Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 613-617.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.07.005
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical value of multimodal ultrasound in screening middle cerebral artery stenosis in hypertensive patients
- Department of Ultrasound, the Second People's Hospital of Jingdezhen, Jingdezhen 333000, China
-
Received:2023-06-19Online:2023-07-20Published:2023-09-01 -
Contact:Li Zhiyong E-mail:448132882@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Zhiyong, Li Xing. Clinical value of multimodal ultrasound in screening middle cerebral artery stenosis in hypertensive patients[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(7): 613-617.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.07.005
| 狭窄程度 | PSV(cm/s) | EDV(cm/s) | PSVICA/PSVCCA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50%~69% | ≥125,<230 | ≥40,<100 | 2.0~4.0 |
| 70%~99% | ≥230 | ≥100 | ≥4.0 |
Tab.1 Hemodynamic criteria for internal carotid artery stenosis
| 狭窄程度 | PSV(cm/s) | EDV(cm/s) | PSVICA/PSVCCA |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50%~69% | ≥125,<230 | ≥40,<100 | 2.0~4.0 |
| 70%~99% | ≥230 | ≥100 | ≥4.0 |
| 狭窄程度 | PSV(cm/s) | MV(cm/s) | PSVV1/PSVV2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度(<50%) | ≥140,<180 | ≥90,<120 | / |
| 中度(50%~69%) | ≥180,<220 | ≥120,<140 | 2.0~3.0 |
| 重度(70%~99%) | ≥220 | ≥140 | ≥3.0 |
Tab.2 Hemodynamic criteria for middle cerebral artery stenosis
| 狭窄程度 | PSV(cm/s) | MV(cm/s) | PSVV1/PSVV2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度(<50%) | ≥140,<180 | ≥90,<120 | / |
| 中度(50%~69%) | ≥180,<220 | ≥120,<140 | 2.0~3.0 |
| 重度(70%~99%) | ≥220 | ≥140 | ≥3.0 |
| 组别 | 例数 | 内中膜厚度 (mm) | 斑块发生率[例(%)] | 累及血管数目[例(%)] | 颈总动脉、颈内动脉狭窄[例(%)] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无 | 有 | 1 | ≥2 | 无 | 有 | |||||
| 试验组 | 30 | 1.20±0.11 | 2(6.67) | 28(93.3) | 3(10.0) | 27(90.0) | 21(70.0) | 9(30.0) | ||
| 对照组 | 30 | 1.15±0.16 | 5(16.7) | 25(83.3) | 10(33.3) | 20(66.7) | 28(93.3) | 2(6.67) | ||
| t/χ2值 | 2.045 | 1.456 | 4.812 | 5.822 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.49 | 0.228 | 0.028 | 0.016 | ||||||
Tab.3 Comparison of carotid artery ultrasound morphology of patients between two groups
| 组别 | 例数 | 内中膜厚度 (mm) | 斑块发生率[例(%)] | 累及血管数目[例(%)] | 颈总动脉、颈内动脉狭窄[例(%)] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无 | 有 | 1 | ≥2 | 无 | 有 | |||||
| 试验组 | 30 | 1.20±0.11 | 2(6.67) | 28(93.3) | 3(10.0) | 27(90.0) | 21(70.0) | 9(30.0) | ||
| 对照组 | 30 | 1.15±0.16 | 5(16.7) | 25(83.3) | 10(33.3) | 20(66.7) | 28(93.3) | 2(6.67) | ||
| t/χ2值 | 2.045 | 1.456 | 4.812 | 5.822 | ||||||
| P值 | 0.49 | 0.228 | 0.028 | 0.016 | ||||||
| 组别 | 例数 | PSV(m/s) | EDV(m/s) | RI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 30 | 0.89±0.16 | 0.35±0.09 | 0.76±0.06 |
| 对照组 | 30 | 0.96±0.13 | 0.43±0.07 | 0.63±0.05 |
| t值 | 1.673 | 3.843 | 9.116 | |
| P值 | 0.06 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
Tab.4 Comparison of ultrasound hemodynamic parameters of the affected internal carotid artery of patients between two groups( x -±s)
| 组别 | 例数 | PSV(m/s) | EDV(m/s) | RI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 试验组 | 30 | 0.89±0.16 | 0.35±0.09 | 0.76±0.06 |
| 对照组 | 30 | 0.96±0.13 | 0.43±0.07 | 0.63±0.05 |
| t值 | 1.673 | 3.843 | 9.116 | |
| P值 | 0.06 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
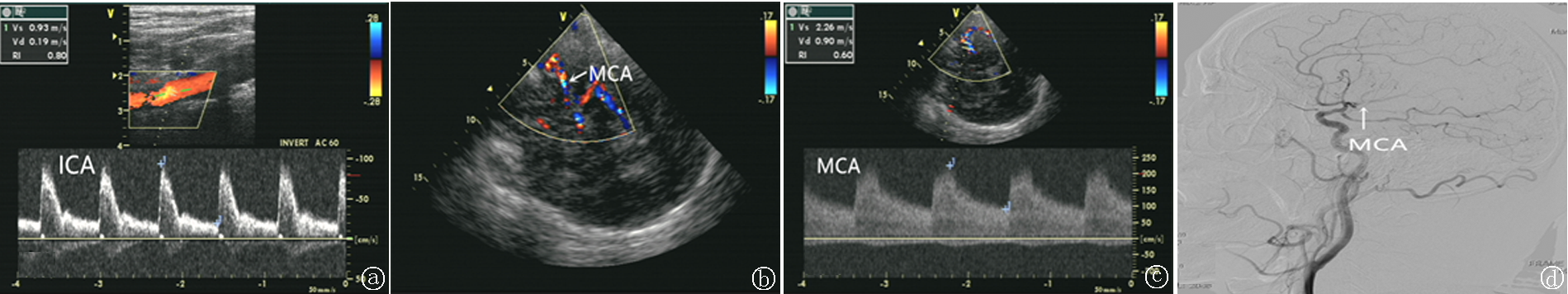
Fig.1 Typical cases(ICA internal carotid artery; MCA middle cerebral artery) a. Carotid artery ultrasound shows hemodynamic parameters of the right inte rnal carotid artery: PSV:0.93m/s,EDV:0.19 m/s RI:0.80; b. TCCD shows that the Ml segment of the right middle cerebral arte ry presents a“waist band sign”(arrow);c. TCCD shows the hemodynamic parameters of the M1 segment of the right mid dle cerebral artery,PSV:2.26 m/s,EDV: 0.90 m/s RI:0.60;d. DSA shows stenosis of the Ml segment of the right middle cerebral artery(arrow)
| 项目 | 大脑中动脉狭窄 | |
|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | |
| EDV | -0.39 | 0.02 |
| RI | 0.28 | 0.01 |
Tab.5 Correlation analysis between hemodynamic parameters of the affected internal carotid artery and stenosis of the middle cerebral artery
| 项目 | 大脑中动脉狭窄 | |
|---|---|---|
| r值 | P值 | |
| EDV | -0.39 | 0.02 |
| RI | 0.28 | 0.01 |
| TCCD | DSA | 合计 | Kappa值 | P值 | 95%CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度 | 中度 | 重度 | |||||
| 轻度 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |||
| 中度 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 13 | 0.895 | <0.001 | 0.756~1.034 |
| 重度 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 | |||
| 合计 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 30 | |||
Tab. 6 Consistency analysis between TCCD diagnosis of middle cerebral artery stenosis and DSA
| TCCD | DSA | 合计 | Kappa值 | P值 | 95%CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 轻度 | 中度 | 重度 | |||||
| 轻度 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | |||
| 中度 | 1 | 11 | 1 | 13 | 0.895 | <0.001 | 0.756~1.034 |
| 重度 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 12 | |||
| 合计 | 6 | 11 | 13 | 30 | |||
| [1] | 马林, 巢宝华, 曹雷, 等. 2007-2017年中国脑卒中流行趋势及特征分析[J]. 中华脑血管病杂志(电子版), 2020, 14(5):253-257. |
| [2] | 蔡星星, 薛晓冬. 阿司匹林和氯吡格雷在老年缺血性脑卒中二级预防的应用进展[J]. 老年医学与保健, 2023, 29(1):156-159. |
| [3] | 黄德波, 毛献泉, 徐振强, 等. 支架取栓与静脉溶栓治疗急性大动脉闭塞型脑梗死的疗效对比[J]. 临床荟萃, 2019, 34(7):617-621. |
| [4] | 贾凌云, 华扬, 惠品晶, 等. 血管超声对短暂性脑缺血发作(TIA)与缺血性脑卒中住院患者颅内外动脉病变的多中心检查登记研究设计方案[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2017, 14(6):281-284. |
| [5] | 冯雁明, 杨佳, 王剑文. 缺血性脑卒中老年患者颅内外动脉狭窄分布及危险因素分析[J]. 中国临床神经科学, 2020, 28(4):440-443. |
| [6] | 崔柳平, 陈盈, 陈虹秀, 等. 基于多参数特征构建列线图评估动脉粥样硬化性卒中风险[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志, 2023, 40(1):39-43. |
| [7] | 贺翔渝, 潘燕, 张小林. 血清脂蛋白相关磷脂酶A2水平与急性缺血性脑卒中病情及预后的关系[J]. 临床荟萃, 2023, 38(4):315-318. |
| [8] | 成倩倩, 李军, 黄慧, 等. 多模态血管超声成像在脑卒中高危人群中的应用价值[J]. 淮海医药, 2021, 39(5):458-460. |
| [9] | 宋玉娟. 经颅彩色多普勒超声及颈动脉血管超声联合应用对大脑中动脉粥样硬化性脑梗塞的诊断价值[J]. 菏泽医学专科学校学报, 2018, 30(1):11-33. |
| [10] | 《中国高血压防治指南》修订委员会. 中国高血压防治指南2018年修订版[J]. 心脑血管病防治, 2019, 19(1):1-32. |
| [11] | 国家卫生计生委脑卒中防治工程委员会. 中国脑卒中血管超声检查指导规范[J/CD]. 中华医学超声杂志(电子版), 2015, 12(8):599-610. |
| [12] | 朱新庆, 程林, 芦英云, 等. 老年大脑中动脉狭窄或闭塞致缺血性脑卒中的预后影响因素[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2020, 40(3):473-475. |
| [13] | 中国脑卒中防治报告编写组. 《中国脑卒中防治报告2020》概要[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2022, 19(2):136-144. |
| [14] | 伞小旭, 王健. 缺血性脑卒中风险评估模型研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2023, 21(1):93-95. |
| [15] | 何洪真, 吕佩源. 调节性T细胞与缺血性脑卒中危险因素的相关性[J]. 临床荟萃, 2022, 37(4):369-372. |
| [16] |
Liu R, Li J, Hua Y, et al. Transcranial color-coded sonography criteria for moderate and severe middle cerebral artery stenosis[J]. Ultrasound Med Biol, 2021, 47(1):25-32.
doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.09.008 pmid: 33069442 |
| [17] | 雷娜, 华扬, 杨洁, 等. 颈内动脉颅外段血流动力学变化与颅内段病变的相关分析[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2020, 17(1):39-41. |
| [18] | 张岩. 经颅彩色多普勒超声联合颈动脉血管超声对大脑中动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死诊断分析[J]. 首都食品与医药, 2018, 25(19):49-50. |
| [19] | 冯朝申, 何文涛, 张新丽. 颈动脉粥样硬化发生的危险因素及预防对策[J]. 新疆医学, 2023, 53(3):305-308,373. |
| [20] | 薛丽丽, 王灵杰, 石彩云, 等. 颅内外动脉并存粥样硬化斑块的研究进展[J]. 实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2023, 31(2):130-134. |
| [21] | 刘文智, 刘莹, 罗院明. 斑块偏心分布影响下多组分两相血流动力学数值模拟[J]. 介入放射学杂志, 2019, 28(10):969-973. |
| [22] | 侍艳, 张迎春. 经颅彩色多普勒超声联合颈动脉血管超声对大脑中动脉粥样硬化性脑梗死患者的应用价值[J]. 安徽医药, 2016, 20(2):320-323. |
| [23] | 王晖, 苏娅, 黄大刚. 大脑中动脉中重度狭窄或闭塞性病变患者同侧颅外颈动脉血流动力学的分析[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2019, 25(10):792-796. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
