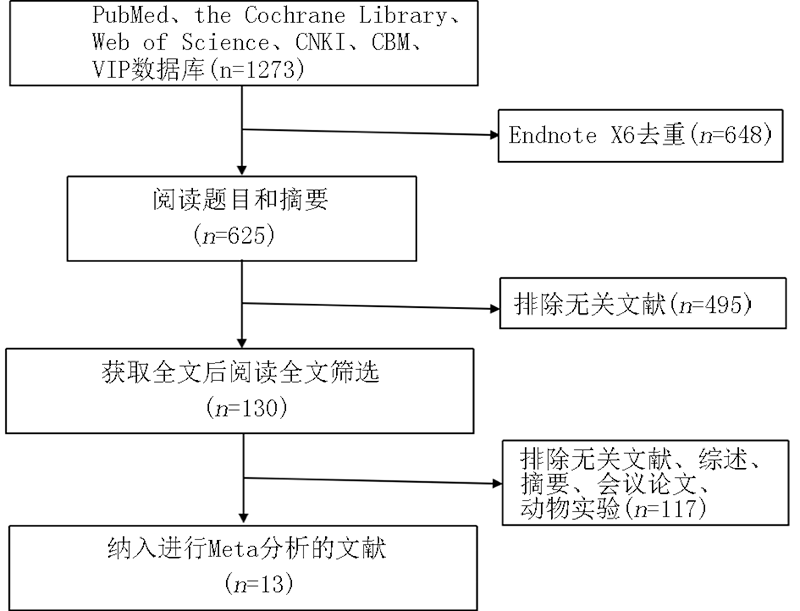
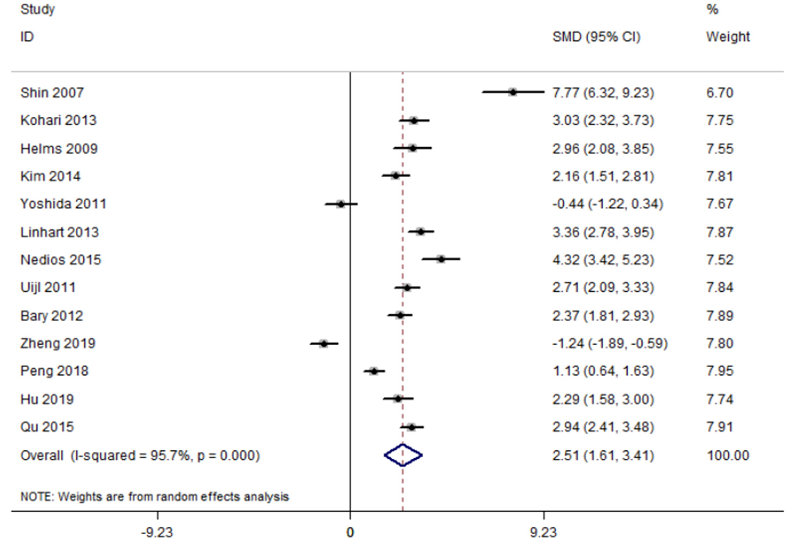
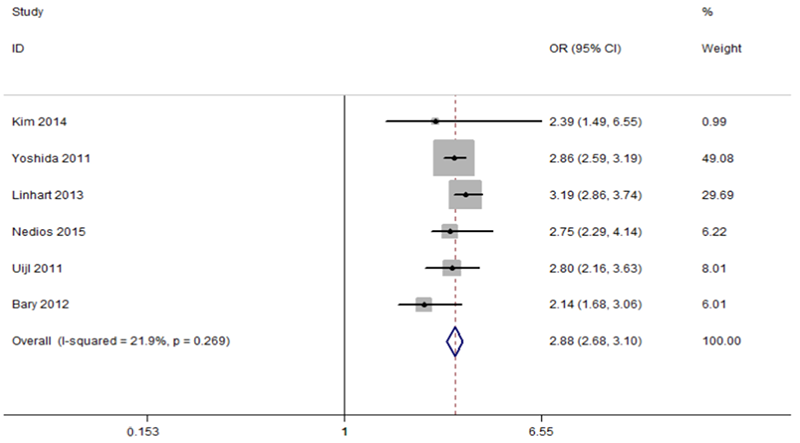
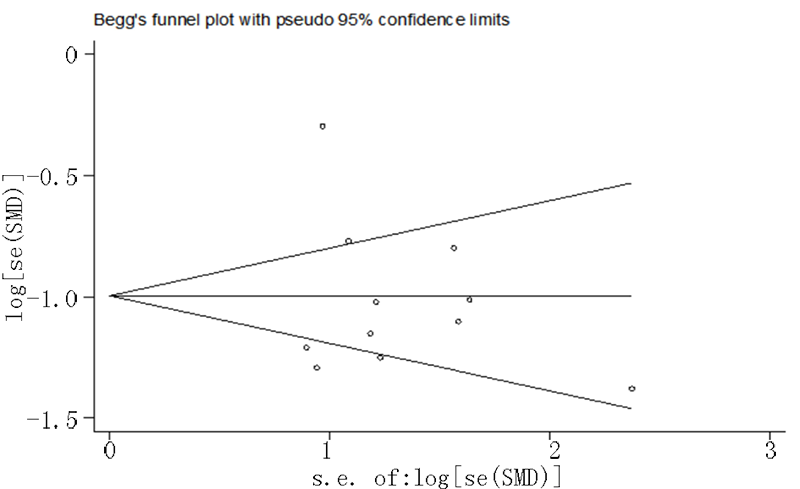
Clinical Focus ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 965-968.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.11.001
Left atrial volume index predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after radiofrequency ablation: A meta-analysis
- Department of Internal Medicine Emergency,Lanzhou University Second Hospital,Lanzhou 730000,China
-
Received:2022-08-06Online:2022-11-20Published:2023-01-02 -
Contact:Li Weiwei E-mail:lww0226516@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Weiwei, Li Yanan. Left atrial volume index predicts atrial fibrillation recurrence after radiofrequency ablation: A meta-analysis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2022, 37(11): 965-968.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2022.11.001
| 纳入研究 | 地区 | 患者数量(例) | 研究类型 | 随访时间(月) | 检测方法 | RFA方法 | 复发检测 | NOS评分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胡晓等[ | 亚洲 | 54 | 回顾性 | 24 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| Shin等[ | 亚洲 | 68 | 前瞻性 | 6 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| Kohári等[ | 欧洲 | 125 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | 心电图 | 8 |
| Helms等[ | 北美 | 73 | 前瞻性 | 12 | CT | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| Kim等[ | 亚洲 | 130 | 前瞻性 | 24 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| Linhart等[ | 欧洲 | 205 | 前瞻性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| Yoshida等[ | 北美 | 79 | 前瞻性 | 6 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | 心电图 | 9 |
| Nedios等[ | 欧洲 | 103 | 回顾性 | 36 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| Bary等[ | 欧洲 | 202 | 回顾性 | 6 | MRI | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| 郑贻升等[ | 亚洲 | 54 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| 彭红博等[ | 亚洲 | 138 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| 曲红培等[ | 亚洲 | 118 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | 心电图 | 8 |
| Uijl等[ | 欧洲 | 170 | 前瞻性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| 纳入研究 | 地区 | 患者数量(例) | 研究类型 | 随访时间(月) | 检测方法 | RFA方法 | 复发检测 | NOS评分 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胡晓等[ | 亚洲 | 54 | 回顾性 | 24 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| Shin等[ | 亚洲 | 68 | 前瞻性 | 6 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| Kohári等[ | 欧洲 | 125 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | 心电图 | 8 |
| Helms等[ | 北美 | 73 | 前瞻性 | 12 | CT | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| Kim等[ | 亚洲 | 130 | 前瞻性 | 24 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| Linhart等[ | 欧洲 | 205 | 前瞻性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| Yoshida等[ | 北美 | 79 | 前瞻性 | 6 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | 心电图 | 9 |
| Nedios等[ | 欧洲 | 103 | 回顾性 | 36 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| Bary等[ | 欧洲 | 202 | 回顾性 | 6 | MRI | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| 郑贻升等[ | 亚洲 | 54 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| 彭红博等[ | 亚洲 | 138 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 9 |
| 曲红培等[ | 亚洲 | 118 | 回顾性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | 心电图 | 8 |
| Uijl等[ | 欧洲 | 170 | 前瞻性 | 12 | 超声心动图 | 环肺静脉消融 | Holter | 8 |
| 纳入研究 | 平均年龄(岁) | 男性(%) | 合并高血压 | 合并糖尿病 | 合并冠心病 | AF类型(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阵发性 | 持续性 | 长期持续性 | ||||||
| 胡晓等[ | 51.2 | 21 | NR | NR | NR | 54 | 0 | 0 |
| Shin等[ | 55 | 95.72 | 45.58 | 8.99 | 13.77 | 58.8 | 41.3 | 0 |
| Kohári等[ | 61.3 | 79.66 | 68.23 | 14.97 | 13.76 | 0 | 77 | 23 |
| Helms等[ | 56 | 81.5 | 50.83 | 13.13 | 17.21 | 66 | 34 | 0 |
| Kim等[ | 54.6 | 86.01 | 40.53 | 5.26 | NR | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Linhart等[ | 60 | 68.33 | 58 | 9.74 | 16.09 | 67 | 33 | 0 |
| Yoshida等[ | 62 | 83.16 | 50.35 | 22.2 | 20.57 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Nedios等[ | 59 | 69.29 | 60.28 | 16.17 | 9.95 | 61.2 | 38.8 | 0 |
| Bary等[ | 60 | 56.91 | 40.74 | NR | 21.24 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 郑贻升等[ | 53.56 | 71.9 | 16 | NR | NR | 32 | 22 | 0 |
| 彭红博等[ | 65.06 | 68 | 50 | 16 | NR | 107 | 31 | 0 |
| 曲红培等[ | 55.4 | NR | 26 | 19 | NR | 118 | 0 | 0 |
| Uijl等[ | 55.9 | 77.00 | 45 | NR | NR | 71 | 29 | 0 |
| 纳入研究 | 平均年龄(岁) | 男性(%) | 合并高血压 | 合并糖尿病 | 合并冠心病 | AF类型(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阵发性 | 持续性 | 长期持续性 | ||||||
| 胡晓等[ | 51.2 | 21 | NR | NR | NR | 54 | 0 | 0 |
| Shin等[ | 55 | 95.72 | 45.58 | 8.99 | 13.77 | 58.8 | 41.3 | 0 |
| Kohári等[ | 61.3 | 79.66 | 68.23 | 14.97 | 13.76 | 0 | 77 | 23 |
| Helms等[ | 56 | 81.5 | 50.83 | 13.13 | 17.21 | 66 | 34 | 0 |
| Kim等[ | 54.6 | 86.01 | 40.53 | 5.26 | NR | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Linhart等[ | 60 | 68.33 | 58 | 9.74 | 16.09 | 67 | 33 | 0 |
| Yoshida等[ | 62 | 83.16 | 50.35 | 22.2 | 20.57 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Nedios等[ | 59 | 69.29 | 60.28 | 16.17 | 9.95 | 61.2 | 38.8 | 0 |
| Bary等[ | 60 | 56.91 | 40.74 | NR | 21.24 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 郑贻升等[ | 53.56 | 71.9 | 16 | NR | NR | 32 | 22 | 0 |
| 彭红博等[ | 65.06 | 68 | 50 | 16 | NR | 107 | 31 | 0 |
| 曲红培等[ | 55.4 | NR | 26 | 19 | NR | 118 | 0 | 0 |
| Uijl等[ | 55.9 | 77.00 | 45 | NR | NR | 71 | 29 | 0 |
| [1] | 胡翔稳, 张先林. 射频消融术治疗心房颤动术后复发相关因素的研究进展[J]. 实用心电学杂志, 2020, 150(2):62-65. |
| [2] |
杨丹丹, 李学斌. 心房颤动合并心力衰竭的治疗进展[J]. 中国实用内科杂志, 2020, 40(3):187-190.
doi: 10.19538/j.nk2020030103 |
| [3] | 陈璇, 王雨锋, 张筑欣, 等. 中国心律失常现状及治疗进展[J]. 中国研究型医院, 2020,(1): 3-5. |
| [4] | 胡晓, 谷阳, 蒙涛, 等. 维生素D水平、左房容积指数与阵发性房颤患者射频消融术后复发的相关性研究[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2019, 11(1):65-68. |
| [5] | Margulis AV, Pladeval lM, Riera-Guardia N, et al. Quality assessment of observational studies in a drug-safety systematic review, comparison of two tools: The Newcastle-Ottawa scale and the RTI item bank[J]. Clin Epidemiol, 2014, 5(3):22-34. |
| [6] |
Shin SH, Park MY, Oh WJ, et al. Left atrial volume is a predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation[J]. J Am Soc Echocardiogr, 2008, 21(6):697-702.
doi: 10.1016/j.echo.2007.10.022 URL |
| [7] |
Kohári M, Zado E, Marchlinski FE, et al. Left atrial volume best predicts recurrence after catheter ablation in patients with persistent and longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation[J]. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 2014, 37(4):422-429.
doi: 10.1111/pace.12279 URL |
| [8] |
Helms AS, West JJ, Patel A, et al. Relation of left atrial volume from three-dimensional computed tomography to atrial fibrillation recurrence following ablation[J]. Am J Cardiol, 2009, 103(7):989-993.
doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2008.12.021 pmid: 19327428 |
| [9] |
Kim MN, Lee JJ, Kim SA, et al. The difference of predictors for recurrence after catheter ablation of non-paroxysmal atrial fibrillation according to follow-up period[J]. Int Heart J, 2014, 55(4):312-318.
doi: 10.1536/ihj.13-370 URL |
| [10] |
Linhart M, Lewalter T, Mittmann-Braun EL, etal. Left atrial pressure as predictor for recurrence of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2013, 38(2):107-114.
doi: 10.1007/s10840-013-9803-9 pmid: 23793444 |
| [11] |
Yoshida K, Rabbani AB, Oral H, et al. Left atrial volume and dominant frequency of atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing catheter ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2011, 32(2): 155-161.
doi: 10.1007/s10840-011-9590-0 pmid: 21671071 |
| [12] |
Nedios S, Kosiuk J, Koutalas E, et al. Comparison of left atrial dimensions in CT and echocardiography as predictors of long-term success after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2015, 43(3):237-244
doi: 10.1007/s10840-015-0010-8 pmid: 25956477 |
| [13] |
Bary CV, Dornia C, Eissnert C, et al. Predictive value of left atrial volume measured by non-invasive cardiac imaging in the treatment of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation[J]. J Interv Card Electrophysiol, 2012, 34(2):181-188.
doi: 10.1007/s10840-011-9641-6 pmid: 22228410 |
| [14] | 郑贻升. 胱抑素C及左房容积指数对心房颤动患者导管消融术后早期复发的预测价值[D]. 南宁: 广西医科大学, 2019. |
| [15] | 彭红博. 左房容积指数(LVAI)与NT-proBNP对房颤射频消融术后早期复发的预测价值[D]. 大连: 大连医科大学, 2018. |
| [16] | 曲红培, 宋溢娟, 汪砚雨, 等. 左房容积指数与射频消融术后房颤复发的关系[J]. 医药论坛杂志, 2015, 36(2):88-90. |
| [17] |
DenUijl DW, Delgado V, Bertini M, et al. Impact of left atrial fibrosis and left atrial size on the outcome of catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation[J]. Heart, 2011, 97(22):1847-1851.
doi: 10.1136/hrt.2010.215335 pmid: 21357370 |
| [18] | 周英, 张林潮. 心房颤动患者发生抗凝相关出血后重启抗凝治疗的研究进展[J]. 海南医学, 2019, 30(15):2017-2021. |
| [19] | 史展, 孙雪荣, 田颖, 等. 心房颤动患者口服抗凝药物依从性的研究进展[J]. 心血管病学进展, 2020, 41(1):18-22. |
| [20] |
Haïssaguerre M, JaïsP, Shah DC, et al. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins.[J]. N Engl J Med, 1998, 339(10):659-666.
doi: 10.1056/NEJM199809033391003 URL |
| [21] | 卫越, 吴立群. 导管消融治疗心房颤动伴心力衰竭的新进展[J]. 中国心脏起搏与心电生理杂志, 2019, 33(3):252-254. |
| [22] | 王海军, 史扬, 李健, 等. 左房增大对起搏器术后的老年阵发性房颤患者再发房颤的影响[J]. 中国应用生理学杂志, 2017, 33(3):257-261. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||