Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (2): 121-125.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.02.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Predictive values of serum homocysteine, cystatin C and high sensitive C-reactive protein levels on heart failure after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction
- Department of Cardiovascular Medicine, Postgraduate Training Base of Jinzhou Central Hospital, Jinzhou Medical University, Jinzhou 121000, China
-
Received:2022-06-24Online:2023-02-20Published:2023-03-31 -
Contact:Jiang Shan E-mail:Jiangshan_j@163.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Nana, Jiang Shan. Predictive values of serum homocysteine, cystatin C and high sensitive C-reactive protein levels on heart failure after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(2): 121-125.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.02.004
| 项目 | HF组( | 非HF组( | 统计值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 72.52±6.97 | 65.05±6.25 | 0.000 | |
| 男性[例(%)] | 43(46.7) | 40(52.6) | χ2=0.578 | 0.447 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 46(50.0) | 35(46.1) | χ2=0.260 | 0.610 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 27(29.3) | 20(26.3) | χ2=0.190 | 0.663 |
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 21(22.8) | 16(21.1) | χ2=0.076 | 0.782 |
| 高血压史[例(%)] | 48(52.2) | 30(39.5) | χ2=2.699 | 0.100 |
| 单支血管病变[例(%)] | 25(27.2) | 18(23.7) | χ2=0.266 | 0.606 |
| 心率(次/min) | 83.24±13.48 | 79.45±13.89 | 0.075 | |
| LVEF(%) | 47.34±5.78 | 51.02±6.03 | 0.000 | |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 23.61±1.05 | 23.40±1.34 | 0.270 |
Tab. 1 Comparison of general data between the two groups
| 项目 | HF组( | 非HF组( | 统计值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄(岁) | 72.52±6.97 | 65.05±6.25 | 0.000 | |
| 男性[例(%)] | 43(46.7) | 40(52.6) | χ2=0.578 | 0.447 |
| 吸烟史[例(%)] | 46(50.0) | 35(46.1) | χ2=0.260 | 0.610 |
| 饮酒史[例(%)] | 27(29.3) | 20(26.3) | χ2=0.190 | 0.663 |
| 糖尿病史[例(%)] | 21(22.8) | 16(21.1) | χ2=0.076 | 0.782 |
| 高血压史[例(%)] | 48(52.2) | 30(39.5) | χ2=2.699 | 0.100 |
| 单支血管病变[例(%)] | 25(27.2) | 18(23.7) | χ2=0.266 | 0.606 |
| 心率(次/min) | 83.24±13.48 | 79.45±13.89 | 0.075 | |
| LVEF(%) | 47.34±5.78 | 51.02±6.03 | 0.000 | |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 23.61±1.05 | 23.40±1.34 | 0.270 |
| 项目 | HF组( | 非HF组( | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肌钙蛋白T(mg/ml) | 6.53±0.48 | 6.47±0.43 | 0.812 | 0.481 |
| 肌酸激酶同工酶(U/L) | 73.39±15.02 | 70.97±13.54 | 1.082 | 0.281 |
| 甘油三脂(mmol/L) | 2.71±0.68 | 2.66±0.59 | 0.456 | 0.649 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 2.09±0.50 | 2.18±0.42 | -1.285 | 0.200 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 3.38±0.92 | 3.33±1.06 | 0.311 | 0.756 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 337.00±84.49 | 318.34±89.30 | 1.388 | 0.167 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 77.06±15.37 | 72.85±16.11 | 1.728 | 0.086 |
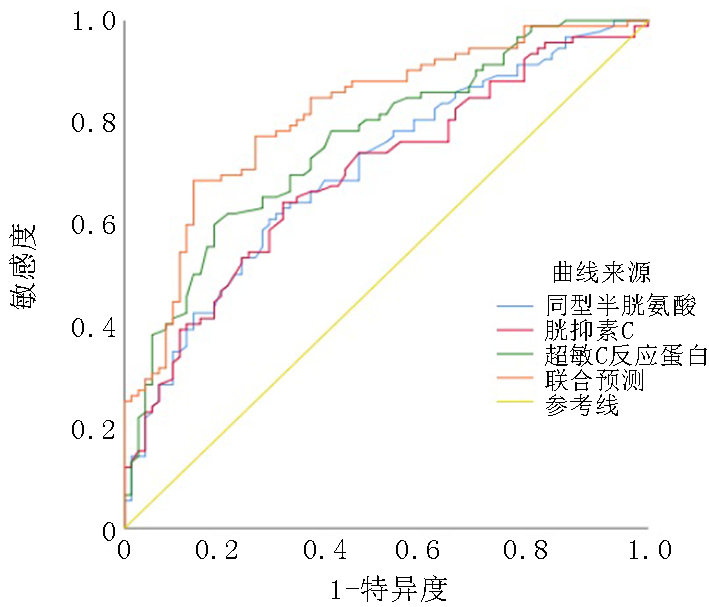
| 同型半胱氨酸(mmol/L) | 21.02±6.84 | 16.03±6.15 | 4.921 | 0.000 |
| 胱抑素C(mg/L) | 1.73±0.48 | 1.39±0.42 | 4.740 | 0.000 |
| 超敏C-反应蛋白(mg/L) | 14.42±3.78 | 10.61±3.60 | 6.660 | 0.000 |
Tab. 2 Comparison of biochemical index between the two groups
| 项目 | HF组( | 非HF组( | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 肌钙蛋白T(mg/ml) | 6.53±0.48 | 6.47±0.43 | 0.812 | 0.481 |
| 肌酸激酶同工酶(U/L) | 73.39±15.02 | 70.97±13.54 | 1.082 | 0.281 |
| 甘油三脂(mmol/L) | 2.71±0.68 | 2.66±0.59 | 0.456 | 0.649 |
| 高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 2.09±0.50 | 2.18±0.42 | -1.285 | 0.200 |
| 低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(mmol/L) | 3.38±0.92 | 3.33±1.06 | 0.311 | 0.756 |
| 尿酸(μmol/L) | 337.00±84.49 | 318.34±89.30 | 1.388 | 0.167 |
| 肌酐(μmol/L) | 77.06±15.37 | 72.85±16.11 | 1.728 | 0.086 |
| 同型半胱氨酸(mmol/L) | 21.02±6.84 | 16.03±6.15 | 4.921 | 0.000 |
| 胱抑素C(mg/L) | 1.73±0.48 | 1.39±0.42 | 4.740 | 0.000 |
| 超敏C-反应蛋白(mg/L) | 14.42±3.78 | 10.61±3.60 | 6.660 | 0.000 |
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 0.150 | 0.034 | 18.976 | 0.000 | 1.161 | 1.086 | 1.242 |
| LVEF | -0.099 | 0.037 | 7.272 | 0.007 | 0.906 | 0.843 | 0.973 |
| 同型半胱氨酸 | 0.080 | 0.033 | 5.909 | 0.015 | 1.083 | 1.016 | 1.155 |
| 胱抑素C | 1.062 | 0.488 | 4.726 | 0.020 | 2.892 | 1.110 | 7.533 |
| 超敏C-反应蛋白 | 0.153 | 0.058 | 6.949 | 0.008 | 1.165 | 1.040 | 1.306 |
Tab. 3 Analysis of HF risk factors after PCI in STEMI patients
| 变量 | 回归系数 | 标准误 | Wald χ2值 | 95% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 下限 | 上限 | ||||||
| 年龄 | 0.150 | 0.034 | 18.976 | 0.000 | 1.161 | 1.086 | 1.242 |
| LVEF | -0.099 | 0.037 | 7.272 | 0.007 | 0.906 | 0.843 | 0.973 |
| 同型半胱氨酸 | 0.080 | 0.033 | 5.909 | 0.015 | 1.083 | 1.016 | 1.155 |
| 胱抑素C | 1.062 | 0.488 | 4.726 | 0.020 | 2.892 | 1.110 | 7.533 |
| 超敏C-反应蛋白 | 0.153 | 0.058 | 6.949 | 0.008 | 1.165 | 1.040 | 1.306 |
| [1] |
Wang Y, Peng Z. Prognostic value of platelet/lymphocyte ratio and CAMI-STEMI score for major adverse cardiac events in patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: A prospective observational study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2021, 100(33):e26942.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026942 URL |
| [2] |
Jeremias A, Davies JE, Maehara A, et al. Blinded physiological assessment of residual ischemia after successful angiographic percutaneous coronary intervention: The DEFINE PCI Study[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2019, 12(20):1991-2001.
doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.05.054 URL |
| [3] |
陈鑫森, 邵萌, 张天, 等. 血液学参数预测急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者经皮冠状动脉介入治疗术后发生主要不良心血管事件的价值研究[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(27):3389-3395.
doi: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2020.00.245 |
| [4] | 张丽萍, 王军, 李世敬, 等. 血清炎性标志物对急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死患者冠状动脉侧支循环未形成的预测价值研究[J]. 临床误诊误治, 2016, 29(1):75-79. |
| [5] |
Lyu WY, Qin CY, Wang XT, et al. The application of myocardial contrast echocardiography in assessing microcirculation perfusion in patients with acute myocardial infarction after PCI[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2022, 22(1):233.
doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-02404-9 |
| [6] |
Jenča D, Melenovský V, Stehlik J, et al. Heart failure after myocardial infarction: Incidence and predictors[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2021, 8(1):222-237.
doi: 10.1002/ehf2.13144 pmid: 33319509 |
| [7] |
Sulo G, Igland J, Vollset SE, et al. Heart failure complicating acute myocardial infarction; burden and timing of occurrence: A nation-wide analysis including 86 771 patients from the cardiovascular disease in Norway (CVDNOR) project[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2016, 5(1):e002667.
doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002667 URL |
| [8] | Parenica J, Kala P, Jarkovsk J, et al. The Acute heart failure and the early development of left ventricular dysfunction in patients with ST segment elevation acute myocardial infarction managed With primary percutaneous coronary intervention[J]. Vnitr Lek, 2011, 57(7):43-51. |
| [9] | Brenner GB, Giricz Z, Garamvölgyi R, et al. Post-myocardial infarction heart failure in closed-chest coronary occlusion/reperfusion model in göttingen minipigs and landrace pigs[J]. J Vis Exp, 2021, (170). |
| [10] |
李若颖. Gal-3在老年急性心肌梗死伴心力衰竭患者中的表达及与心功能的相关性研究[J]. 中国疗养医学, 2021, 30(7):760-761.
doi: 10.13517/j.cnki.ccm.2021.07.033 |
| [11] |
Bajic Z, Sobot T, Skrbic R, et al. Homocysteine, vitamins B6 and folic acid in experimental models of myocardial infarction and heart failure-how strong is that link?[J]. Biomolecules, 2022, 12(4):536.
doi: 10.3390/biom12040536 URL |
| [12] |
Raffield LM, Ellis J, Olson NC, et al. Genome-wide association study of homocysteine in African Americans from the Jackson Heart Study, the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis, and the Coronary Artery Risk in Young Adults study[J]. J Hum Genet, 2018, 63(3):327-337.
doi: 10.1038/s10038-017-0384-9 pmid: 29321517 |
| [13] | 刘艳凤, 柯建玲. 同型半胱氨酸水平在急性心肌梗死患者伴充血性心力衰竭中的临床价值[J]. 特别健康, 2020, 16(13):242. |
| [14] | 于艳丽. Hcy在急性心肌梗死伴充血性心力衰竭中的表达及相关性分析[J]. 医学信息, 2021, 34(12):118-120. |
| [15] | Wu X, Xu G, Zhang S. Association between cystatin c and cardiac function and long-term prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2020, 26:e919422. |
| [16] | Chen B, Ma ZH, Zhang YJ, et al. Correlation analysis between serum cystatin C and Hcy levels and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome[J]. Chin J Integr Med on Cardio-Cerebrovasc Dis, 2018, 16(6):2054-2056. |
| [17] |
Ballew SH, Matsushita K. Cardiovascular risk prediction in CKD[J]. Semin Nephrol, 2018, 38(3):208-216.
doi: S0270-9295(18)30023-8 pmid: 29753398 |
| [18] | Verbree-Willemsen L, Zhang YN, Ibrahim I, et al. Extracellular vesicle cystatin C and CD14 are associated with both renal dysfunction and heart failure[J]. ESC Heart Fail, 2020, 7(5):2240-2249. |
| [19] | 杨岸霖. 重组人脑利钠肽治疗急性心肌梗死合并心力衰竭患者的临床研究[J]. 黑龙江医药, 2022, 35(2):334-337. |
| [20] |
Xu M, Yan L, Xu J, et al. Predictors and prognosis for incident in-hospital heart failure in patients with preserved ejection fraction after first acute myocardial infarction: An observational study[J]. Medicine (Baltimore), 2018, 97(24):e11093.
doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011093 URL |
| [21] | 刘玉宁, 李杰, 吴振华. 血清超敏C反应蛋白和前白蛋白在急性心肌梗死发病早期心力衰竭中的临床诊断价值[J]. 当代医学, 2019, 25(28):53-55. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||