Clinical Focus ›› 2023, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 241-244.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.008
Previous Articles Next Articles
Correlation between vascular endothelial function and serum uric acid in gouty arthritis
Shen Xuejiao, Li Yan, Wang Ting, Wang Yuan( )
)
- Department of Ultrasound,Lanzhou University Second Hospital,Lanzhou 730030,China
-
Received:2022-11-04Online:2023-03-20Published:2023-05-11 -
Contact:Wang Yuan E-mail:51695179@qq.com
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shen Xuejiao, Li Yan, Wang Ting, Wang Yuan. Correlation between vascular endothelial function and serum uric acid in gouty arthritis[J]. Clinical Focus, 2023, 38(3): 241-244.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://huicui.hebmu.edu.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.1004-583X.2023.03.008
| 组别 | 例数 | 病程 (年) | BMI (kg/m2) | SUA (μmol/L) | ESR (mm/h) | CRP (mg/L) | TC (mmol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA组 | 45 | 4.91±4.76 | 27.30±3.80 | 520.71±113.23 | 11.72±13.64 | 10.29±17.23 | 4.12±0.79 | ||||
| 对照组 | 35 | - | 23.05±1.81 | 313.54±87.57 | 3.40±0.64 | 1.47±0.62 | 3.87±0.63 | ||||
| - | -6.130 | -8.940 | -2.200 | -2.990 | -4.400 | ||||||
| - | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.031 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||||
| 组别 | TG (mmol/L) | LDL (mmol/L) | HDL (mmol/L) | SBP (mmHg) | FMD (%) | CIMT (mm) | |||||
| GA组 | 1.64±0.88 | 2.55±0.74 | 1.19±0.26 | 117.93±8.46 | 9.35±2.94 | 0.69±0.15 | |||||
| 对照组 | 1.25±0.29 | 2.18±0.48 | 1.24±0.12 | 114.51±6.69 | 13.49±1.02 | 0.66±0.07 | |||||
| -2.120 | -2.570 | 0.960 | -3.680 | 7.950 | -1.160 | ||||||
| 0.043 | 0.012 | 0.339 | 0.214 | <0.01 | 0.249 | ||||||
Tab.1 Comparison of clinical and laboratory values between the two groups ( x -±s)
| 组别 | 例数 | 病程 (年) | BMI (kg/m2) | SUA (μmol/L) | ESR (mm/h) | CRP (mg/L) | TC (mmol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA组 | 45 | 4.91±4.76 | 27.30±3.80 | 520.71±113.23 | 11.72±13.64 | 10.29±17.23 | 4.12±0.79 | ||||
| 对照组 | 35 | - | 23.05±1.81 | 313.54±87.57 | 3.40±0.64 | 1.47±0.62 | 3.87±0.63 | ||||
| - | -6.130 | -8.940 | -2.200 | -2.990 | -4.400 | ||||||
| - | <0.01 | <0.01 | 0.031 | <0.01 | <0.01 | ||||||
| 组别 | TG (mmol/L) | LDL (mmol/L) | HDL (mmol/L) | SBP (mmHg) | FMD (%) | CIMT (mm) | |||||
| GA组 | 1.64±0.88 | 2.55±0.74 | 1.19±0.26 | 117.93±8.46 | 9.35±2.94 | 0.69±0.15 | |||||
| 对照组 | 1.25±0.29 | 2.18±0.48 | 1.24±0.12 | 114.51±6.69 | 13.49±1.02 | 0.66±0.07 | |||||
| -2.120 | -2.570 | 0.960 | -3.680 | 7.950 | -1.160 | ||||||
| 0.043 | 0.012 | 0.339 | 0.214 | <0.01 | 0.249 | ||||||
| FMD | ||
|---|---|---|
| BMI(kg/m2) | -0.158 | 0.300 |
| SUA(μmol/L) | -0.393 | 0.007 |
| ESR(mm/h) | -0.219 | 0.149 |
| CRP(mg/L) | -0.322 | 0.030 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 0.273 | 0.069 |
| TG(mmol/L) | -0.180 | 0.238 |
| LDL(mmol/L) | 0.124 | 0.416 |
| HDL(mmol/L) | 0.224 | 0.139 |
| SBP(mmHg) | -0.242 | 0.109 |
| CIMT(mm) | -0.458 | 0.001 |
| 病程 | -0.431 | 0.003 |
Tab.2 Correlation analysis between FMD and other variables
| FMD | ||
|---|---|---|
| BMI(kg/m2) | -0.158 | 0.300 |
| SUA(μmol/L) | -0.393 | 0.007 |
| ESR(mm/h) | -0.219 | 0.149 |
| CRP(mg/L) | -0.322 | 0.030 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 0.273 | 0.069 |
| TG(mmol/L) | -0.180 | 0.238 |
| LDL(mmol/L) | 0.124 | 0.416 |
| HDL(mmol/L) | 0.224 | 0.139 |
| SBP(mmHg) | -0.242 | 0.109 |
| CIMT(mm) | -0.458 | 0.001 |
| 病程 | -0.431 | 0.003 |
| 组别 | 偏回归 系数 | 标准误 | 标准化偏 回归系数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | 常数项 | 14.677 | 1.941 | 7.560 | <0.01 | |
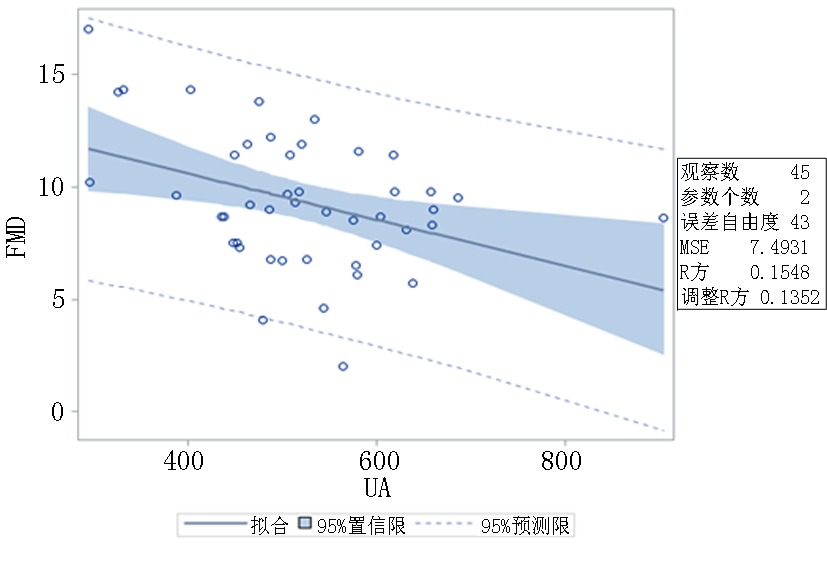
| SUA | -0.010 | 0.004 | -0.393 | -2.810 | 0.008 |
Tab.3 Regression analysis of FMD and SUA
| 组别 | 偏回归 系数 | 标准误 | 标准化偏 回归系数 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA | 常数项 | 14.677 | 1.941 | 7.560 | <0.01 | |
| SUA | -0.010 | 0.004 | -0.393 | -2.810 | 0.008 |
| [1] |
Çukurova S, Pamuk ÖN, Ünlü E, et al. Subclinical atherosclerosis in gouty arthritis patients: A comparative study[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2012, 32(6):1769-1773.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-011-1900-4 pmid: 21442166 |
| [2] | Choi YJ, Yoon Y, Lee KY, et al. Uric acid induces endothelial dysfunction by vascular insulin resistance associated with the impairment of nitric oxide synthesis[J]. 2014, 28(7): 3197-3204. |
| [3] |
Perez-Ruiz F, Becker MA. Inflammation: A possible mechanism for a causative role of hyperuricemia/gout in cardiovascular disease[J]. Curr Med Res Opin, 2015, 31(Suppl 2): 9-14.
doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1087980 URL |
| [4] | 李文博, 陈岩, 安松涛, 等. 血管紧张素Ⅱ1型受体基因多态性对动脉硬化影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2019, 27(9):802-807. |
| [5] |
Martín-Martínez MA, González-Juanatey C, Castañeda S, et al. Recommendations for the management of cardiovascular risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Scientific evidence and expert opinion[J]. Semin Arthritis Rheum, 2014, 44(1):1-8.
doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2014.01.002 URL |
| [6] |
Arévalo-Lorido JC, Carretero-Gómez J, Robles Pérez-Monteoliva NR. Association between serum uric acid and carotid disease in patients with atherosclerotic acute ischemic stroke[J]. Vascular, 2019, 27(1):19-26.
doi: 10.1177/1708538118797551 pmid: 30205779 |
| [7] | Bertolazzi C, Gutierrez M, Espinosa R, et al. SAT0613 High prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis in gout and asymptomatic hyperuricemia: A study based on carotid ultrasound[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2017, 76(Suppl 2):6363. |
| [8] | Gancheva R, Kundurdjiev A, Nikolova G, et al. Serum oxidative stress markers are not associated with renal and common carotid arteries arteriosclerotic vascular changes in patients with gout[J]. Acta Med Bulgarica, 2019, 46(3):37-43. |
| [9] |
Gancheva R, Kundurdjiev A, Ivanova M, et al. Evaluation of cardiovascular risk in stages of gout by a complex multimodal ultrasonography[J]. Rheumatol Int, 2017, 37(1):121-130.
doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3556-6 pmid: 27577941 |
| [10] | Toyoda S, Tokoi S, Takekawa H, et al. Relationship between brachial flow-mediated dilation and carotid intima-media thickness in patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Int Angiol, 2020, 39(5):433-442. |
| [11] | Pacholczak-Madej R, Kuszmiersz P, Bazan-Socha S, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in patients with systemic sclerosis[J]. Postepy Dermatol Alergol, 2020, 37(4):495-502. |
| [12] |
Krasnokutsky S, Romero AG, Bang D, et al. Impaired arterial responsiveness in untreated gout patients compared with healthy non-gout controls: Association with serum urate and C-reactive protein[J]. Clin Rheumatol, 2018, 37(7):1903-1911.
doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4029-y pmid: 29450849 |
| [13] | 尤杨, 戚国庆, 高宏阳, 等. 匹伐他汀对高尿酸血症大鼠血尿酸、炎症因子、血管内皮功能的影响[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2020, 36(19):2361-2365. |
| [14] |
Komori H, Yamada K, Tamai I. Hyperuricemia enhances intracellular urate accumulation via down-regulation of cell-surface BCRPABCG2 expression in vascular endothelial cells[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr, 2018, 1860(5):973-980.
doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.01.006 URL |
| [15] |
Apraş Bilgen Ş, Kalyoncu U, Erden A, et al. Assessment of subclinical atherosclerosis in psoriatic arthritis patients without clinically overt cardiovascular disease or traditional atherosclerosis risk factors[J]. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars, 2018, 46(5):358-365.
doi: 10.5543/tkda.2018.36169 pmid: 30024392 |
| [16] |
Neogi T, Jansen TL, Dalbeth N, et al. 2015 gout classification criteria: An american college of rheumatology european league against rheumatism collaborative initiative[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015, 67(10):2557-2568.
doi: 10.1002/art.39254 URL |
| [17] | Mónica FZ, Bian K, Murad F. The endothelium-dependent nitric oxide-cGMP pathway[J]. Adv Pharmacol, 2016, 77:1-27. |
| [18] | 王飞, 郑雅朦, 吴言, 等. 新型超声评分法评估痛风性关节炎的可行性研究[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2019, 35(7):650-652. |
| [19] |
Toprover M, Shah B, Oh C, et al. Initiating guideline-concordant gout treatment improves arterial endothelial function and reduces intercritical inflammation: A prospective observational study[J]. Arthritis Res Ther, 2020, 22(1):169.
doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02260-6 pmid: 32653044 |
| [20] | 李红艳, 秦历杰, 李静宇, 等. 降尿酸治疗对脑梗死患者血管内皮功能的影响[J]. 中华急诊医学杂志, 2021, 30(6):744-748. |
| [21] | Abhishek A, Valdes AM, Zhang W, et al. Association of serum uric acid and disease duration with frequent gout attacks:A case-control study[J]. Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken), 2016, 68(10):1573-1577. |
| [22] |
Zou Z, Yang M, Wang Y, et al. Association of urate deposition shown by ultrasound and frequent gout attacks[J]. Z Rheumatol, 2021, 80(6):565-569.
doi: 10.1007/s00393-020-00913-0 pmid: 33034681 |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||