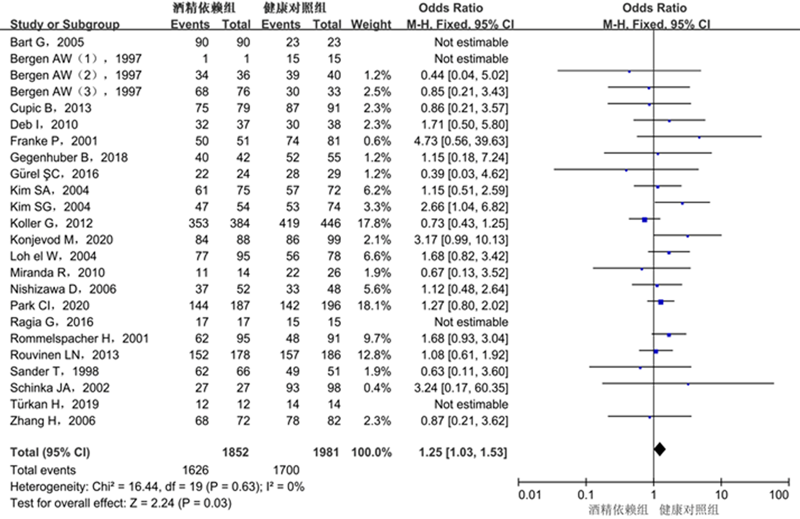
| AG vs. GG | 1.25 | 1.03 ~ 1.53 | 0.03 | 20 | 0 | 0.63 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.15 | 0.96 ~ 1.38 | 0.14 | 20 | 0 | 0.47 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.87 | 0.74 ~ 1.02 | 0.08 | 24 | 68 | <0.01 | R |
| 亚洲人 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.87 | 0.69 ~ 1.10 | 0.25 | 6 | 60 | 0.03 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.03 | 0.76 ~ 1.39 | 0.85 | 6 | 46 | 0.10 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.43 | 1.06 ~ 1.92 | 0.02 | 6 | 0 | 0.73 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.21 | 0.92 ~ 1.59 | 0.18 | 6 | 0 | 0.48 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.69 | 0.48 ~ 1.01 | 0.06 | 6 | 64 | 0.02 | R |
| 高加索人 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.95 | 0.81 ~ 1.10 | 0.48 | 18 | 67 | <0.01 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.08 | 0.84 ~ 1.39 | 0.55 | 14 | 17 | 0.55 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.13 | 0.86 ~ 1.47 | 0.39 | 14 | 0 | 0.52 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.09 | 0.85 ~ 1.40 | 0.49 | 14 | 5 | 0.40 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.93 | 0.78 ~ 1.11 | 0.43 | 18 | 67 | <0.01 | R |
| 男/女性混合 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.89 | 0.76 ~ 1.05 | 0.17 | 17 | 72 | <0.01 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.00 | 0.80 ~ 1.25 | 1.00 | 14 | 31 | 0.13 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.21 | 0.96 ~ 1.53 | 0.11 | 14 | 0 | 0.55 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.09 | 0.87 ~ 1.36 | 0.45 | 14 | 5 | 0.39 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.97 | 0.89 ~ 1.06 | 0.56 | 17 | 74 | <0.01 | R |
| 男性 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 1.02 | 0.89 ~ 1.17 | 0.77 | 9 | 17 | 0.29 | F |
| AA vs. GG | 1.18 | 0.83 ~ 1.69 | 0.36 | 8 | 0 | 0.54 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.31 | 0.92 ~ 1.87 | 0.21 | 8 | 0 | 0.64 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.26 | 0.90 ~ 1.77 | 0.17 | 8 | 0 | 0.65 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.98 | 0.83 ~ 1.15 | 0.77 | 9 | 25 | 0.2 | F |
| 遗传模型 | 遗传关联 | 研究 数量 | 异质性检验 | 统计 模型 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR值 | 95%CI | P值 | I2(%) | P值 | |||
| 总人群 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.93 | 0.82 ~ 1.05 | 0.24 | 24 | 65 | <0.01 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.06 | 0.87 ~ 1.28 | 0.56 | 20 | 24 | 0.16 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.25 | 1.03 ~ 1.53 | 0.03 | 20 | 0 | 0.63 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.15 | 0.96 ~ 1.38 | 0.14 | 20 | 0 | 0.47 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.87 | 0.74 ~ 1.02 | 0.08 | 24 | 68 | <0.01 | R |
| 亚洲人 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.87 | 0.69 ~ 1.10 | 0.25 | 6 | 60 | 0.03 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.03 | 0.76 ~ 1.39 | 0.85 | 6 | 46 | 0.10 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.43 | 1.06 ~ 1.92 | 0.02 | 6 | 0 | 0.73 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.21 | 0.92 ~ 1.59 | 0.18 | 6 | 0 | 0.48 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.69 | 0.48 ~ 1.01 | 0.06 | 6 | 64 | 0.02 | R |
| 高加索人 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.95 | 0.81 ~ 1.10 | 0.48 | 18 | 67 | <0.01 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.08 | 0.84 ~ 1.39 | 0.55 | 14 | 17 | 0.55 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.13 | 0.86 ~ 1.47 | 0.39 | 14 | 0 | 0.52 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.09 | 0.85 ~ 1.40 | 0.49 | 14 | 5 | 0.40 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.93 | 0.78 ~ 1.11 | 0.43 | 18 | 67 | <0.01 | R |
| 男/女性混合 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 0.89 | 0.76 ~ 1.05 | 0.17 | 17 | 72 | <0.01 | R |
| AA vs. GG | 1.00 | 0.80 ~ 1.25 | 1.00 | 14 | 31 | 0.13 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.21 | 0.96 ~ 1.53 | 0.11 | 14 | 0 | 0.55 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.09 | 0.87 ~ 1.36 | 0.45 | 14 | 5 | 0.39 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.97 | 0.89 ~ 1.06 | 0.56 | 17 | 74 | <0.01 | R |
| 男性 | |||||||
| A vs. G | 1.02 | 0.89 ~ 1.17 | 0.77 | 9 | 17 | 0.29 | F |
| AA vs. GG | 1.18 | 0.83 ~ 1.69 | 0.36 | 8 | 0 | 0.54 | F |
| AG vs. GG | 1.31 | 0.92 ~ 1.87 | 0.21 | 8 | 0 | 0.64 | F |
| AA+AG vs. GG | 1.26 | 0.90 ~ 1.77 | 0.17 | 8 | 0 | 0.65 | F |
| AA vs. AG+GG | 0.98 | 0.83 ~ 1.15 | 0.77 | 9 | 25 | 0.2 | F |
| [1] |
Rehm J, Allamani A, Della Vedova R, et al. General practitioners recognizing alcohol dependence: A large cross-sectional study in 6 European countries[J]. Ann Fam Med, 2015,13(1):28-32.
doi: 10.1370/afm.1742 URL |
| [2] |
Ji A, Lou P, Dong Z, et al. The prevalence of alcohol dependence and its association with hypertension: A population-based cross-sectional study4 in Xuzhou city, China[J]. BMC Public Health, 2018,18(1):364.
doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5276-1 URL |
| [3] |
Probst C, Kilian C, Sanchez S, et al. The role of alcohol use and drinking patterns in socioeconomic inequalities in mortality: A systematic review[J]. Lancet Public Health, 2020,5(6):e324-e332.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30052-9 URL |
| [4] |
Kendler KS, Prescott CA, Neale MC, et al. Temperance board registration for alcohol abuse in a national sample of Swedish male twins, born 1902 to 1949[J]. Arch Gen Psychiatry, 1997,54(2):178-184.
doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1997.01830140090015 URL |
| [5] |
Mitsuru K, Higuchi S. Genetics of alcohol dependence[J]. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci, 2011,65(3):213-225.
doi: 10.1111/pcn.2011.65.issue-3 URL |
| [6] |
Bergen AW, Kokoszka J, Peterson R, et al. Mu opioid receptor gene variants: Lack of association with alcohol dependence[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 1997,2(6):490-494.
doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000331 URL |
| [7] | Ryckman K, Williams SM. Calculation and use of the Hardy-Weinberg model in association studies[M]. Curr Protoc Hum Genet, 2008, Chapter 1:Unit 1.18. |
| [8] | 张天嵩, 钟文昭, 李博. 实用循证医学[M]. 2版. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2014: 305-413. |
| [9] |
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses[J]. BMJ, 2003,327(7414):557-560.
doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 URL |
| [10] |
Ioannidis JP, Trikalinos TA. The appropriateness of asymmetry tests for publication bias in meta-analyses: A large survey[J]. CMAJ, 2007,176(8):1091-1096.
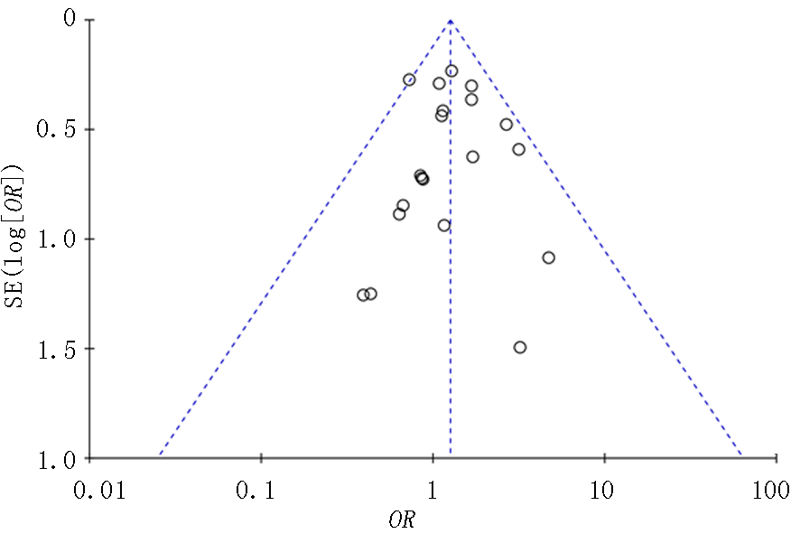
pmid: 17420491 |
| [11] |
Kim SA, Kim JW, Song JY, et al. Association of polymorphisms in nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 subunit gene (CHRNA4), mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1), and ethanol-metabolizing enzyme genes with alcoholism in Korean patients[J]. Alcohol, 2004,34(2-3):115-120.
doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2004.06.004 URL |
| [12] |
Rommelspacher H, Smolka M, Schmidt LG, et al. Genetic analysis of the mu-opioid receptor in alcohol-dependent individuals[J]. Alcohol, 2001,24(2):129-135.
pmid: 11522434 |
| [13] |
Kim SG, Kim CM, Kang DH, et al. Association of functional opioid receptor genotypes with alcohol dependence in Koreans[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 2004,28(7):986-890.
doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000130803.62768.AB URL |
| [14] |
Koller G, Zill P, Rujescu D, et al. Possible association between OPRM1 genetic variance at the 118 locus and alcohol dependence in a large treatment sample: Relationship to alcohol dependence symptoms[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 2012,36(7):1230-1236.
doi: 10.1111/acer.2012.36.issue-7 URL |
| [15] |
Lohel W, Fann CS, Chang YT, et al. Endogenous opioid receptor genes and alcohol dependence among Taiwanese Han[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 2004,28(1):15-19.
doi: 10.1097/01.ALC.0000106303.41755.B8 URL |
| [16] |
Miranda R, Ray L, Justus A, et al. Initial evidence of an association between OPRM1 and adolescent alcohol misuse[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 2010,34(1):112-122.
doi: 10.1111/acer.2009.34.issue-1 URL |
| [17] |
Sander T, Gscheidel N, Wendel B, et al. Human mu-opioid receptor variation and alcohol dependence[J]. Alcohol Clin Exp Res, 1998,22(9):2108-2110.
pmid: 9884158 |
| [18] |
Franke P, Wang T, Nöthen MM, et al. Nonreplication of association between mu-opioid-receptor gene (OPRM1) A118G polymorphism and substance dependence[J]. Am J Med Genet, 2001,105(1):114-119.
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1096-8628 URL |
| [19] |
Türkan H, Karahalil B, Kadıoˇglu E, et al. The association between the OPRM1 A118G polymorphism and addiction in a Turkish population[J]. Arh Hig Rada Toksikol, 2019,70(2):97-103.
doi: 10.2478/aiht-2019-70-3153 pmid: 31246565 |
| [20] |
Park CI, Hwang SS, Kim HW, et al. Association of opioid receptor gene polymorphisms with drinking severity and impulsivity related to alcohol use disorder in a Korean population[J]. CNS Neurosci Ther, 2020,26(1):30-38.
doi: 10.1111/cns.v26.1 URL |
| [21] | Ragia G, Veresies I, Veresie L, et al. Association study of DRD2 A2/A1, DRD3 Ser9Gly, DbetaH -1021C>T, OPRM1 A118G and GRIK1 rs2832407C>A polymorphisms with alcohol dependence[J]. Drug Metab Pers Ther, 2016,31(3):143-150. |
| [22] |
Gegenhuber B, Weinland C, Kornhuber J, et al. OPRM1 A118G and serum beta-endorphin interact with sex and digit ratio (2D:4D) to influence risk and course of alcohol dependence[J]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 2018,28(12):1418-1428.
doi: S0924-977X(18)30814-9 pmid: 30322771 |
| [23] |
Zhang H, Luo X, Kranzler HR, et al. Association between two mu-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) haplotype blocks and drug or alcohol dependence[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2006,15(6):807-819.
doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl024 URL |
| [24] |
Deb I, Chakraborty J, Gangopadhyay PK, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphism (A118G) in exon 1 of OPRM1 gene causes alteration in downstream signaling by mu-opioid receptor and may contribute to the genetic risk for addiction[J]. J Neurochem, 2010,112(2):486-496.
doi: 10.1111/jnc.2009.112.issue-2 URL |
| [25] |
Schinka JA, Town T, Abdullah L, et al. A functional polymorphism within the mu-opioid receptor gene and risk for abuse of alcohol and other substances[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2002,7(2):224-228.
doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000951 URL |
| [26] |
Cupic B, Stefulj J, Zapletal E, et al. Opioid system genes in alcoholism: A case-control study in Croatian population[J]. Neuropeptides, 2013,47(5):315-319.
doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2013.08.002 pmid: 24035285 |
| [27] |
Nishizawa D, Han W, Hasegawa J, et al. Association of mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism A118G with alcohol dependence in a Japanese population[J]. Neuropsychobiology, 2006,53(3):137-141.
pmid: 16679777 |
| [28] |
Bart G, Kreek MJ, Ott J, et al. Increased attributable risk related to a functional mu-opioid receptor gene polymorphism in association with alcohol dependence in central Sweden[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2005,30(2):417-422.
doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300598 URL |
| [29] |
Konjevod M, Nikolac Perkovic M, et al. Significant association of mu-opioid receptor 1 haplotype with tobacco smoking in healthy control subjects but not in patients with schizophrenia and alcohol dependence[J]. Psychiatry Res, 2020,291:113278.
doi: S0165-1781(20)31407-4 pmid: 32763540 |
| [30] | Gürelş C, Ayhan Y, Karaaslan Ç, et al. μ-opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) polymorphisms A118G and C17T in alcohol dependence: A Turkish sample[J]. Turk Psikiyatri Derg, 2016,27(2):0. |
| [31] |
Rouvinen-Lagerström N, Lahti J, Alho H, et al. μ-Opioid receptor gene (OPRM1) polymorphism A118G: Lack of association in Finnish populations with alcohol dependence or alcohol consumption[J]. Alcohol Alcohol, 2013,48(5):519-525.
doi: 10.1093/alcalc/agt050 URL |
| [32] |
Matthes HW, Maldonado R, Simonin F, et al. Loss of morphine-induced analgesia, reward effect and withdrawal symptoms in mice lacking the mu-opioid-receptor gene[J]. Nature 1996; 383(6603):819-823.
pmid: 8893006 |
| [33] |
Huang P, Chen C, Mague SD, et al. A common single nucleotide polymorphism A118G of the μ opioid receptor alters its N-glycosylation and protein stability[J]. Biochem J, 2012,441(1):379-386.
doi: 10.1042/BJ20111050 URL |
| [34] |
Keating GM. Nalmefene: A review of its use in the treatment of alcohol dependence[J]. CNS Drugs, 2013,27(9):761-772.
doi: 10.1007/s40263-013-0101-y URL |
| [35] |
Schacht JP, Randall PK, Latham PK, et al. Predictors of naltrexone response in a randomized trial: Reward-related brain activation, OPRM1 genotype, and smoking status[J]. Neuropsychopharmacology, 2017,42(13):2654.
doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.185 pmid: 29123234 |
| [36] |
Korucuoglu O, Gladwin TE, Baas F, et al. Neural response to alcohol taste cues in youth: Effects of the OPRM1 gene[J]. Addict Biol, 2017,22(6):1562-1575.
doi: 10.1111/adb.12440 pmid: 27594419 |
| [37] |
Bach P, Vollsta Dt-Klein S, Kirsch M, et al. Increased mesolimbic cue-reactivity in carriers of the mu-opioid-receptor gene OPRM1 A118G polymorphism predicts drinking outcome: A functional imaging study in alcohol dependent subjects[J]. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol, 2015,25(8):1128-1135.
doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.04.013 URL |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||