Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 325-328.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.04.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
The relationship between serum homocysteine levels and SYNTAX score in patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction
Wang Yajie, Lin Wenhua( ), Jing Rui, Liu Jingjing, Lu Yujie
), Jing Rui, Liu Jingjing, Lu Yujie
- First department of internal medicine, TEDA International Cardiovascular Hospital, Tianjin 300457, China
-
Received:2021-09-16Online:2022-04-20Published:2022-05-13 -
Contact:Lin Wenhua E-mail:linwernhua@sina.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wang Yajie, Lin Wenhua, Jing Rui, Liu Jingjing, Lu Yujie. The relationship between serum homocysteine levels and SYNTAX score in patients with non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(4): 325-328.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.04.007
| 项目 | 低SS组 | 中等SS组 | 高SS组 | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 59.4±11.1 | 63.7±11.3* | 65.4±12.3* | 7.161 | 0.001 |
| 男性[例(%)] | 130(73.4) | 48(62.3) | 32(72.7) | 3.308 | 0.191 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | 107(60.5) | 48(62.3) | 27(61.4) | 0.082 | 0.960 |
| 糖尿病[例(%)] | 65(36.7) | 27(35.1) | 28(63.6)* | 11.781 | 0.003 |
| 目前仍吸烟[例(%)] | 94(53.1) | 37(48.1) | 23(52.3) | 0.556 | 0.757 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 63.8±13.3 | 63.9±12.4 | 70.2±13.6* | 4.431 | 0.013 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.4±1.0 | 4.5±1.1 | 4.5±0.8 | 0.116 | 0.891 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 2.81±0.86 | 2.81±0.94 | 2.85±0.77 | 0.039 | 0.962 |
| 白细胞总数(×109/L) | 8.14±2.38 | 8.08±2.50 | 8.86±2.77 | 1.693 | 0.186 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 147.7±18.1 | 142.2±20.4* | 139.7±16.3* | 4.564 | 0.011 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 231.8±62.5 | 222.0±52.5 | 217.5±50.3 | 1.457 | 0.235 |
| HCY(μmol/L) | 16.1±9.1 | 20.3±9.1* | 27.5±9.5* | 28.827 | <0.01 |
| LVEF(%) | 63.5±6.6 | 62.5±6.1 | 60.7±7.1* | 3.254 | 0.040 |
| 项目 | 低SS组 | 中等SS组 | 高SS组 | 统计值 | P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 59.4±11.1 | 63.7±11.3* | 65.4±12.3* | 7.161 | 0.001 |
| 男性[例(%)] | 130(73.4) | 48(62.3) | 32(72.7) | 3.308 | 0.191 |
| 高血压[例(%)] | 107(60.5) | 48(62.3) | 27(61.4) | 0.082 | 0.960 |
| 糖尿病[例(%)] | 65(36.7) | 27(35.1) | 28(63.6)* | 11.781 | 0.003 |
| 目前仍吸烟[例(%)] | 94(53.1) | 37(48.1) | 23(52.3) | 0.556 | 0.757 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 63.8±13.3 | 63.9±12.4 | 70.2±13.6* | 4.431 | 0.013 |
| 总胆固醇(mmol/L) | 4.4±1.0 | 4.5±1.1 | 4.5±0.8 | 0.116 | 0.891 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 2.81±0.86 | 2.81±0.94 | 2.85±0.77 | 0.039 | 0.962 |
| 白细胞总数(×109/L) | 8.14±2.38 | 8.08±2.50 | 8.86±2.77 | 1.693 | 0.186 |
| 血红蛋白(g/L) | 147.7±18.1 | 142.2±20.4* | 139.7±16.3* | 4.564 | 0.011 |
| 血小板计数(×109/L) | 231.8±62.5 | 222.0±52.5 | 217.5±50.3 | 1.457 | 0.235 |
| HCY(μmol/L) | 16.1±9.1 | 20.3±9.1* | 27.5±9.5* | 28.827 | <0.01 |
| LVEF(%) | 63.5±6.6 | 62.5±6.1 | 60.7±7.1* | 3.254 | 0.040 |
| 变量 | SYNTAX评分 | |
|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | 0.226 | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病 | 0.112 | 0.055 |
| 肌酐 | 0.087 | 0.133 |
| 血红蛋白 | -0.193 | 0.001 |
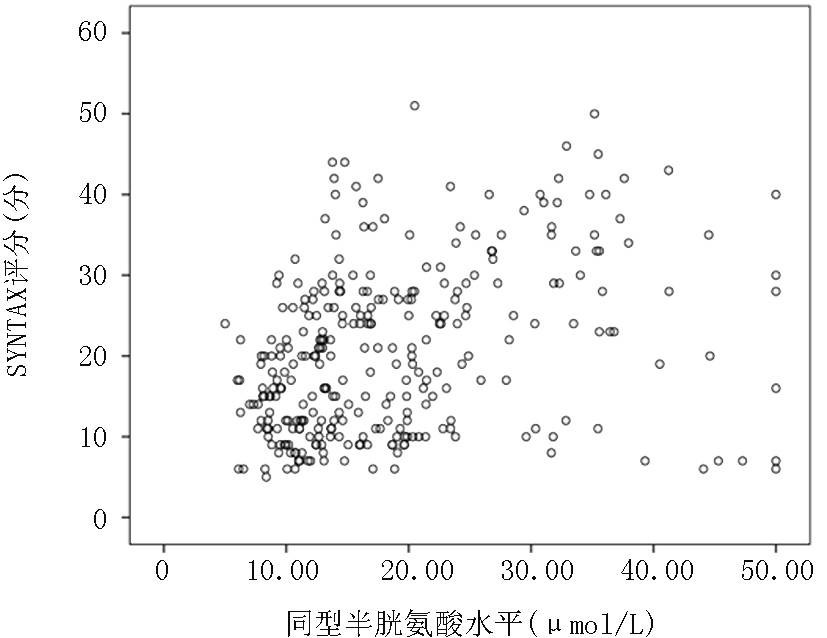
| 同型半胱氨酸 | 0.358 | <0.01 |
| LVEF | -0.116 | 0.046 |
| 变量 | SYNTAX评分 | |
|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | |
| 年龄 | 0.226 | <0.01 |
| 糖尿病 | 0.112 | 0.055 |
| 肌酐 | 0.087 | 0.133 |
| 血红蛋白 | -0.193 | 0.001 |
| 同型半胱氨酸 | 0.358 | <0.01 |
| LVEF | -0.116 | 0.046 |
| 变量 | 未标准化系数 | 标准化系数 β | t值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 标准误差 | ||||
| 同型半胱氨酸 | 0.328 | 0.056 | 0.316 | 5.906 | <0.01 |
| 年龄 | 0.202 | 0.048 | 0.224 | 4.192 | <0.01 |
| 变量 | 未标准化系数 | 标准化系数 β | t值 | P值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | 标准误差 | ||||
| 同型半胱氨酸 | 0.328 | 0.056 | 0.316 | 5.906 | <0.01 |
| 年龄 | 0.202 | 0.048 | 0.224 | 4.192 | <0.01 |
| [1] |
Antoniades C, Antonopoulos AS, Tousoulis D. et al. Homocysteine and coronary atherosclerosis: From folate fortification to the recent clinical trials[J]. Eur Heart J, 2009, 30(1): 6-15.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehn515 URL |
| [2] | Smith SC Jr. Current and future directions of cardiovascular risk prediction[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2006, 97(2a): 28a-32a. |
| [3] |
Miao L, Deng GX, Yin RX. et al. No causal effects of plasma homocysteine levels on the risk of coronary heart disease or acute myocardial infarction: A Mendelian randomization study[J]. Eur J Prev Cardiol, 2021, 28(2): 227-234.
doi: 10.1177/2047487319894679 |
| [4] | Wu HY, Gao TJ, Cao YW. et al. Analysis of the association and predictive value of hyperhomocysteinaemia for obstructive coronary artery disease[J]. J Int Med Res, 2021, 49(7): 3000605211033495. |
| [5] |
Shih CC, Shih YL, Chen JY. The association between homocysteine levels and cardiovascular disease risk among middle-aged and elderly adults in Taiwan[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2021, 21(1): 191.
doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02000-x URL |
| [6] | Muzaffar R, Khan MA, Mushtaq MH. et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia as an independent risk factor for coronary heart disease. Comparison with conventional risk factors[J]. Braz J Biol, 2021, 83: e249104. |
| [7] |
Markovi'c-Boras M, ˇCauševi'c A, 'Curlin M. A relation of serum homocysteine and uric acid in Bosnian diabetic patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. J Med Biochem, 2021, 40(3): 261-269.
doi: 10.5937/jomb0-28391 URL |
| [8] |
Guan J, Wu L, Xiao Q. et al. Levels and clinical significance of serum homocysteine (Hcy), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), vaspin, and visfatin in elderly patients with different types of coronary heart disease[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2021, 10(5): 5679-5686.
doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1001 URL |
| [9] |
Yadav M, Palmerini T, Caixeta A. et al. Prediction of coronary risk by SYNTAX and derived scores: synergy between percutaneous coronary intervention with taxus and cardiac surgery[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2013, 62(14): 1219-1230.
doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.06.047 URL |
| [10] |
Collet JP, Thiele H, Barbato E. et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the management of acute coronary syndromes in patients presenting without persistent ST-segment elevation[J]. Eur Heart J, 2021, 42(14): 1289-1367.
doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa575 URL |
| [11] |
Shenoy V, Mehendale V, Prabhu K. et al. Correlation of serum homocysteine levels with the severity of coronary artery disease[J]. Indian J Clin Biochem, 2014, 29(3): 339-344.
doi: 10.1007/s12291-013-0373-5 URL |
| [12] |
Wu Y, Yang L, Zhong L. Decreased serum levels of thioredoxin in patients with coronary artery disease plus hyperhomocysteinemia is strongly associated with the disease severity[J]. Atherosclerosis, 2010, 212(1): 351-355.
doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.06.002 URL |
| [13] |
Joubran R, Asmi M, Busjahn A. et al. Homocysteine levels and coronary heart disease in Syria[J]. J Cardiovasc Risk, 1998, 5(4): 257-261.
pmid: 9919474 |
| [14] | Fu Z, Qian G, Xue H. et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia is an independent predictor of long-term clinical outcomes in Chinese octogenarians with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Clin Interv Aging, 2015, 10: 1467-1474. |
| [15] | Zhao Y, Zhang J. Clinical implication of homocysteine in premature acute coronary syndrome female patients: Its distribution and association with clinical characteristics and major adverse cardiovascular events risk[J]. 2021, 100(18): e25677. |
| [16] |
Ma Y, Li L, Geng XB. et al. Correlation between hyperhomocysteinemia and outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction[J]. Am J Ther, 2016, 23(6): e1464-e1468.
doi: 10.1097/MJT.0000000000000130 URL |
| [17] |
Tyagi N, Sedoris KC, Steed M. et al. Mechanisms of homocysteine-induced oxidative stress[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2005, 289(6): H2649-2656.
doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00548.2005 URL |
| [18] | 王慧清, 王琰娜, 金耀来, 等. 血浆同型半胱氨酸与冠状动脉病变的关系探讨[J]. 疑难病杂志, 2014, 13(9):888-890. |
| [19] | Faeh D, Chiolero A, Paccaud F. Homocysteine as a risk factor for cardiovascular disease: Should we (still) worry about?[J]. Swiss Med Wkly, 2006, 136(47-48): 745-756. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||