Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (10): 887-892.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.10.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Influencing factors for mild cognitive impairment in type H hypertension patients combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Department of Cardiology,Anshan Central Hospital, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Jinzhou Medical University, Anshan 114000, China
-
Received:2023-04-27Online:2023-10-20Published:2024-01-03 -
Contact:Xu Yang E-mail:1966961034@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xu Yang, Xue Ling. Influencing factors for mild cognitive impairment in type H hypertension patients combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(10): 887-892.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.10.004
| 组别 | 例数(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | 受教育程度(年) | 吸烟史 | 饮酒史 | 高血压病史(年) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101(60/41) | 74.880±7.658 | 8.140±2.054 | 51(50.2) | 47(46.5) | 11.510±6.437 |
| NMCI组 | 62(46/16) | 59.100±9.769 | 11.970±2.673 | 20(32.3) | 32(51.6) | 7.080±3.923 |
| 3.645 | 11.483 | -10.281 | 5.197 | 0.397 | 5.465 | |
| 0.055 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | 0.529 | <0.001 | |
| 组别 | 糖尿病病史(年) | 冠心病病史 | 高脂血症史 | BMI(kg/m2) | SBP(mmHg) | DBP(mmHg) |
| MCI组 | 10.900±6.900 | 34(33.7) | 31(30.7) | 24.670±3.175 | 149.190±12.335 | 85.800±13.369 |
| NMCI组 | 5.630±3.838 | 20(32.3) | 15(24.2) | 25.150±3.578 | 145.320±15.982 | 83.980±12.570 |
| 5.511 | 0.034 | 0.801 | -0.908 | -2.457 | 1.732 | |
| <0.001 | 0.853 | 0.371 | 0.365 | 0.015 | 0.085 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of general information between groups ($\bar{x}$±s, n[%])
| 组别 | 例数(男/女) | 年龄(岁) | 受教育程度(年) | 吸烟史 | 饮酒史 | 高血压病史(年) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101(60/41) | 74.880±7.658 | 8.140±2.054 | 51(50.2) | 47(46.5) | 11.510±6.437 |
| NMCI组 | 62(46/16) | 59.100±9.769 | 11.970±2.673 | 20(32.3) | 32(51.6) | 7.080±3.923 |
| 3.645 | 11.483 | -10.281 | 5.197 | 0.397 | 5.465 | |
| 0.055 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.023 | 0.529 | <0.001 | |
| 组别 | 糖尿病病史(年) | 冠心病病史 | 高脂血症史 | BMI(kg/m2) | SBP(mmHg) | DBP(mmHg) |
| MCI组 | 10.900±6.900 | 34(33.7) | 31(30.7) | 24.670±3.175 | 149.190±12.335 | 85.800±13.369 |
| NMCI组 | 5.630±3.838 | 20(32.3) | 15(24.2) | 25.150±3.578 | 145.320±15.982 | 83.980±12.570 |
| 5.511 | 0.034 | 0.801 | -0.908 | -2.457 | 1.732 | |
| <0.001 | 0.853 | 0.371 | 0.365 | 0.015 | 0.085 |
| 组别 | 例数 | WBC (109/L) | RBC (1012/L) | HGB (g/L) | PLT (109/L) | FBG (mmol/L) | HbA1c (%) | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101 | 6.360±1.240 | 4.540±0.520 | 144.530±25.454 | 213.100±49.814 | 7.720±1.972 | 6.800±0.830 | 5.200±1.620 | 2.250±1.550 | |||||||
| NMCI组 | 62 | 6.790±1.650 | 4.690±0.570 | 148.350±16.268 | 221.600±39.979 | 7.200±2.052 | 7.370±1.420 | 5.000±1.710 | 2.740±1.860 | |||||||
| -1.888 | -1.771 | -1.056 | -1.198 | 0.397 | -2.865 | 0.785 | -1.823 | |||||||||
| 0.061 | 0.078 | 0.293 | 0.233 | 0.038 | 0.005 | 0.434 | 0.070 | |||||||||
| 组别 | HDL-C (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | ApoA-1 (g/L) | ApoB (g/L) | LPa (mg/L) | Scr (μmol/L) | SUA (mmol/L) | Hcy (μmol/L) | ALB (mg/L) | |||||||
| MCI组 | 1.000±0.310 | 3.360±0.990 | 1.130±0.280 | 1.000±0.340 | 216.140±145.210 | 72.740±10.060 | 306.510±93.440 | 23.340±6.520 | 61.820±56.110 | |||||||
| NMCI组 | 1.200±0.370 | 3.200±1.170 | 1.220±0.300 | 1.050±0.250 | 202.700±139.260 | 71.870±14.880 | 358.490±90.420 | 20.740±5.660 | 50.370±56.400 | |||||||
| -3.743 | -2.241 | -1.989 | -1.249 | 0.583 | 0.306 | -3.420 | 2.598 | 0.469 | ||||||||
| <0.001 | 0.025 | 0.048 | 0.214 | 0.561 | 0.760 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.640 | ||||||||
Tab. 2 Comparison of laboratory indexes between groups ($\bar{x}$±s)
| 组别 | 例数 | WBC (109/L) | RBC (1012/L) | HGB (g/L) | PLT (109/L) | FBG (mmol/L) | HbA1c (%) | TC (mmol/L) | TG (mmol/L) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101 | 6.360±1.240 | 4.540±0.520 | 144.530±25.454 | 213.100±49.814 | 7.720±1.972 | 6.800±0.830 | 5.200±1.620 | 2.250±1.550 | |||||||
| NMCI组 | 62 | 6.790±1.650 | 4.690±0.570 | 148.350±16.268 | 221.600±39.979 | 7.200±2.052 | 7.370±1.420 | 5.000±1.710 | 2.740±1.860 | |||||||
| -1.888 | -1.771 | -1.056 | -1.198 | 0.397 | -2.865 | 0.785 | -1.823 | |||||||||
| 0.061 | 0.078 | 0.293 | 0.233 | 0.038 | 0.005 | 0.434 | 0.070 | |||||||||
| 组别 | HDL-C (mmol/L) | LDL-C (mmol/L) | ApoA-1 (g/L) | ApoB (g/L) | LPa (mg/L) | Scr (μmol/L) | SUA (mmol/L) | Hcy (μmol/L) | ALB (mg/L) | |||||||
| MCI组 | 1.000±0.310 | 3.360±0.990 | 1.130±0.280 | 1.000±0.340 | 216.140±145.210 | 72.740±10.060 | 306.510±93.440 | 23.340±6.520 | 61.820±56.110 | |||||||
| NMCI组 | 1.200±0.370 | 3.200±1.170 | 1.220±0.300 | 1.050±0.250 | 202.700±139.260 | 71.870±14.880 | 358.490±90.420 | 20.740±5.660 | 50.370±56.400 | |||||||
| -3.743 | -2.241 | -1.989 | -1.249 | 0.583 | 0.306 | -3.420 | 2.598 | 0.469 | ||||||||
| <0.001 | 0.025 | 0.048 | 0.214 | 0.561 | 0.760 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.640 | ||||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | CIMT(mm) | 颈动脉斑块检出率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101 | 2.06±0.77 | 66(60.0) |
| NMCI组 | 62 | 1.32±0.31 | 29(46.0) |
| 7.318 | 5.450 | ||
| <0.001 | 0.020 |
Tab. 3 Comparison of carotid artery ultrasound results between groups ($\bar{x}$±s, n[%])
| 组别 | 例数 | CIMT(mm) | 颈动脉斑块检出率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101 | 2.06±0.77 | 66(60.0) |
| NMCI组 | 62 | 1.32±0.31 | 29(46.0) |
| 7.318 | 5.450 | ||
| <0.001 | 0.020 |
| 组别 | 例数 | MMSE | MOCA | 视空间与 执行能力 | 命名 | 注意力 | 语言 | 抽象 | 延迟记忆 | 定向力 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101 | 23.140±1.710 | 20.580±2.132 | 2.640±0.810 | 2.750±0.430 | 2.610±0.790 | 2.770±0.420 | 1.950±0.220 | 2.380±0.750 | 5.480±0.540 |
| NMCI组 | 62 | 27.600±0.640 | 26.160±0.410 | 3.940±0.770 | 2.870±0.340 | 4.790±0.520 | 2.890±0.320 | 1.960±0.210 | 4.100±0.590 | 5.630±0.490 |
| -23.660 | -25.523 | -10.114 | -1.947 | -21.305 | -1.969 | -0.032 | -16.273 | -1.877 | ||
| <0.01 | <0.01 | -10.114 | 0.053 | <0.01 | 0.051 | 0.975 | <0.01 | 0.063 |
Tab. 4 Comparison of cognitive function scores between MCI group and NMCI group ($\bar{x}$±s, Score)
| 组别 | 例数 | MMSE | MOCA | 视空间与 执行能力 | 命名 | 注意力 | 语言 | 抽象 | 延迟记忆 | 定向力 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCI组 | 101 | 23.140±1.710 | 20.580±2.132 | 2.640±0.810 | 2.750±0.430 | 2.610±0.790 | 2.770±0.420 | 1.950±0.220 | 2.380±0.750 | 5.480±0.540 |
| NMCI组 | 62 | 27.600±0.640 | 26.160±0.410 | 3.940±0.770 | 2.870±0.340 | 4.790±0.520 | 2.890±0.320 | 1.960±0.210 | 4.100±0.590 | 5.630±0.490 |
| -23.660 | -25.523 | -10.114 | -1.947 | -21.305 | -1.969 | -0.032 | -16.273 | -1.877 | ||
| <0.01 | <0.01 | -10.114 | 0.053 | <0.01 | 0.051 | 0.975 | <0.01 | 0.063 |
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -1.821 | 0.631 | 8.335 | 0.004 | 0.162 | 0.047~0.557 |
| 受教育程度 | -2.966 | 1.578 | 3.532 | 0.060 | 0.052 | 0.002~1.136 |
| 高血压病程 | 0.081 | 0.155 | 0.271 | 0.603 | 1.084 | 0.799~1.471 |
| T2DM病程 | 0.002 | 0.168 | 0.001 | 0.990 | 1.002 | 0.721~1.392 |
| 吸烟史 | 0.908 | 1.060 | 0.734 | 0.392 | 2.478 | 0.311~4.950 |
| HbA1c | 0.577 | 0.618 | 0.873 | 0.350 | 1.781 | 0.531~5.974 |
| HDL-C | 1.333 | 0.622 | 4.583 | 0.032 | 3.791 | 1.119~12.841 |
| ApoA-1 | 0.660 | 0.680 | 0.941 | 0.322 | 1.934 | 0.510~7.332 |
| SUA | 0.010 | 0.007 | 2.300 | 0.129 | 1.010 | 0.997~1.024 |
| Hcy | -0.075 | 0.031 | 6.214 | 0.013 | 0.928 | 0.875~0.984 |
| CIMT | -3.047 | 0.686 | 25.329 | <0.01 | 0.032 | 0.008~0.121 |
Tab. 5 Logistic regression analysis of risk factors for MCI in type H hypertension patients combined with T2DM
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | -1.821 | 0.631 | 8.335 | 0.004 | 0.162 | 0.047~0.557 |
| 受教育程度 | -2.966 | 1.578 | 3.532 | 0.060 | 0.052 | 0.002~1.136 |
| 高血压病程 | 0.081 | 0.155 | 0.271 | 0.603 | 1.084 | 0.799~1.471 |
| T2DM病程 | 0.002 | 0.168 | 0.001 | 0.990 | 1.002 | 0.721~1.392 |
| 吸烟史 | 0.908 | 1.060 | 0.734 | 0.392 | 2.478 | 0.311~4.950 |
| HbA1c | 0.577 | 0.618 | 0.873 | 0.350 | 1.781 | 0.531~5.974 |
| HDL-C | 1.333 | 0.622 | 4.583 | 0.032 | 3.791 | 1.119~12.841 |
| ApoA-1 | 0.660 | 0.680 | 0.941 | 0.322 | 1.934 | 0.510~7.332 |
| SUA | 0.010 | 0.007 | 2.300 | 0.129 | 1.010 | 0.997~1.024 |
| Hcy | -0.075 | 0.031 | 6.214 | 0.013 | 0.928 | 0.875~0.984 |
| CIMT | -3.047 | 0.686 | 25.329 | <0.01 | 0.032 | 0.008~0.121 |
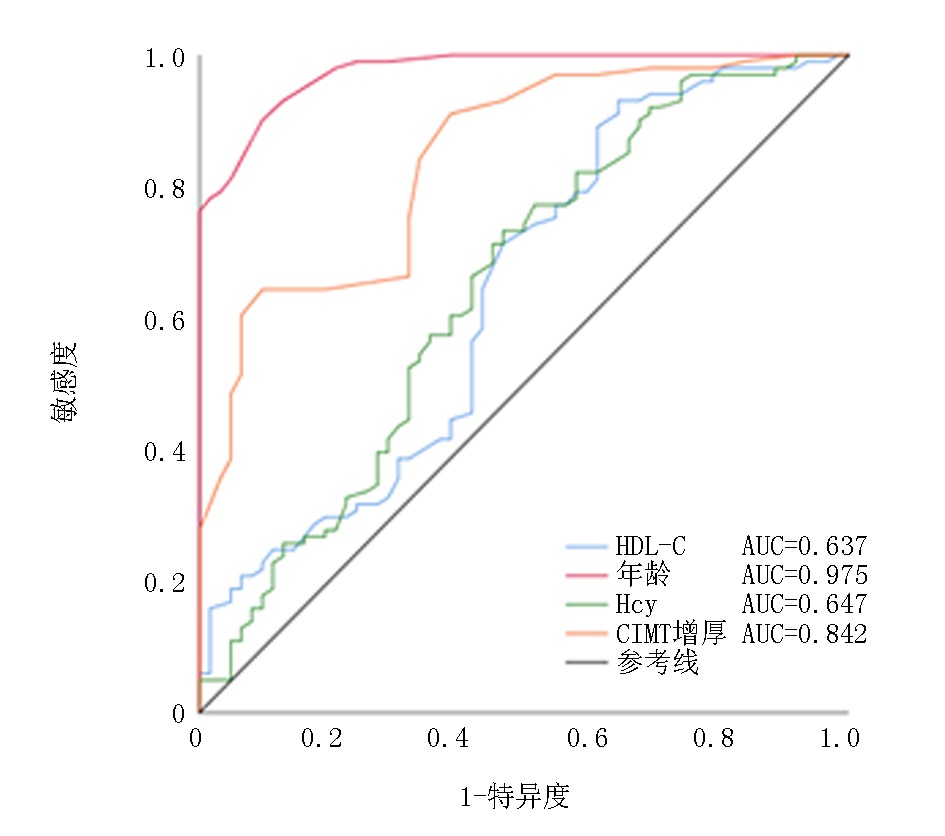
| 变量 | AUC | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | 最佳阈值 | 95% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.975 | 0.901 | 0.903 | 0.804 | 66.500 | 0.957~0.993 | |||||||
| HDL-C | 0.637 | 0.931 | 0.355 | 0.286 | 0.745 | 0.546~0.728 | |||||||
| Hcy | 0.647 | 0.733 | 0.532 | 0.265 | 18.550 | 0.557~0.736 | |||||||
| CIMT | 0.842 | 0.644 | 0.903 | 0.547 | 1.625 | 0.701~0.902 | |||||||
Tab. 6 AUC and 95% CI of age, HDL-C, Hcy, and CIMT
| 变量 | AUC | 敏感度 | 特异度 | 约登指数 | 最佳阈值 | 95% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 0.975 | 0.901 | 0.903 | 0.804 | 66.500 | 0.957~0.993 | |||||||
| HDL-C | 0.637 | 0.931 | 0.355 | 0.286 | 0.745 | 0.546~0.728 | |||||||
| Hcy | 0.647 | 0.733 | 0.532 | 0.265 | 18.550 | 0.557~0.736 | |||||||
| CIMT | 0.842 | 0.644 | 0.903 | 0.547 | 1.625 | 0.701~0.902 | |||||||
| [1] |
Jia L, Du Y, Chu L, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: A cross-sectional study[J]. The Lancet Public health, 2020, 5(12): e661-e671.
doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30185-7 URL |
| [2] |
Ye Z, Wang C, Zhang Q, et al. Prevalence of homocysteine-related hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease[J]. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich), 2017, 19(2): 151-160.
doi: 10.1111/jch.12881 pmid: 27440006 |
| [3] |
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu HB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(2): 88-98.
doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.151 pmid: 29219149 |
| [4] | Antal B, McMahon LP, Sultan SF, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus accelerates brain aging and cognitive decline: complementary findings from UK biobank and meta-analyses[J]. ELife, 2022, 5(11):e73138. |
| [5] |
Wang X, Qiao T, Liu M, et al. Homocysteine associated with low cognitive function independent of asymptomatic intracranial and carotid arteries stenoses in Chinese elderly patients: An outpatient-based cross-sectional study[J]. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol, 2022, 35(3): 302-308.
doi: 10.1177/0891988720988914 URL |
| [6] |
Chang WW, Fei SZ, Pan N, et al. Incident Stroke and its influencing factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and/or hypertension: A prospective cohort study[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9(9): 770025.
doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.770025 URL |
| [7] |
Byeon G, Byun MS, Yi D, et al. Synergistic effect of serum homocysteine and diabetes mellitus on brain alterations[J]. J Alzheimers Dis, 2021, 81(1): 287-295.
doi: 10.3233/JAD-210036 URL |
| [8] | Unger T, Borghi C, Charchar F, et al. 2020 International society of hypertension global hypertension practice guidelines[J]. Hypertension (Dallas, Tex: 1979), 2020, 75(6): 1334-1357. |
| [9] |
Zeña-Huancas PA, Iparraguirre-López H, Gamboa-Cárdenas RV, et al. Homocysteine levels are independently associated with damage accrual in systemic lupus erythematosus patients from a Latin-American cohort[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2019, 38(4): 1139-1146.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4389-3 pmid: 30539353 |
| [10] | 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2020年版)(上)[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2021, 41(8): 668-695. |
| [11] | 郭琼, 张建起, 石蕊. 高血压合并糖尿病与老年人认知功能的关系[J]. 中华老年多器官疾病杂志, 2017, 16(1): 38-42. |
| [12] | Wang YY, Zhang M, Wang XX, et al. Correlates of cognitive impairment in the elderly in China: A cross-sectional study[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 20(10): 973661. |
| [13] | Li W, Sun L, Li G, et al. Prevalence, influence factors and cognitive characteristics of mild cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2019, 30(11): 180. |
| [14] | 李晗, 赵晨, 林中樵, 等. 老年原发性高血压病人认知功能障碍的临床特点及其危险因素分析[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2022, 20(3): 565-569. |
| [15] | Fu J, Liu Q, Du Y, et al. Age-and sex-specific prevalence and modifiable risk factors of mild cognitive impairment among older adults in China: A population-based observational study[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2020, 30(12): 578742. |
| [16] | Anusheel? Avula SN, Joseph KN, et al. the role of high-density lipoprotein in lowering risk of dementia in the elderly: A review[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(4): e24374. |
| [17] |
Lee J, Lee S, Min JY, et al. Association between serum lipid parameters and cognitive performance in older adults[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(22):5405.
doi: 10.3390/jcm10225405 URL |
| [18] |
Wang Y, Liu J, Jiang Y, et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia is associated with decreased apolipoprotein AI levels in normal healthy people[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2016, 13(16): 10.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2261-13-10 URL |
| [19] |
Washida K, Hattori Y, Ihara M. Animal models of chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: From mouse to primate[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(24):6176.
doi: 10.3390/ijms20246176 URL |
| [20] | Chen WH, Jin W, Lyu PY, et al. Carotid atherosclerosis and cognitive impairment in nonstroke patients[J]. Chin Med J, 2017, 130(19): 2375-2379. |
| [21] |
Zhou H, Zhong X, Chen B, et al. Interactive effects of elevated homocysteine and late-life depression on cognitive impairment[J]. J Affect Disord, 2020, 277: 212-217.
doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.08.022 URL |
| [22] |
Biessels GJ, Despa F. Cognitive decline and dementia in diabetes mellitus: mechanisms and clinical implications[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2018, 14(10): 591-604.
doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0048-7 pmid: 30022099 |
| [23] | Wan C, Zong RY, Chen XS. The new mechanism of cognitive decline induced by hypertension: High homocysteine-mediated aberrant DNA methylation[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 24(9): 928701. |
| [24] |
Platt DE, Hariri E, Salameh P, et al. Type II diabetes mellitus and hyperhomocysteinemia: A complex interaction[J]. Diabetol Metab Syndr, 2017, 9(21):19.
doi: 10.1186/s13098-017-0218-0 URL |
| [25] | Yang Y, Xu P, Liu Y, et al. Vascular inflammation, atherosclerosis, and lipid metabolism and the occurrence of non-high albuminuria diabetic kidney disease: A cross-sectional study[J]. Diabetes Vasc Dis Re, 2021, 18(1): 1479164121992524. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||